Coag Final
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
191 Terms
Coag cascade
Virchows Triad
All work together to impact how clotting would happen:
changes in the vessel wall
changes in the blood composition
changes in the blood flow
Role of intact endothelium
-thrombo resistant ( resist blood clotting)
-first to respond to injury by vasoconstriction
How is the Endothelium Thrombo resistant?
secretes substances to keep plts from sticking
makes thrombomodulin
releases t-PA (tissue plasminogen activator)
Heparan sulfate
What occurs when endothelium is damaged?
Thrombogenic (clot inducing) by
exposing collagen receptors to trigger plt adhesion
endothelial cells release TXA2 to activate plts
Weibel Palade bodies release vWf (bind plts)
release of tissue factor (trigger extrinsic)
release of PAI 1, 2, 3, 4 (limit fibrinolysis)
Maturation sequence of plts
Megakaryoblast
Promegakaryocyte
Megakaryocyte
plt
Lifespan of plts
7-10 days
Where do plts reside?
1/3 spleen
2/3 in circulation
What are the 4 zones of plts (MOPS)
membranous: facilitates granule release
organelle: release alpha granules and dense bodies
peripheral zone: glycoprotein receptors, phospholipids (pf3)
structural: shape change
What receptor on plts binds vWF
GPIb-IX
What receptor on plts binds fibrinogen
GPIIb-IIIa
What do alpha granules contain?
platelet factor 4
PDGF
Beta thromboglobulin
coag factors (1, vWF, 5, 8, 11, 13, protein S, plasminogen, PAI-1)
plt factor 4 neautralizes____
heparin
PDGF starts ______repair with fibroblasts
wound
Beta thromboglobulin neautralizes_____
heparin
What do dense bodies contain?
ADP and calcium
Serotonin
Serotonin is an _____agent
aggregating
Which granules in plts are more numerous?
alpha granules
Which granules in plts play a bigger role?
dense bodies
Describe the process of aggregation (4xA)
Activation: collagen exposed
Adhesion: vWF binds to exposed endothelium and plts bind to it via GPIb/IX
Activation: GPIIb/IIIa on plts is exposed and granules release
Aggregation: fibrinogen can then bind and clot
Which CD marker detects GPIb/IX
CD42
Which CD marker detects GPIIb/IIIa
CD41
A stimulating chemical is called an____
agonist
Dense bodies release ____and____
ADP and calcium
What role does ADP play?
binds to plt membrane—→ activates enzymes——> arachidonic acid released
Archidonic acid ——(cyclooxygenase+ thromboxane synthase)——> _________
Thromboxane A2
What does Thromboxane A2 do?
complete or amplify aggregation
What inactivates cyclooxygenase?
aspirin
How would you determine if bleeding is due to plts (primary)?
family history
Type of bleeding
Screening tests
What type of bleeding occurs in primary hemostasis (due to plts)
epistaxis (nose bleeds)
mucous membrane
external skin: bruising, petechiae
What are the screening tests for primary hemostasis?
plt count
plt function
List disorders of primary hemostasis (HOME)
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
Osteogensis imperfecta
Marfans syndrome
Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
They all lack the right amount or composition of collagen
Thrombocytopenia
low plts
Normal range for plts
150-400
List some disease that have decr plts
Myelophthisic
Aplastic
Myelodysplastic
Acute Leukemia
Megaloblastic anemia
Chemotherapy
What are immune mechanism that destroy plts?
Chronic ITP (immune thrombocytopenic purpura)
Acute ITP
HIT (heparin induced thrombocytopenia)
Acute ITP
.
Age range:
Gender:
Treatment:
Age range: kids post viral
Gender: any
Treatment: self limiting
Chronic ITP
.
Age range:
Gender:
Treatment:
Age range: child bearing age
Gender: females
Treatment: steroids, splenectomy, doesn’t resolve
HIT antibodies made against:
-plt- factor 4 complex
-Can cause bleeding or clotting
bleeding: destroys plts
clots: activates plts
What are non-immune mechanism that destroy plts?
TTP (Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura)
HUS (Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome )
DIC (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation)
TTP
Trigger:
Coag results:
Trigger: ADAMS 13
Coag results:
large vWF
PT normal
PTT normal
D-dimer (-)
HUS
Trigger:
Coag results:
Trigger: Ecoli O157 ( endotoxin exposes sub endothelial in kidneys)
Coag results:
PT normal
PTT normal
(it is not a systemic problem therefore normal)
DIC
Trigger:
Coag results:
Trigger: OB, Sepsis, Leukemia, Burns, Trauma
Coag results:
all factors consumed
PT long
PTT long
D-dimers (+)
Secondary fibrinolysis occurs in ___ where clots are being lysed
DIC
Which disorder corrects itself if given enough ADP?
