CH 39 Neurons and synapses
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
function of nervous sys
1. communicate bt external and internal environment
2. center of all mental activity
3. w/endocrine -> regulate homeostasis
4. receives info and generates response
components of neural signaling
reception, transmission, integration, response
info-processing steps
1. sensory receptors on afferent neurons receive a stimulus (reception)
2. afferent neurons transmit the info to interneurons (transmission)
3. interneurons integrate the neural messages (integration)
4. efferent neurons transmit the neural messages to effectors (response)
neurons
- basic functional unit
- capable of receiving, conducting, and transmitting electrical impulses
- info -> dendrites -> cell body -> axon -> terminal synapses
- collection of info from other neurons or environment
structure of neurons
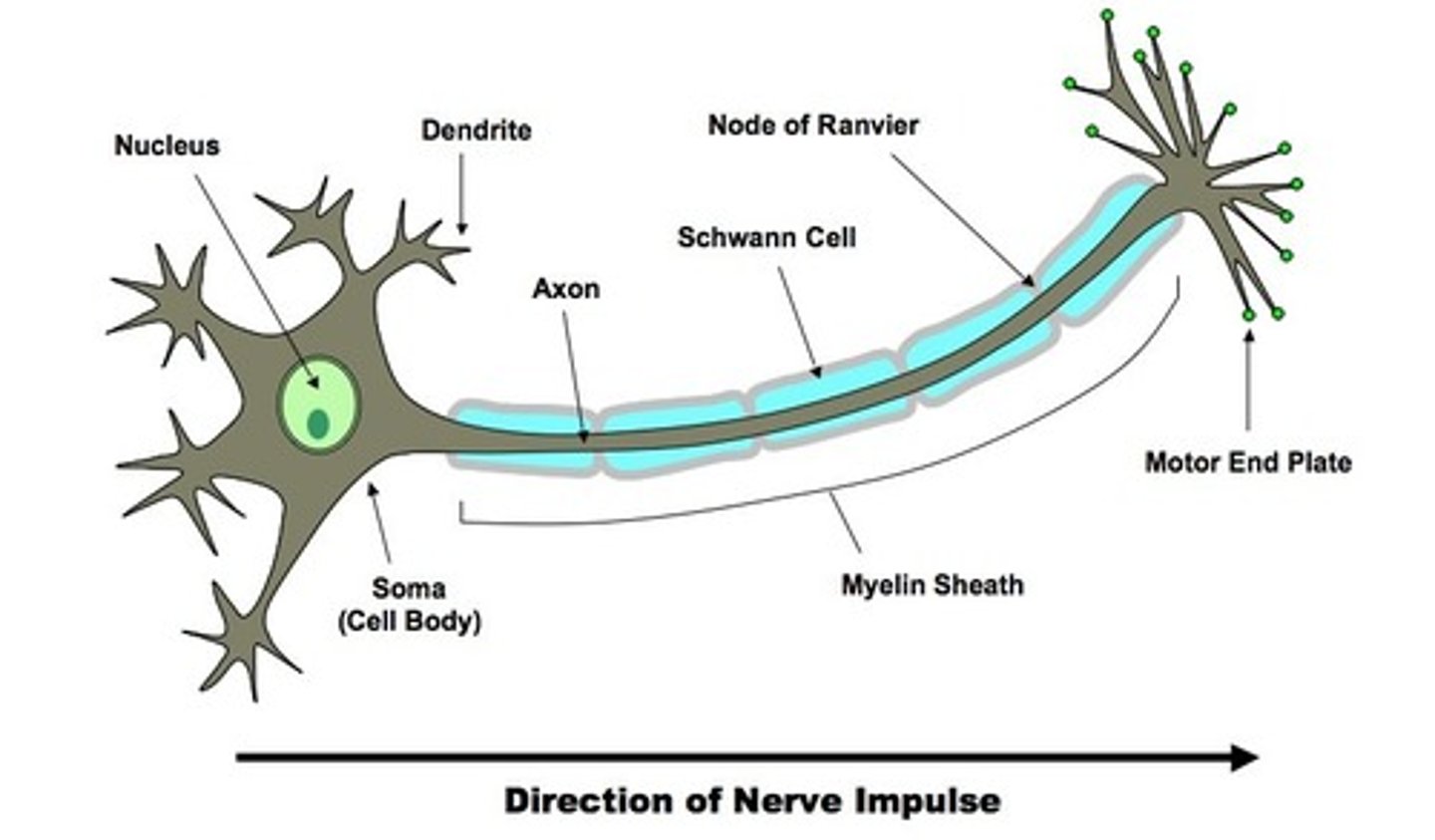
cell body (soma)
contains nucleus and prominent nucleous
perikaryon
cytoplasm around the nucleus; contains organelles (ie RER and mitochondria) -> grainy appearance
nissl bodies
clusters of RER; grey color/matter
neurofibrils
support and transport substances throughout the neurons
dendrites
- receive stimuli from other nerve cells
- contain receptors for neurotransmitters released by the axon terminals
- densely branched
axons (nerve fibers)
- form the impulse generating and conduction region of the neurons
- transmit AWAY from nucleus
