BIOLOGY TEST
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
cell theory
All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
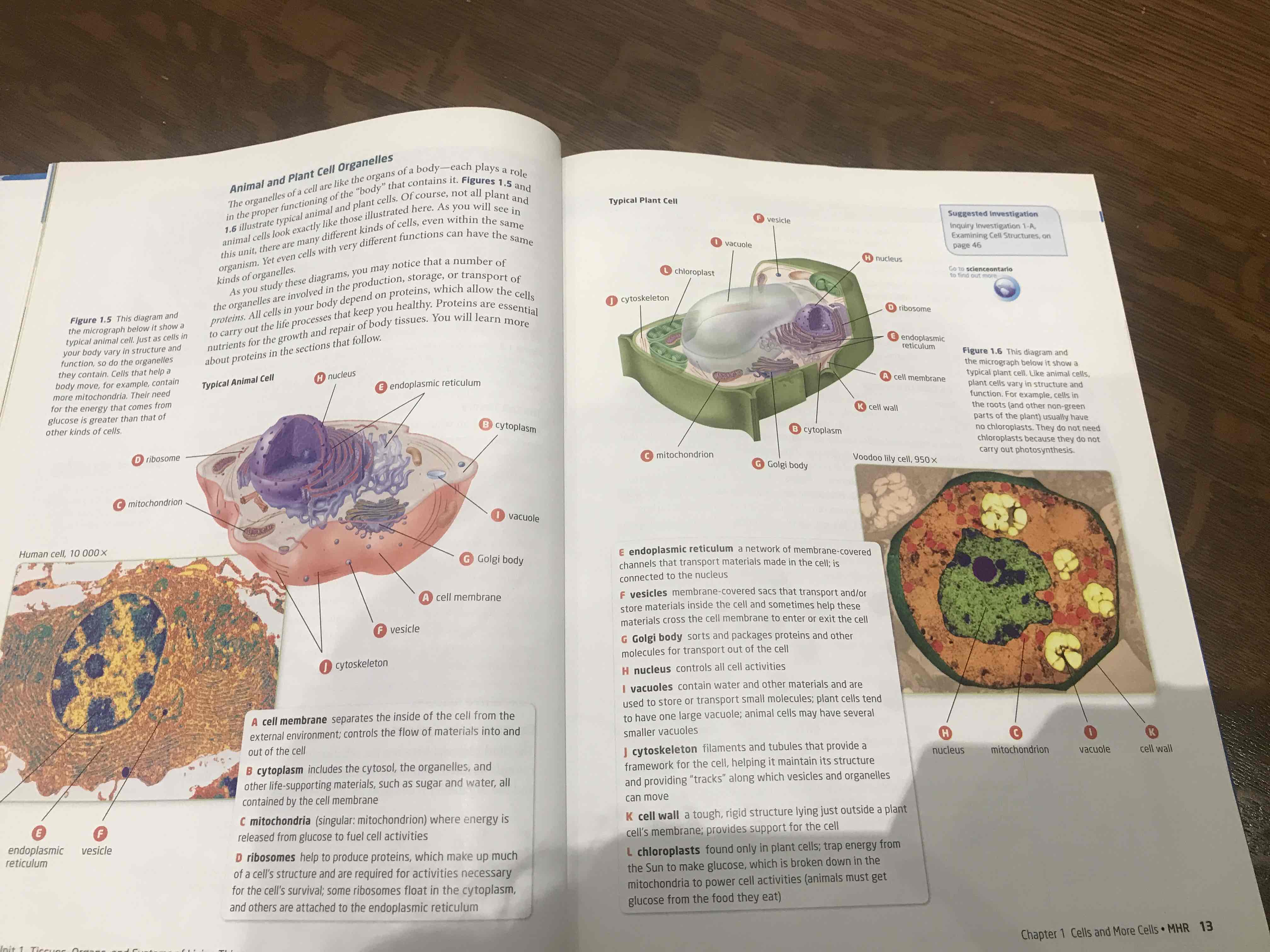
Animal cell organelles
nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, vacuole, golgi body, cell membrane, vesicle, cytoskeleton, mitochondrion, ribosome
cell membrane
separates the inside of the cell from the external enviroment; controls the flow of materials into and out of the cell, semi-permeable membrane
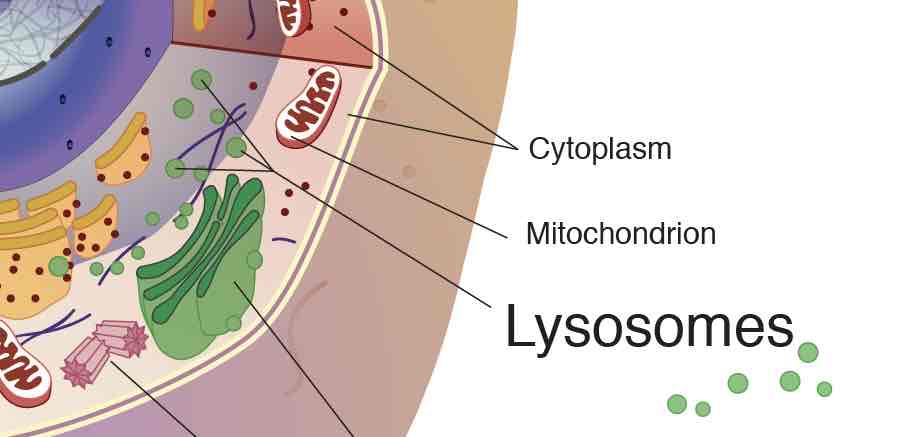
Cytoplasm
includes the cytosol, the organelles, and other life-supporting materials, such as sugar and water, all contained by the cell membrane, mostly water
Mitochondria
(singular: mitochondrion) where energy is released from glucose to fuel activities through process called cellular respiration
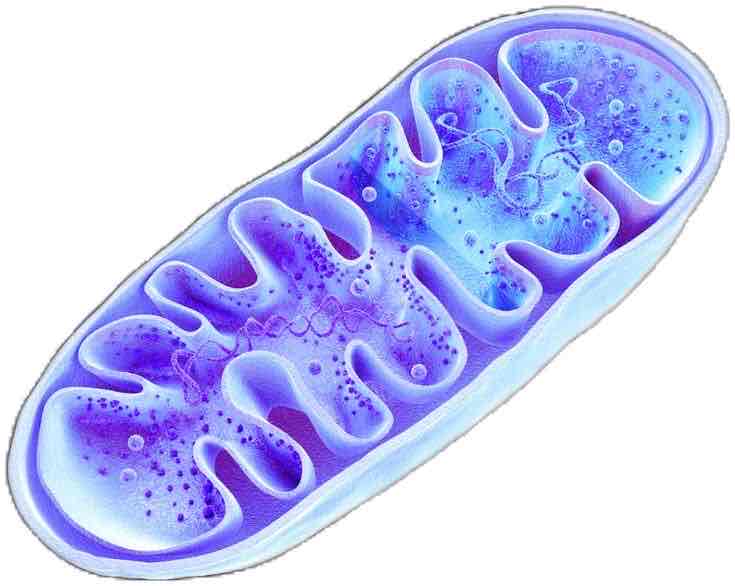
Ribosomes
