molecular genetics quick flashcards
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what is classical genetics
based on observable traits and the inheritance patterns they follow as they pass from parents to offspring
what is molecular genetics
focuses on the molecules of inheritance, and the mechanisms that underlie the inheritance patterns of classical genetics
what is the central dogma
DNA replicates itself, is transcribed into RNA, and RNA is translated into proteins
where does replication of DNA and transcription from DNA to mRNA occur
in the nucleus
where does the translation from RNA to proteins occur
in the ribosome within the cytoplasm
what does a silent mutation do
do not affect the protein produced
what is a nonsense mutation
an amino acid is replaced by a stop codon
what is a missense mutation
an amino acid is replaced with a different amino acid
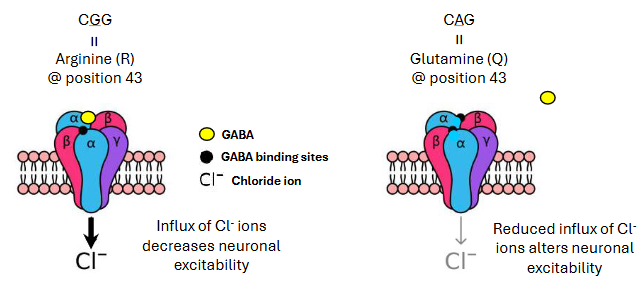
R43Q mutations
cause childhood febrile seizures due to change in shape of the protein due to 1 amino acid change
disrupts the transport of Cl- into neurons
monogenic disorder
what is a monogenic vs polygenic disease
monogenic - single gene mutation is primary cause
polygenic - multiple gene mutations contribute to disease risk, along with environmental factors
how can we identify monogenic disorders
linkage analysis to identify DNA variations causing the disorder
how can we identify polygenic disorders
genome wide association studies to identify the co-occurrence of DNA variation of the disorder
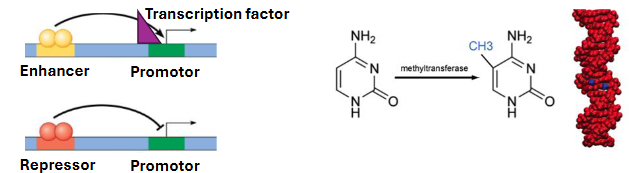
what does genetic regulation involve
regulatory non coding DNA sequences - promoters, enhancers, repressors
regulatory DNA-coded proteins - transcription factors
regulatory epigenetic signals - DNA methylation, histone modification, non coding RNA
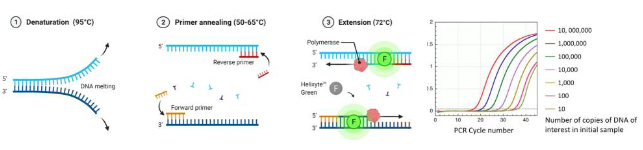
what is PCR
amplifies DNA & uses gel electrophoresis for visualization
heat unzips DNA, special enzyme used to build new DNA with using the og strand as a template, DNA is amplified
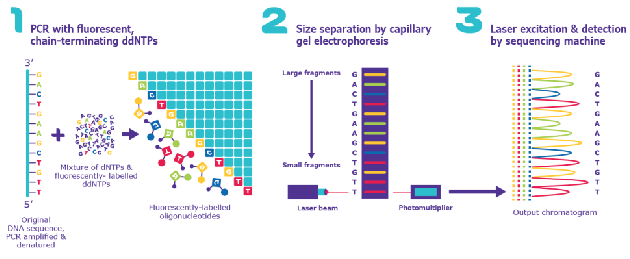
what is DNA sequencing
uses modified PCR with fluorescent labels to “read” DNA
DNA broken into pieces → machine reads DNA letters and puts in order → helps scientists find mutations that cause disease
what is gene expression analysis
quantitative PCR measures mRNA levels to analyze gene expression
measure amt of mRNA - > if gene active, lots of mRNA/if gene not active, less mRNA
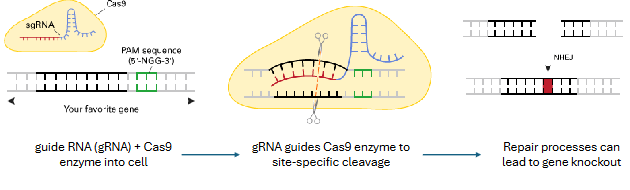
what is CRISPR
uses guide RNA to guide Cas9 enzyme & cut DNA at a specific site
cell repairs the DNA, allowing scientists to remove or edit genes