Aspirin induced
Test for plt function
Bleeding time (obsolete)
Plt function analyzer (PFA-100)
Verify Now test for P2Y12 (ADP) inhibition
Plavix
Plavix
Antiplatelet drug that blocks P2Y12 ADP receptor site on plts
PFA-100 results for Aspirin
EPI: abnormal
ADP: norm
PFA-100 results for vWD
EPI: abnormal
ADP: abnormal
PFA-100 results for Bernard Soulier
EPI: abnormal
ADP: abnormal
PFA-100 results for Glanzmans
EPI: abnormal
ADP: abnormal
Defect of Glanzmans
GP IIB/IIIA
Defect of Bernard Soulier Syndrome
GP IB/IX
Defect of vWD
vWF
Defect of storage pool disorders (includes aspirin)
Lack of granule release
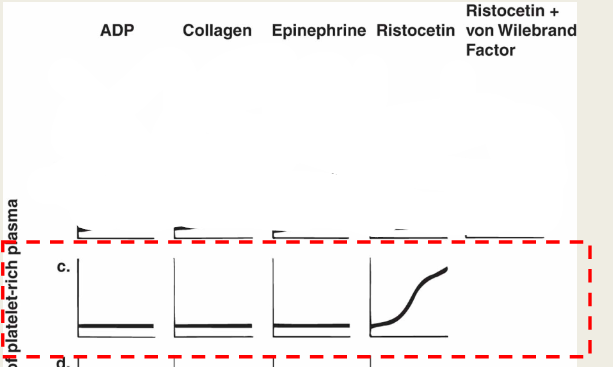
Plt Agg results for Bernard Soulier
ADP: norm
Collagen: norm
Epinephrine: norm
Ristocetin: abnormal
Ristocetein +NL plasma: abnormal

Plt Agg results for vWD
ADP: norm
Collagen: norm
Epinephrine: norm
Ristocetin: abnormal
Ristocetein +NL plasma: norm
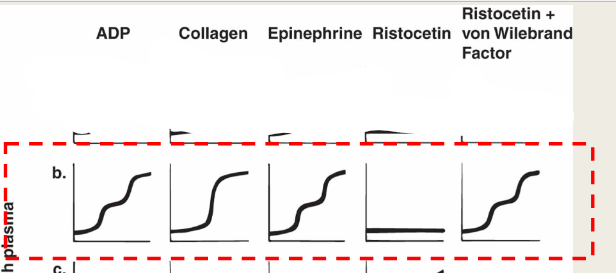
Plt Agg results for Glanzman’s
ADP: abnormal
Collagen: abnormal
Epinephrine: abnormal
Ristocetin: norm
Ristocetein +NL plasma: norm
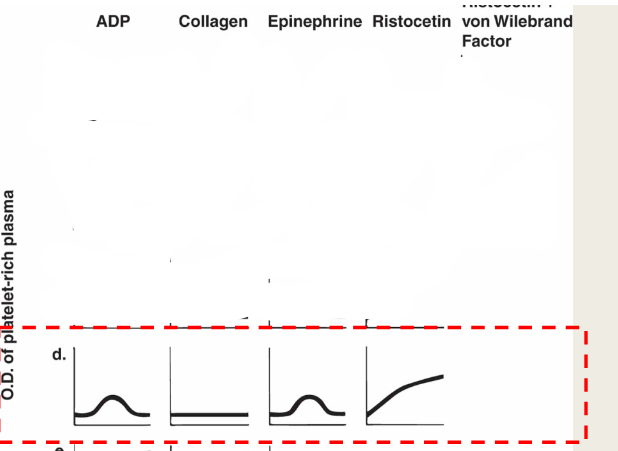
Plt Agg results for storage pool disorders
ADP: starts then disintegrates
Collagen: starts then disintegrates
Epinephrine: starts then disintegrates
Ristocetin: norm
Ristocetein +NL plasma: norm
Archidonic acid: if still abnormal then aspirin
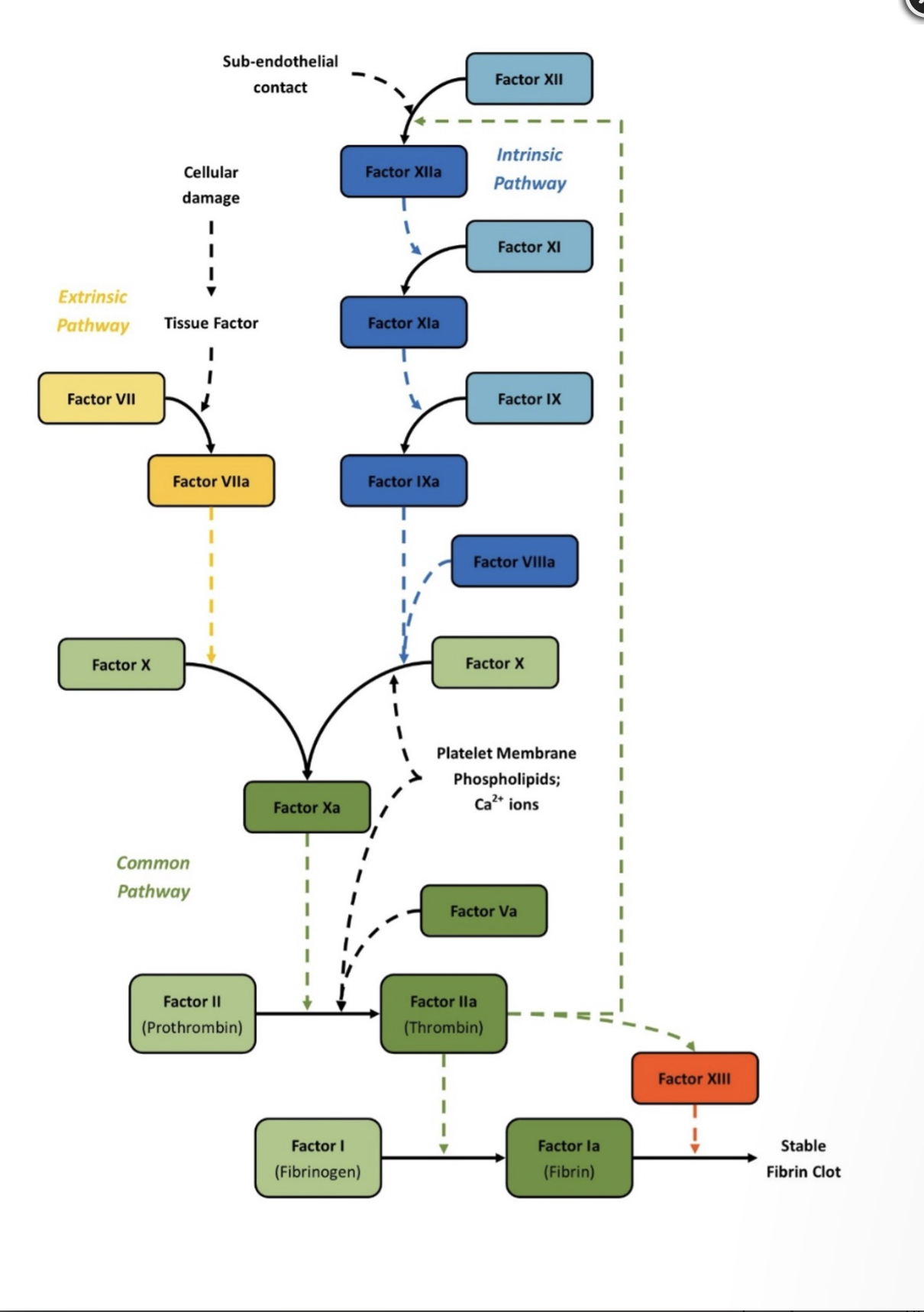
Extrinsic factors
7 (common-10, 5, 2, 1)
Extrinsic measured by
PT
Instrinsic
12, 11, 9, 8, (common 10, 5, 2, 1)
Intrinsic measured by
PTT
Common pathway
10, 5, 2, 1
Common pathway measured by
PT and PTT
What is another name for Factor I
Fibrinogen
What is another name for Factor II
Prothrombin
Contact factors
12, 11, Prekalikrein, HMWK
Vit K dependent factors
2, 7, 9, 10
Fibrinogen group (cofactors)
1 (fibrinogen), 5, 8, 13
What is used to preserve factors 5, 8, 13
cryo-pcpt