help to produce proteins, which make up much of a cell's structure and are required for activities necessary for the cell's survival; some ribosomes float in the cytoplasm, and others are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
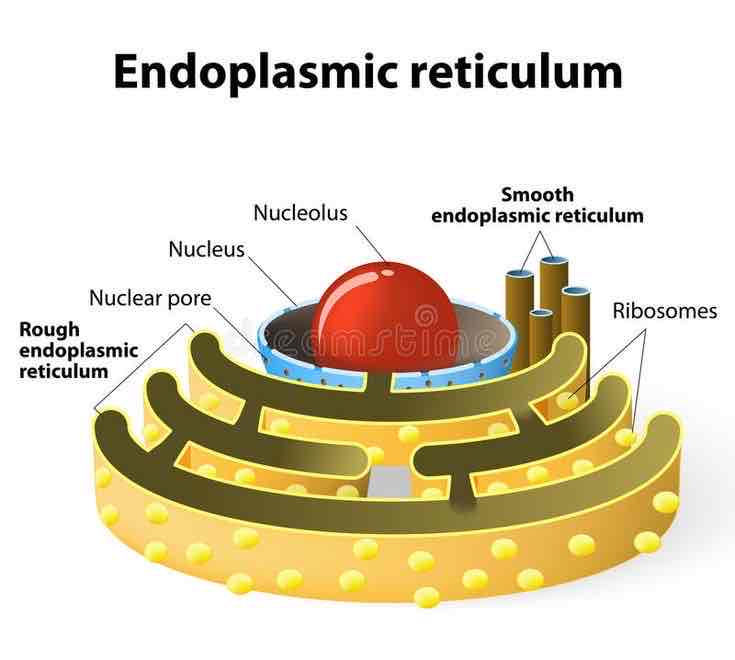
Endoplasmic Reticulum
a network of membrane-covered channels that transport materials made in the cell; is connected to the nucleus, three-dimensional network of branching tubes and pockets, extends throughout cytoplasm from the nuclear membrane, fluid-filled tubes transport materials i.e proteins, thru cell
vesicles
membrane-covered sacs that transport and/or store materials inside the cell and sometimes help these materials cross the cell membrane to enter or exit the cell
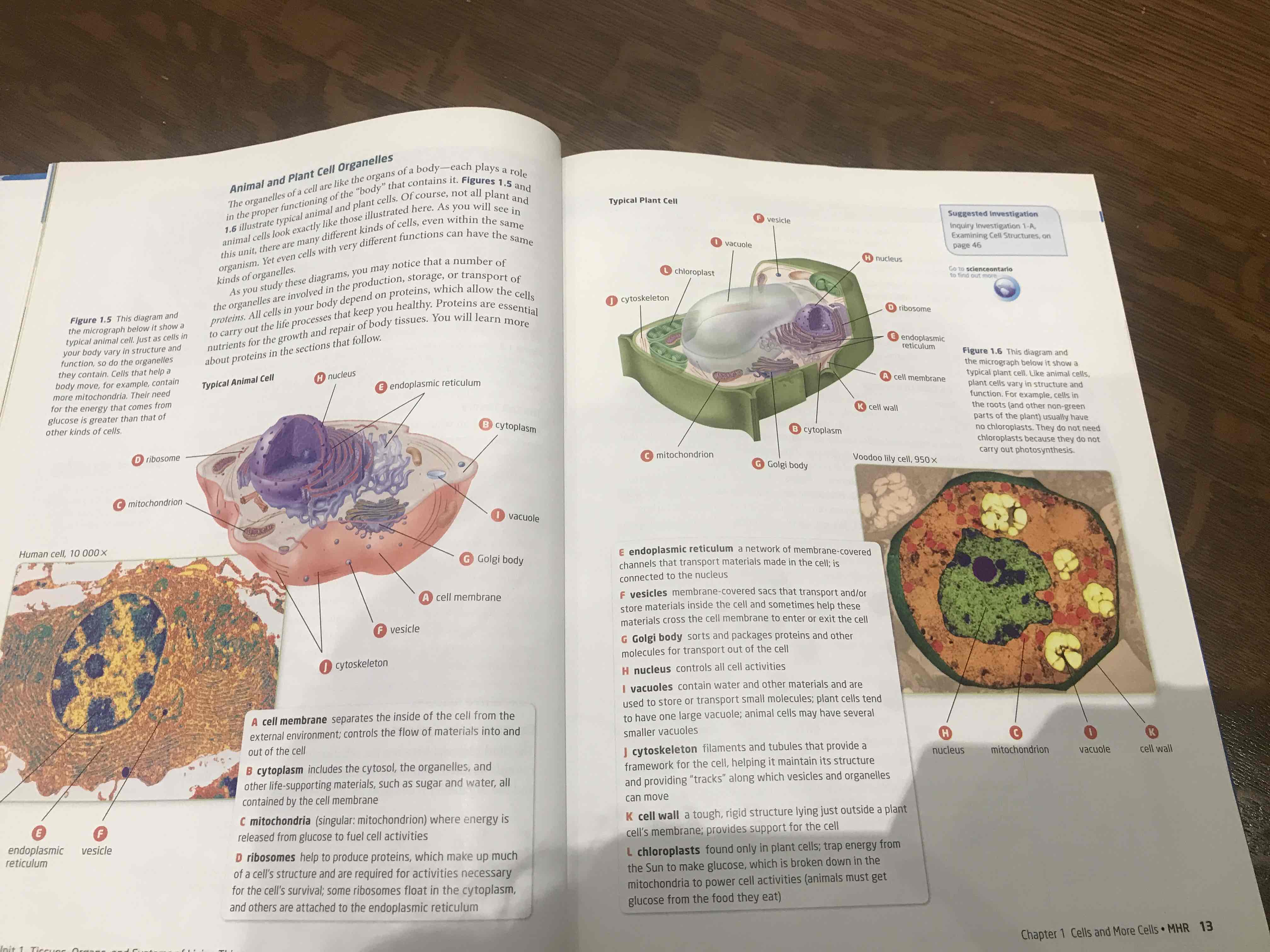
Golgi body
sorts and packages proteins and other molecules for transport out of the cell, make and secrete mucus (cells secrete a lot, i.e intestine cell have many of golgi)
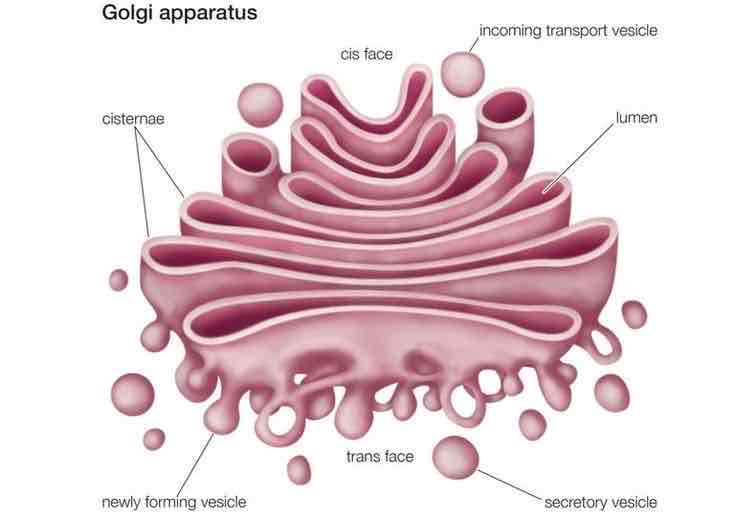
Nucleus
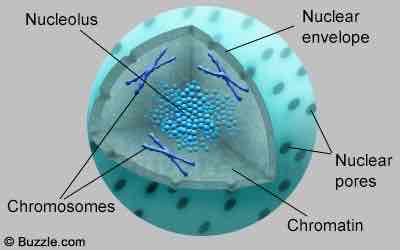
Control center of the cell, has chromosomes that contain your DNA, separated by rest of cell by nuclear membrane
Vacuoles in animal cell
contain water and other materials and are used to store or transport small molecules; plant cells tend to have one large vacuole; animal cells may have several smaller vacuoles.
How many cells are humans made of
100 trillion cells
celullar metabolism
Set of chemical reactions occur in living organisms to mantain life, processes carried out by the individual cells that make up the organism
what essential tasks do all cells have to do for cellular metabolism
obtain food and energy, convert energy for use inside the cell
construct + mantain cell structures
carry out chemical reactions
eliminate wastes
reproduce, keep blueprints for constructing cell structures (chromosomes)
Unicellular
A single celled organism
Multicellular
Made up of more than one cell.
