Chapter 14b: Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
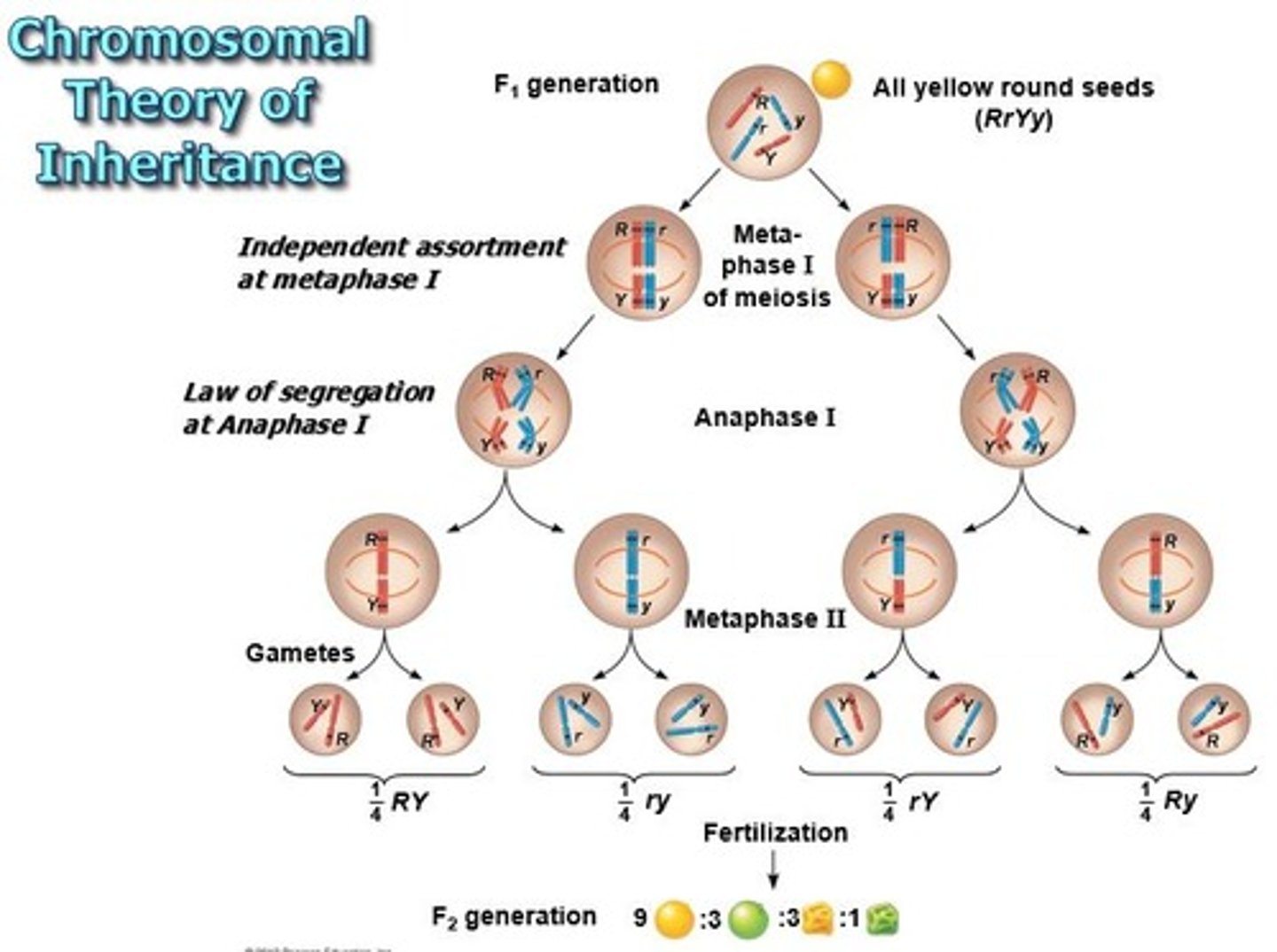
chromosome theory of inheritance
-proposed by Sutton and Boveri
-asserted that the genes are located on chromosomes and inheritance patterns are determined by chromosome behavior during Meiosis
sex linkage + chromosome theory
-supported by experiments on the sex chromosomes
-in some animals there were sex chromosomes called X and Y chromosomes (they determine the sex of offspring)
-found by Nettie Stevens
X-linked
gene located on the X chromosome
