Unit 1: Chemistry of Life
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and proteins
what are the four main organic macromolecules?
monomers
several copies of a single unit that make up macromolecules
polymers
monomers link to form blank
nucleotides
nucleic acids are made of blank
monosaccharides composed of C,H, and O
carbohydrates are made of blank
amino acids linked by peptide bonds
proteins are made of blank
fatty acids and glycerol
lipids are made of blank and blank
source of energy
function of carbohydrates
antibodies, musclefibers
function of proteins
make up genetic info
function of nucleic acids
makes up cell membranes
function of lipids
table sugar, milk
food sources of carbohydrates
meat, nuts, beans
food sources of proteins
plants, fish
food sources of nucleic acids
vegetables, oils
food sources of lipids
glucose, fructose, sucrose
examples of carbohydrates
enzymes
examples of proteins
DNA, RNA
examples of nucleic acids
phospholipids, cholesterol
examples of lipids
triglycerides
one of the most common dietary lipid groups, found the most in body tissue
1. The protein test in Figure 1 might be surprising because we would expect there to be protein from sources like the beef patty.
2. I would infer that since fast food is very cheap, chains like McDonald's aren't able to afford quality, protein rich meat.
Why might the protein test results shown in figure 1 be somewhat surprising?
Given what you know about fast food, what would you infer is the rationale behind these results?
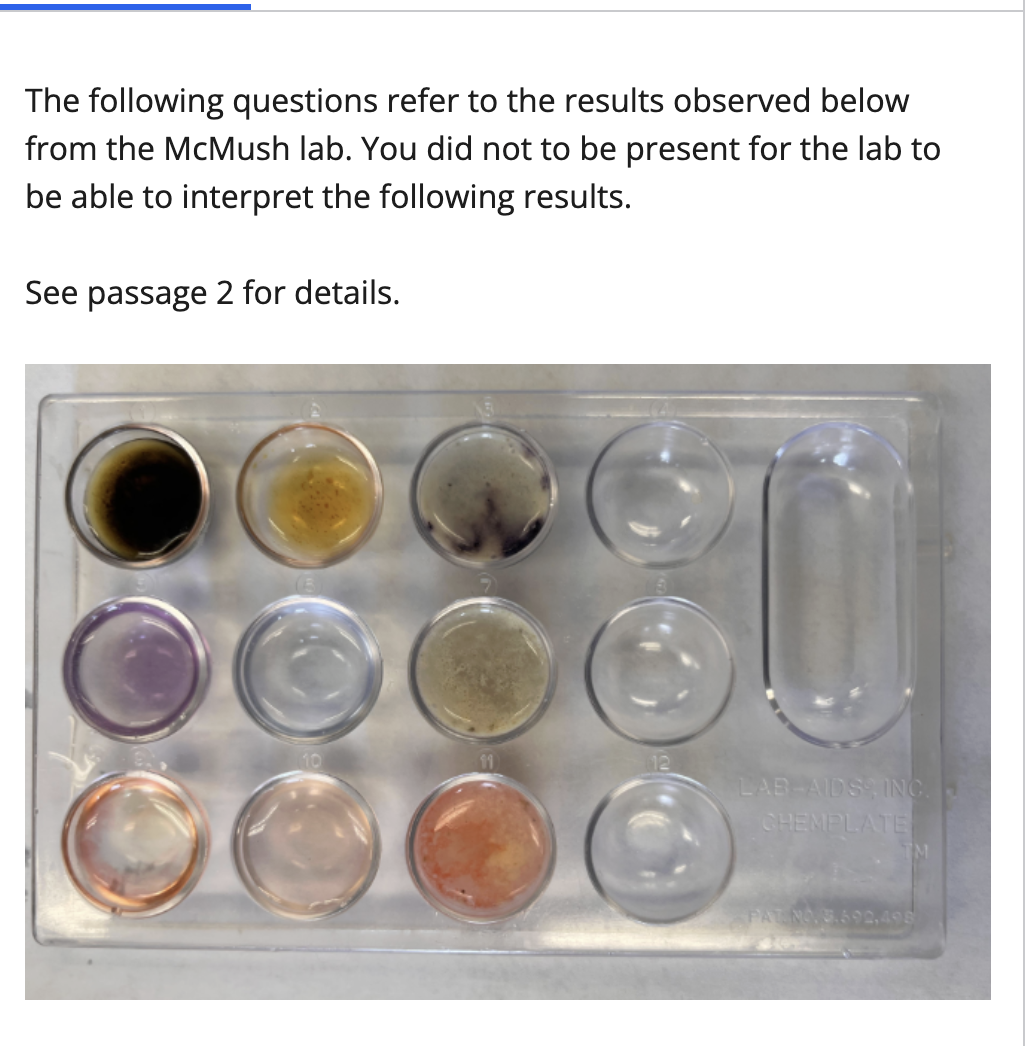
Polysaccharides and lipids are present, proteins are hard to tell in this sample.