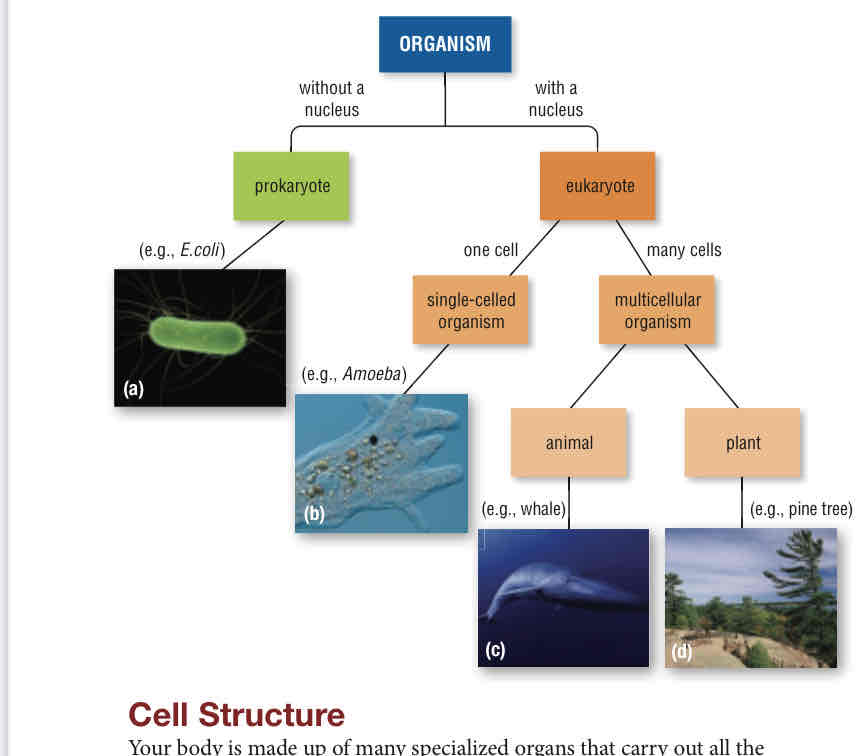
what two groups are all living things categorized into based on features of cells
prokaryotes and eukaryotes
vacuole in plant cell
usually have one large vacuole take up all space, when full of water, tugor pressure keeps cells plump which keep plant stem + leaves firm
Organelle
specialized cell structure that has a specific function, usually enclosed within its own membrane
Prokaryotes
cells w/ very simple cell structure, do NOT have nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, free floating, unicellular, most have cell wall, smaller than eukaryotic, rhymes with NO, no mitochondria, no ER, no Golgi Apparatus
Eukaryotes
rhymes with DO, more complex internal organization, contain nucleus and membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, ER, golgi apparatus, can form both unicellular and multicellular, larger than prokaryotes
example of prokaryote
Bacteria and Archaea (single-celled life forms)
Examples of eukaryotic cells
Amoeba (single-celled), whales and trees (multi-cellular)
Relationship between prokaryotes and eukaryotes chart
chloroplast
found only in plant cells; trap energy from the Sun to make glucose, which is broken down in the mitochondria to power cell activities (animals must get glucose from the food they eat), contain chlorophyll (give leaf green color)

name two diff. in plant and animal cells
cell wall and chloroplasts
purpose of cell division
allows organisms to reproduce, allow organisms to grow, allows organisms to repair damage
what are the two types of reproduction
asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction
asexual reproduction
one parent, genetically identical to parents
sexual reproduction
offspring gets genetic info from 2 parents, each parent contribute one gamete which fuses with other
gamete
come from normal body cell, contain half of DNA found in cell, to make, some parent cell go thru meiosis,
why do the size of cells not increase
bc too large chemicals, water and waste cannot be transported quickly enough
how to chemicals in a cell move by
diffusion
diffusion
a transport mechanism for moving chemicals into and out of the cell, from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
