Meteorology Midterm
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
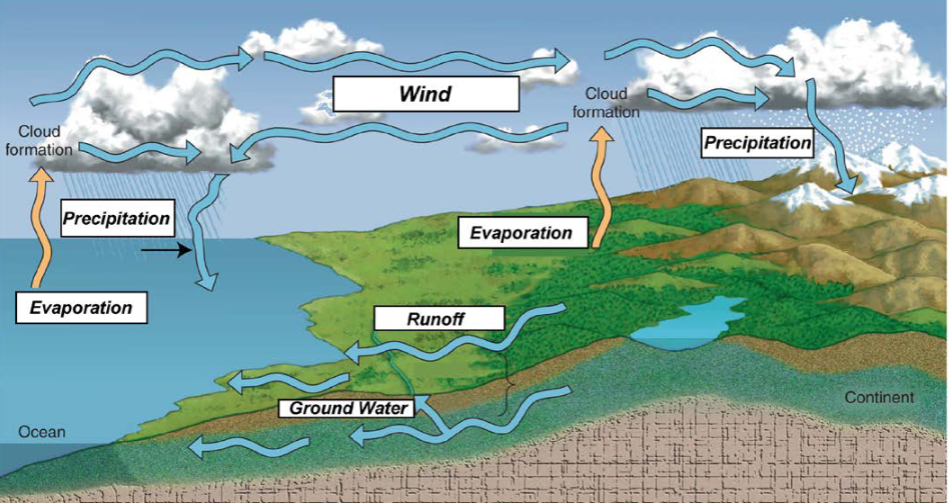
Identify the Phases of the Hydrologic Cycle
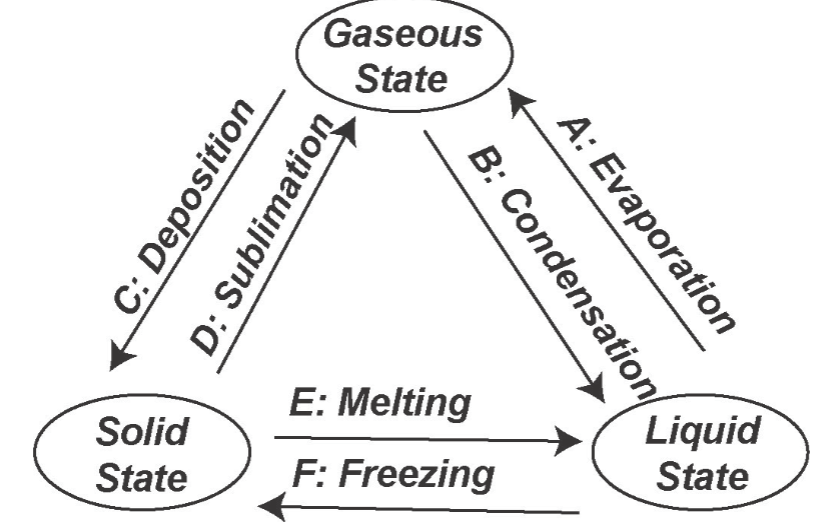
Phase Changes of Water
Melting (Solid → Liquid)
Freezing (Liquid → Solid)
Vaporization (Liquid → Gas)
Condensation (Gas → Liquid)
Deposition (Gas → Solid)
Sublimation (Solid → Gas)
Measures of water vapor content
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air.
Measuring humidity
The vapor content of air is measured with devices known as hygrometers.
Adiabatic and Environmental Lapse Rates
Adiabatic: Drops temperature without exchanging energy. Expansion of air causes cooling and compressing air causes warming.
Environmental Lapse Rate: compares air in and out. Overall decrease in air temperature with height. Changes from place to place.
Forms of condensation
Dew, Frozen Dew, frost, fog and clouds.
Mechanisms of lifting air
Orographic: Lifting caused by a mountain, causes precip.
Frontal Lifting: Boundaries between different air masses, warm or moist air forces to rise and form clouds.