In this example, which macromolecules seems to be present in the McMush slurry?
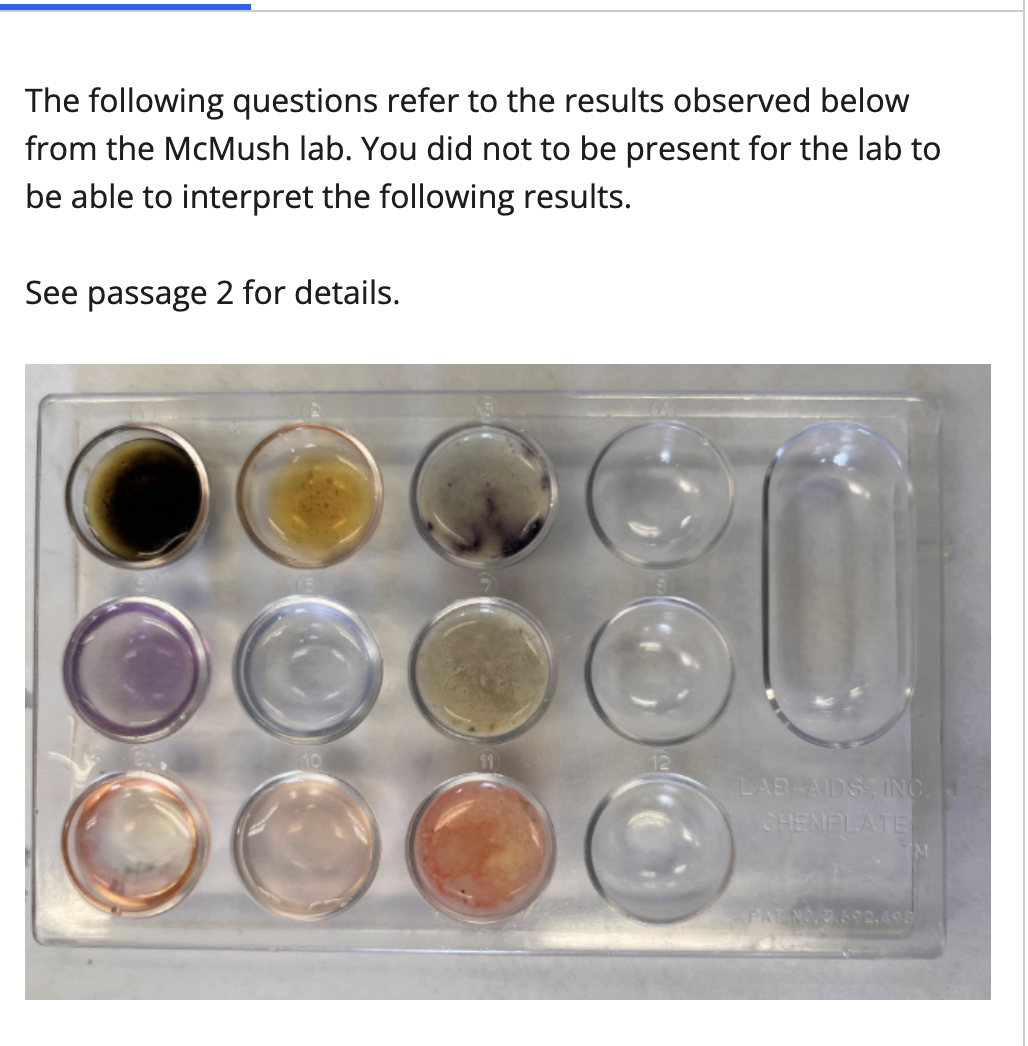
The positive and negative control tests act as standards of comparison for the substance we are testing, which in this case was the Mcslush.