- axon hillock is the point of the membrane where the axon contracts the membrane of cell body
- branch -> axon collateral
- finite extensions
- axonal terminals: end of axon collateral; button-like
neural circuits
connections bt axon terminals of one neuron and the dendrites of another; contains afferent (sensory), >= 1 interneurons, and efferent (motor) neuron
functional classes of neurons
afferent, efferent, interneurons, motor
afferent neurons
transmit stimuli collected by their sensory receptors to interneurons
interneurons
integrate the info to generate an appropriate response; 99% of neurons
efferent neurons
carry the signals indicating a response away from interneurons to the effectors (muscles and glands)
motor neurons
specific efferent neurons that carry the signal to the skeletal muscles
neuroglia (glial cells)
- maintaining environment for normal neuronal function and structural support
- can undergo cell division and replace damaged cells
- do not propagate action potentials
- 1/2 volume of nervous system
glial cells of CNS
astrocytes, ependymal, oligodendrocytes, and microglia
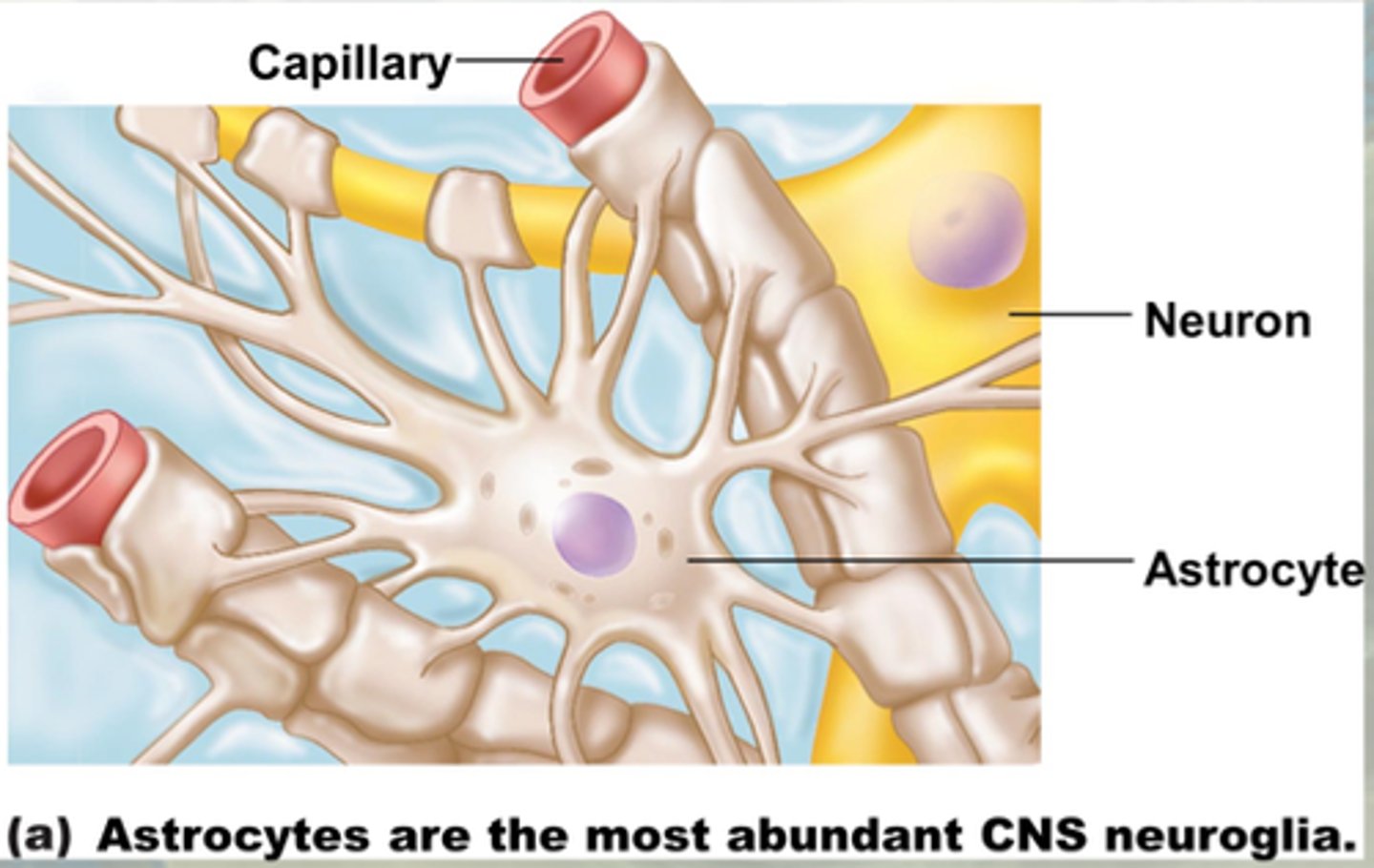
astrocytes
- largest and most amt
- stellate appearance
- cover the surface of blood vessels
- provide physical support
- maintain concentration of ions
- maintain blood-brain barrier
- guide neuronal development
- repair damaged neural tissue
- provide structural framework for CNS
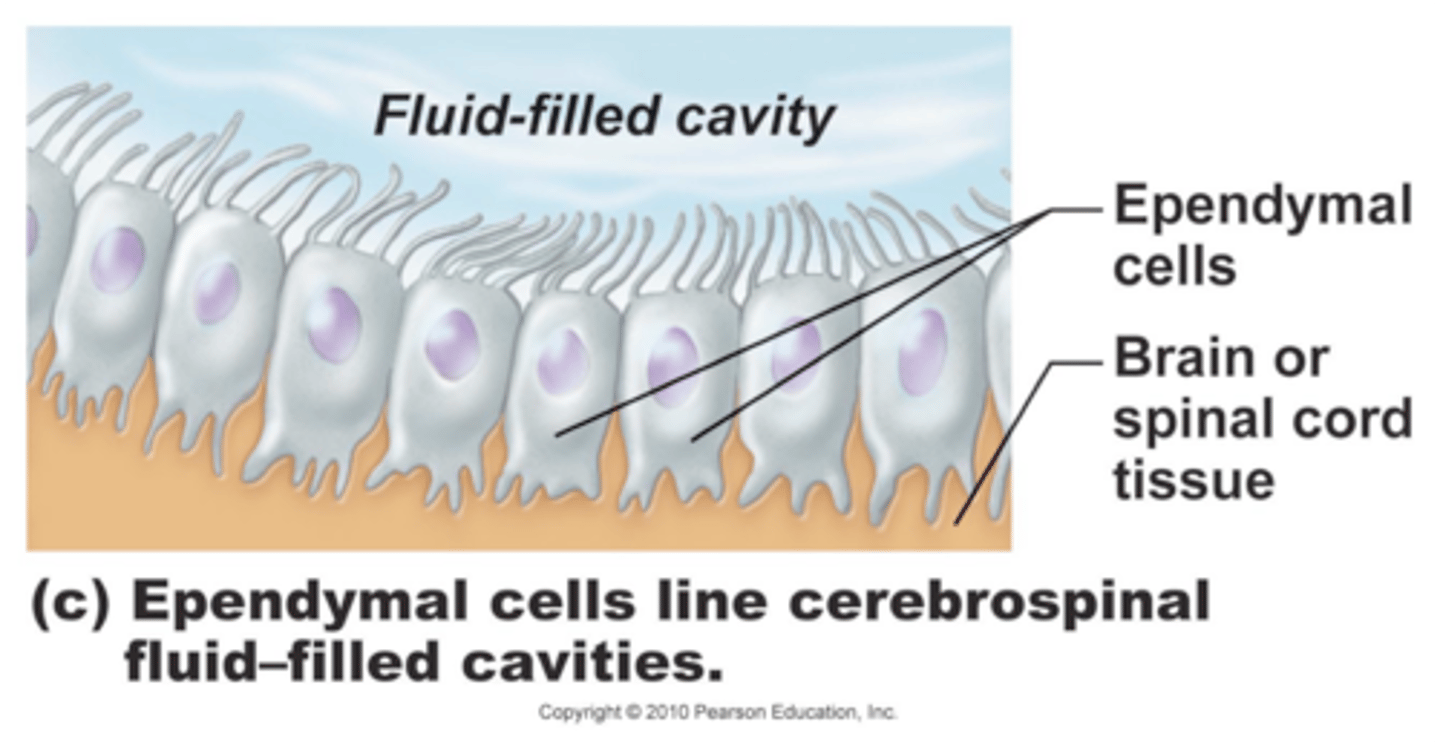
ependymal