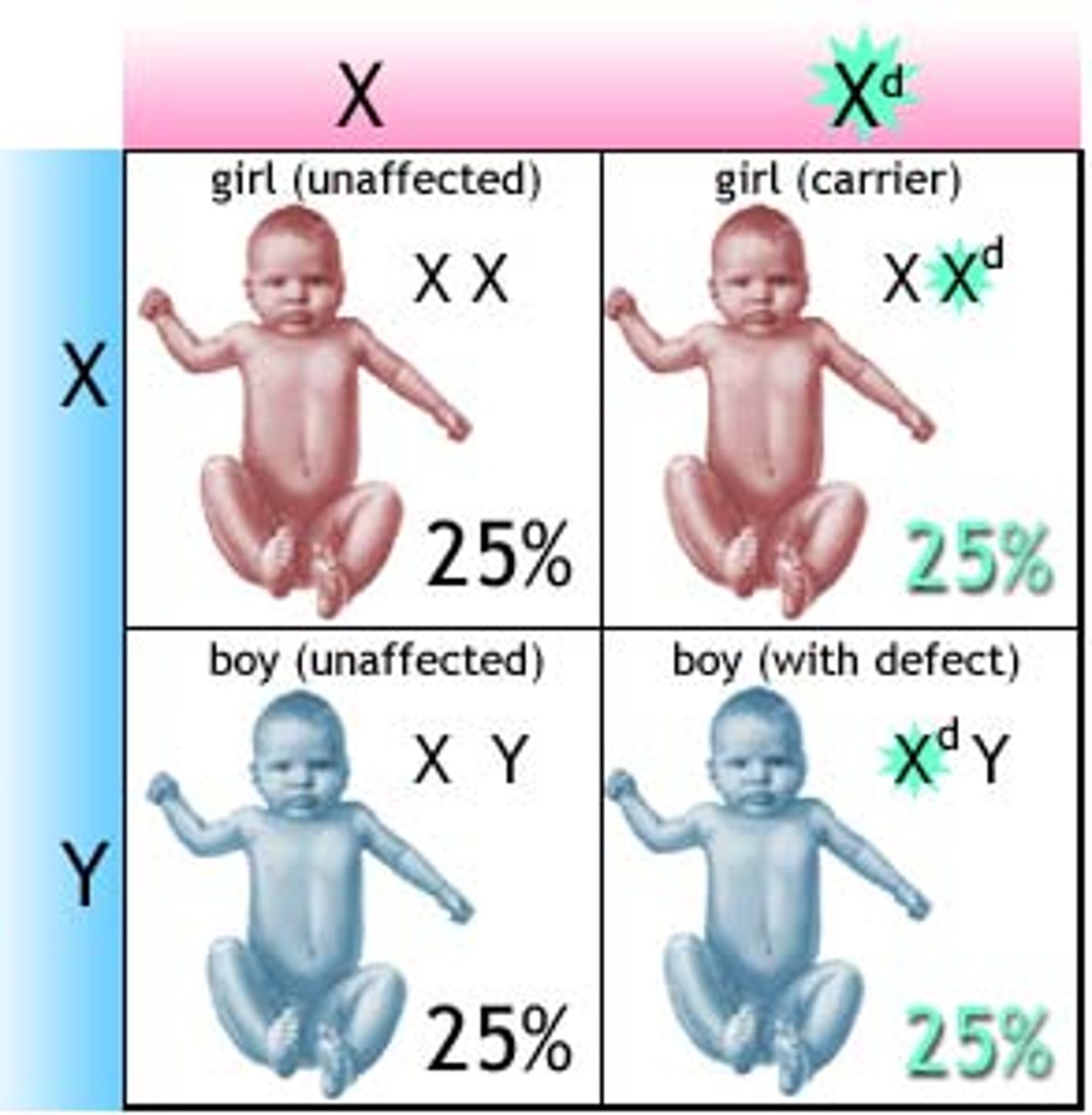
Y-linked
gene located on the Y chromosome
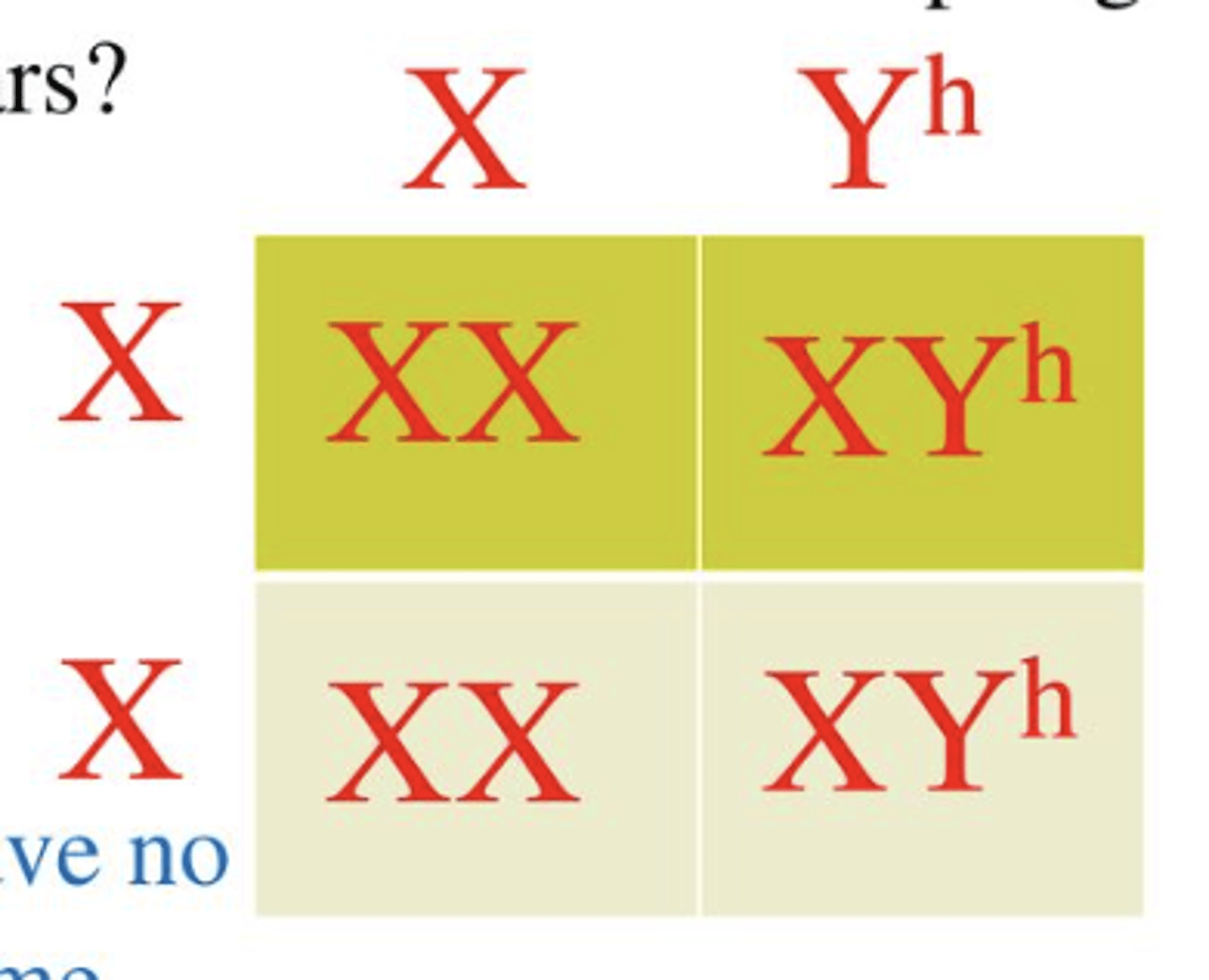
sex linked
genes being on either sex chromosome
sex chromosomes
-pair during meiosis I (synapsis occurs but no recombination or crossing over)
-segregate during meiosis II
-gametes have either an X or Y chromosome
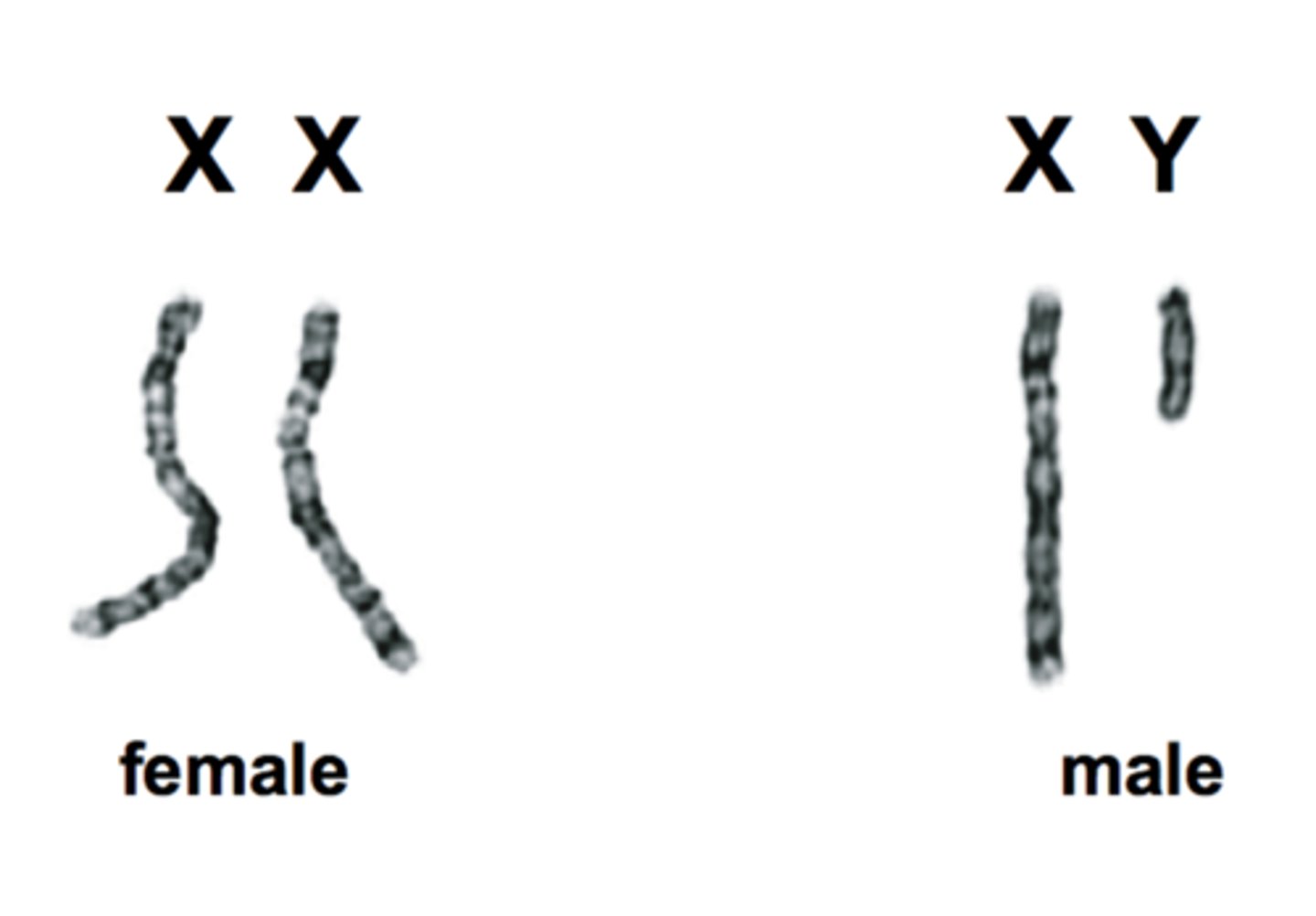
homogametic
females since they only produce X gametes
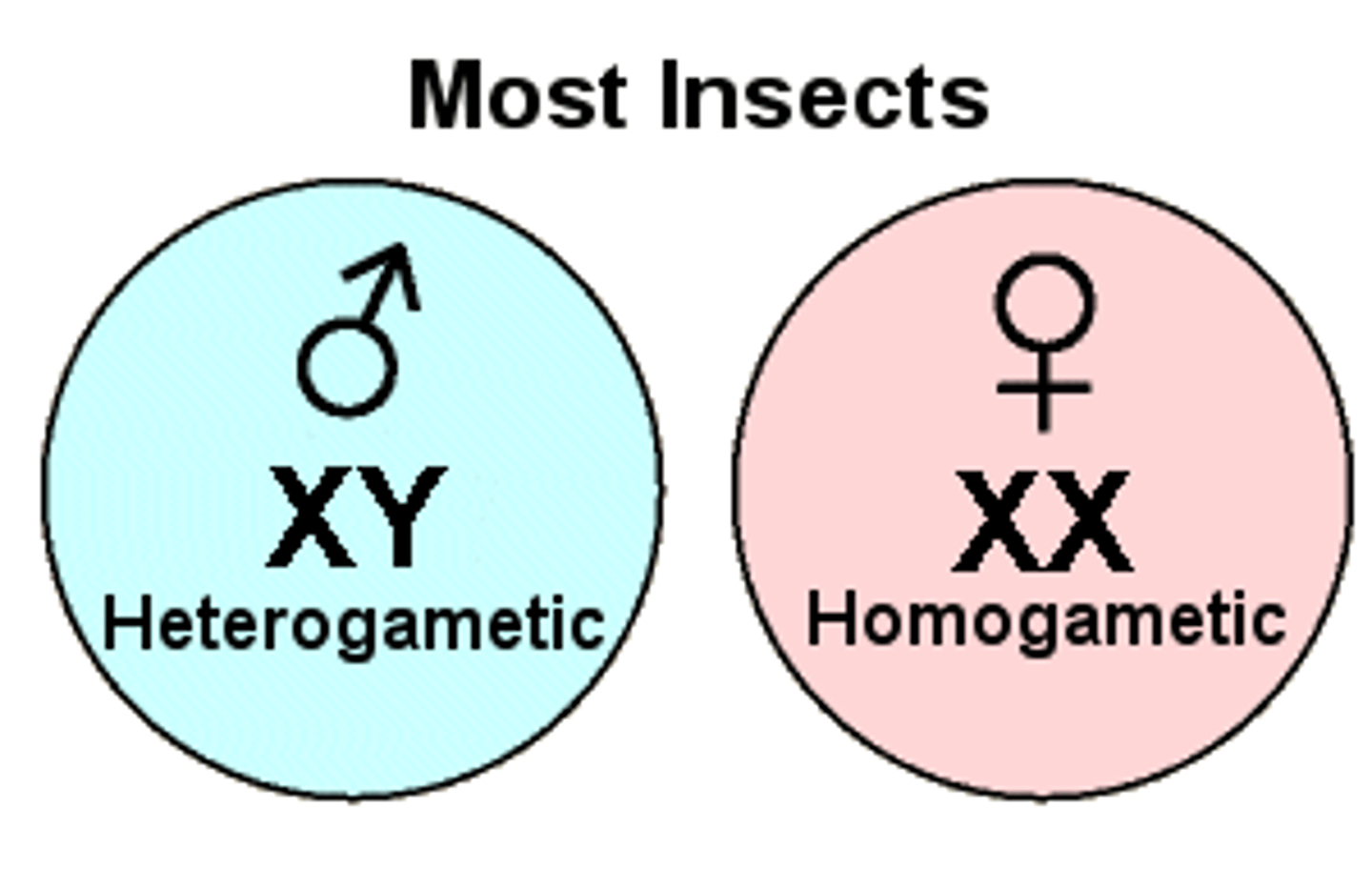
heterogametic
-males produce half X gametes and half Y gametes
-50% of sperm contain X chromosome and 50% contain Y chromosome