concentration
the amount of a substance (solute) present in a given volume of solution
osmosis
the movement of a fluid, usually water, across a membrane toward an area of high solute concentration
how much cell division for skin cells
every day, millions of cells must be replaced
how much cell divide in red blood cells
each cell is replaced every 120 days
How cell divide when broken bones, cuts and blister
new cells needed to fill in gaps
DNA, and structure of DNA
Holds genetic code for your body to develop, survive and produce. Chromatin is a thread-like material inside the nucleus, material contains genetic info called DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) a substance that chromosomes are composed of that make up the genetic code
lysosomes
membrane bound organelles who have digestive enzymes to process energy
photosynthesis equation
carbon dioxide + water —> glucose, oxygen and energy
cellular respiration equation
glucose + oxygen —> water and carbon dioxide
what are the stages of the cell cycle
interphase, mitosis (cell division of nucleus) cytokinesis (cytoplasm division)
how long does embryonic cells take to divide
long time
how long does it take for adult nerve cells to divide
may never divide
Interphase
Longest stage of cell cycle, perform normal functions and prepare for cell division by duplicating genetic material (DNA) strands, first stage, also doubles centrosomes
order of mitosis
PMAT, prophase, metaphase, anaphase telophase
what happens when something goes wrong in interphase
copying errors are detected and fixed by special proofreading and repair proteins
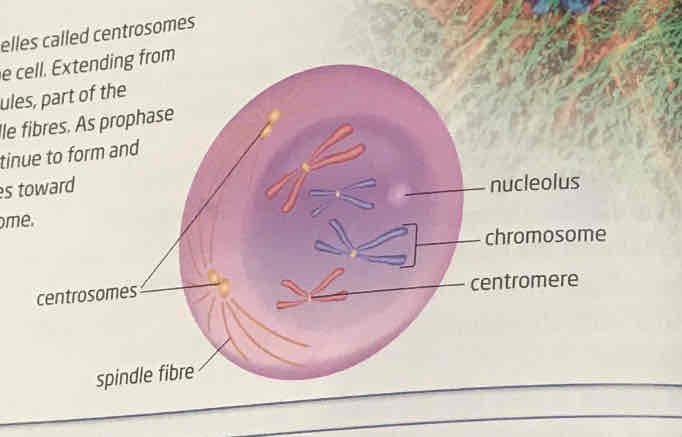
prophase
replicated chromosomes coil in various ways until they are condensed and thick enough to be visible under microscope. membrane around nucleus breaks down and nucleolus disappears. each chromosome are joined together by centromere. chromosome contain two strands called sister chromatids. the two centrosomes (part of cytoskeleton) begin to form spindle fibers and go to opposite ends. As prophase progress, spindle fibres extend away from centrosomes to each centromere on chromosome