- line the ventricles w/in the brain and spinal cord
- assist in producing and monitoring CSF -> help circulate CSF
microglia
- least amt and smallest
- touch nearby neurons to monitor the health and engulf cellular debris, wastes, and pathogens
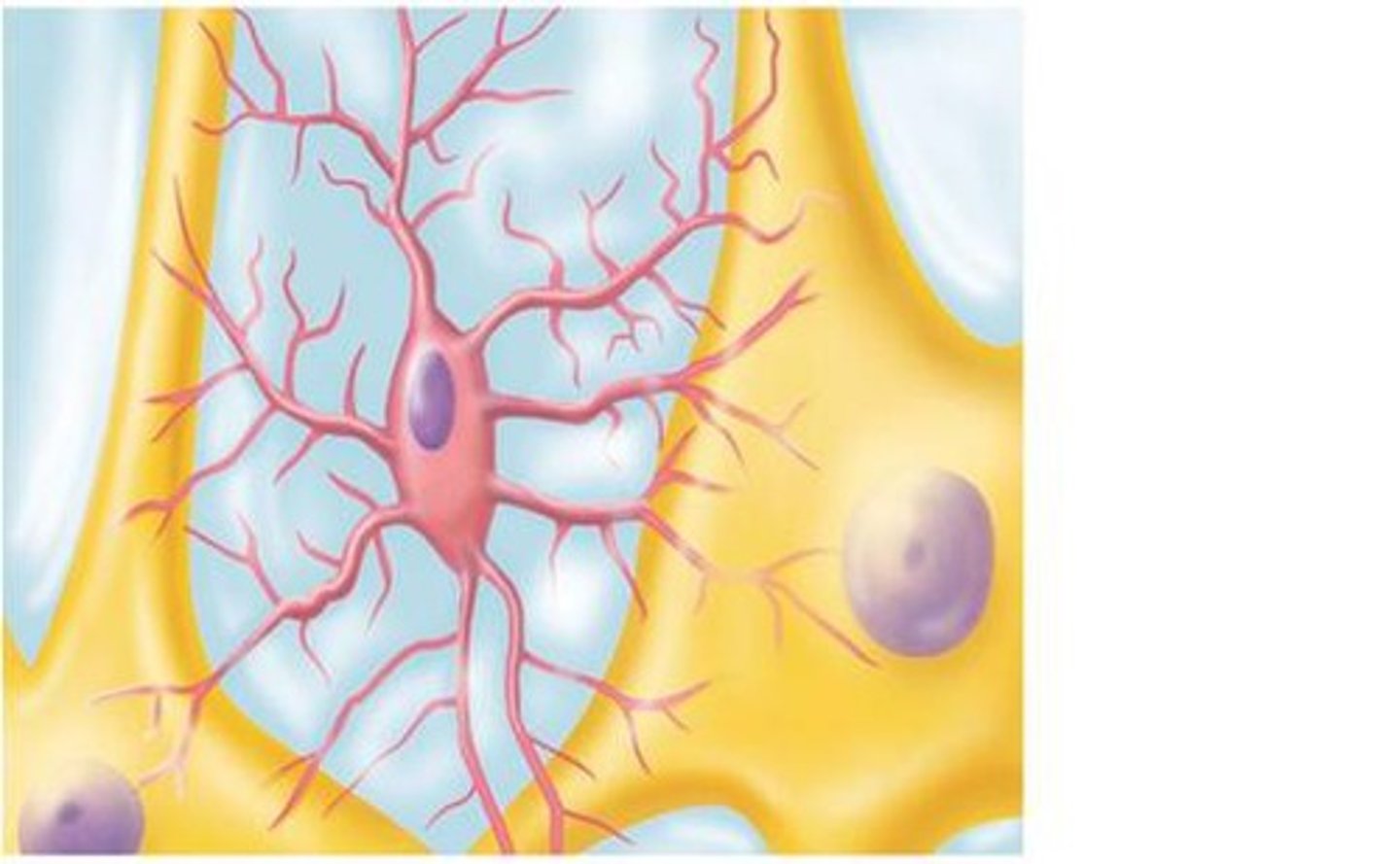
oligodendrocytes
- most prevalent glial cells
- in contact w/ the exposes surfaces of neurons -> wrap around axon -> form myelin sheath -> electrical insulation
- myelinated axons are the white matter of CNS
- 1 oligodendrocyte for multiple axons
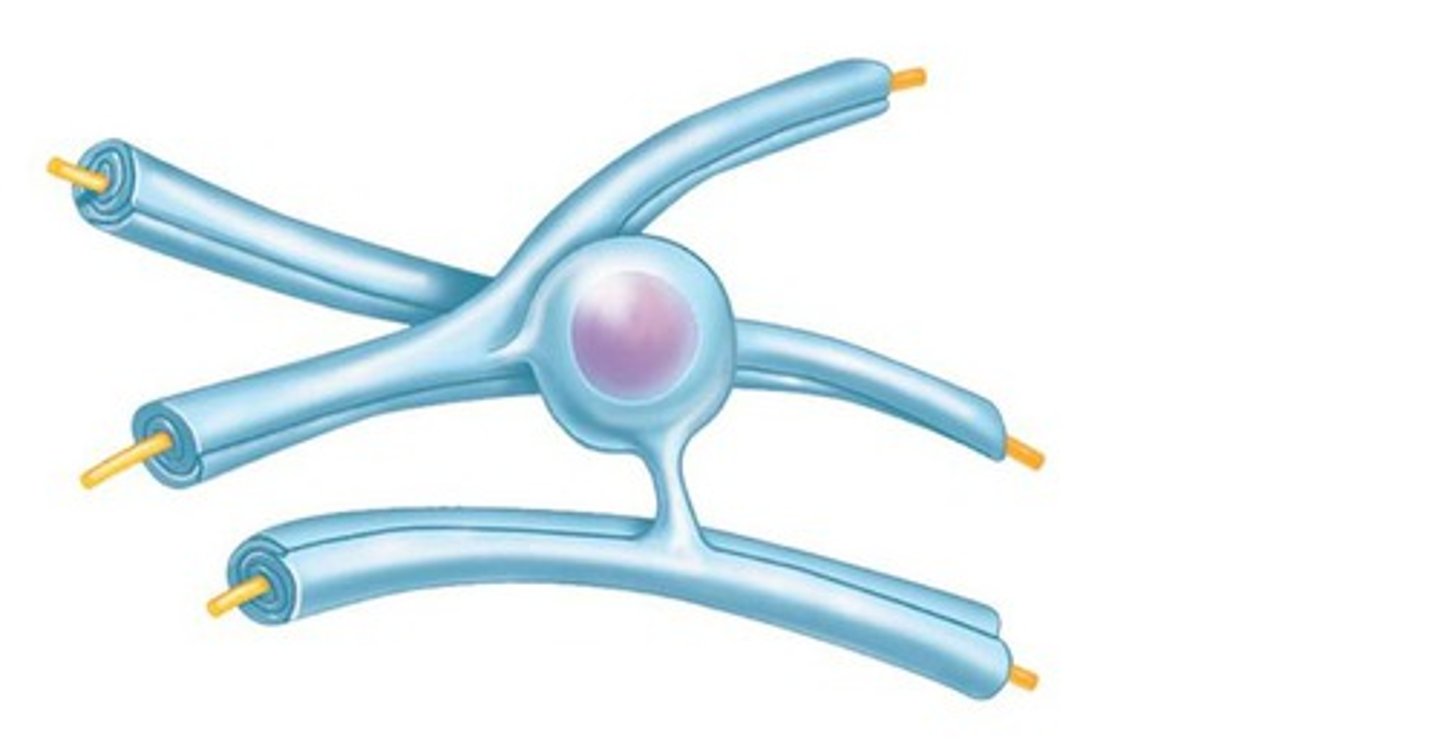
glial cells of PNS
satellite and schwann
satellite
- surround neuron cell bodies in ganglia
- regulate interstitial fluid like astrocytes
- provide nutrients and structural support for neurons
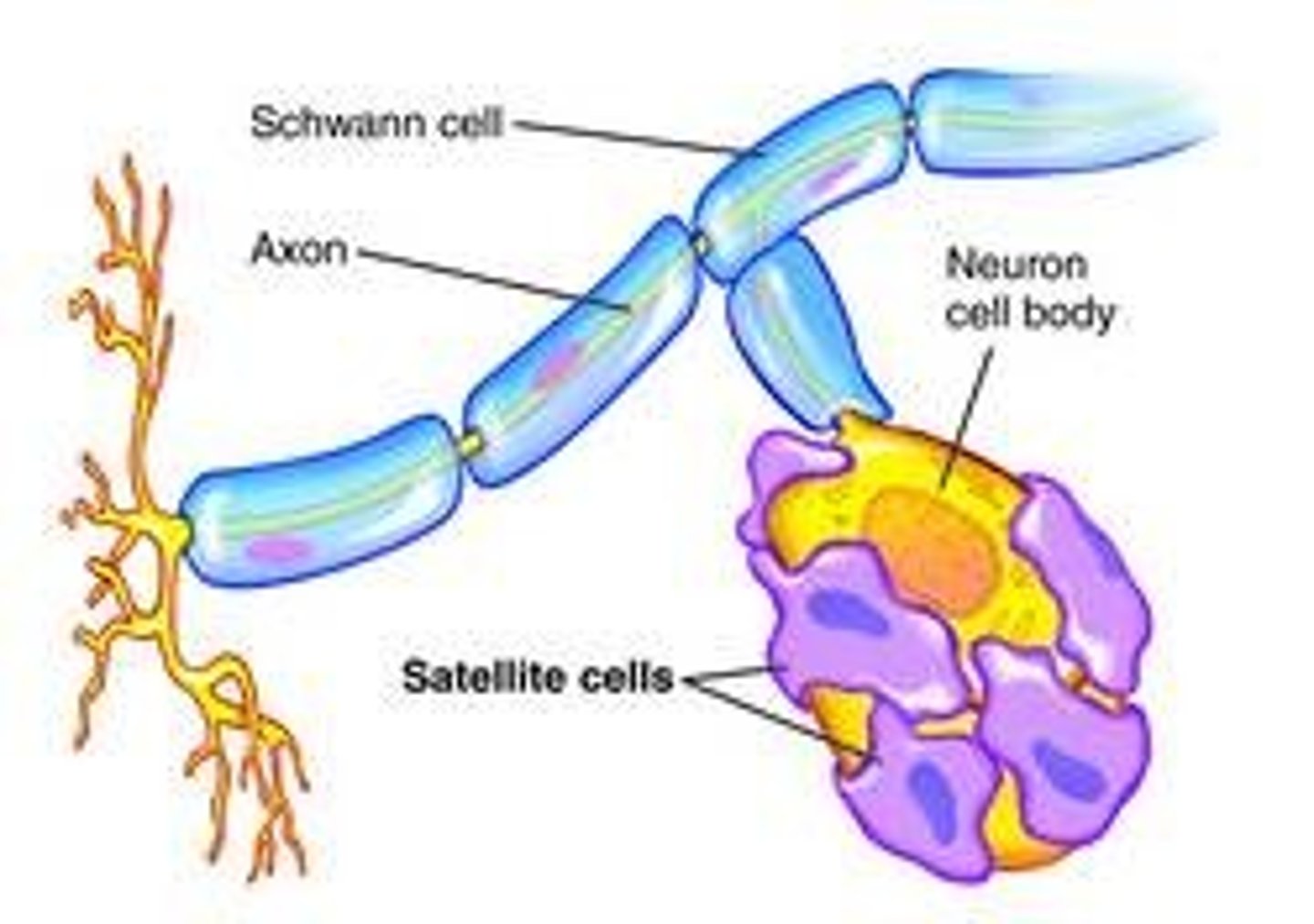
schwann (neurolemmocytes)
- form thick, myelin sheath, or indented folds of the plasma membrane around peripheral axons
- 1 schwann for 1 axon
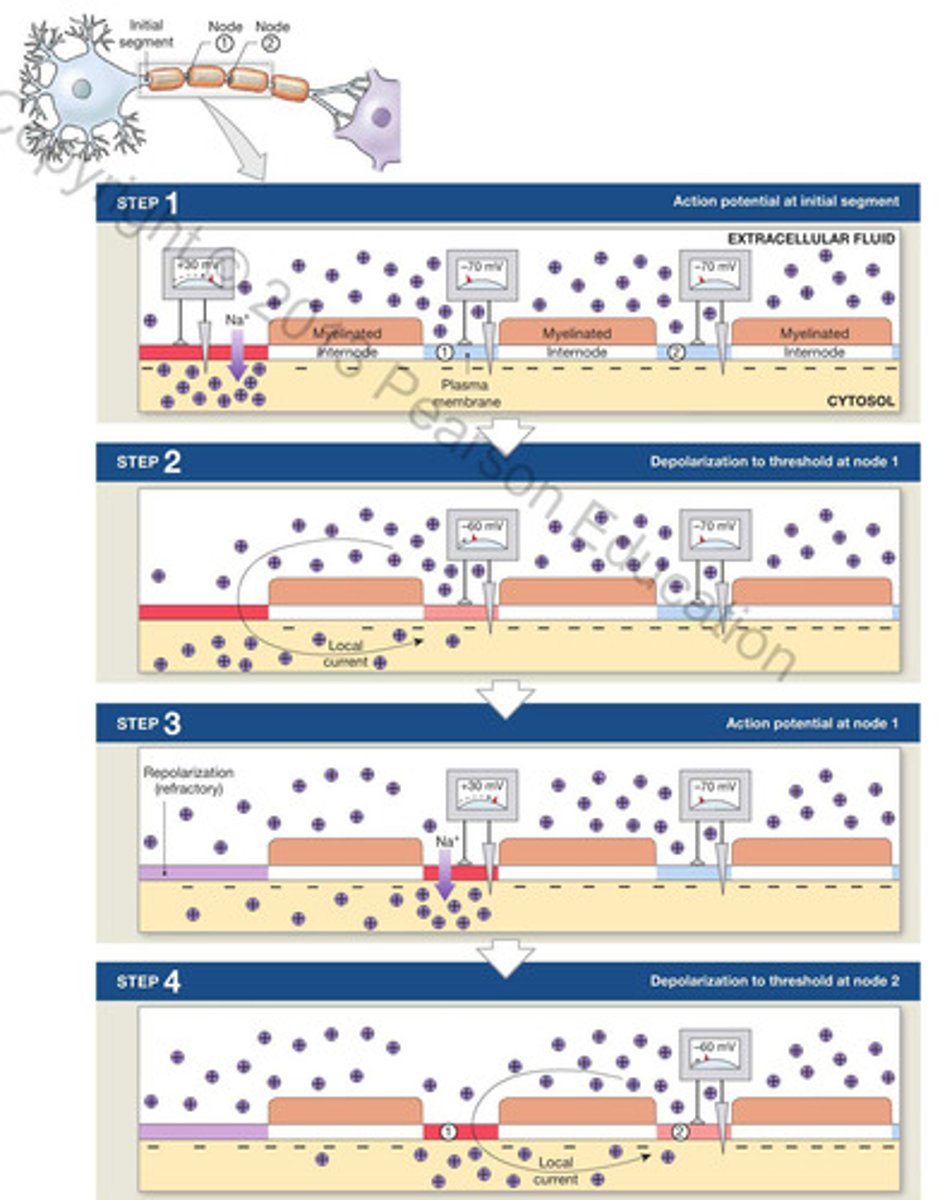
node of ranvier
exposed axon gap where there is no sheath to insulate; periodic; action potentials leap from one node to another
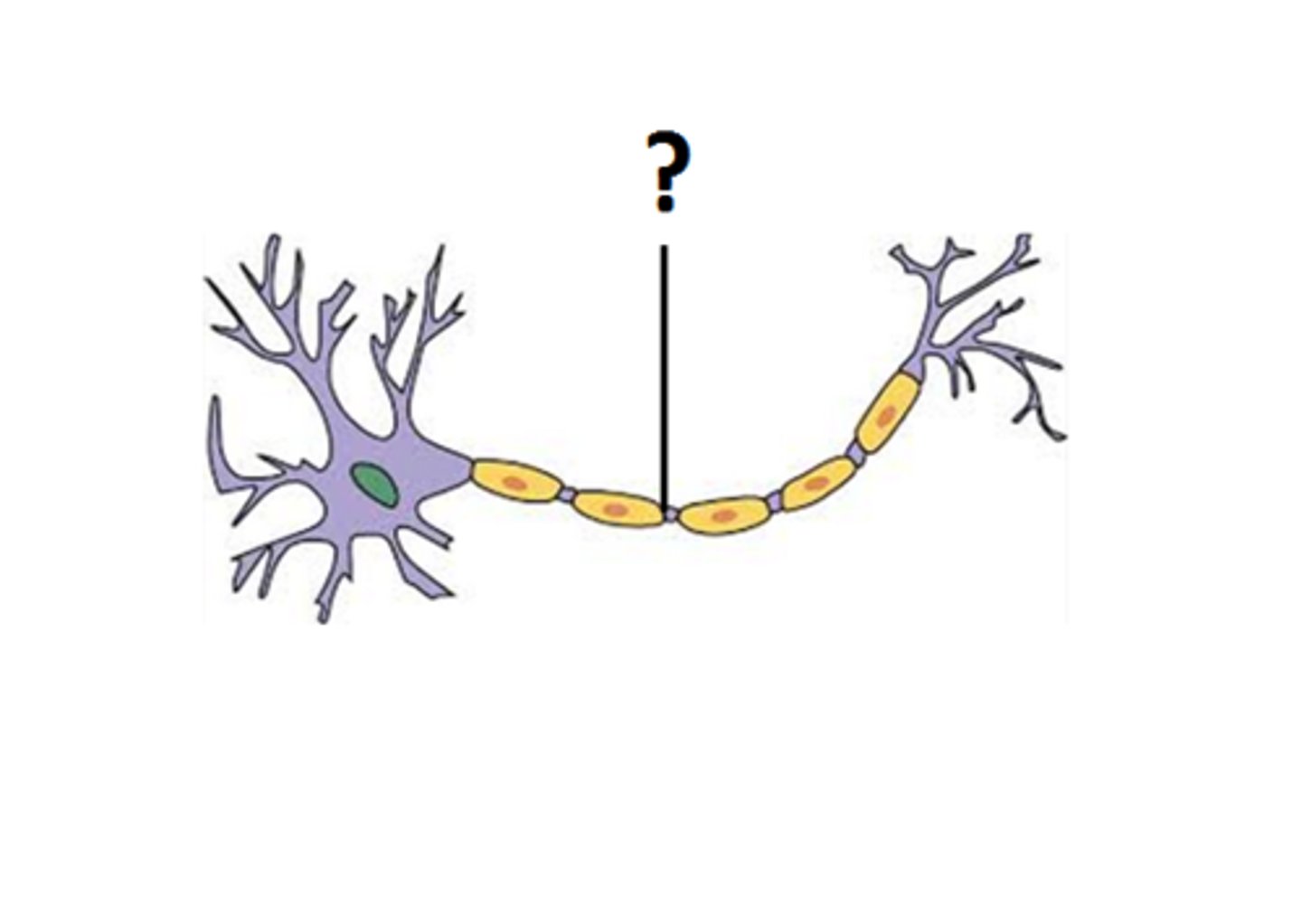
myelinations _______ neuronal conduction
SPEEDS UP
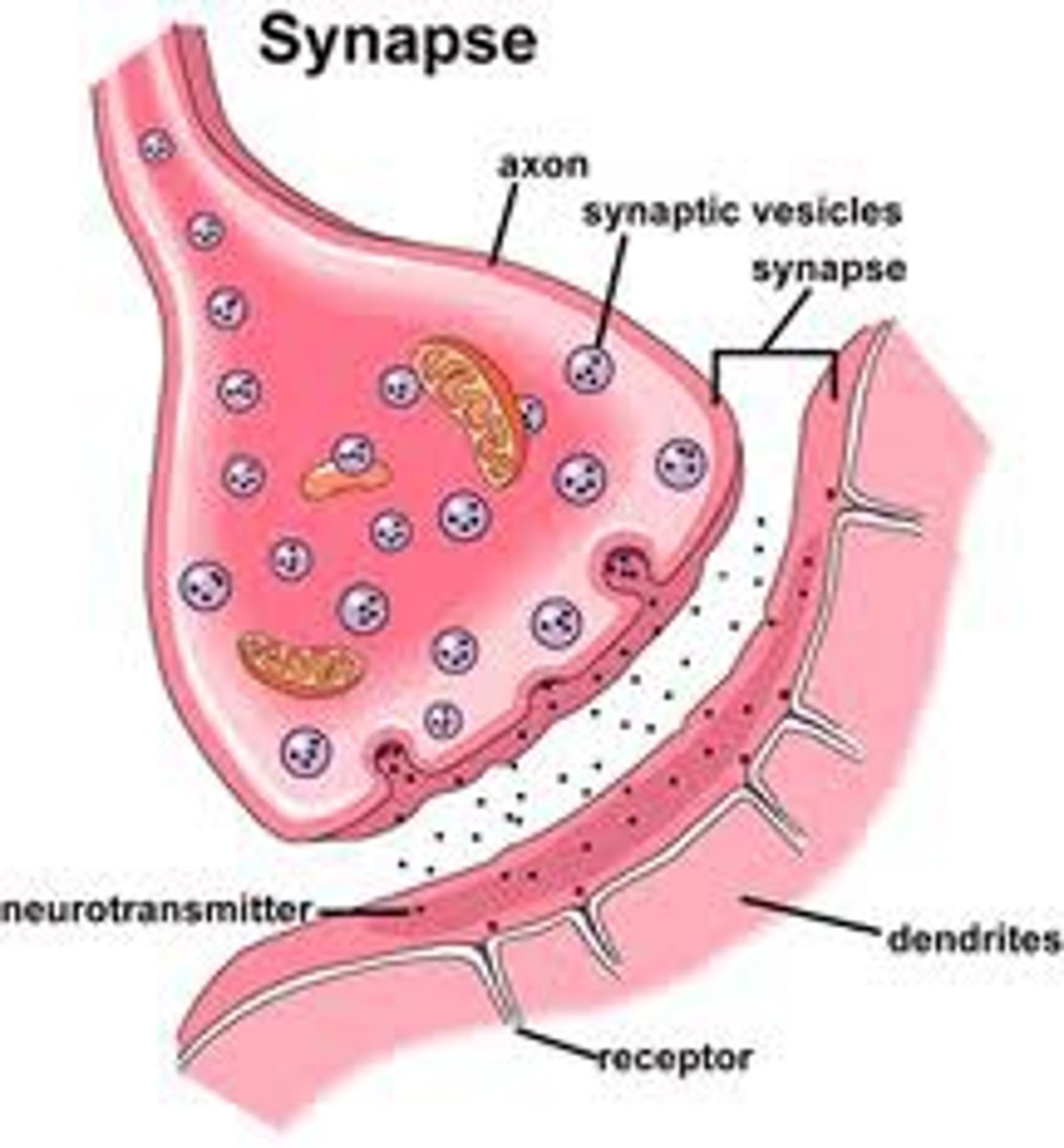
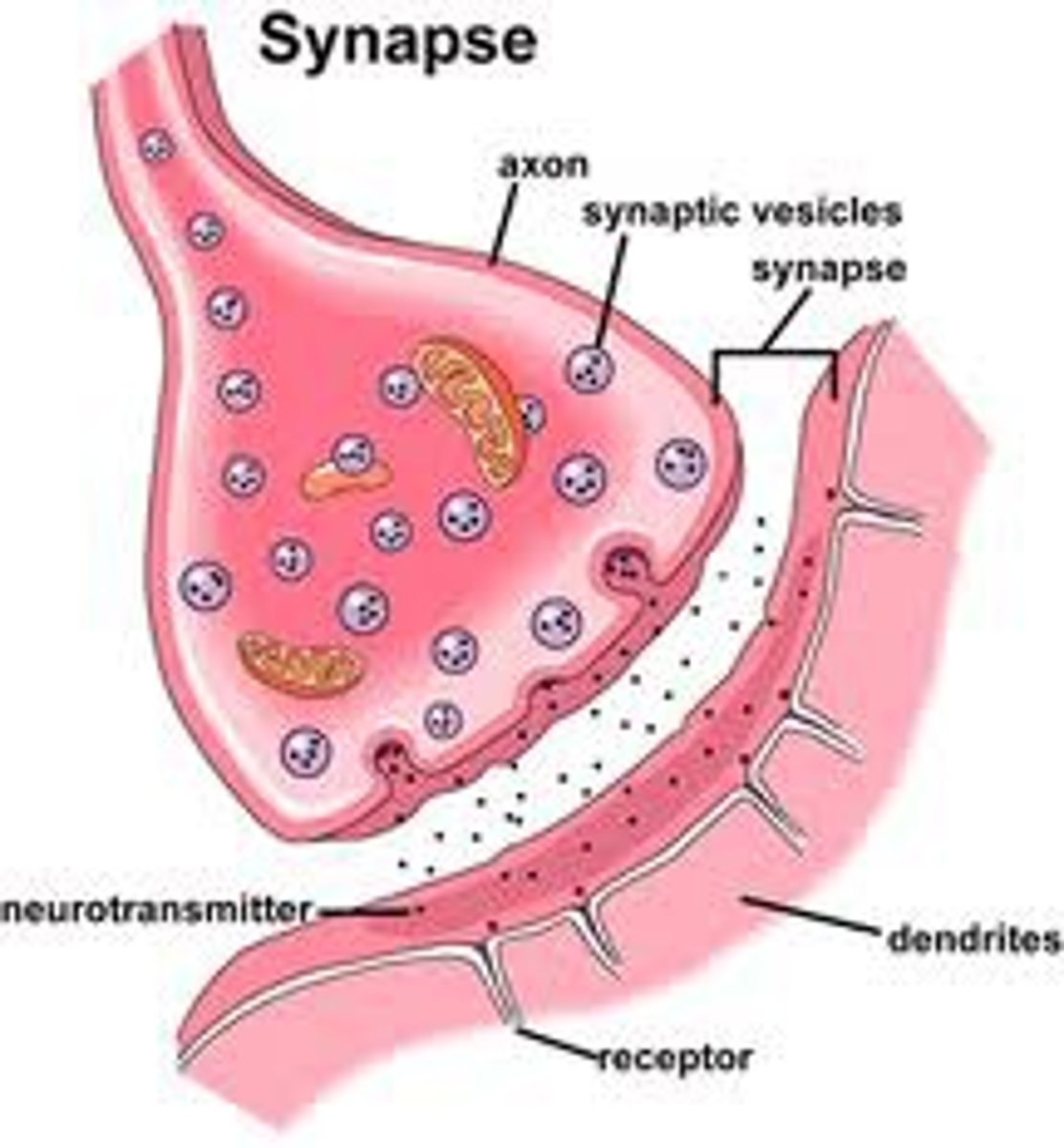
synapses
- where a neuron makes a communicating connection w/another neurons or effector
- axon terminal (presynaptic) -> dendrite/effector (post synaptic)