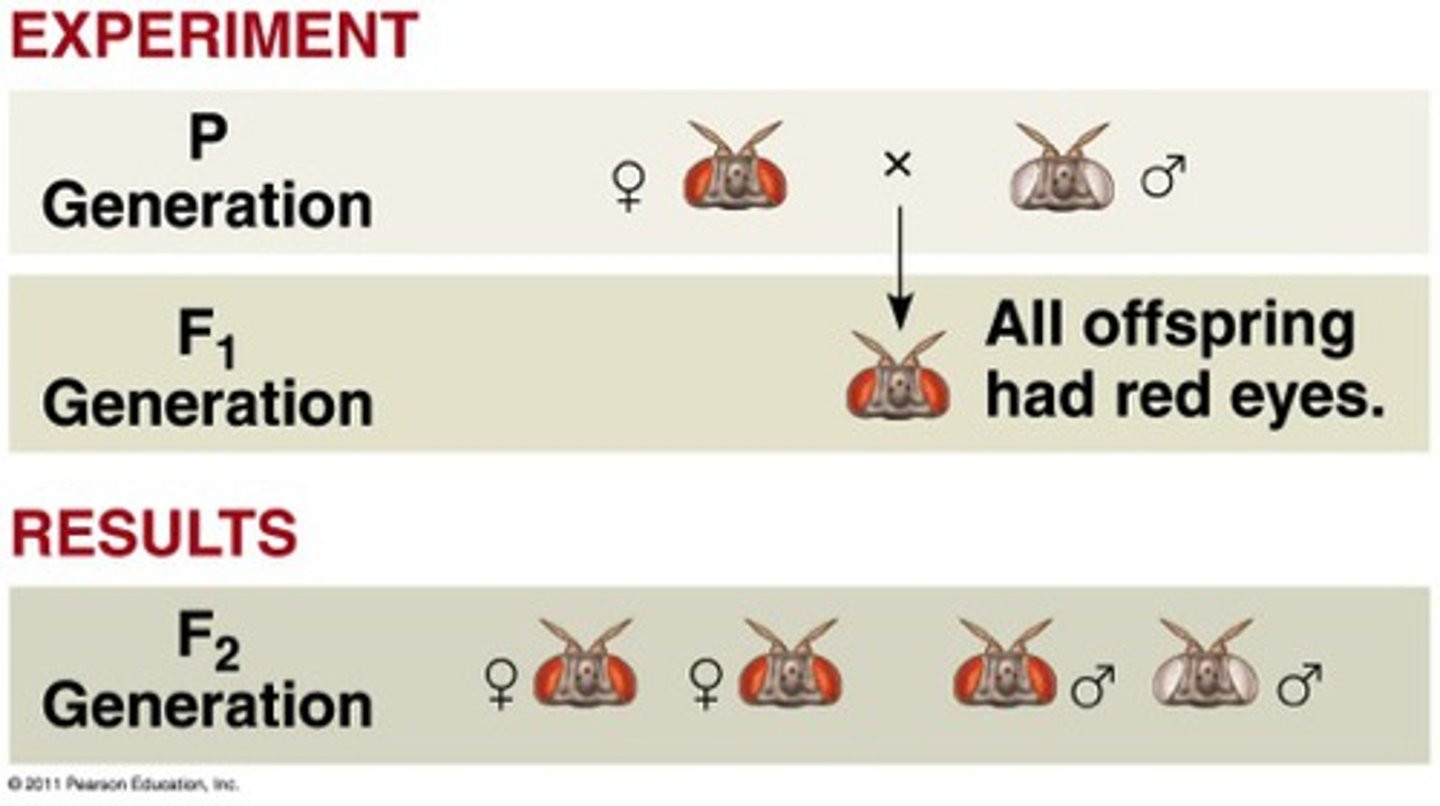
Thomas Morgan
-adopted fruit flies as model organisms
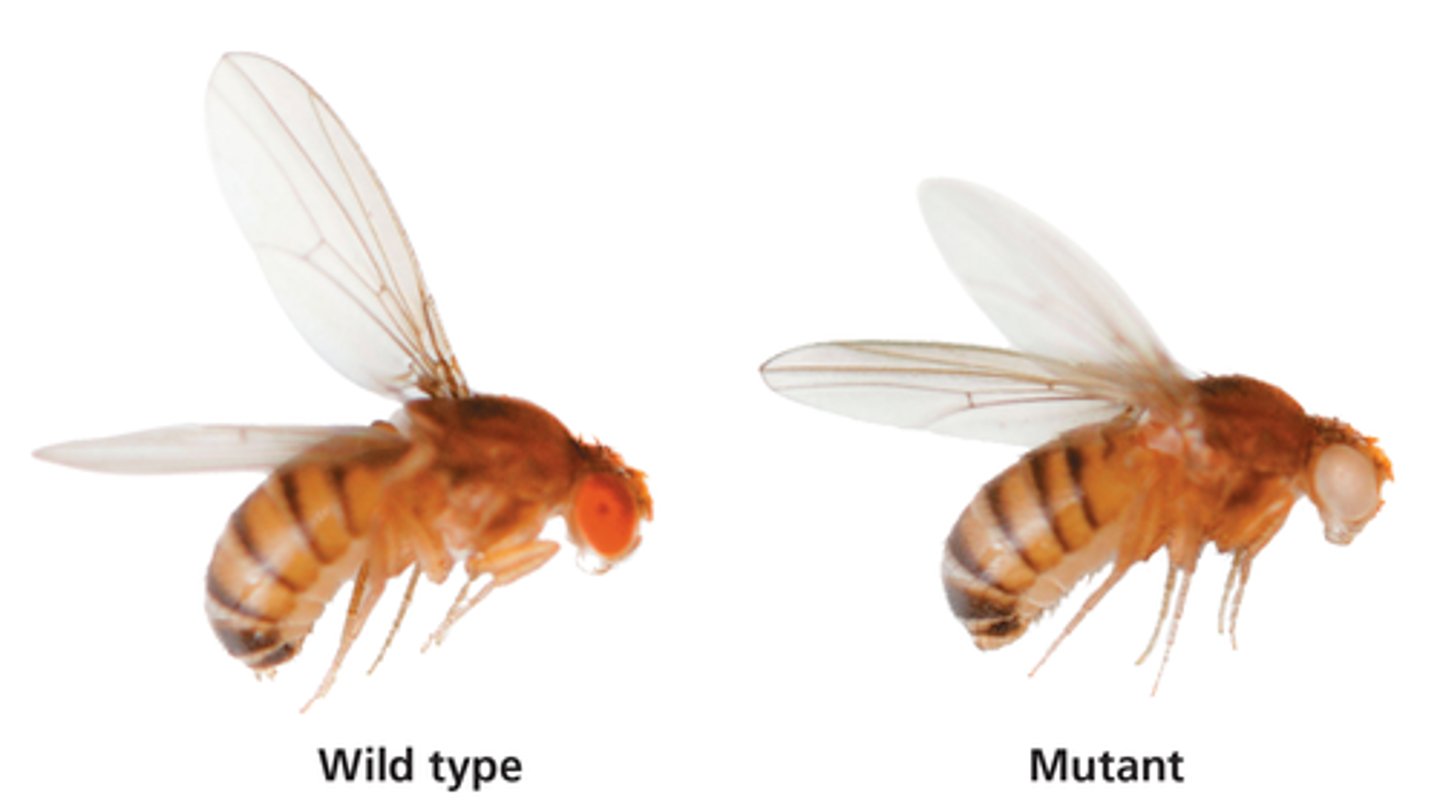
-used reciprocal cross to find that some patterns don't follow Mendelian behavior
-when the F1 and/or F2 ratios are different in recip. cross it means the genes are sex linked(X-linked in this case of fruit fly eye color)
fruit flies
-diploid and have 4 pairs of chromosomes
-females have 4 homologous pairs and males have 3 because X and Y are not homologous
inheritance for males
