Tutorial 3: long term memory
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
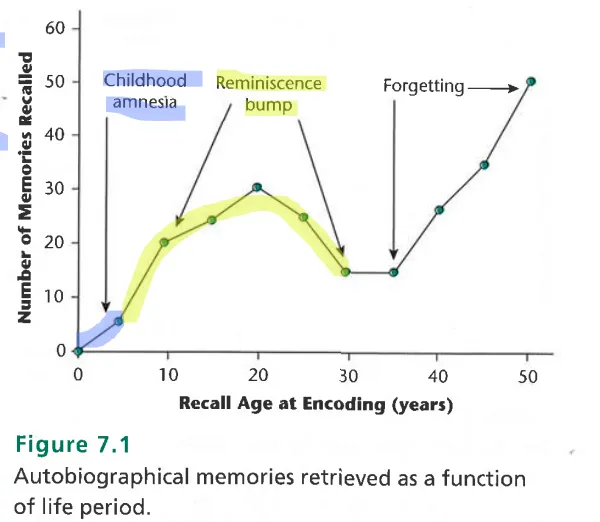
What is childhood amnesia?
no memories from 0-3 years and very few before 10
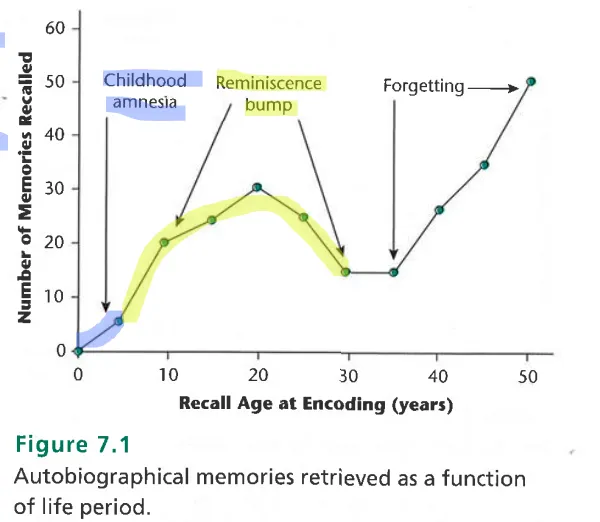
what is the reminiscence bump?
disproportionally many memories between ages 10-30
what does teh role of rehearsing in strengthening memory depend on?
age
→ below 3 : rehearsal can lead to worse memory, since memory is still fragile
→ 4-5 onwards : rehearsal is beneficial for memory
which one develops earlier in children, implicit or exlpicit memory?
implicit (basic skills, making simple associations)
What has been found out about memory and narrative style?
elaboratove → encourages more rich memory
pragmatic → less detailed memory
what has been found out about the emergence of autobiographical memory in american vs. taiwanese people?
americans tend to develop autobiographic memory earlier than taiwanese people
→ americans have a more self centred self concept, might develop sense of self and therefore memories of themselves earlier
what factors does the social cognitive development view on autobiographical memory consider?
basic explicit memory abilities
language
consciousness about past
theory of mind
What is the “wane of childhood amnesia”?
the transitioning point where memories transition from “known” to “recollect” memories
(offset of childhood amnesia)
what has been found out about the nature of memories that are so well retained during the reminiscence bump?
they are often quite mundane and theoretically shouldnt be that memorable
Is Brain development neccessary and sufficient for the offset of childhood amnesia?
no, only neccessary but not sufficient
is brain development neccessary and sufficient for the reminiscence bump?
yes
what are the two major components of the self-memory system model ?
autobiographical memory knowldge base
working self
what are the three levels within the autobiographical memory knowledge base?
lifetime periods
general events
event specific knowledge (episodes)
what are the two kinds of retrieval ?
generative retrieval (deliberate)
direct retrieval (automatic)
what different brain parts are activated for generative vs. direct retrieval ?
generative = prefrontal cortex
direct retrieval = other areas such as hippocampus
what has been found to be a memory-related risk factor for depression?
overgeneralized memory
how does the memory of the own life history differ for healthy vs. depressed individuals?
depressed people have a more negative and less integrated record of their life histoy
what is retrograde amnesia?
lack of ability to remember events before brain injury
what is anterograde amnesia?
impaired ability to form new memories
what is the effect on amnesia on explicit and implicit memory?
explicit memory is significantly affected while implicit memory is still intact
which kind of memory might play an especially important role in the effect of amnesia on explicit memory?
contextual memory is impaired
what is “source amnesia”?
struggling to remember the source of an information
what does “semantic residue” refer to ?
proposed in the “modal model of amnesia”
refers to the idea that semantic memory is the “residue” of many episodic memories
what are two reasons why jon unlike many other patients with amnesia had intact recognizing ability ?
his damage to hippocampus happened early, at birth
the damage is strongly confined to only the hippocampus and surrounding areas were spared
What is consolidation?
the process by which memories are strengthened
what has been found out about amnesic patients and consolidation?
they might be especially vulnerable to disruptions in the consolidation process
What is the “Ribots law”?
ealiere memories are more durable and better preserverd than the more recent ones
What did the study find out with respect to the “offloading hypothesis”
unlikely or can be rejected sinde even when knowing that we cant rely on the photos, memory is still impaired after taking a picture