organic chem 1 - basics
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
organic compounds contain:
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
multiple bonding and substituents can
Different atoms/group of atoms can be placed on carbons
Basic atoms is hydrogen but groups contain oxygen, nitrogen, halogens and sulphur are common
Chemistry of organic compound is determined by functional group
molecular formula
exact no. of atoms of each element present in molecule
empirical formula
simplest whole number ratio of atoms in molecule
structural formula
minimal detail using conventional groups
displayed formula
shows bonds
skeletal formula
removes H atoms leaving carbon skeleton
general formula
represents any member of a homologous series
alkanes
CnH2n
only C and H
all single bonds
alkenes
only C and H
C=C
alcohols
only one O
has O-H group
can classify as 1o, 2o, 3o according to position of O-H group on carbon skeleton
aldehydes
only one O
has C=O
C=O is at end of chain so next door is H atom
ketones
only one O
has C=O
C=O group isnt at end of chain
carboxylic acids
has 2 O
has O-H and C=O on same carbon
-COOH has to be at end of chain
esters
has 2 O
one O is part of C=O bond
ethers
has 1 O
O is sandwiched between two carbon atoms
amines
1 N
has N-H group
Classified as 1o/2o/3o according to position of N-H group on carbon skeleton
amide
1 N and 1 O
One O is part of C=O and nitrogen is next door
nitrile
Has 1N
Has C-N triple bond
thiols
Has 1 S
Has H-S bond
e.g. methanethiol
haloalkanes
Contains carbon halogen bonds
e.g. F, Cl, Br, I
classified according to environment of halogen
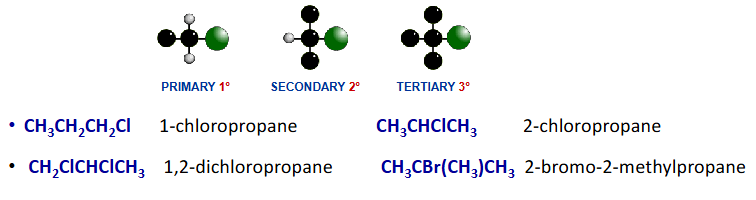
isomerism in haloalkanes

chains and rings
Carbon can be arranged in straight chains or branched chains or rings
naming
Trivial: based on some property or historical aspect; the name tells you little about structure