are hemizygous for genes on the X and Y chromosomes (heterogametic)
inheritance for females
can be heterozygous or homozygous for X-linked genes (homogametic)
wild type
most common phenotype in the natural population and typically the result of natural selection
mutants
all other phenotypes besides wild type that arise by mutations

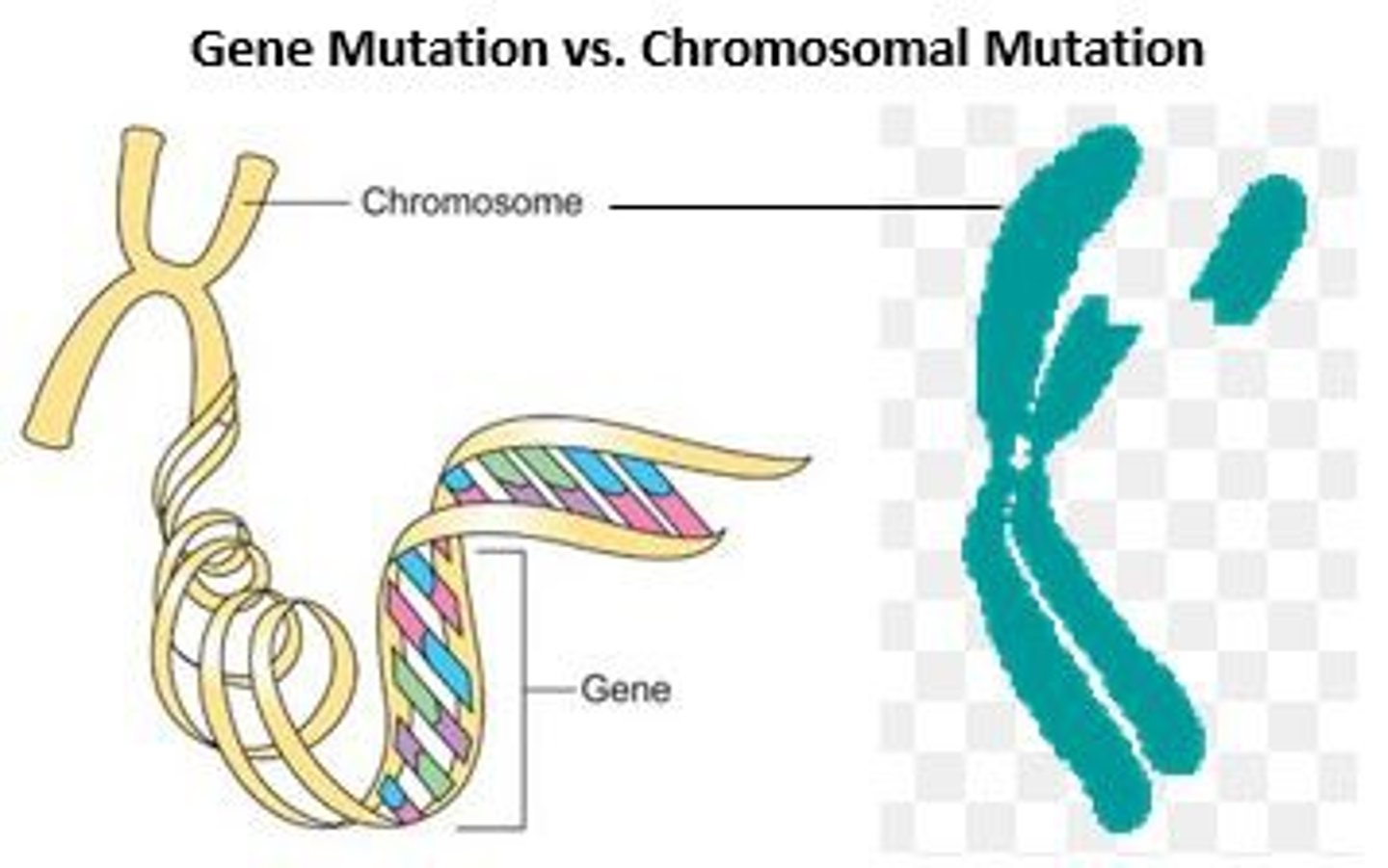
mutation
a stable and heritable change in the nucleotide sequence and only mutations in gametes are heritable since mutations in somatic cells can't be passed down
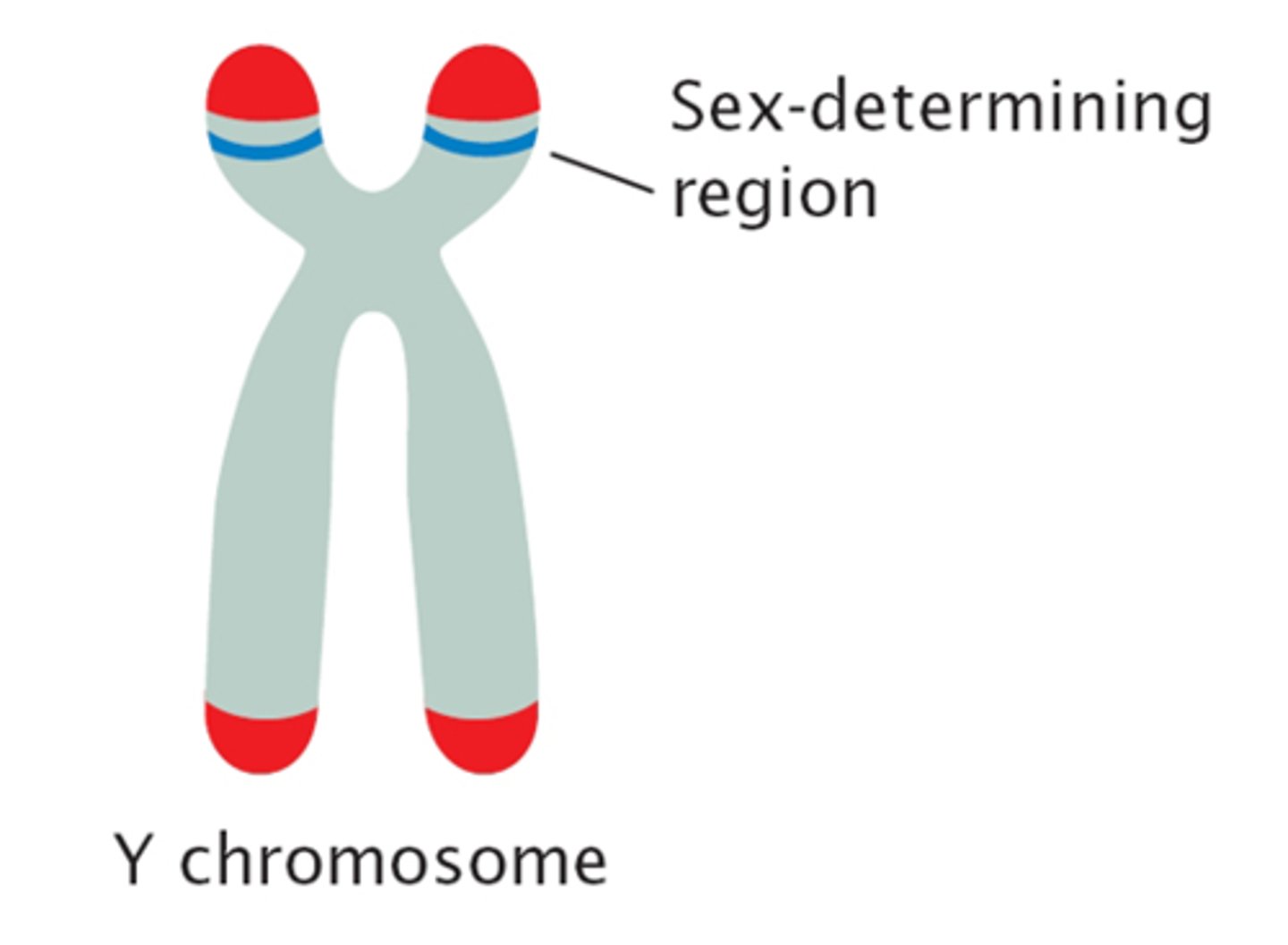
Y chromosome mechanism