- electrical or chemical synapse (usually chemical)
- presynaptic: where electrical (action potential) is converted to chemical (neurotransmitter)
neuromuscular junction
synaptic connection between a neuron and a muscle cell
types of synapses
electrical, chemical
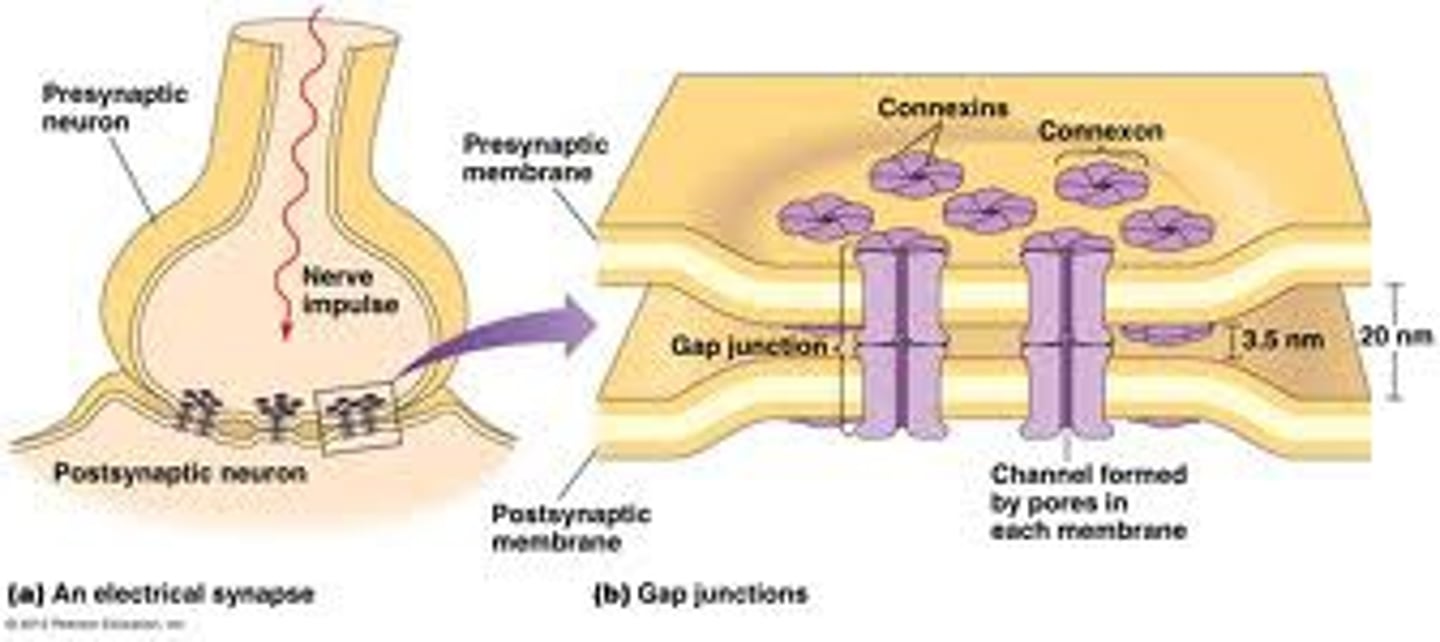
electrical synapse
- aka gap junction
- mechanical link bt neurons that allows for conduction of electricity (flow of ions)
- plasma membranes of pre-/post-synaptic cells are direct contact
- rapid signal conduction -> unregulated
- rare
chemical synapses
- most common and affected by ingested chemicals
- uses neurotransmitters
- pre- and post-synaptic cells are separated by narrow synaptic cleft
- needs enough neurotransmitters to bind w/receptors to generate an electrical impulse
steps of chem. synapse
1. arrival of action potential
2. neurotransmitter molecules released by exocytosis
3. neurotransmitters diffuse across synaptic cleft and bind to receptor proteins
4. activation of receptors leads to altered flux of ions in postsynaptic neuron -> transmission of impulse
5.
role of Ca2+ in chem synapses
- arrival of action potential: increase of Ca2+ entering -> depolarized
- increased Ca2+ via ion channels -> bind to proteins that attach to synaptic vesicles to plasma membranes -> two membranes fuse and release neurotransmitters -> Ca2+ pumped out via active transport -> neurotransmitter removed from synaptic cleft by enzymatic degradation
K+/Na+ pump
- K+ in cytosol and Na+ in ECF