Convergence: air converges into low-pressure regions, air rises up to form storms, and convergence causes air to rise and cool.
Localized Convection: “Bubbles rise”, air heated at the surface becomes warmer and less dense and rises freely into updrafts.
Absolutely Unstable Air
If air is forced to rise and it continues rising freely
positive buoyancy
DAR and WAR are less than ELR
Creates clouds and storms, associated with low pressure
Absolutely Stable Air
If air is forced to rise it sinks back to its original position.
negatively buoyancy
inversions = stable
DAR and WAR is greater than the ELR
creates clear skies and dry conditions, associated with high pressure.
Absolutely Neutral Air
if air is forced to rise, the parcel remains in the location where lifting ceased.
Conditionally Unstable Air
parcel of air is forced to rise is initially stable but eventually becomes unstable after saturation is reached.
ELR is between DAR and WAR
can cause thunderstorms and thundersnows
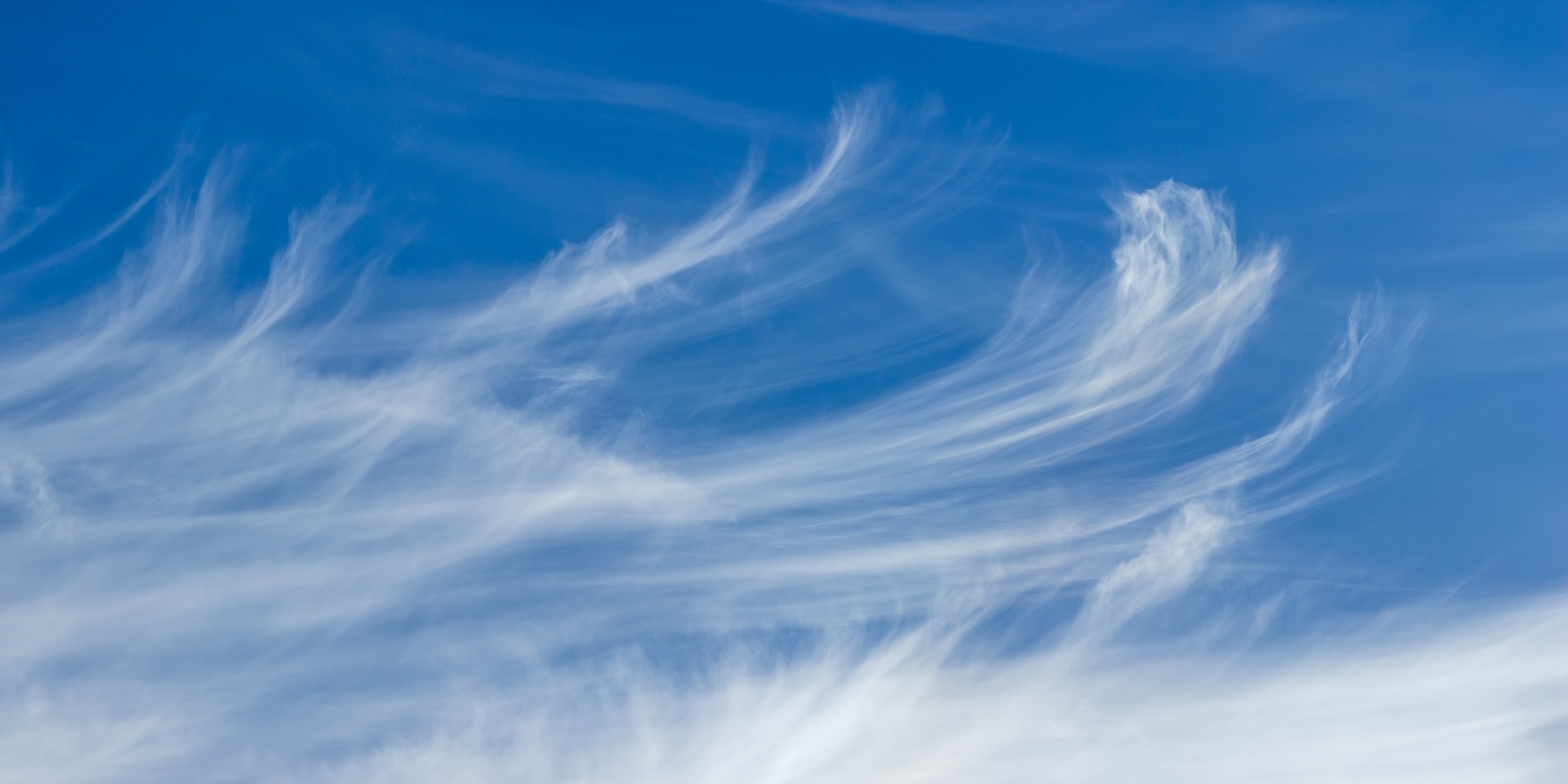