presence of Y causes male development
X chromosome - autosome balance
-number of copies of X determines sex
-Y chromosome may or may not be present but determines fertility
-1.0 ratio is female and 0.5 is male, in between is intersex

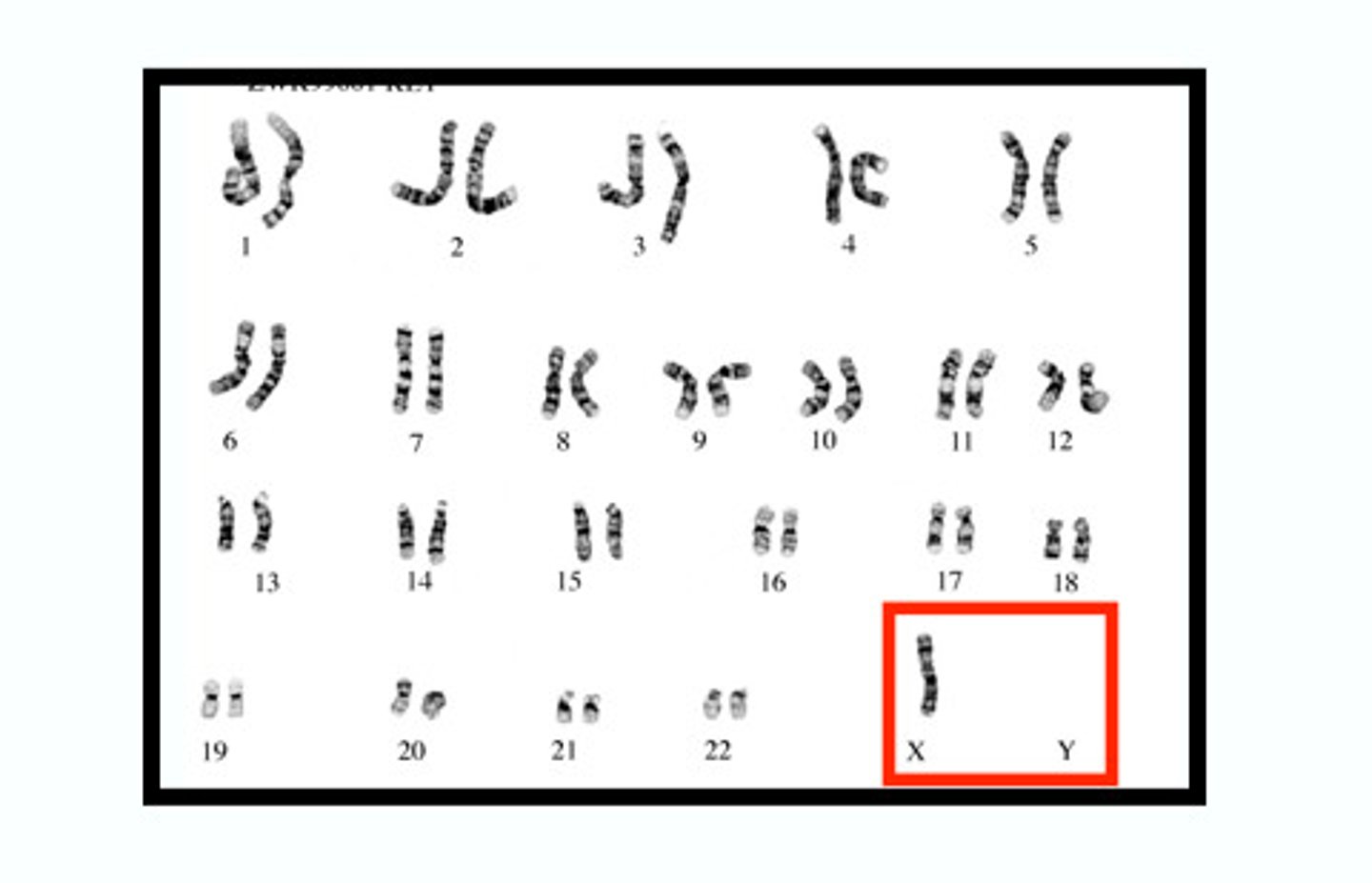
turner syndrome
females with only one X sex chromosome who are short, often sterile, and have low sexual development
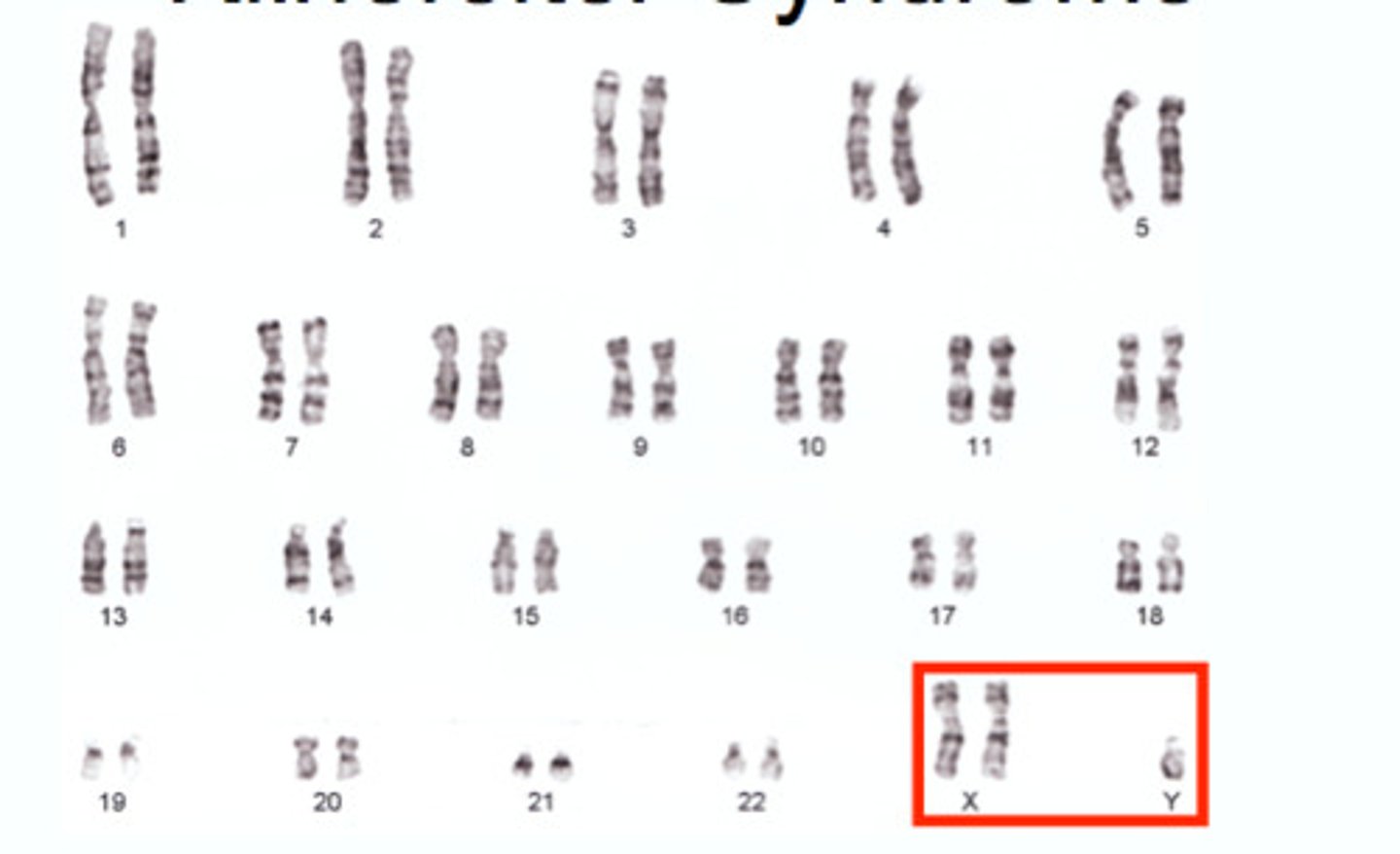
klinefelter syndrome
A chromosomal disorder in which males have an extra X chromosome, making them XXY, XXXY, or XXYY instead of XY.
