Chapter 28
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
1
New cards
Monetary Policy
Intelligent management of the money supply performed by the central bank
2
New cards
fiscal policy
where the government has to decide how to adjust their budget balance
3
New cards
When was the Federal Reserve Banking System made and for what reason?
Founded in 1913 to assist in the banking problems in the US
4
New cards
The Board of Governors consists of ____ board members and each serves for ____ years and are appointed by the _________. Every ____ years, one of the members is replaced.
7, 14, President, 2
5
New cards
How many Federal Reserve banks are there?
12
6
New cards
What relation do Federal Reserve Banks and the Central Bank have?
They’re the same
7
New cards
Quasi-public banks
Owned by private banks but take care of the public
8
New cards
Banker’s bank
Banks can borrow money from federal reserves
9
New cards
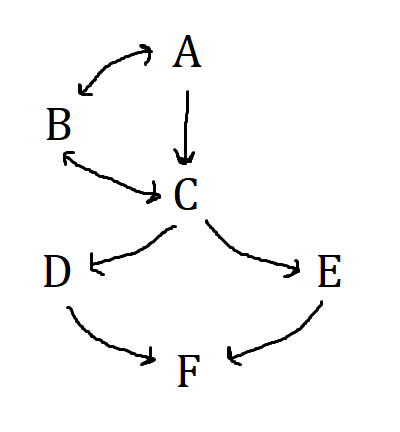
What does A stand for?
Board of Governors
10
New cards
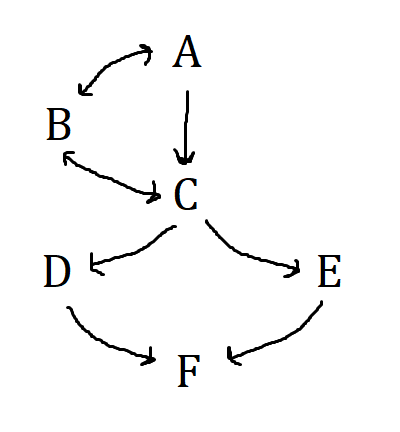
What does B stand for?
Federal Open Market Committee
11
New cards
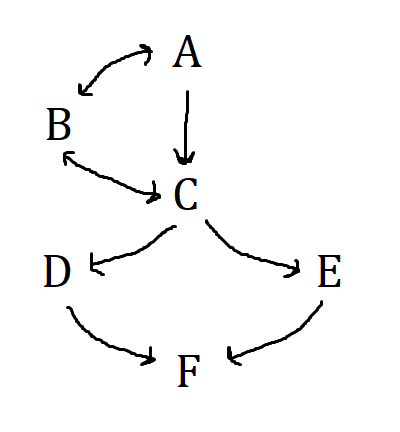
What does C stand for?
12 Federal Banks
12
New cards
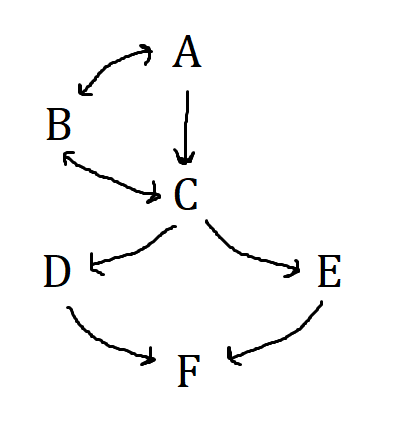
What does D stand for?
Commercial Banks
13
New cards
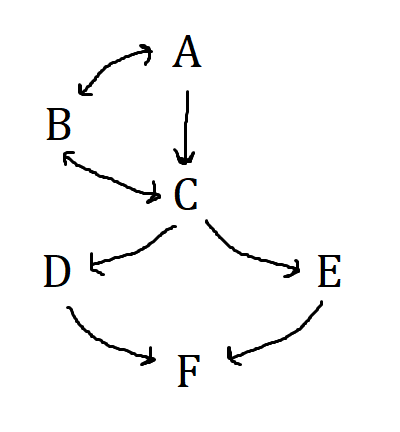
What does E stand for?
Thrift Institutions(Savings + Loan Associations, mutual savings banks, credit unions)
14
New cards
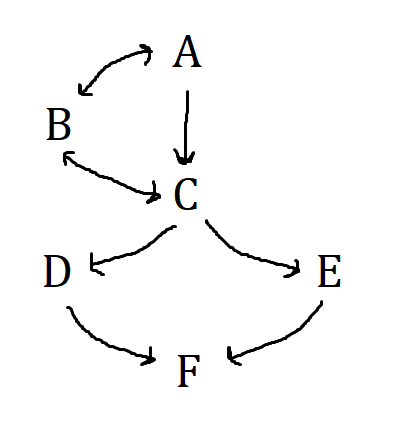
What does F stand for?
The public(households and businesses)
15
New cards
What is the Federal Open Market Committee?
Also known as FOMC, this is where monetary policy decisions are made.
16
New cards
The Federal Open Market Committee was created by ___________ and ___________ . There are _____ members in total. _____ consist of those on the first committee and _____consist of those on the second committee.
Board of governors, 12 federal banks, 12, 7, 5
17
New cards
What does the FOMC do?
Aids Board of Governors in setting monetary policy, conducts open market operations
18
New cards
What does it mean to conduct open market operations?
Where the FOMC either buys/sells security/federal bonds to the public
19
New cards
If the FOMC is buying bonds, what happens?
The government will need to pay the public, which increases the money supply
20
New cards
If the FOMC is selling bonds, what happens?
The public needs to pay the government, which decreases the money supply
21
New cards
What tools are implemented for monetary policy?
Federal open market committee, changing reserve requirements, and changing the discount rate
22
New cards
What does a decreased required reserve ratio mean?
Banks can lend more money to the public, leading to an increase in the money supply
23
New cards
What does an increased required reserve ratio mean?
Banks can’t lend as much money to the public, leading to a decrease in the money supply
24
New cards
What is the discount rate?
This is the interest rate paid by banks to the federal reserve
25
New cards
What does decreasing the discount rate do?
Banks not having to pay as much to the reserve means interest rates lower in commercial banks, leading to an increase in the money supply
26
New cards
What does increasing the discount do?
Banks have to pay more to the reserve means interest rates increase in commercial banks, leading to a decrease in the money supply
27
New cards
Does the Federal Reserve issue currency or print money?
Issues currency
28
New cards
What significance does the federal reserve have to banks?
They’re a lender of last resort
29
New cards
When is expansionary monetary policy used?
During a recession to increase money supply. Called quantitative easing
30
New cards
When is contractionary monetary policy used?
During inflation to decrease money supply
31
New cards
What is the Central Bank’s most important task?
Determining the quantity of money in the economy
32
New cards
Does the Federal Reserve decide interest rates?
No