cirrus

cirrostratus

cirrocumulus
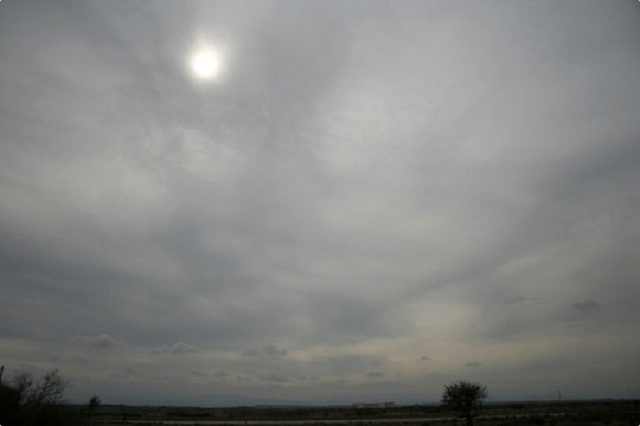

altostratus
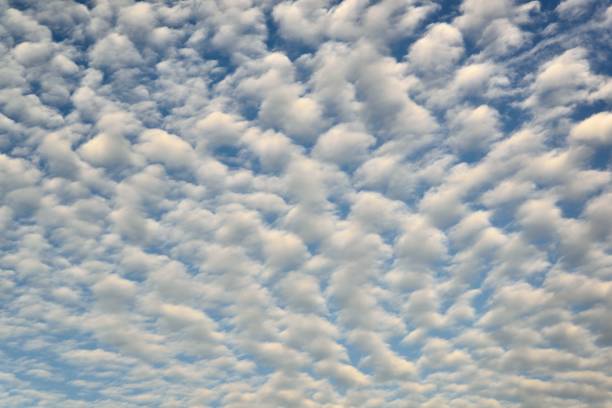

altocumulus
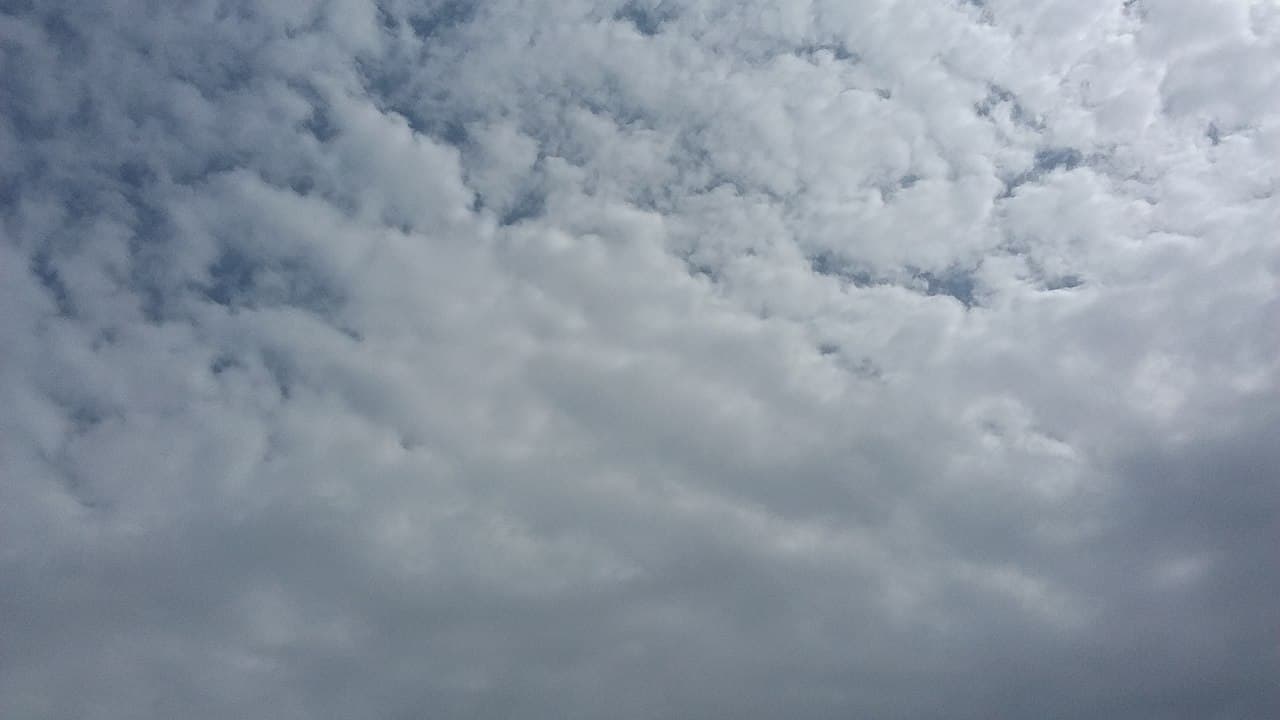

stratus
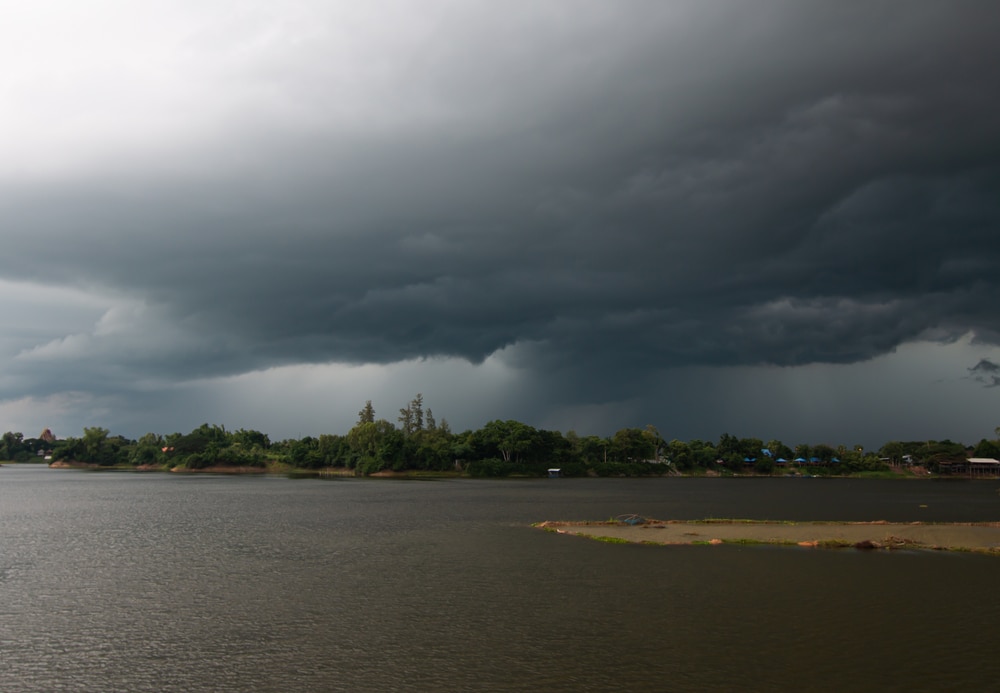

nimbostratus
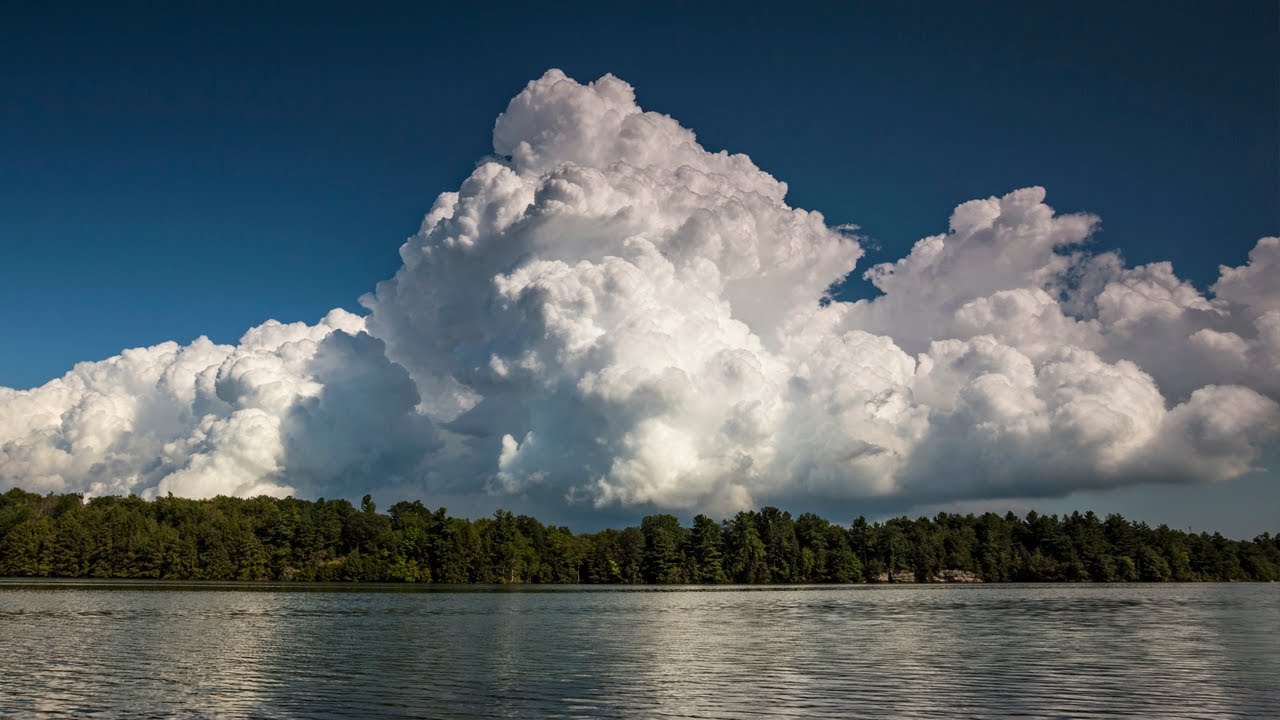

cumulus congestus
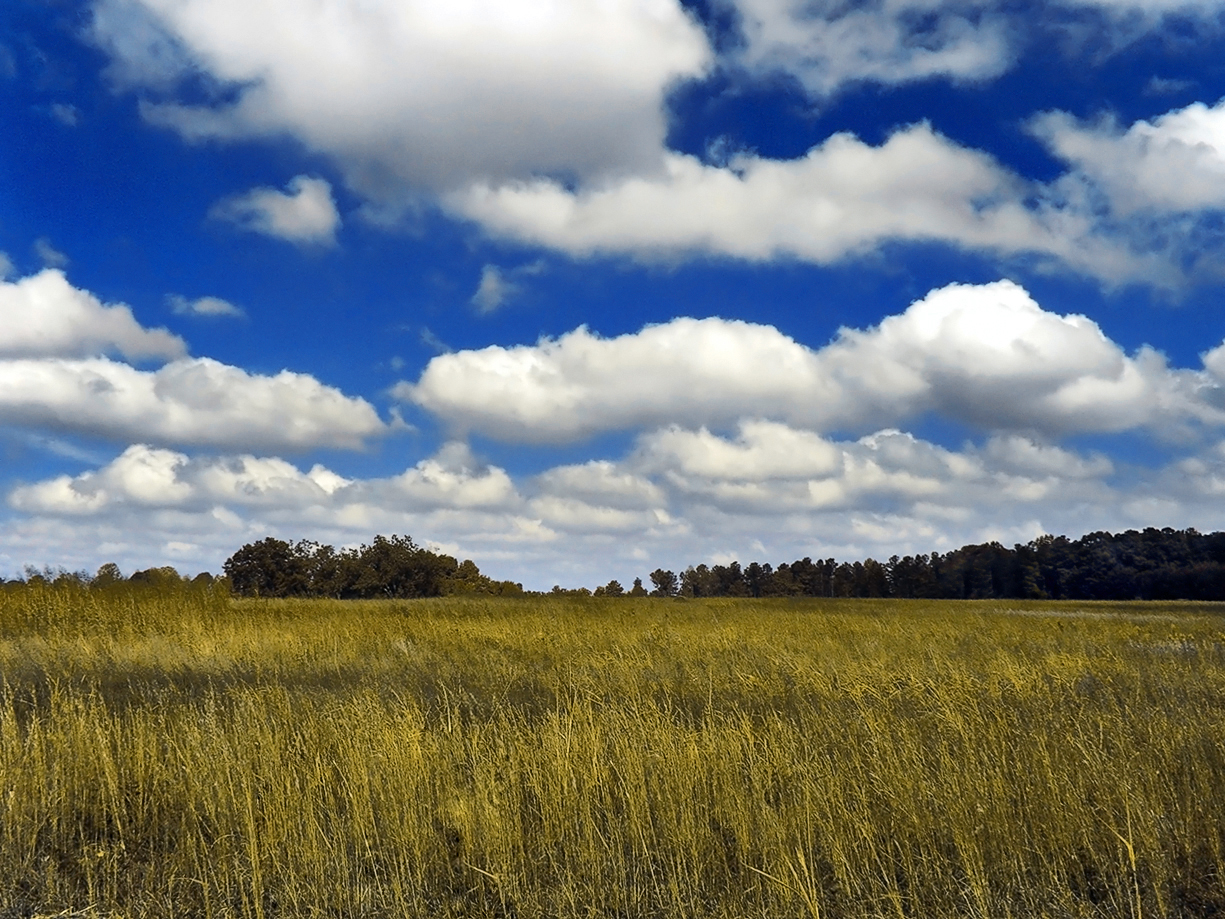

cumulus

cumulonimbus

lenticular
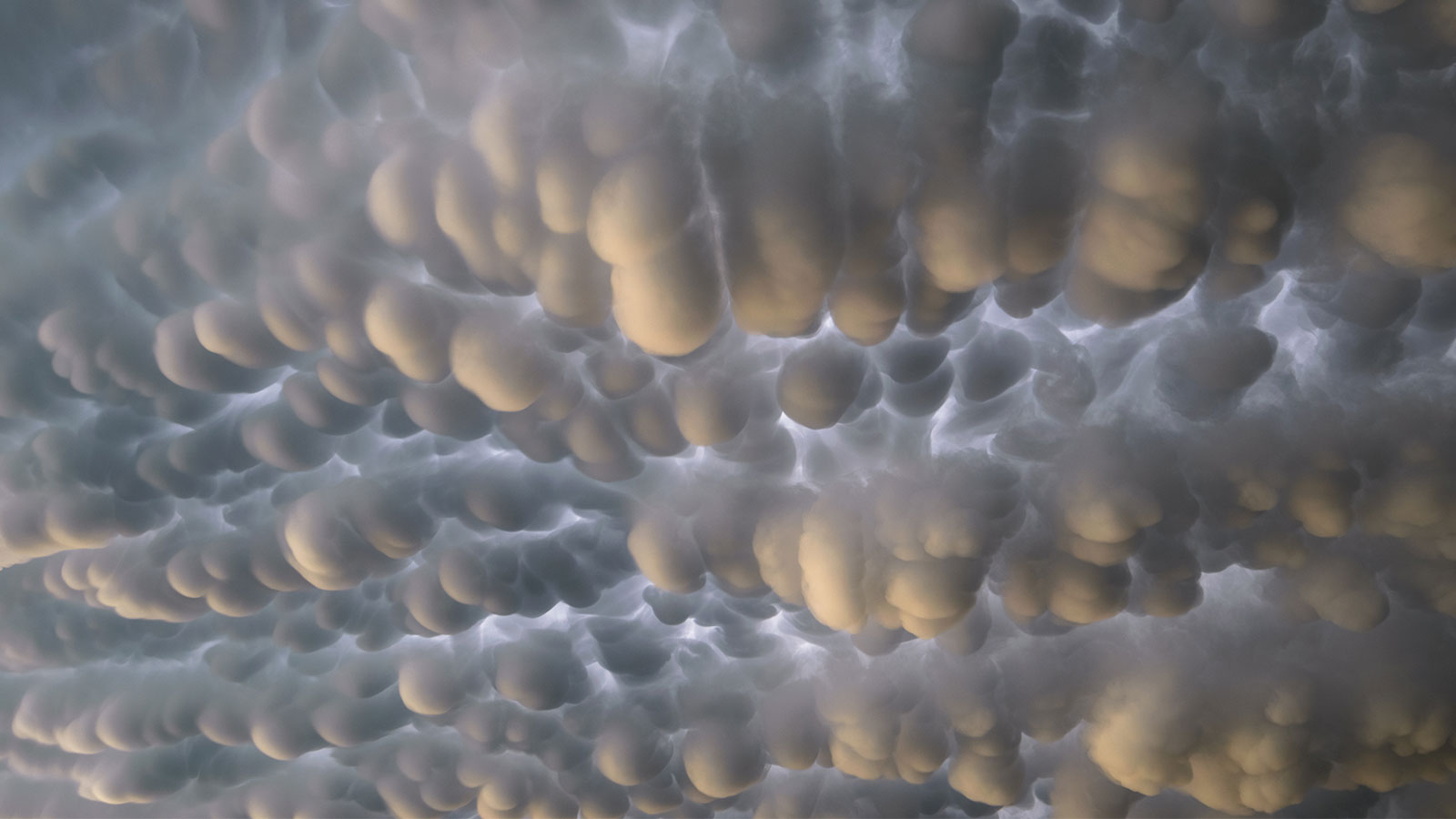

mammatus
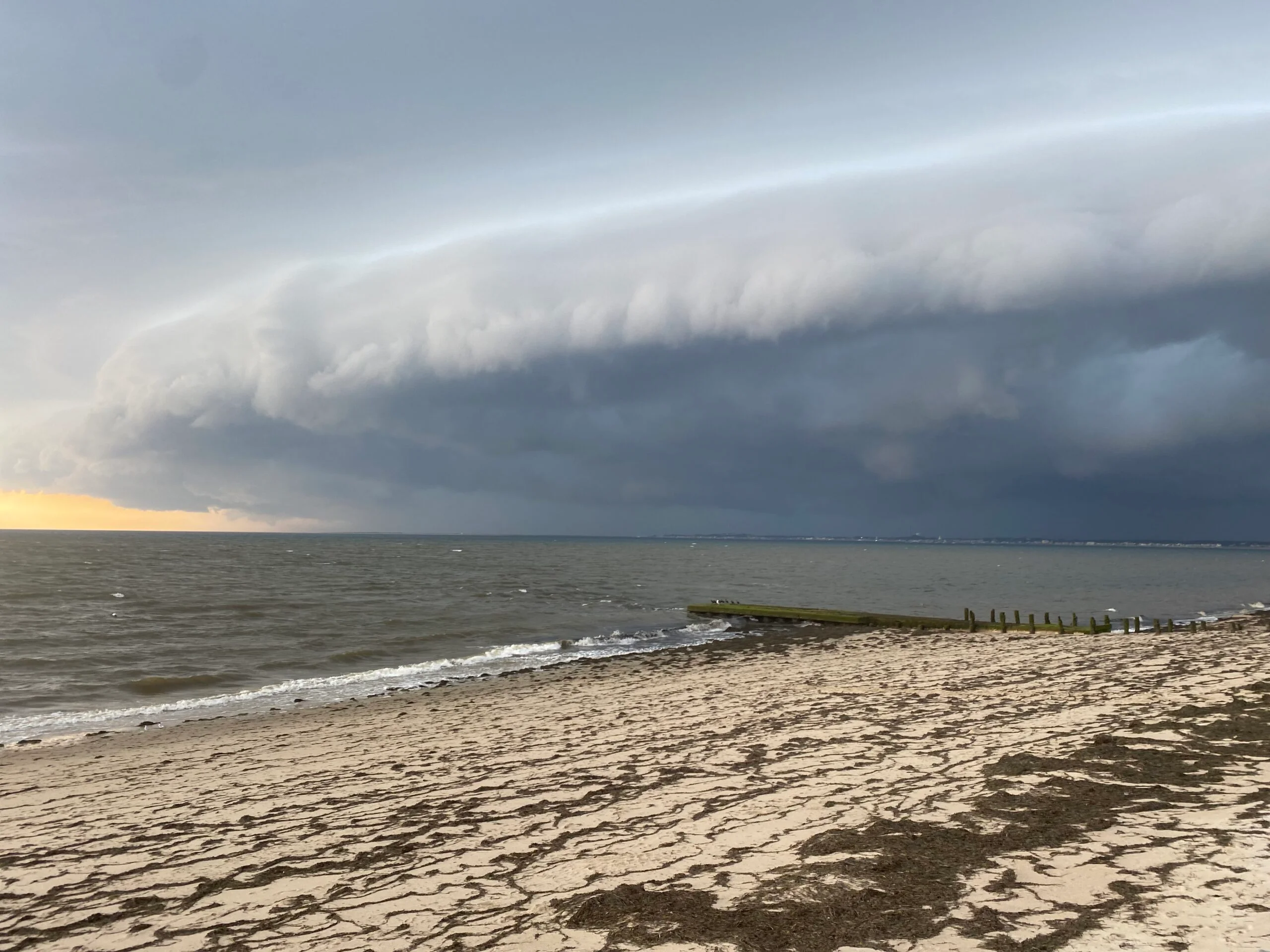

shelf cloud
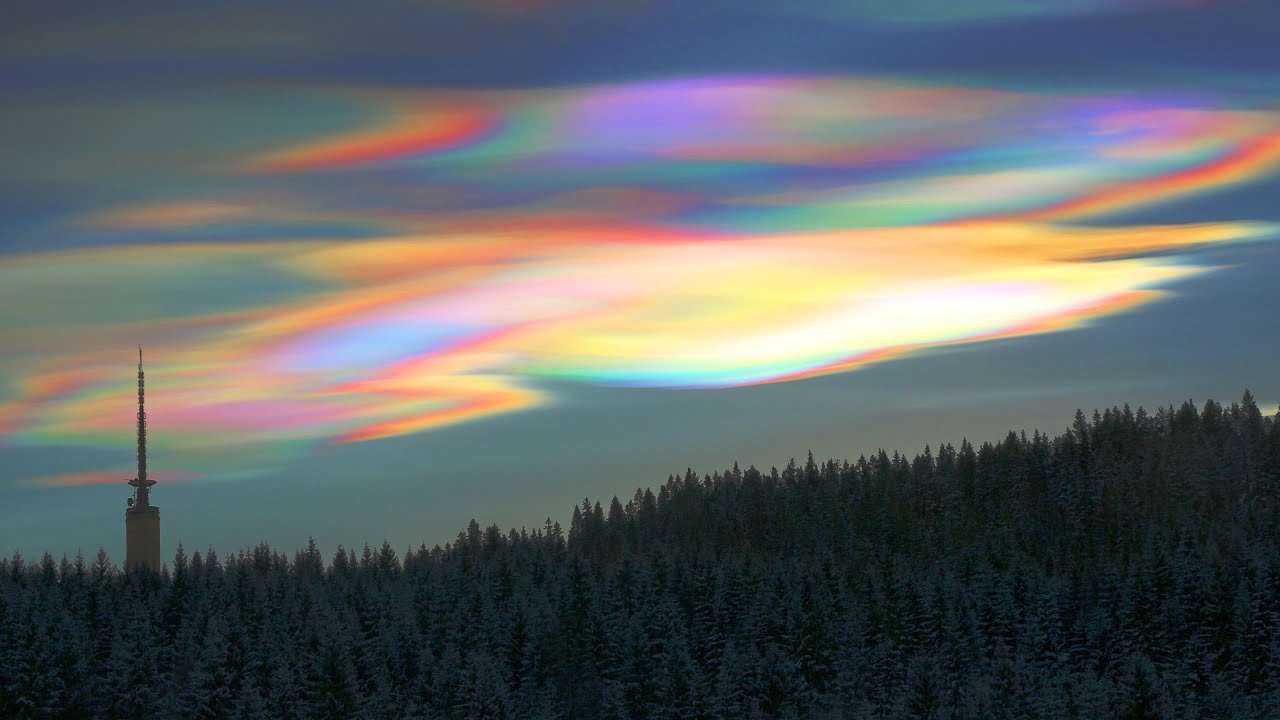

nacreous (mother of pearl)
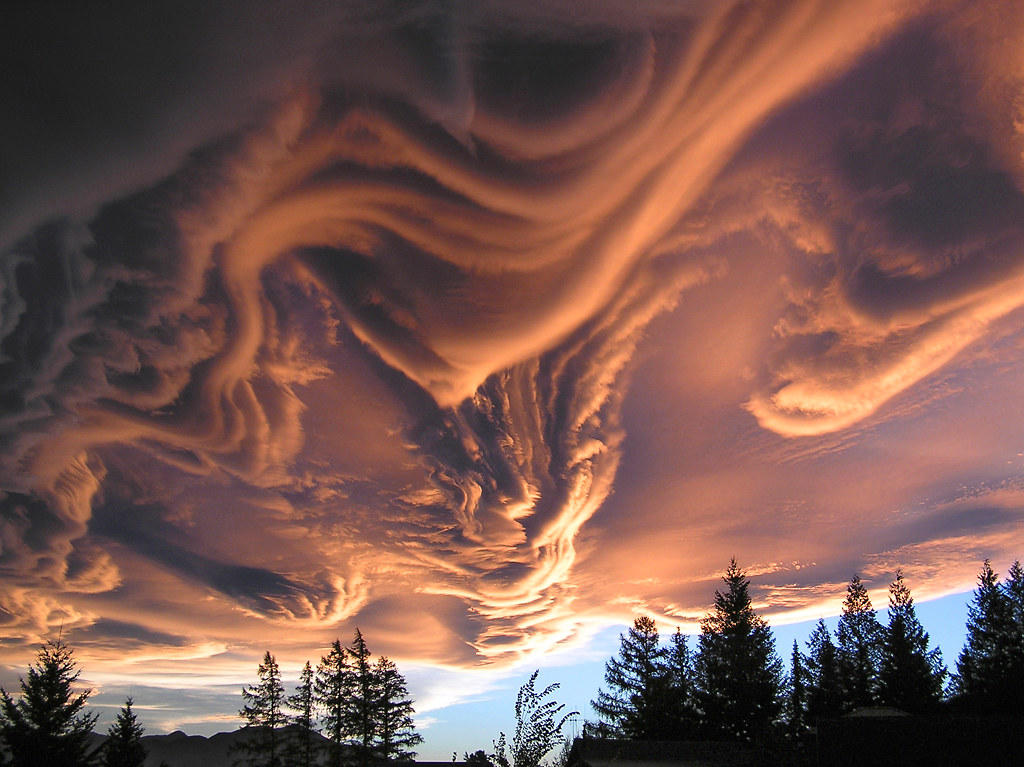

undulatus asperatus
Measuring precip.
Raingages
Forms of precip.
snow
Lake effect snow
rain
graupel (soft snow pellets)
hail
sleet
freezing rain
Warm Cloud Process
collision - coalesense
entire cloud is above freezing
produces rain in tropical region
Cold Cloud Process
Bergeron Process
produces the most precip. in the mid-latitudes
cloud comprised of liquid drops and ice
most our precip. originally begins as snow
mixing ratio
mass of water vapor relative to mass of dry air
relative humidity
amount of water vapor present related to the amount air can hold
dew point
temp where saturation occurs
hygroscopic nuclei
condensation nuclei that readily attract water (salt)
cloud condensation nuclei
natural and anthropogenic sources that water condenses onto.
ceilometer