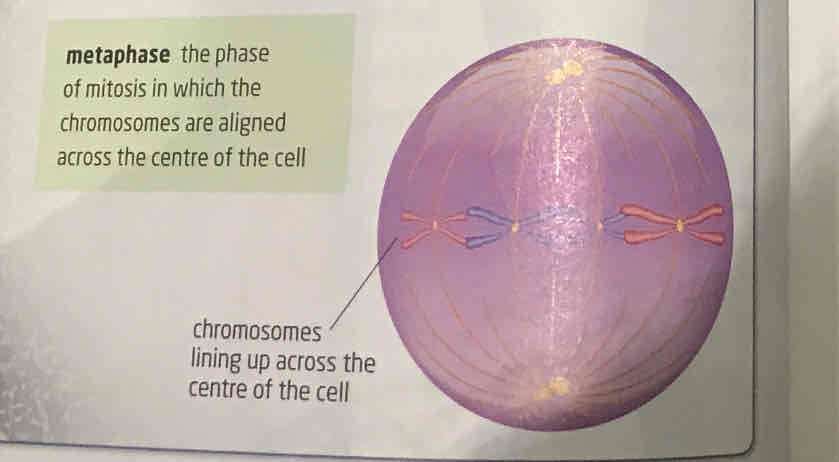
metaphase
Longest phase in mitosis, centrosomes reach end of cell, chromosomes move to line up in centre of cell. spindle fibres stretched to centromeres. each centromere becomes attached to two spindle fibres-one from each end of cell
anaphase
one of shortest stage, centromere holding two chromatids together break apart as the spindle fibres stretch to chromosomes pull back said chromatid, then chromatid become daughter chromosomes as their own, this point cell has twice as many chromosomes
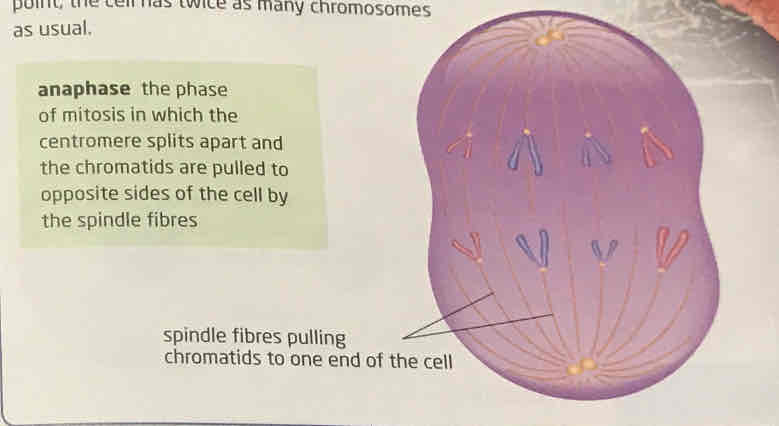
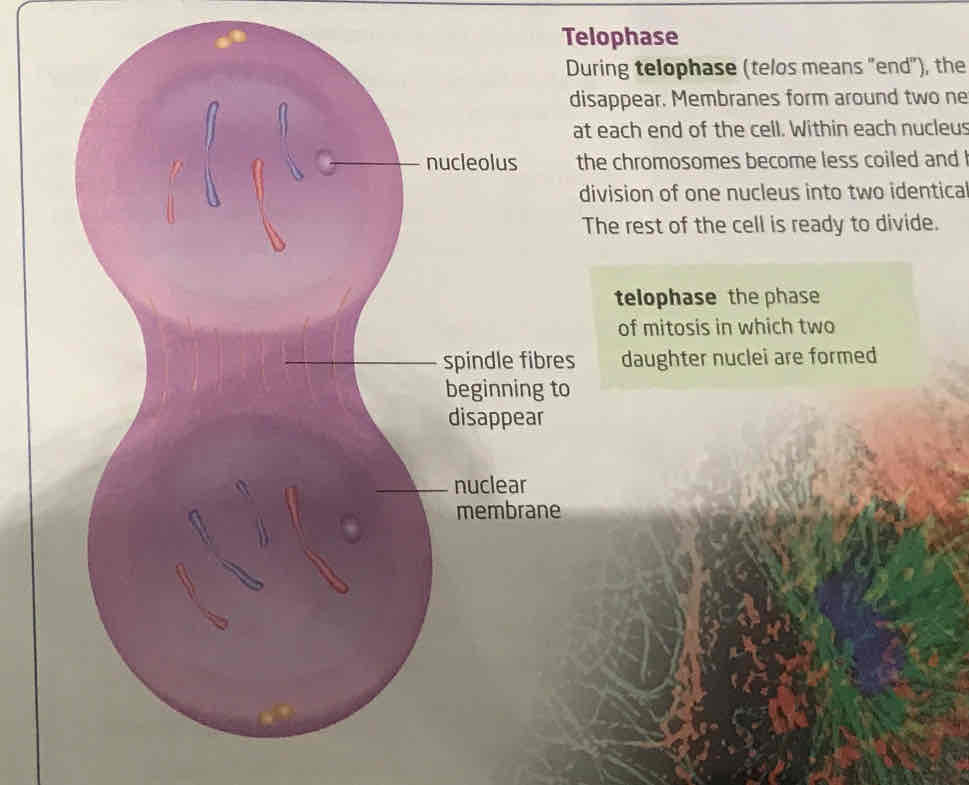
telophase
spindle fibres disappear, and membrane form around new daughter chromosomes and in the membrane, a nucleolus appears, chromosomes uncoil become harder to see. Mitosis, the division of one nucleus into two identical nuclei is now complete, rest of cell is ready to divide
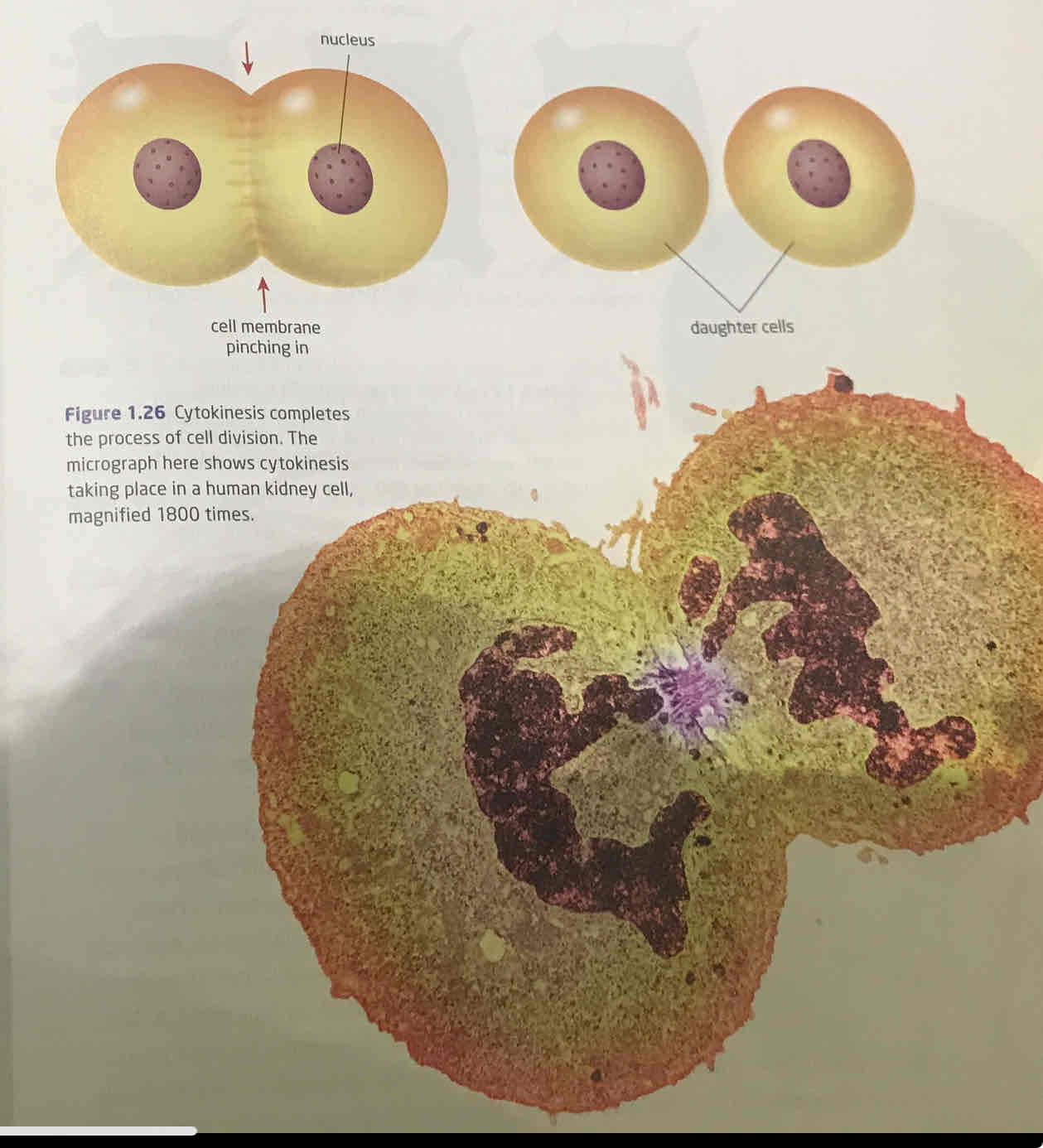
cytokinesis
final stage of cell division, division of everything else except nuclei, specifically of the cytoplasm though
cytokinesis in animal cells
start in anaphase end in telophase, where ring of specialized proteins around middle of cell start to contract, pinches cell membrane until divided into two daughter cells
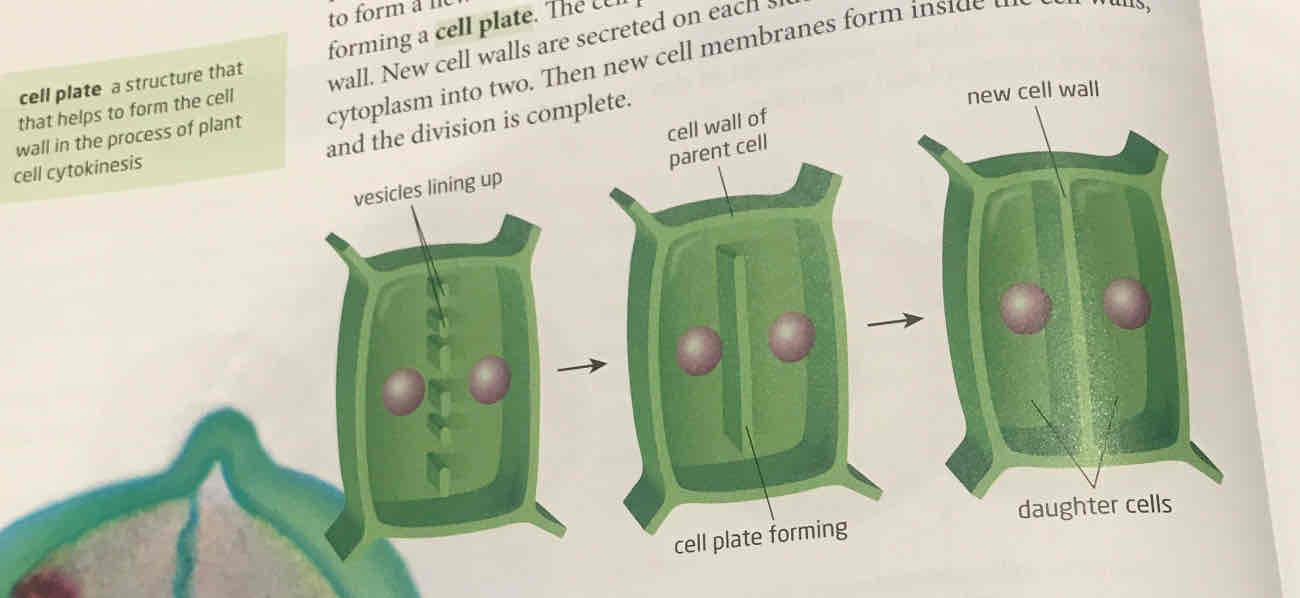
cytokinesis in plant cell
cell wall makes cytokinesis different. golgi body make new vesicles (tiny vacuoles) which carry material needed to make a new cell wall. The vesicles line up between two nuclei in a line forming a cell plate. cell plate grows outwards and joins cell wall which makes new cell walls on each side
two types of ways cells get destroyed
cell death and cell suicide
cell death
contents leaks out, often irritating surrounding cells, causing swelling and redness in that body part.
cell suicide
breaks down in organized way, contents packaged + distributed for other cells usage, this is pre-programmed into cells, determind by suicide genes
cancer cell
continues to divide ignoring stop signs in the cell cycle, so instead of dying, they divide repeatedly and excessively, forming a tumor
where does cancer occur usually give examples
