National Parks Test 2
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
resource significance, volcanic features: primary resources
park units set aside specifically for their volcanic features
resource significance, volcanic features: high significance
park units with volcanic resources as major features of their landscape and ecosystems
resource significance, volcanic features: moderate significance
park units with volcanic resources that contribute to their ‘geodiversity’
volcanic age: active/recent
parks with eruptions in the Holocene (the last 10,000 years) or that have been identified as being potentially active during that time
volcanic age: young
most recent eruption in the Pleistocene (10,000-2.6 million years ago)
volcanic age: cenozoic
parks with volcanoes or volcanic rocks dating to the cenozoic (2.6-65 million years ago)
volcanic age: older
parks with volcanoes or volcanic rocks older than the cenozoic
volcanic landform type: volcano / volcanic center
parks with volcanic vents and / or related features
volcanic landform type: volcanic deposit
parks with only volcanic rocks or other deposits distal from the vent that produced them
volcanic landform type: ash beds / sedimentary
parks with ash beds in sedimentary sequences
convergence of tectonic plates
leads to subduction where one plate slides under another
melting crust feeds ______
subsurface magma chambers, creating a chain of volcanoes near the convergence zone
the current setting in the pacific NW
cascade mountains (WA, OR, CA): Juan de Fuca and Gorda Plates are being subducted below North America
Mount Mazama
destroyed during an enormous explosive eruption 7,700 years ago. the summit collapsed during the eruption, forming large volcanic depression (caldera)
formation of crater lake
the caldera filled with rain and meltwater
more recent activity created Wizard Island, which projects 764 feet above the lake’s surface
North American-Pacific Plates: Alaska and the Aleutians
contain over 100 volcanoes / volcanic fields that have been active in the last two million years. Over 40 of these have been active in historic time.
Alaskan volcanoes make up about ___% of all active volcanoes in the US and ___% of all active above-water volcanoes on earth
80%, 8%
Islands formed as the Pacific plate drifted northwest over a _________
hot spot: a hot plume of rising magma that creates localized volcanism (not formed by subduction)
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
extremely fluid lava, Mauna Loa is the world’s largest shield volcano, and Kilauea is one of the most active volcanoes in the world.
The Yellowstone Hotspot
a plume of superheated material that formed ca. 17 to 18 million years ago in the NW US
flood basalts
massive accumulations of lava covering vast areas and formed by an outpouring of large volumes of fluid basalt lava through fissures
when the hot spot plume of yellowstone broke through the crust, it produced immense flood basalts
craters of the moon
between ca. 8-10 million years ago, the Yellowstone Hotspot was located beneath what is now Craters of the Moon NM
Unlike Hawaii, the Yellowstone Hotspot has produced large, explosive _____ forming eruptions because of differences in the magma chemistry
caldera
Yellowstone: Geothermal Features
fueled by its underlying hotspot, Yellowstone is one of the world’s largest volcanic systems, containing half of the world’s geothermal features
Hot Springs
spring with temperature above body temperature (98.6 °F)
Geyser
a spring characterized by an intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by steam
pluton
a large body of intrusive igneous rock (eg. granite) that forms when magma cools and solidifies underground. these can be exposed by uplift and erosion (tectonic processes)
Half Dome, Yosemite (CA) - mile below surface, pushed up by creation of Sierra Nevada
Denali, Denali NP (AK)
Devil’s Tower, Devil’s Tower NM (WY)
Definition of a Desert
a) that receive an average annual precipitation of < 10”