lasers used to measure cloud coverage at different heights
EXTRA CREDIT: Average first day of frost
September 29th
cloud seeding
weather modification technique that improves a cloud's ability to produce rain or snow by introducing tiny ice nuclei into certain types of subfreezing clouds.
water equivalent of snow
10:1 ratio (can vary)
Be able to list and understand all the steps associated with the hydrologic cycle.
Understand all 6 phase changes of water
Be able to explain why relative humidity is a poor indicator of the actual water vapor in the air.
Because it is temperature dependent and it is inversely proportional to air temperature. Therefore, high relative humidity values in cold air actually relate to minuscule absolute humidity values.
Be able to explain what happens to air as it’s lifted over a mountain and continues on the downwind side.
Orographic lifting. Air hits a mountain and is forced upwards which causes precip. on the windward side resulting in cooling as air rises, also leads to lush vegetation, the leeward side is the downwind side of the mountain and the sinking air causes warming and a lack of precip, know as the rainshadow effect (dry)
Be able to compare the 4 major types of stability
Be able to describe the cold cloud or warm cloud process of producing precip.
The collision-coalescence process causes precipitation to form in a warm cloud. This process takes place in clouds made up of cloud droplets of different sizes. Larger droplets, having a higher terminal velocity than smaller droplets, collide and coalesce with smaller droplets in their path. The droplets continue to grow, eventually falling to Earth as precipitation.
Be able to explain how the lake effect snow machine works.
When cold dry air moves over warm water it picks up moisture, moisture that evaporates off the warm lake, heavy snow falls on the downwind side of the lake, downwind side of lake causes convergence and rising motion, snowfall can be very localized.
Name the Structure of the Atmosphere
Troposphere, Tropopause, Stratosphere, Stratopause, Mesosphere, Mesopause, Thermosphere
Understand the brief history of meteorology
Galileo created a prototype thermometer without scales
Fahrenheit and Celsius were created in the 1700’s
Evangelista Torricelli invented the Barometer (1643)
Instruments to measure water vapor invented in 1700’s
First network of weather observers -- 1847
The telegraph aided early weather forecasting
The Army Signal Service was established in 1870, now known as the National Weather Service
Weather Balloons introduced in 1940’s
Radar and Satellites added in 1950’s
Energy Transfer Mechanisms
Conduction: energy through direct contact