The first column has the positive control tests, the second column had the negative control tests. What is the purpose of a positive and negative control test?
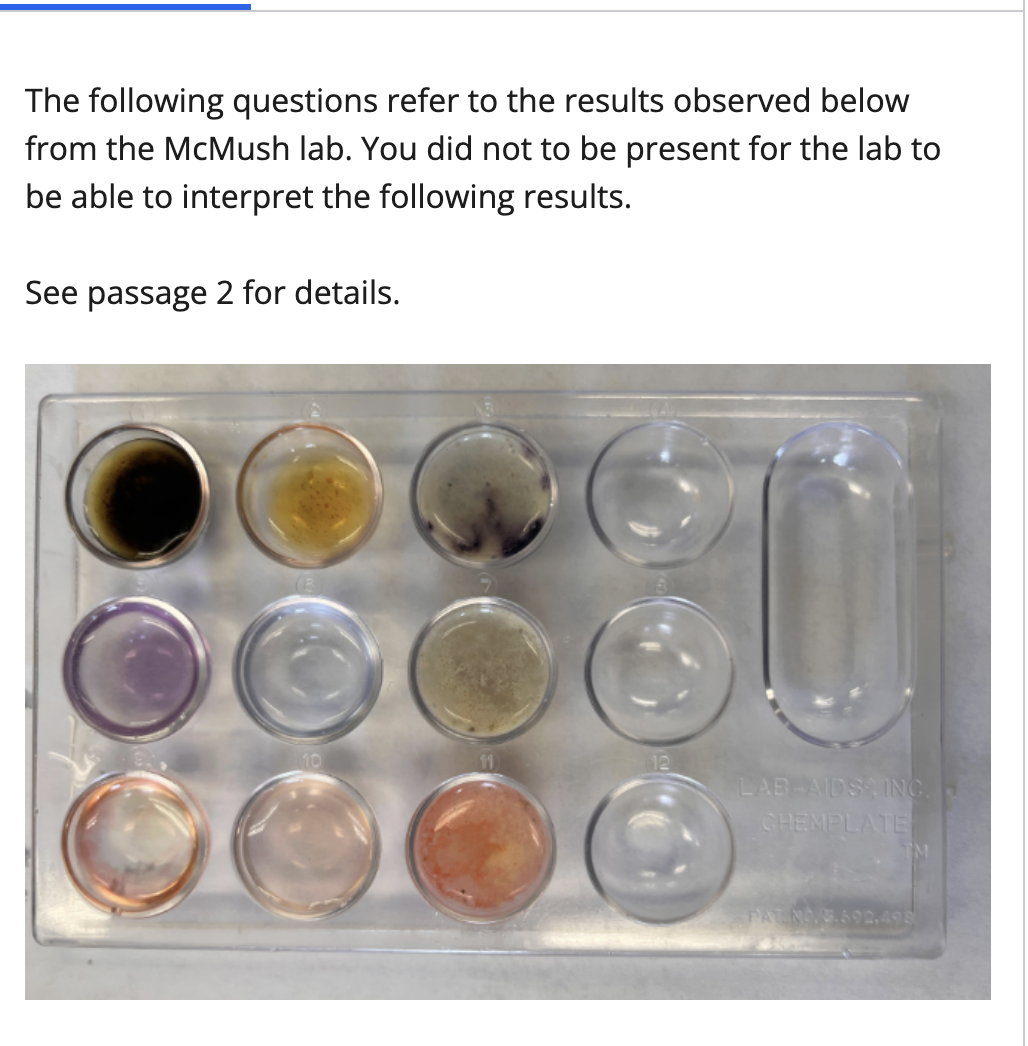
enzymes, antibodies, cell receptors, structural molecules such as keratin in hair, hormone such as insulin
protein examples
oils (from plants), fats (from animals), blubber, most abundant molecules in cell membranes, steroid hormone such as testosterone
lipids examples
Carbohydrates, starch, glycogen, fructose, sucrose
sugars examples
DNA, RNA
nucleic acids examples