in cells that are rapidly dividing like skin, lung, breath, and cells lining intestinal tract
benign tumor
a tumour that does not affect surrounding tissues other than by physically crowding them. not cancerous but can affect function of other tissues when crowding
malignant tumor
a tumour that interferes with the functioning of surrounding cells; a cancerous tumour. interferes with function of cell like ability to produce hormones or enzymes, and can destroy cells
metasis
the process of cancer cells breaking away from the original (primary) tumour and establishing another (secondary) tumour elsewhere in the body
metastatic (cancerous) cells
leave the tumour and start a secondary tumour elsewhere
causes of cancer
mutation, or mutagens and carcinogens
How does mutation happen
normal cell do 20-30 rounds, any more make mutation. most suicide but many cancer cell mutation been found make enzyme called telomerase which signals don’t stop dividing. also mutate so dont have to divide on surface like normal cell. take at least 4 mutations
mutation
a change in the DNA sequence of an organisms
Mutagen
substance of agent that induces heritable change in cells or organisms
carcinogen
any environmental factor that causes cancer
what are some well-known carcinogens
x-rays, UV radiation, smoking, organic solvents, viruses (human papilloma virus HPV)
steps of a secondary tumor formation
step one: primary tumor develops as a group of cells that are growing out of control
step two: the tumor gets bigger and stimulates blood vessels to supply it from the surrounding tissues
step three: tumor cells squeeze into blood and lymph vessels and move to other parts of the body, this is called metasis
step four: as tumor cells reach other parts of body, form secondary tumors.
cancer screening
tests detect cancer even if there are no symptoms so detect at early stage so it can be treated more effectively
PAP test
named after Dr. George Papanicolaou, who invented it, it is done routinely as physical checkup, remove small sample of cells from woman’s cervix then examined for abnormalities. for adult women, around 18 and higher, check for cervical cancer.