Convection: a vertical transport of heat and moisture in the atmosphere, especially by updrafts and downdrafts
Sensible Heat: heat felt by skin
Latent Heat: energy which induces a change of state (usually water)
Absorption
Atmospheric gasses, liquids, and solids that absorb energy and heat up by gaining energy
Albedo
Percentage of reflected energy, 30%
Rayleigh Scattering
agents (what causes) thar are smaller then wavelengths, gases are the scattering agent. creates a blue sky, gases scatter the short, blue, wavelengths.
Mie Scattering
scattering of radiation from larger agents (aerosols) - downward. dust and pollutants, causes a hazy sky.
Nonselective Scattering
Cloudy and humid days, very large scattering agents (water). gives clouds their white/grey color
Net Radiation
difference between absorbed and emitted radiation
Influences on Temperature
Latitude
Altitude
Contrasts between land and water
Local conditions
Daily and annual temp patterns
Winds
Clouds
Daltons Law
sum of partial pressures
measure pressure
barometers
isobars
lines of equal pressures
close=windy
not close = not windy
low = storm
high = nice
pressure gradient force
wind moves from high to low pressure. more pgf = stronger winds
hydrostatic equilibrium
balance of gravity and vertical pressures
Coriolis force
free moving objects affected by earths rotation. no effect at equator, max at poles.
how does friction affect weather