- 3Na+ out of cell and 2 K+ in cell using ATP
- help counter the passive diffusion that leak these ions to maintain membrane potential
resting membrane potential
-70mV
- membrane is unstimulated
- all neural activities begin with change in resting membrane
- ionic gradient from K+/Na+ pump produces the resting membrane potential
passive ion channels
leak channels that are always open; important in establishing the normal membrane potential of the cell
active ion channels (gated)
open or close in response to specific stimuli; chemically, voltage, and mechanically gated
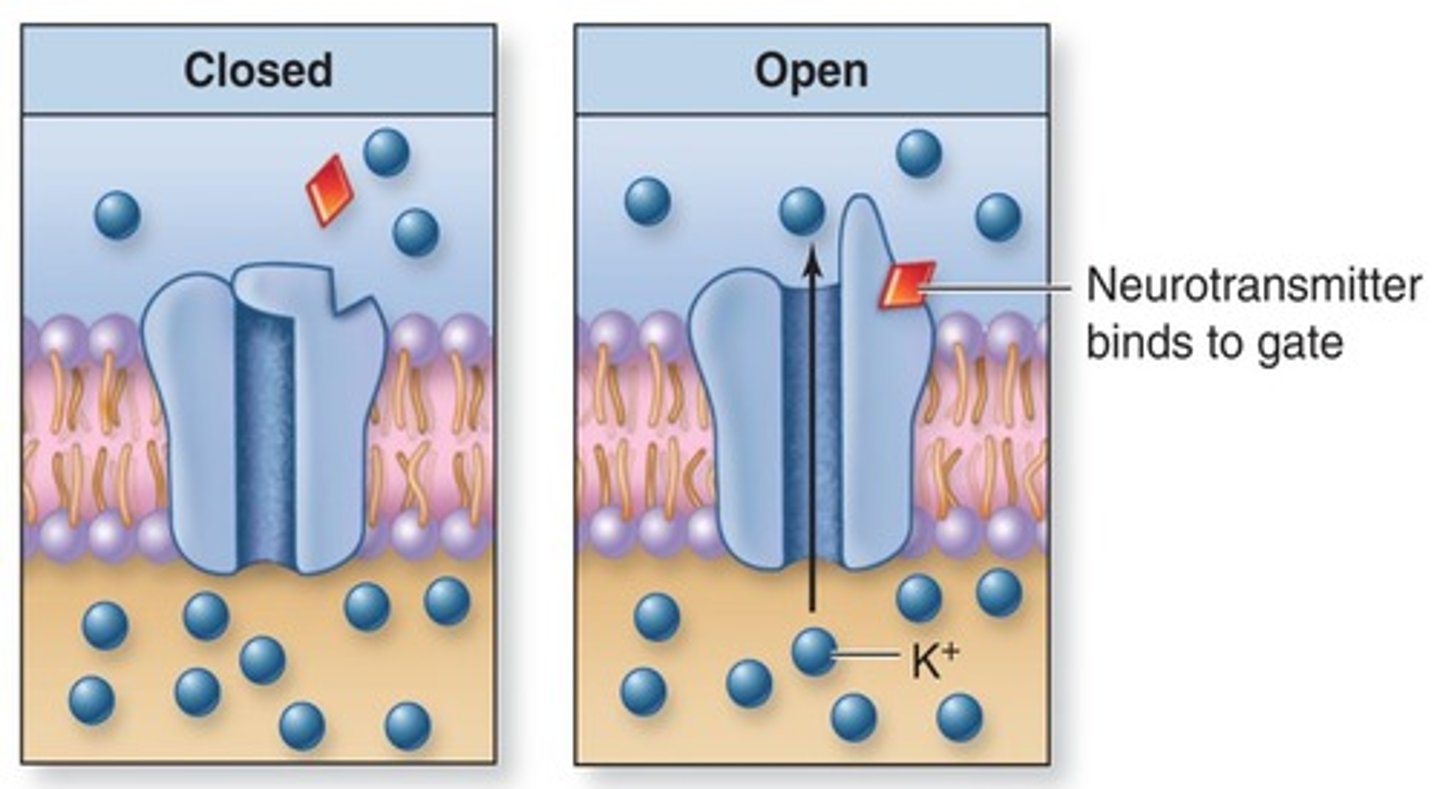
chemically gated (ligand)
- open or close when bind w/ specific chemicals
- ex acetylcholine when binds allows for Na+ and K+ to pass
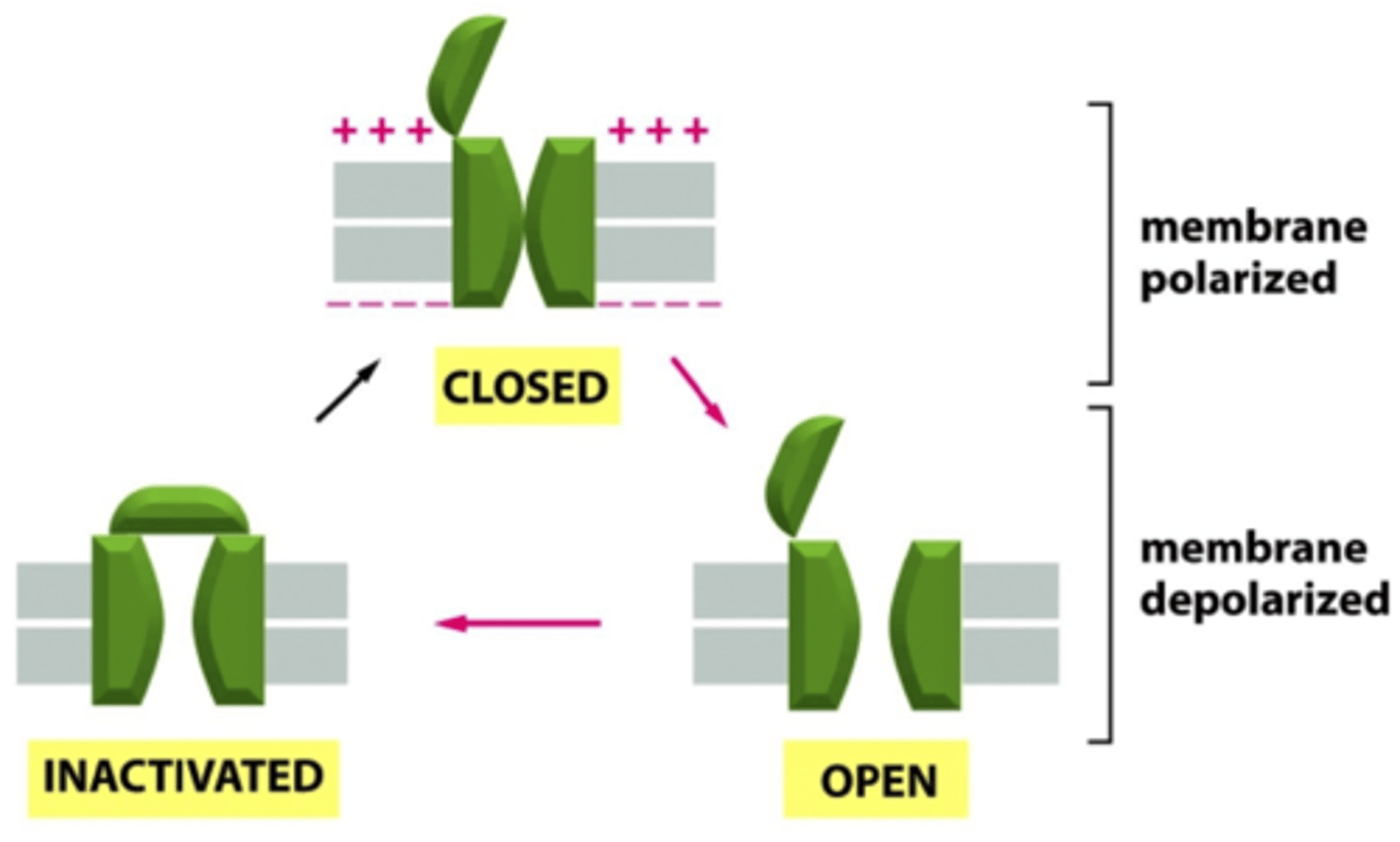
voltage gated
- open or close in response to changes in membrane potential
- characteristics of areas of excitable cell membranes (ie those that can generate and propagate action potential)
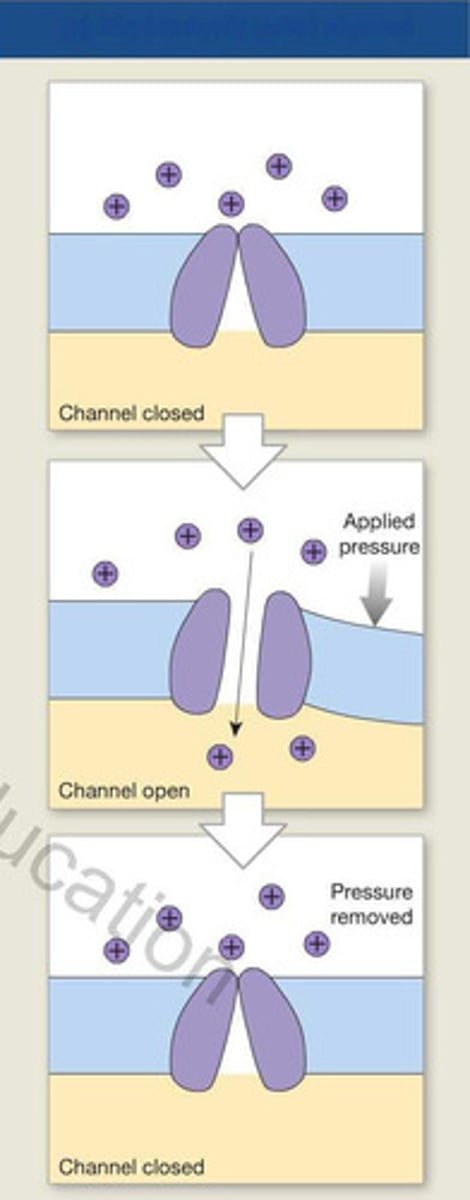
mechanically gated
- open or close in response to physical distortion of the membrane
- opening when pressure is applied due to touch
graded potential
- temporary localized change in the resting membrane potential in response to a stimulus
- effects decrease w/ distances from the stimulus
- important for short distance signaling
steps to produce a graded potential
1. Na+ enters the cell and attracted to the inner surface of membrane (- charge)