What role does thrombin play in plts
trigger for plt activation
Thrombin converts ___to___
fibronogen to fibrin
What role does thrombin play in instrinsic
Amplifies Factor 5, 8, 11, 12
What does thrombin do to factor 13
causes cross linking of fibrin
Thrombin binds to thrombomodulin and causses protein c/s to
activate shut-off mechanism
Endothelial cells bind to _____ to limit action of thrombin
thrombomodulin
What is thrombomodulin?
endothelial cell membrane glycoprotein
Thrombin makes endothelial cells release___
vWF and t-PA
TAFI suppresses___
fibrinolysis
Process of Fibrinogen to fibrin
Thrombin cleaves fibrinopepetide A and B
Fibrin monomer is formed
Fibrin monomer is polymerized
F-13 plus Ca creates cross-linked fibrin
What are some bleeding symptoms of secondary hemostasis (factors)
deep tissue bleeding
blood in joints
delayed bleed
NO petechiae
Hemophilia
Def in clotting proteins
vWD inheritance
Auto Dom
Factor 8 or 9 def inheritance
x-linked recessive
(all other disorders will be recessive)
vWF binds to plt GP____and promotes adhesion to subendothelial collagen
receptors
Why would vWD affect secoondary hemostaisis, specifically factor 8
vWF complexes 1:1 with F-8 to protect and extend its half life
without vWF F-8 may be subpar and PTT may be slightly long
Type O has the ___vWF
least
Type AB has the ____vWF
most
vWD
PT, PTT, and plt count are___
norm
vWD testing includes
vWF antigen
vWF activity
vWF multimer analysis
ADAMS 13 activity
Treatment for vWD
nosespray (DDADP)
cryo-pcpt
Hemophilia A def
F-8
Hemophilia B (Christmas) def
F-9
Treatment for Hemophilia
Recombinant F-8, or F-9 concentrate
Some people develop inhibitors called
F-8 or F-9 autoantibodies
Recessive bleeding disorders include all factors except
F-8 and F-9
Recessive bleeding disorders will show what symptoms?
usually none
Hemophilia C def
F-11
Parahemophilia def
F-5