near the surface it slows down the air/wind
anticyclones
nice weather, center of high pressure, clockwise.
cyclones
bad weather, center of low pressure, counterclockwise.
stefan-boltzmann law
blackbodies emit the maximum amount of energy
emissivity
percentage of energy emission of a substance as compared to a blackbodies
wein’s law
determines peak wavelength, the hotter the object the shorter the wavelength
Be able to Name the layers of the atmosphere and be able to draw the temperature profile.
Troposphere, Tropopause, Stratosphere, Stratopause, Mesosphere, Mesopause, Thermosphere.
Be able to explain the greenhouse effect and how it contributes to planetary warming.
We receive short wave radiation from the sun, and long wave radiation leaves earths surface to cool off, however, the CO2 in the air lets the SW in but not the LW out therefore the earth heats up.
Be able to explain exactly why we have seasons.
We have seasons due to the earths 23.5o tilt. Because of this there are periods where the northern hemisphere is pointed away from the sun creating a colder weather in the north and periods when the northern hemisphere is pointed towards the sun creating warmer climate in the north.
Be able to explain the difference between permanent and variable gases in terms of percentage.
Permanent gases are gases whose levels remain constant in the atmosphere. Nitrogen (78%), Oxygen (21%), Argon (43%). Variable gases are gases whose levels vary over time and can affect the weather. Water Vapor, Carbon Dioxide, Ozone, and Methane.
Be able to place the wavelengths in order from longest to shortest.
radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-ray, and gamma-ray radiation
Be able to explain how pressure gradient force, Coriolis force, and friction determine the wind direction and speed near the ground and at high altitudes.
PGF creates wind because it moves from high to low pressure, so the greater the PGF the greater the wind speed. Coriolis force is the effect of free-moving objects affected by the earth’s rotation. Faster the object more deflection to the right in the northern hemisphere with effects wind direction. Friction slows down air/wind, maximum effect near surface which effects wind speeds and therefore creates a lesser Coriolis deflection.
Differentiate between a cyclone and an anticyclone in terms of pressure, clouds, wind speeds and direction.
Anticyclones are nice weather, center of high pressure, clear skies, light winds, clockwise motion in the northern hemisphere. Cyclones are bad weather, center of low pressure, strong winds, clouds and precipitation, counterclockwise motion int the northern hemisphere.
Celsius to Fahrenheit
1.8*C+32
Fahrenheit to Celsius
(F-32)/1.8