extra sex chromosomes are often result of...
nondisjunction in meiosis
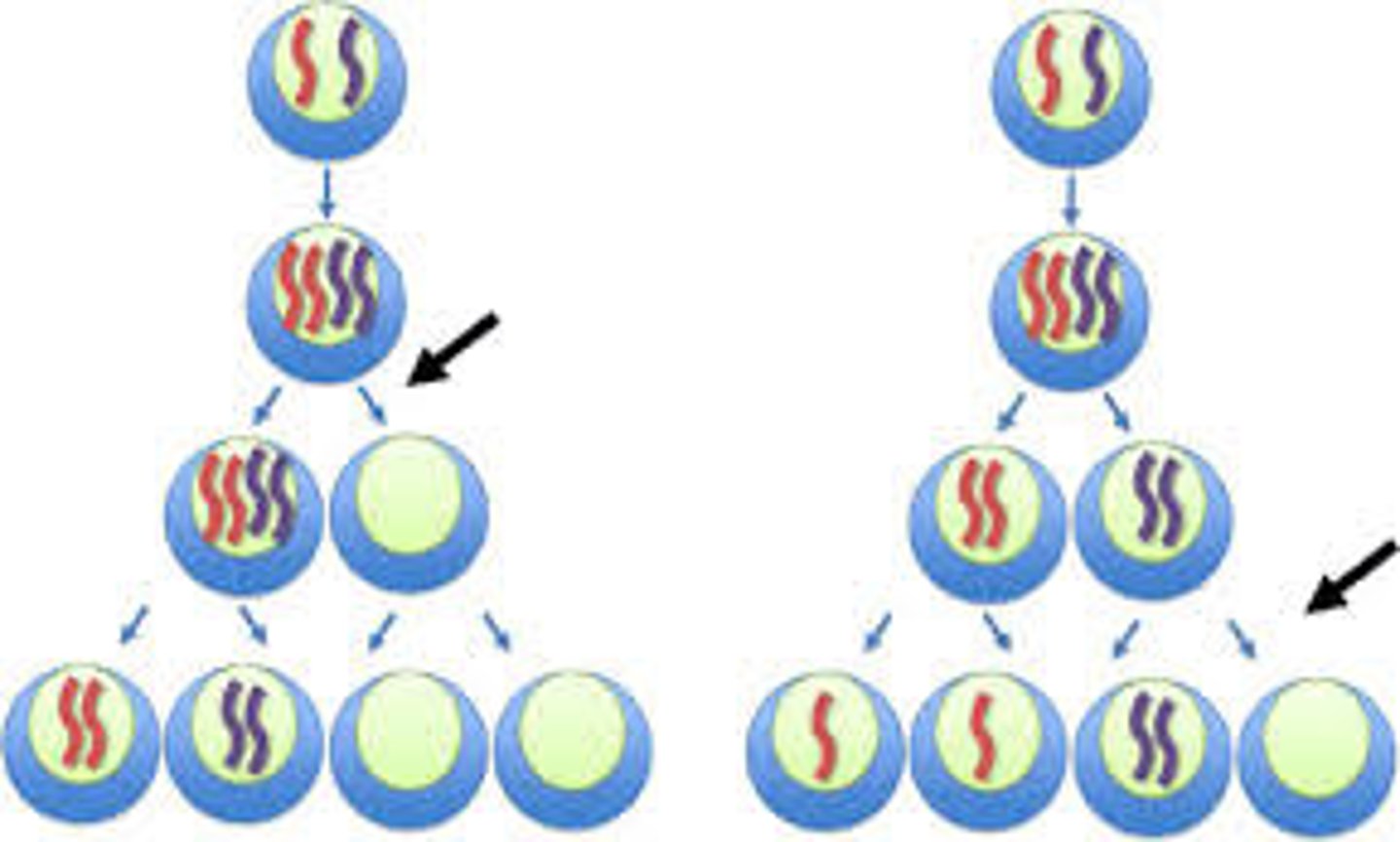
gene dosage
extra chromosomes increase the number of copies of the genes on them
how can they tolerate extra Xs?
-shut off/inactivate all but one X during development(dosage compensation)
Barr Body
an inactivated X chromosome that is condensed and sticks to nuclear envelope
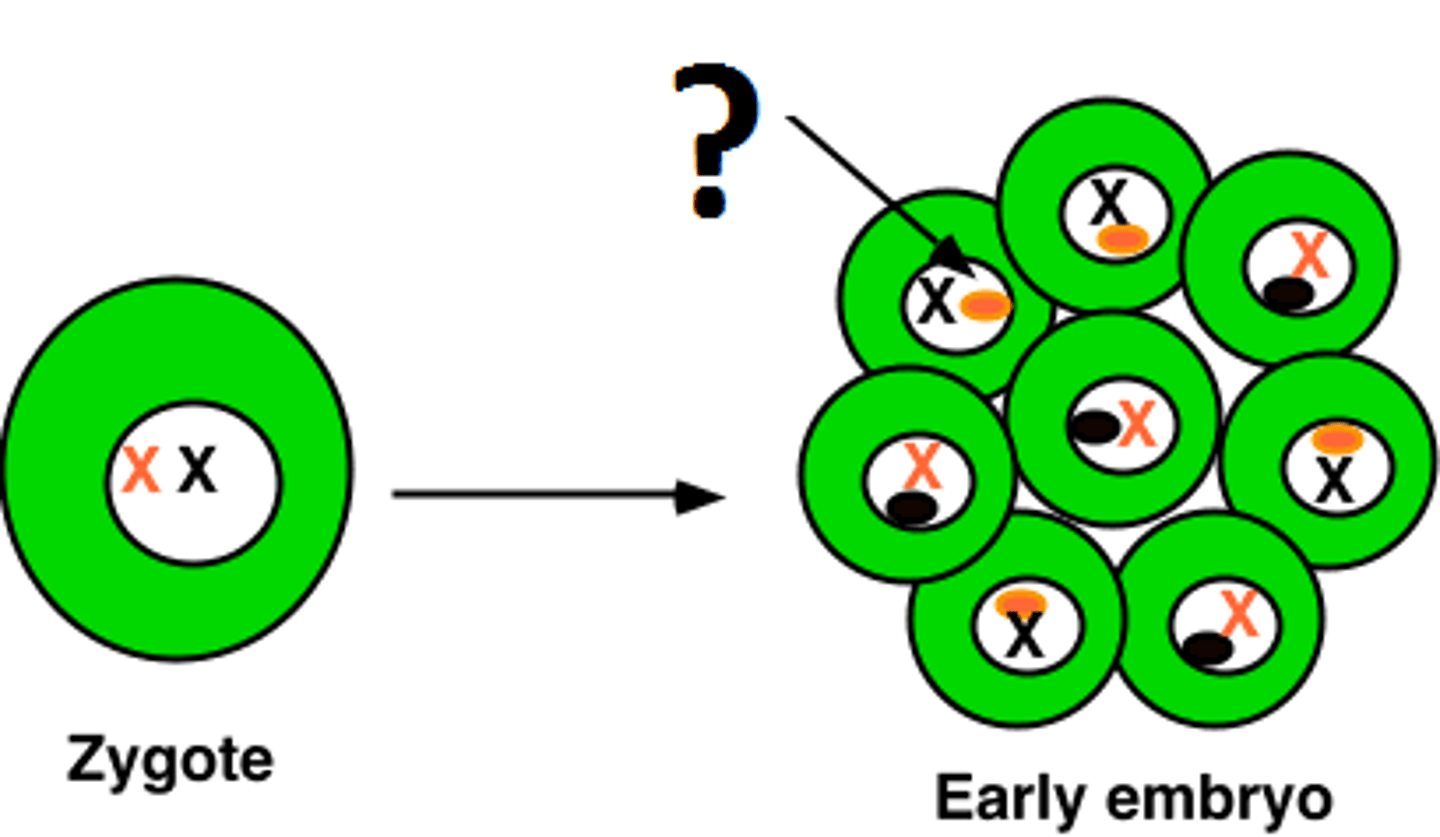
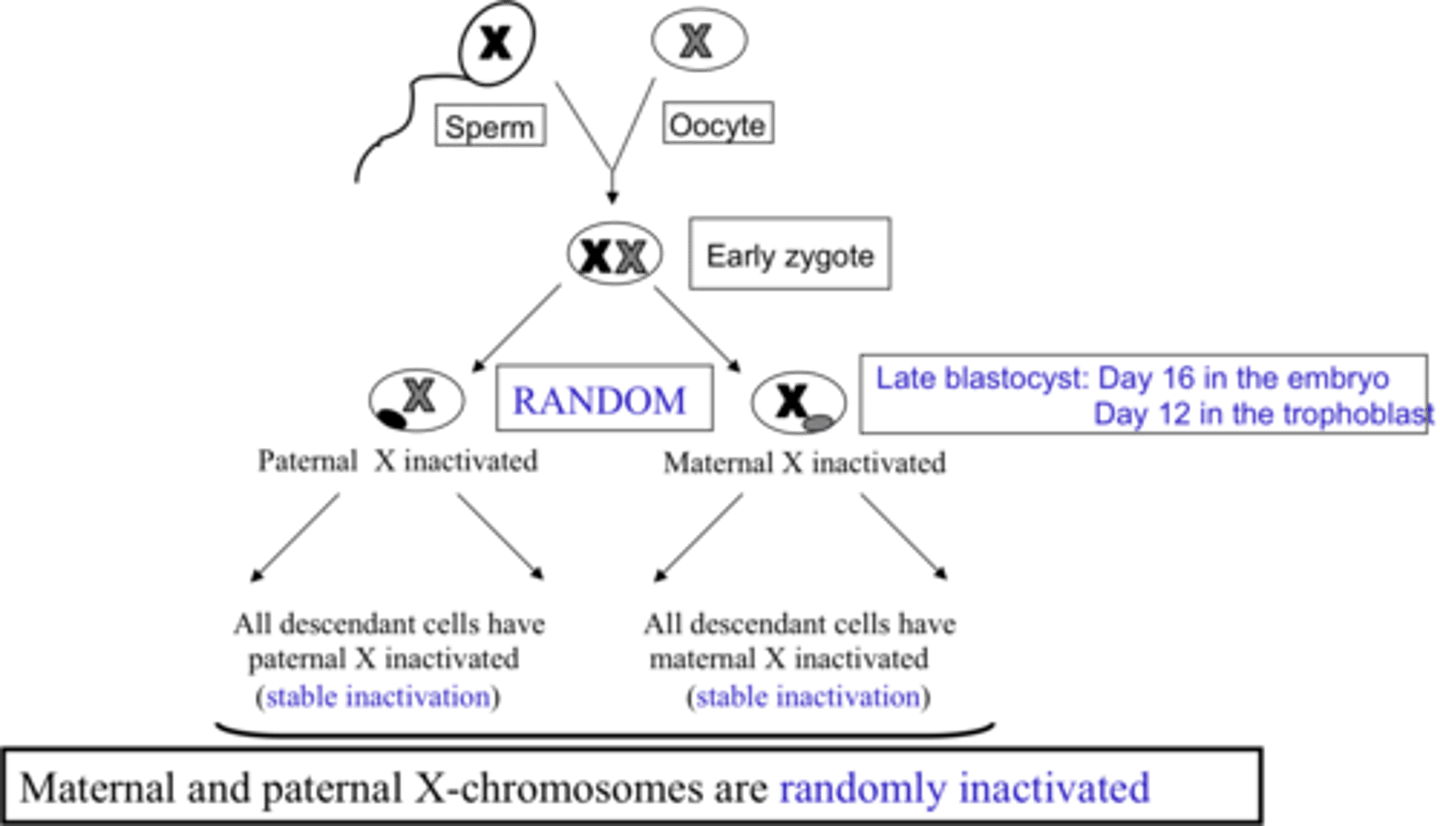
lyonization
-process that created Barr bodies and the chromosome is highly condensed -> heterochromatin
-happens during fetal development (day 16)