b) in which more water is potentially lost through evapotranspiration (evaporation and plant usage) then falls as precipitation
dry, under a foot of precipitation
ex. Antarctica is a desert
orographic uplift
as air is forced to rise over mountains, it cools, condenses, and forms rain on the windward side of the range
when it descends on the back (leeward) side, it warms and dries creating a ‘rain shadow’ effect
rain shadow
shadow behind mountains where there isn’t rain
blocks out moisture
ex. Lake Tahoe and Sierra Nevada
Death Valley (big trees from Sequoia NF, then Inyo NF, High Sierras meadows
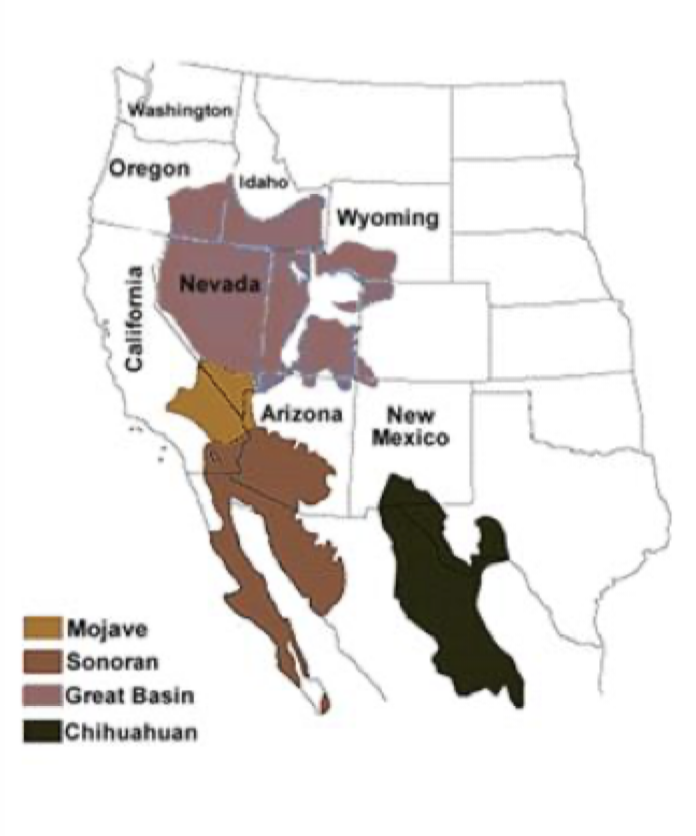
North American Deserts Map
Great Basin
Mojave
Sonoran
Chihuahuan
temp: cold deserts
found in more northerly areas and at higher elevations; mildly hot summers and cold winters
temp: hot deserts
extreme high temps, sparse vegetation; generally found in more southerly areas and at lower elevations
western deserts
hot with low humidity
seasonality of precipitation: northern deserts
more winter precipitation due to the passage of fronts and storm systems
ex. Great Basin
cool, moist
cold desert, winter rain
seasonality of precipitation: southern deserts
more summer precipitation due to thunderstorms fueled by surface heating and convection that tap into moisture pulled into the region by the North American Monsoon
ex. Saguaro NP
hot, dry
more rain in summer months
what differentiates north american deserts?
temperature
seasonality of precipitation
adaptations of saguaro
root system: for getting water
succulence / ‘ribs’: for storing water
spines: for retaining water
to live in a desert with a harsh environment what are some adaptations needed?
Have to have adaptation of living without water at least seasonally
ex. Saguaro can be 50-70 ft tall, huge root system (at least 50 ft radius), succulent spongy tissues for storing water, ribs (skeletal) helps to hold up - functions like a bellows and expands when sucking up water
Things would grow 2-4 inches after rainstorm
Spines on cactus are hollow to allow o2 and co2 to move between
Protect cactus
indicator species
a species that defines a trait or characteristic of the environment, for example, an ecoregion
indicator species of the deserts: Great Basin
sagebrush
indicator species of the deserts: Mojave
joshua tree
indicator species of the deserts: sonoran
saguaro
indicator species of the deserts: chihuahuan
agave lechuguilla
fennec fox vs. arctic fox
desert / fennec have exaggerated ears
arctic need compact furry features to avoid frostbite
kangaroo rat adaptation
dry urine
desert tortoise adaptation
dig into ground
Death Valley
largest NPS unit outside of Alaska
couple inches of rain a year
many different species
mammals, reptiles, birds, plants
nocturnal and other adaptations
role of ‘sky islands’ in desert landscapes
Higher geographic zones
Mountains in death valley
As you go up it gets colder and wetter
Snowfall as you go up
High elevations have different climates - contribute to biodiversity
what is badwater basin and why significant?
Lowest sea level in north america
Can walk out to badwater point
Boardwalk
Not as deep as dead sea (1000 ft)
resource protection:
protecting sensitive resources from damage
PP depends on water
Can't recover as quickly because they don’t have as much water and take hundreds or thousands of years
biological soil crust:
a complex community of cyanobacteria, mosses, lichens, and other organisms that forms a layer on desert surfaces and aids in carbon and nitrogen fixation, moisture absorption, and soil stabilization.
Form surface layer to bring in carbon, provide nutrients to soil, fix atmospheric nitrogen, stabilize soils
Look like little clumps of mud
PS needs to make sure people don't step on them (staying on trails is important)
Protecting unique resources
human safety issues
animals
scorpions, rattlesnakes, gila monsters
abandoned mines
heat-related illnesses
immigration safety
issues with drug running
exposure to elements
what is the colorado plateau?