2. membrane potential shifts towards 0mV -> depolarization
3. when chemical stimulus is removed then normal membrane permeability is restored -> repolarization
if gated K+ opens
- opposite effect from Na+ channel open
- the inside of the cell becomes more negative -> hyperpolarization since K+ is leaving
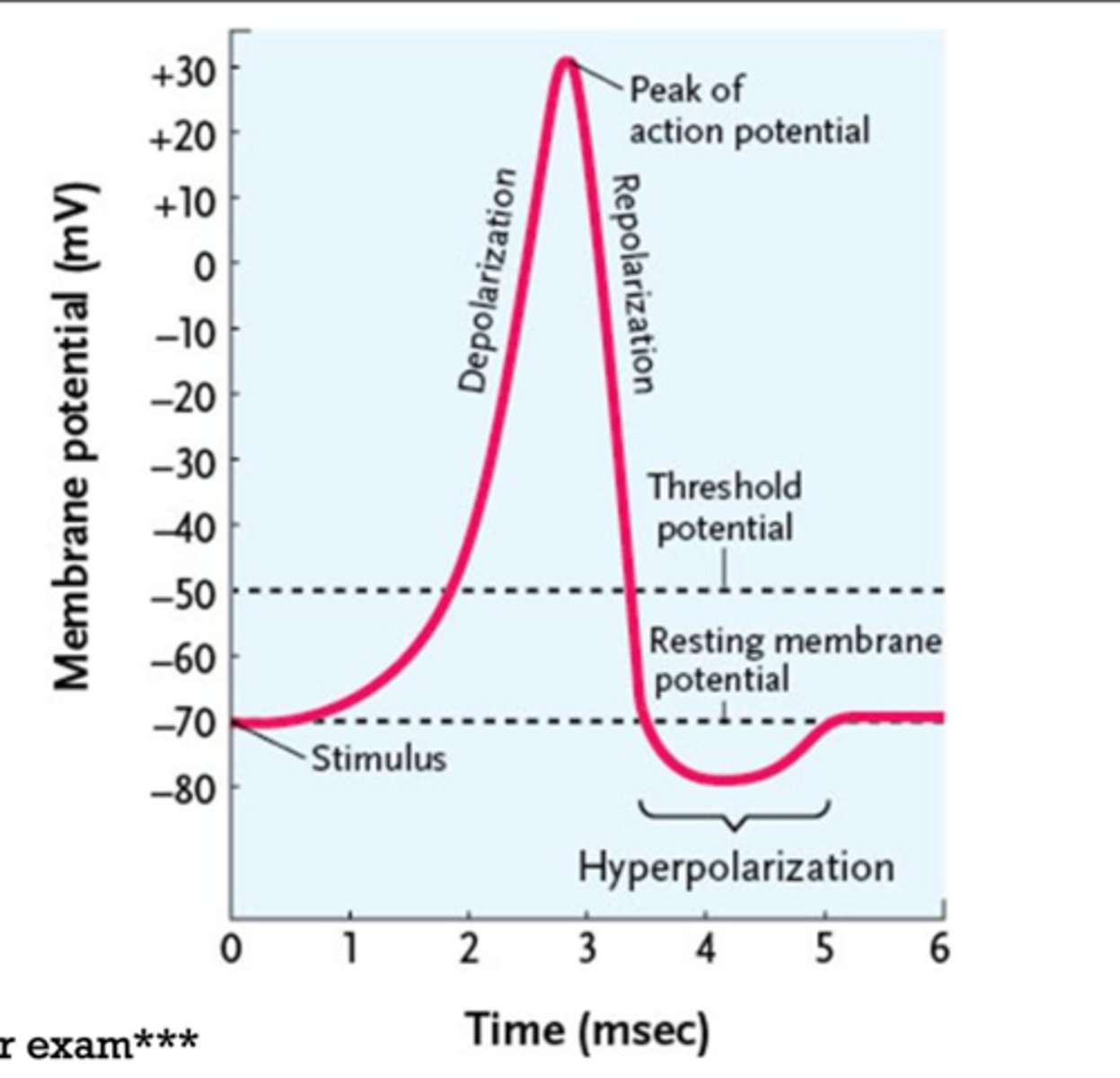
action potential (neuronal impulse)
- electrical potential which is propagated along the entire surface of the axon until it reaches the axon terminals
- does not diminish as it distance is increased
- long distance signaling of nerve and muscle
- triggered when graded potential is large enough and exceeds threshold
- DEPOLARIZATION TO THRESHOLD MUST OCCUR BEFORE ACTIONAL POTENTIAL BEGINS
threshold potential
membrane potential at which an action potential begins; usually -60mV to -55mV
changes in the membrane potential at a single location during the generation of an action potential
refractory period
- plasma membrane does not respond normally to additional depolarizing stimuli
- from the time action potential begins to the normal resting membrane is stabilized -> need Na+ channel inactivation to end
depolarization
membrane potential is getting more positive
repolarization
when a membrane has been depolarization and returning to normal resting value -> gets more negative
hyperpolarization
membrane potential is more negative than the resting level
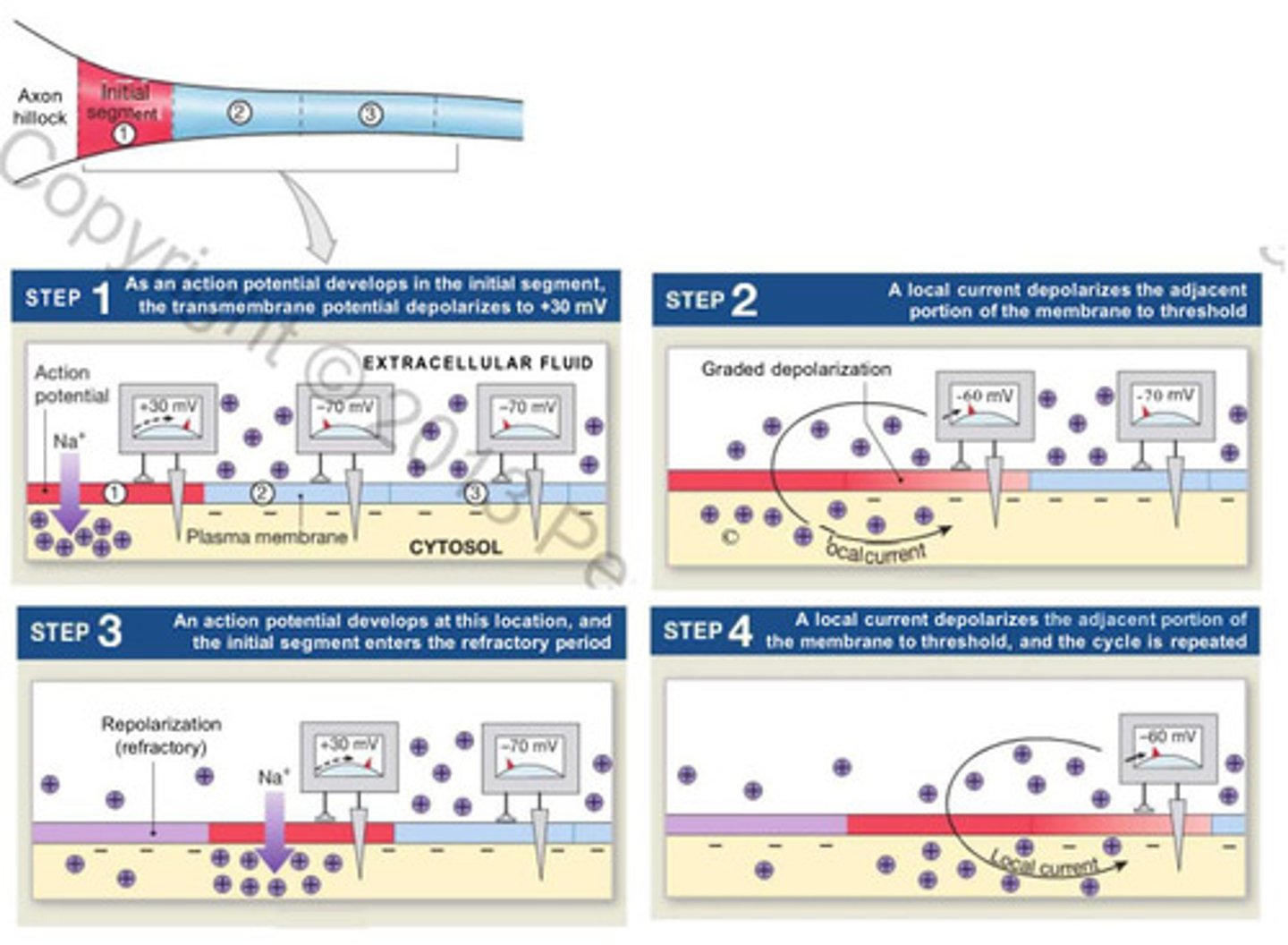
neuronal propagation