Systematic: based on agreed set of rules IUPAC; exact structure can be found from name
e.g. acetone-propanone acetic acid - ethanoic acid
IUPAC nomenclature
Stem and suffix
Stem - how many carbons in longest chain
Suffix - functional group
how long is chain
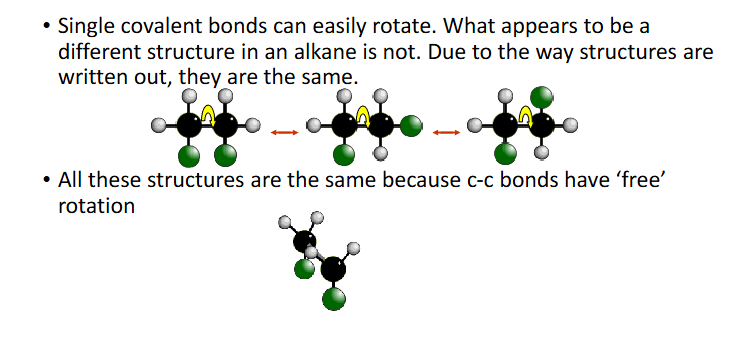
Single covalent bonds free to rotate
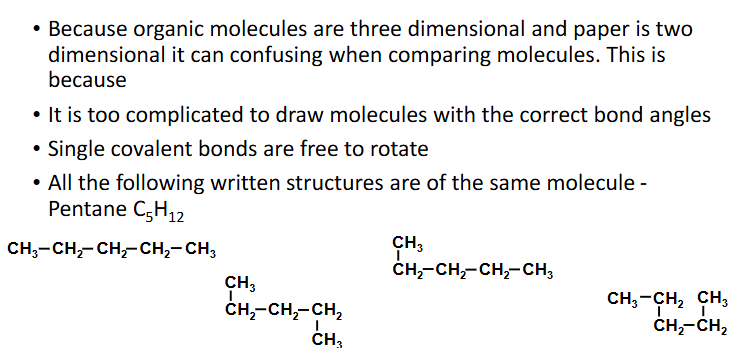
suffix
-ane
-ene
-ol
-al
-one
-oic acid
In many cases position of functional group must be given to avoid any ambiguity
naming alkanes
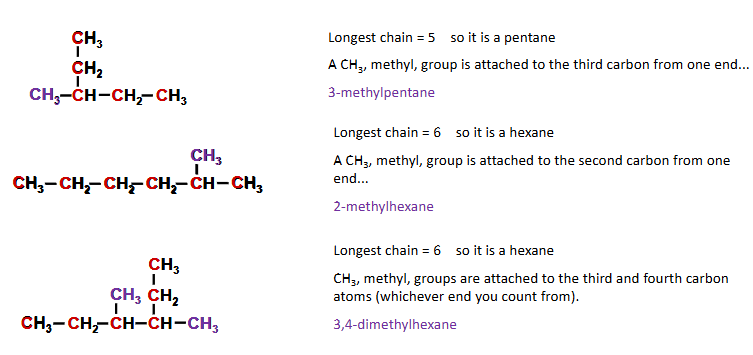
alkanes
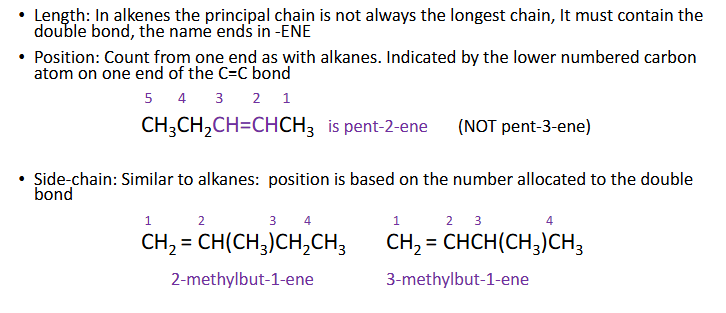
isomerism
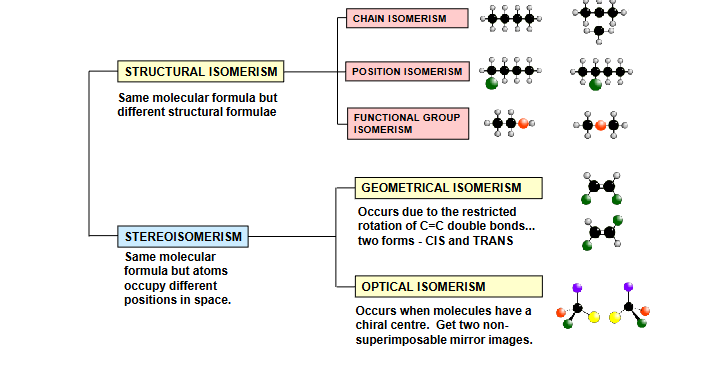
structural
Chain - diff arrangements of carbon skeleton , more branching = lower BP
Positional - same carbon chain, functional group diff place
Functional group - diff functional group, same formula
geometric isomerism
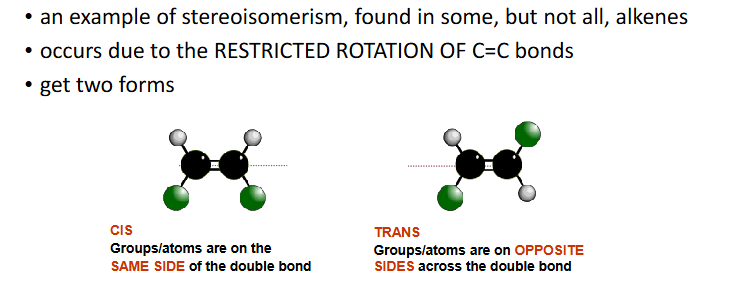
geometric isomerism