-each cell selects an X at random and descendants of cell will have same X shut off
mosaics
individuals whose somatic cells display two different genetic cell lines, each exhibiting a different karyotype. they must have two X chromosomes

testis-determining factor (tdf)
-causes fetal gonads to develop into testes
-testes then produce male sex hormones
-hormones direct the rest of the sex development
X chromosome - autosome balancing system
-Y doesn't determine sex, it is determined by the # of X's
-ratio of copies of X to copies of each autosome
males are homogametic in some organisms...
-in birds, butterflies, moths, and some fish
-they have two homologous sex chromosomes (ZZ)
-females are heterogametic (ZW) -> W causes female development
dioecious
in plants some species have male and female individuals, "two houses"
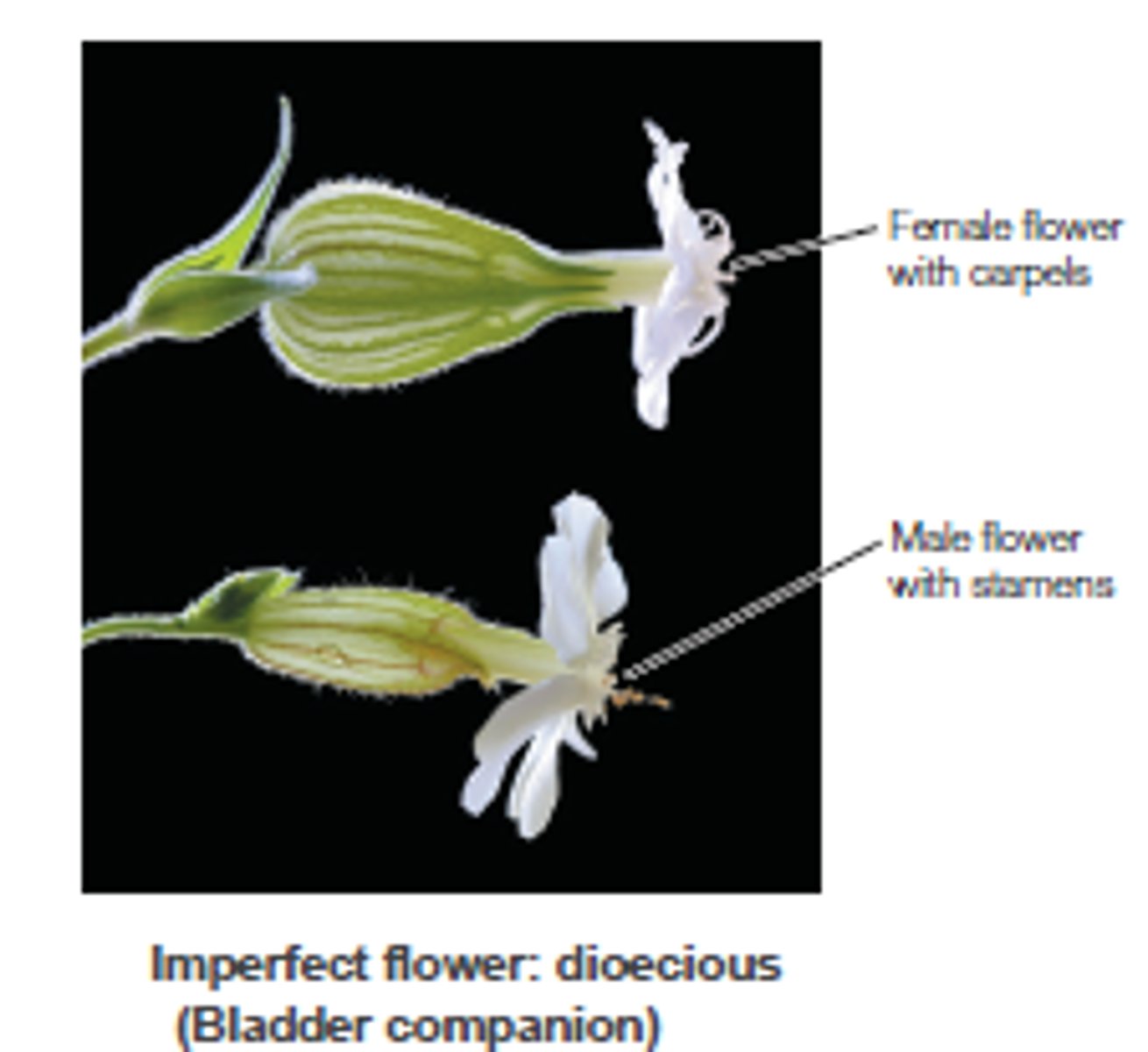

monoecious
-in some plants the individuals are hermaphrodites, "one house"
-perfect flowers produce both male and female gametes together in the same flower
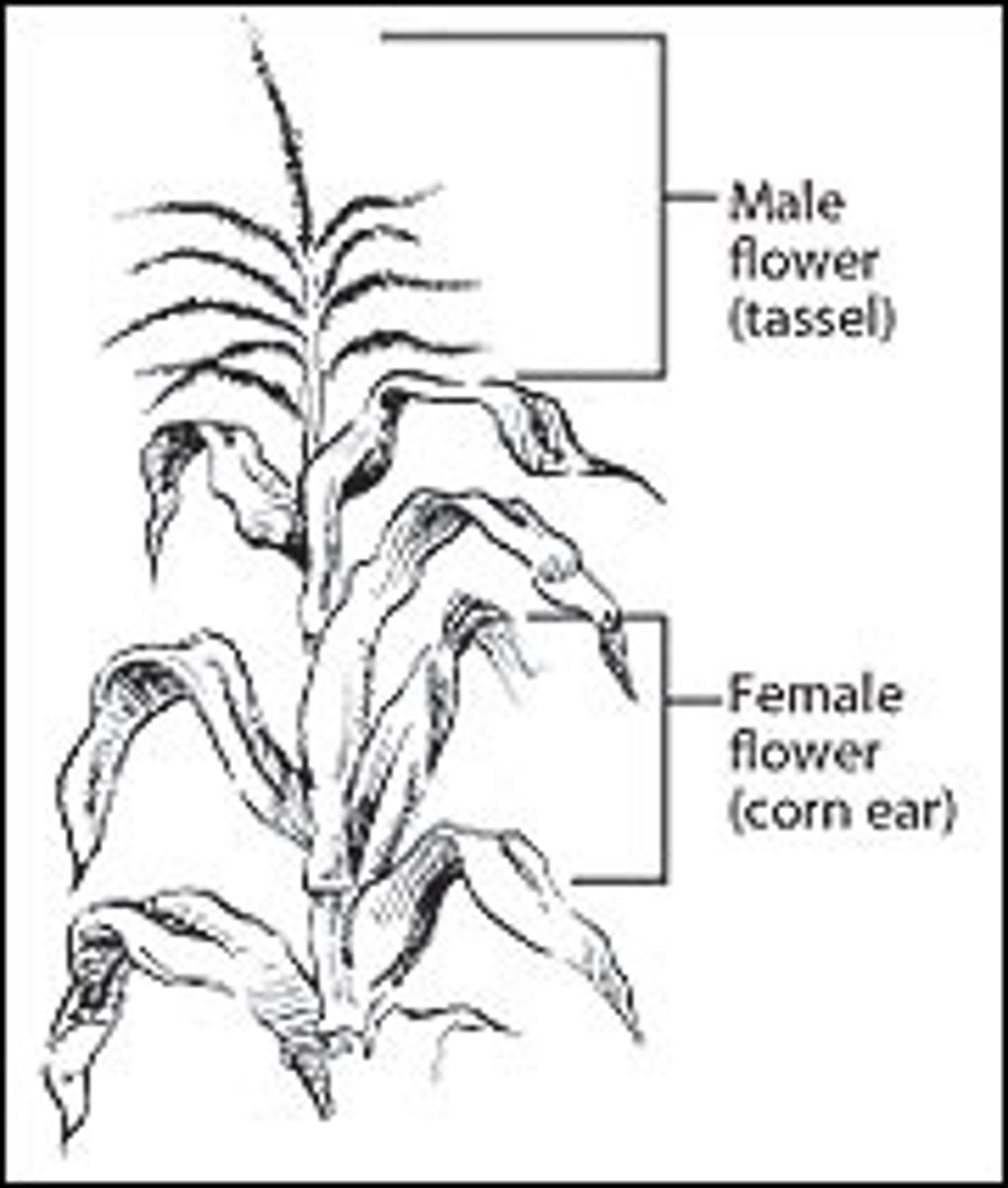
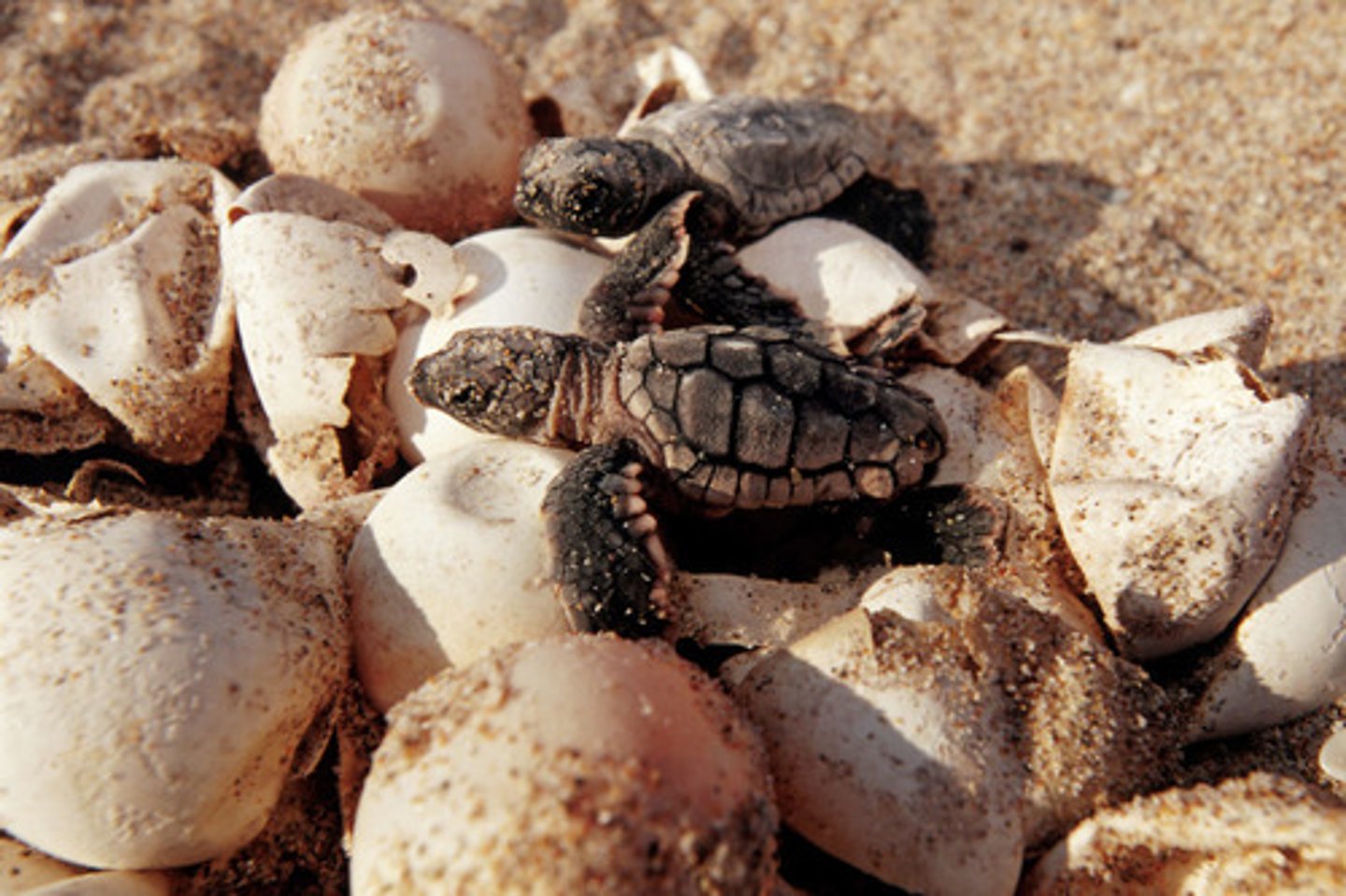
environmental sex determination systems
Environmental conditions control sex of organism
•temperature during incubation controls sex of turtles
•presence of opposite sex
-some organisms (fish) can switch sex if few partners available