chain reaction of Na+ ions moving into the axon and depolarizing adjacent sites until it reaches the axon terminals
two ways: continuous and stationary
continuous propagation
- propagation along unmyelinated axons
- affects on segment of axon at a time
- action potential moves across the surface of the membrane in series of tine steps -> ~1m/s
- cycle repeats at each step
saltatory propagation
- action potential along myelinated axon
- faster and less energy than cont.
- local current "jumps" from node to node
- depolarization only at nodes
types of neurotransmitters
ionotropic and metabotropic
ionotropic receptors
- ligand gated
- rapid but brief change in membrane potential of the postsynaptic cell
- lasts as long as neurotransmitters remain in synaptic cleft
- alter ION movement
metabotropic receptors
- g-protein-coupled receptors -> NOT ION CHANNELS
- production of second messengers (cAMP)
- delayed by longer lasting changes in the membrane potential in the postsynaptic cell
acetylcholine
- released in vertebrate neuromuscular junctions and throughout the brain
- excitatory at neuromuscular junction
- drugs is nicotine, curare, and atropine
- widespread in CNS and PNS
- most studied and best know neurotransmitter
glutamate
- neurotransmitters for sensory inputs and motor outputs
- main excitatory neurotrans.
drugs is ketamine and phencyclidine
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
- main inhibitory neurotransmitters