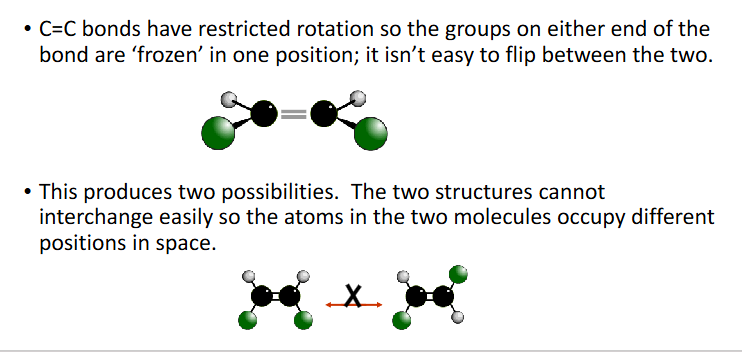
how to tell if isomerism exists
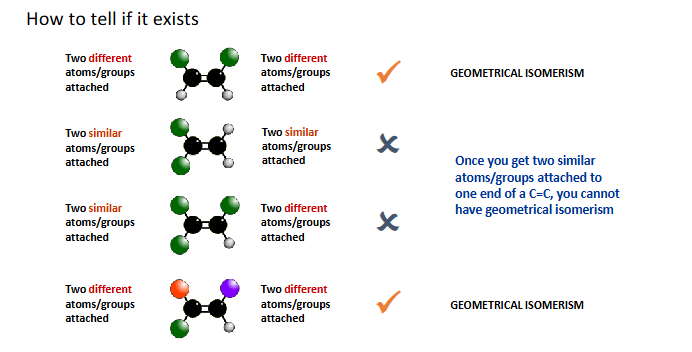
isomerism in butene
3 structural isomers only one shows geometric isomerism
But-1-ene
Cis but-2-ene
Trans but-2-ene
2-methylpropene
E-Z Isomerism
E- opposite
Z- same side

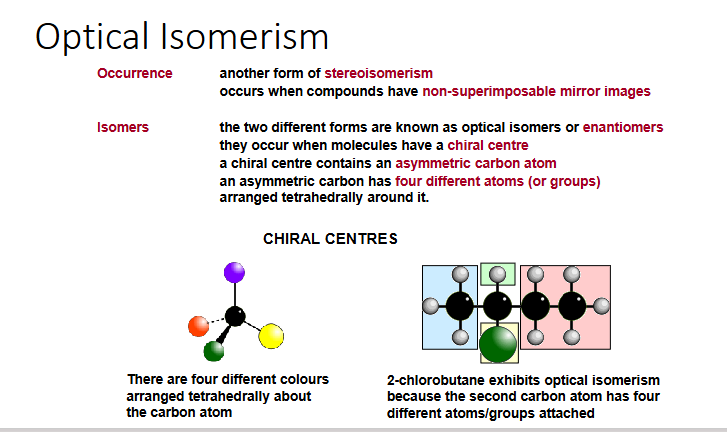
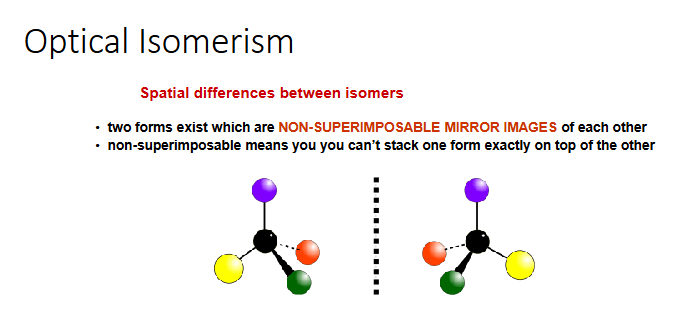
optical isomerism
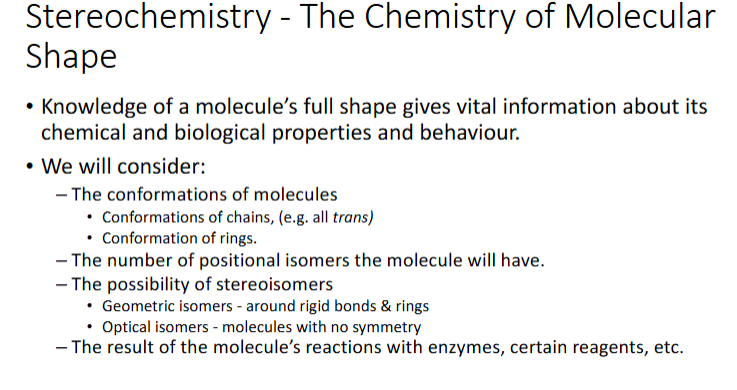
stereochemistry

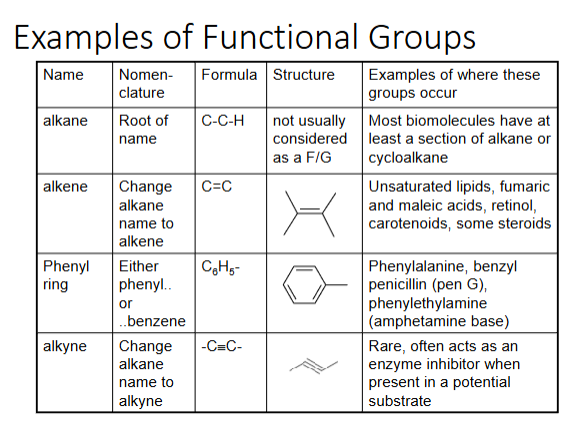
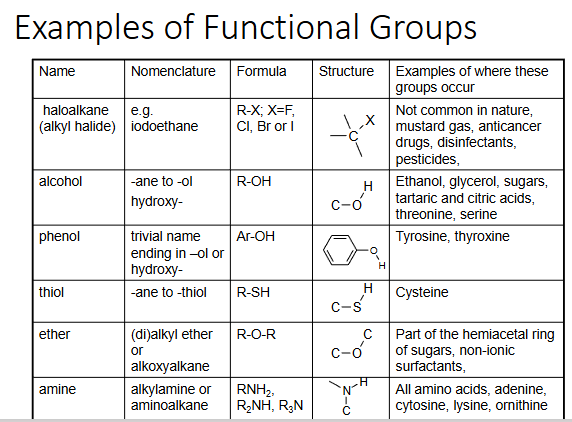
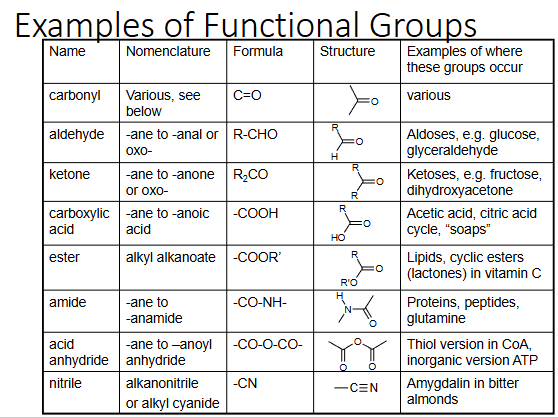
functional groups

polarity of bonds
Most functional groups (except for alkenes, alkynes and phenyl)
Electronegativity difference C to H is very small, thus electron density is nearly uniform around alkane C-H bond
Presence of extra pi bonds between two C s make C-C region slightly delta negative
polarity of bonds

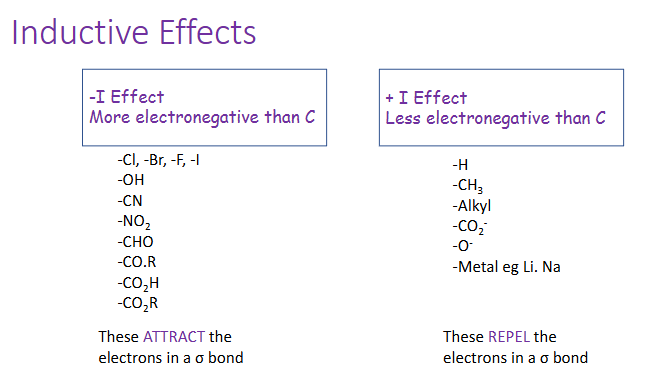
inductive effects