genetic screening
important for people who have family history of cancer, determine if you inherited DNA linked to cancer
different types of cancer screening
PAP test, testicular self-examination, PSA test, breast self examination, mole observation, blood test for colon cancer
PSA test
blood test, screen for prostate cancer and NOT wildly used for men under 50 bc chances for them are low
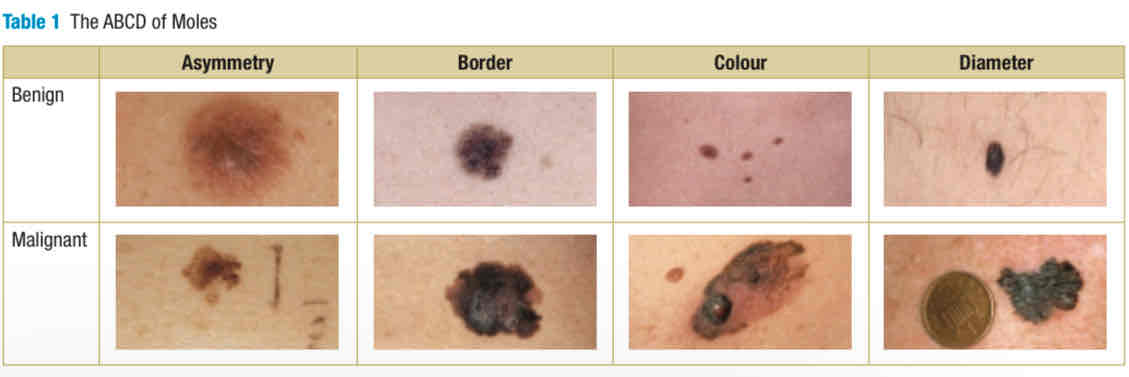
mole observation, skin checks
check own skin using ABCD, Asymmetry, Border, Color, and Diameter
how to reduce risk of cancer
no smoking, healthy diet, exercise
ways to diagnose cancer
imaging tech like endoscopy, x-rays, ultrasounds, CT scanning, and MRI, OR taking a sample of cells under a microscope,
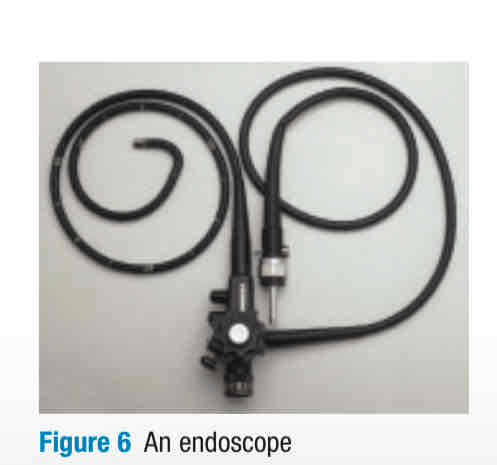
endoscopy, endoscope
used to screen for colon cancer, a tiny camera + fibre-optic light attached to flexible tube find diagnosis. Can have forceps attached to get small sample. ex. Can see stomach ulcer (hole in protective mucous lining of stomach/intestine)
x-ray, specialized example, and damaging effects
produced by transmitting wavelength of electromagnetic radiation through body to expose photographic film on other side (ex. mammogram specialized x-ray technique imaging breast tissue).but can also cause DNA damage, and harmful to rapidly dividing cells (i.e growing fetus).
Ultrasound imaging
Directing high-frequency sound waves at part of body from a microphone attached to computer, create digital image, real-time movement of body parts so good for watching organ function
CT/ CAT scan
computerized axial tomography, take multiple x-rays of thin ‘slices’ of a body part, then images assembled by computer make 3D images.
MRI
magnetic resonance imaging, produced using radio signals in magnetic field create images more detail than CT scan, then computer make three-dimensional models
biopsy
sample of tumor cells removed surgically, tested
Treatments for cancer
chemotherapy, surgery, radiation therapy, biophotonics
chemotherapy
treat cancer using drugs, slows/stops cancer cells from stopping. can be taken orally and side effects include hair loss, nausea, fatigue bc chemo attack all rapidly dividing cells. often first stages to shrink tumor for surgical removal or radiation treatments. Can detect small tumours
radiation
energy from gamma rays or x-rays, cancer cells easily damaged by ionizing radiation bc they divide quickly. DNA of daughter cells damaged by the radiation, so cells cannot divide. can be directed at tumor using focus beam or implanting radioactive source into tumour
biophotonics
use light beams detect + treat cancer. sensitive allowing early detection, fewer side effects and more accurate. pioneered at UOFT
what cells divide quickly and why
skin cells, blood cell, hair cells, stomach cells because they are constantly getting harmed and if they don’t divide that will harm the body and give it less layers of protection
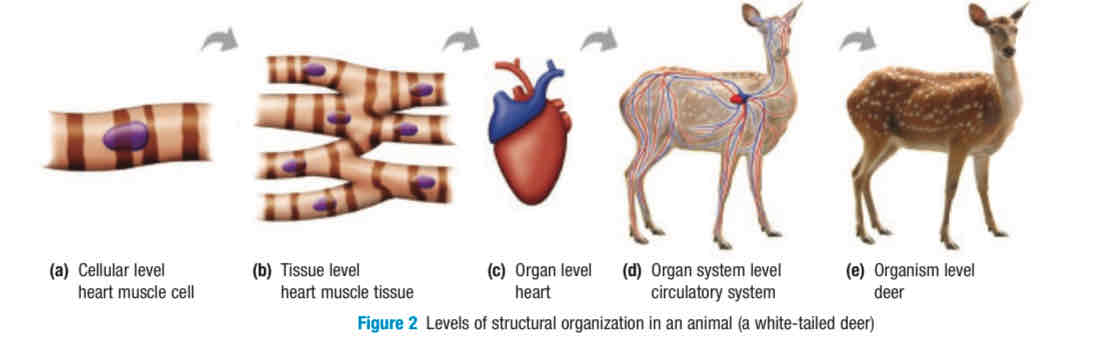
Levels of organization in organisms
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
four major types of tissues
epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nerve tissue
epithelial tissue, where found, function, and descript.
skin, lining of digestive system, protect from dehydration, low-friction surfaces, thin sheets of tightly packed cells covering organs lining internal organs

connective tissue, found where, descript, function
Makes up bones and tendons, support, insulate, connects cells + tissues, cells in extracellular matrix range from liquid (in blood) to elastic materials can stretch (ligaments) to mineral deposits (bone)

types of epithelial tissue
skin epithelia (thin flat cells form sheets, the skin) and columnar epithelia (lining small intestine, stomach + glans, may secree mucus, cilia and absorb materials
muscle tissue found where, function, descript.
Muscle make bones move, surrounding digestive tract, the heart, for movement, designed to change shape by shortening/lengthening

How many types of cells is the body made up of where do they come from
200 different types, come from pool of stem cells from early embryo
cellular differentiation
the process by which a cell becomes specialized to perform a specific function
Stem cell
an undifferentiated cell that can divide to form specialized cells