- often acts in same circuits w/ glutamate
- drugs is alcohol, diazepam, flunitrazepam
nitrous oxide
- diffuses across the plasma membrane of cells
- modulatory
- drug sildenafil
types of postsynaptic potentials
excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP)
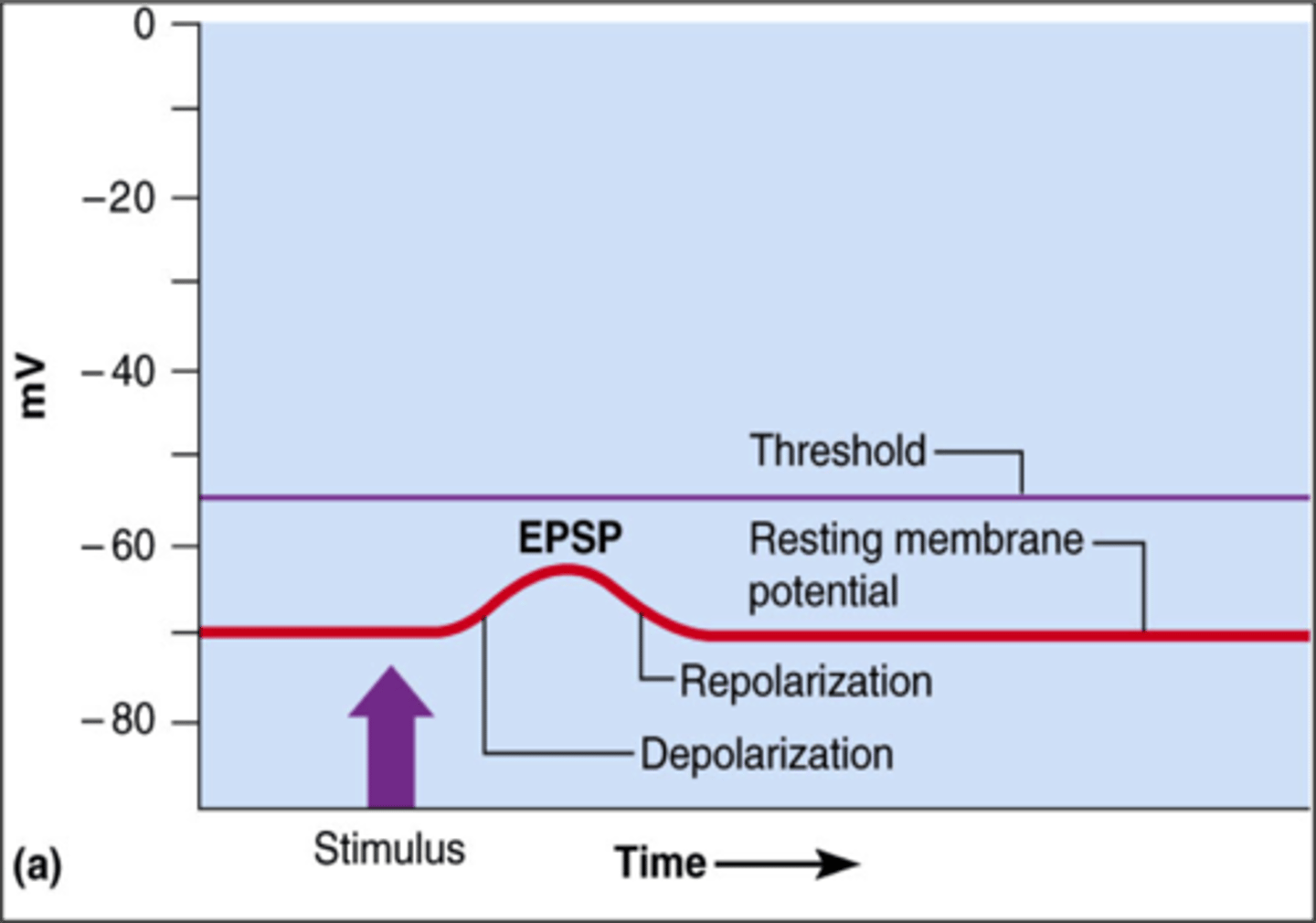
excitatory postsynaptic potentials
- graded depolarization caused by the arrival of a neurotrans. at the postsynaptic membrane
- results form opening of chemically gated Na+ channels
- affects area immediately surrounding the synapse
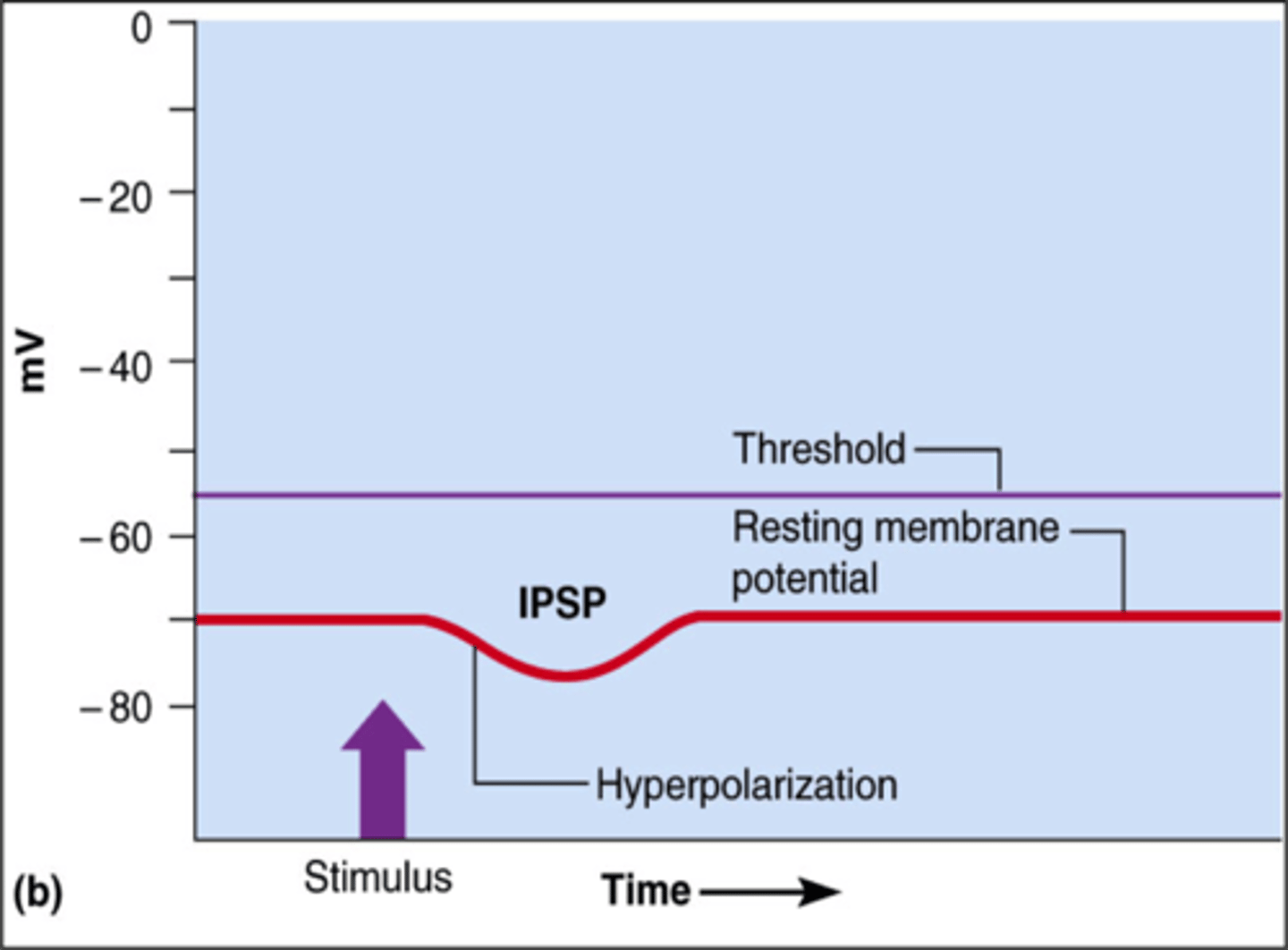
inhibitory postsynaptic potentials
- graded hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane
- results from opening of chemically gated K+ or Cl- channels
- while hyperbolized -> neuron is said to be inhibited
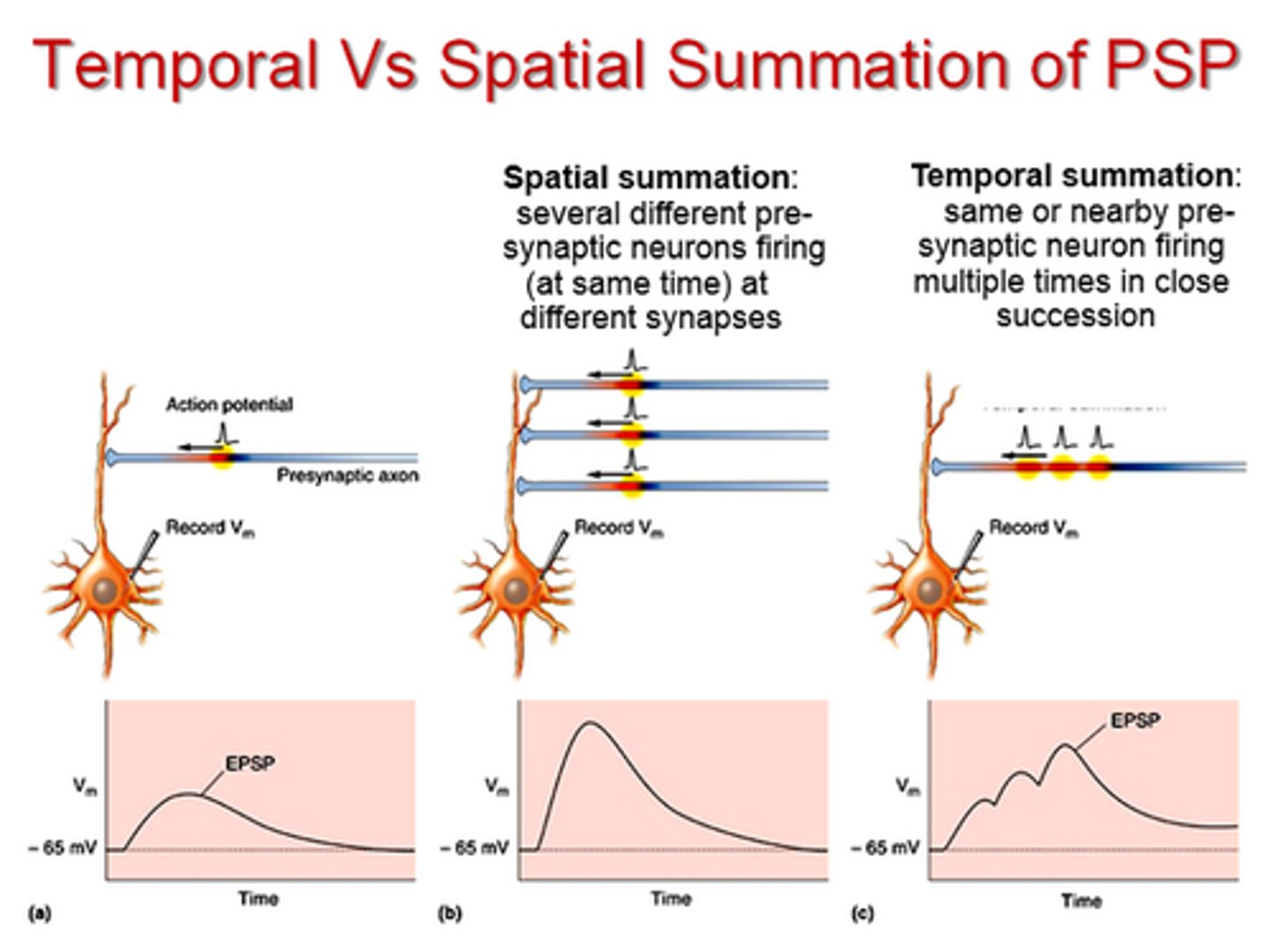
summation
- integration of postsynaptic potentials
- single E/IPSP will not result in an action potential -> need to multiple
- types: temporal and spatial
spatial summation
- when more than 2 stimuli arrive at the same time but at DIFFERENT location
- more than one synapse is active at the same time
- local currents spread the depolarizing effects and areas of overlap experience the combined effects
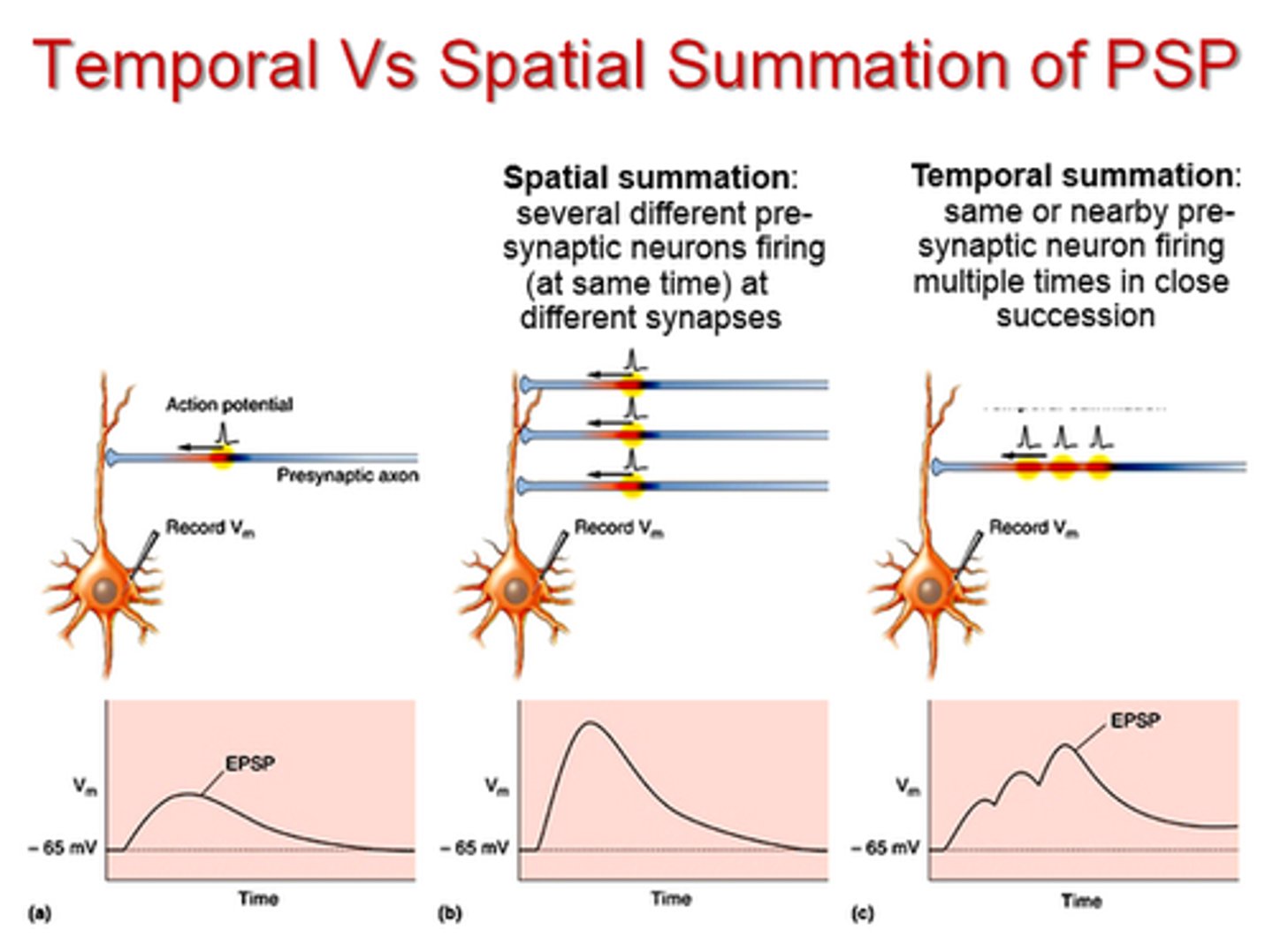
temporal summation
- occurs on a membrane that receives multiple depolarizing stimuli from the SAME source in rapid succession
- effects of second stimulus is added to those of the first