a large plateau centered on the four corners and dominated by tablelands, mesas, buttes, and high mountains that are gashed by river by river canyons and scarred with dry guillies, washes and the beds of intermittent streams
Grand Canyon NP forming process
Step 1:
uplifted by tectonic processes
long period of erosion as surface gradually worn down
remaining strata, hard metamorphic rocks (the Vishnu schist- granite)
formed the ‘basement’ of the Grand Canyon
Step 2:
new layers of rock formed as sediments drifted to bottom of prehistoric seas and hardened, forming layers that include old limestone studded with fossils of algae, the earliest life recorded in the canyon
Step 3:
layers of sedimentary rock were formed from deposits as the ocean continued to advance and retreat
Step 4:
uplifted by 1.5 miles and faulted creating weaknesses in the sedimentary rock
Step 5:
downcutting and erosion by the colorado river and its tributaries
the grand staircase
series of broad cliffs carved from slightly dipping rock strata on the western colorado plateau
cultural and historical resources of colorado plateau parks
river valleys home to prehistoric farmers b/c of access to water and fertile soils
Mesa Verde NP
created to protect remaining homes and villages built by the Pueblan people
Cliff Palace - largest cliff dwelling in NA
hunter-gatherer societies
arrival of corn
developed pueblos, towers, and kivas
Dark Sky - stars
Chaco Culture NHP
Chaco Canyon was the ceremonial, administrative, economic center of San Juan Basin with more than 100 houses located across the basin
Chacoan road system: > 400 miles of prehistoric roads
Hohokam tradition
middle Gila River and lower Salt River watersheds, extending into the Sonoran Desert (southern AZ)
Sinagua tradition
central AZ between Flagstaff and Phoenix
Mogollon tradition
high-altitude desert areas in NM, extreme eastern AZ, northern Mexico and western TX
mountains and the NPS
tectonic forces uplifting the mountains
the processes of weathering and erosion that reshape the landscape
stretching of crust
uplifted areas - ranges
lowered areas - basins
differences between east - west mountains
vegetation
shape of mountains is diff b/c appalachins have been eroded for so long
longer time to be effected by weathering and erosion
west: subduction, hot spots, rifting
east: ancient plate collision
appalachian plateau / valley and ridge
region of relatively horizontal rock layers that have been cut by streams to form hilly / mountainous terrain
Catskill, Pocono, Allegheny
long parallel, NE-SW trending ridges and valleys produced by folding and faulting followed by differential erosion of rock strata
NPS emphasis
outdoor recreation
18th and 19th century American history and culture
water gap
an opening that flowing water has carved through a mountain range
blue ridge
Region of metamorphic and igneous rocks that were pushed up and thrusted over those of the valley & ridge during Pangea's creation
NPS emphasis on scenery, recreation, mountain history and culture
piedmont
lower relief area of igenous and metamorphic rocks that were folded by plate convergence along with ‘accreted terranes’ that were added to NA during Pangea
historic emphasis
New England
part of the appalachian highlands with rock types similar to those found in the Piedmont, but contains more mountains and has been subjected to Pleistone glaciation
emphasis on colonial history
What was the first NP east of Mississippi?
Acadia
Established as national monument
Renamed Lafayette NP
Then named Acadia
why do people visit mountain parks in the east?
Outdoor recreation, see undeveloped areas, history / culture, to learn about resources
Coastal Plain:
a low relief plain formed by the deposition, compaction, and lithification of sands, clays, silts, and other sedimentary materials brought in when the area was submerged by the Atlantic ocean
coastal and marine parks
the NPS manages 88 ocean and great lakes across 23 states
estuaries
partially enclosed areas where seawater mixes with fresh water, resulting in highly productive aquatic ecosystems
mixture results in very productive ecosystems
salt marshes:
coastal wetlands that are regularly flooded and drained by tidal salt water and dominated by salt tolerant herbaceous plants
spartina
north - better adapted to cold water
mangroves:
coastal ‘fringe forests’ where fine sediments with high organic content collect in areas protected from high energy wave action
subtropical and tropic
not northern - warm water
corals
small animals (polyps) related to jellyfish. hard corals build limestone cups around their bases and cement together to make a coral colony
coral reefs
are made of thousands of coral colonies next to and on top of each other
primarily in shallow, clear coastal zones - warm subtropic areas
10 diff NPS units with corals
rocky coastlines
high-energy coasts dominated by erosion, often located on active plate margins with narrow continental shelves
erosion and rocky coastlines
wave energy is concentrated on the shoreline especially exposed headlands
rocky vs. sandy coastlines
shorelines divided into high relief erosional shorelines and relief depositional shorelines
sea cave
cave formed primarily by wave action
sea arch
rock arch formed by erosion of a headland
sea stack
isolated rock formed by collapse of an arch
formation of sea stacks and arches
1- bedrock with fractures and large fault
2- caves develop as waves erode the faults and fractures near the edge of the water
3- with continuing erosion, the cave becomes open at both ends forming an arch
4- arch collapse leaves behind a sea stack and further erosion turns another cave into an arch
fjord
a long, deep, narrow sea inlet between high cliffs formed by submergence of a glaciated valley
sandy coastlines
coastlines dominated by low-wave energy, a wide continental shelf and deposition. often located along ‘passive’ margins
sandy coastline features: beach
collection of loose materials deposited against the coastline by waves
sandy coastline features: spit
a sandy deposit protruding from a shoreline and created by longshore sediment transport
barrier island
offshore sandbar islands shaped by wave driven erosion and deposition and separated from the mainland by a shallow lagoon or sound
lagoon / sound
low energy environment that may contain mudflats and coastal marshes formed where rivers deposit sediment into the quiet waters behind the barrier island
barrier island
form is affected by water and wind based erosion and deposition
Biscayne NP ecosystems
coral reefs
mangroves, salt marshes and benthic habitats
biscayne bay
the northern florida keys
dry tortugas NP
preserves the islands and fort jefferson. it can only be reached by boat or seaplane and visitation is tightly controlled
values of coastal parks
ocean and coastal parks constitute a system of tremendous biological, cultural, historic, and recreational value to the nation, attracting over 88 million annual recreation visits and generating over 4.8 billion in economic benefits to local communities