AP Economics Unit 1
1/44
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Law of Increasing Costs
As you produce more of one thing, you have to give up more and more of something else. This occurs because resources are not equally efficient in producing all goods, leading to a higher sacrifice of other goods as production shifts.

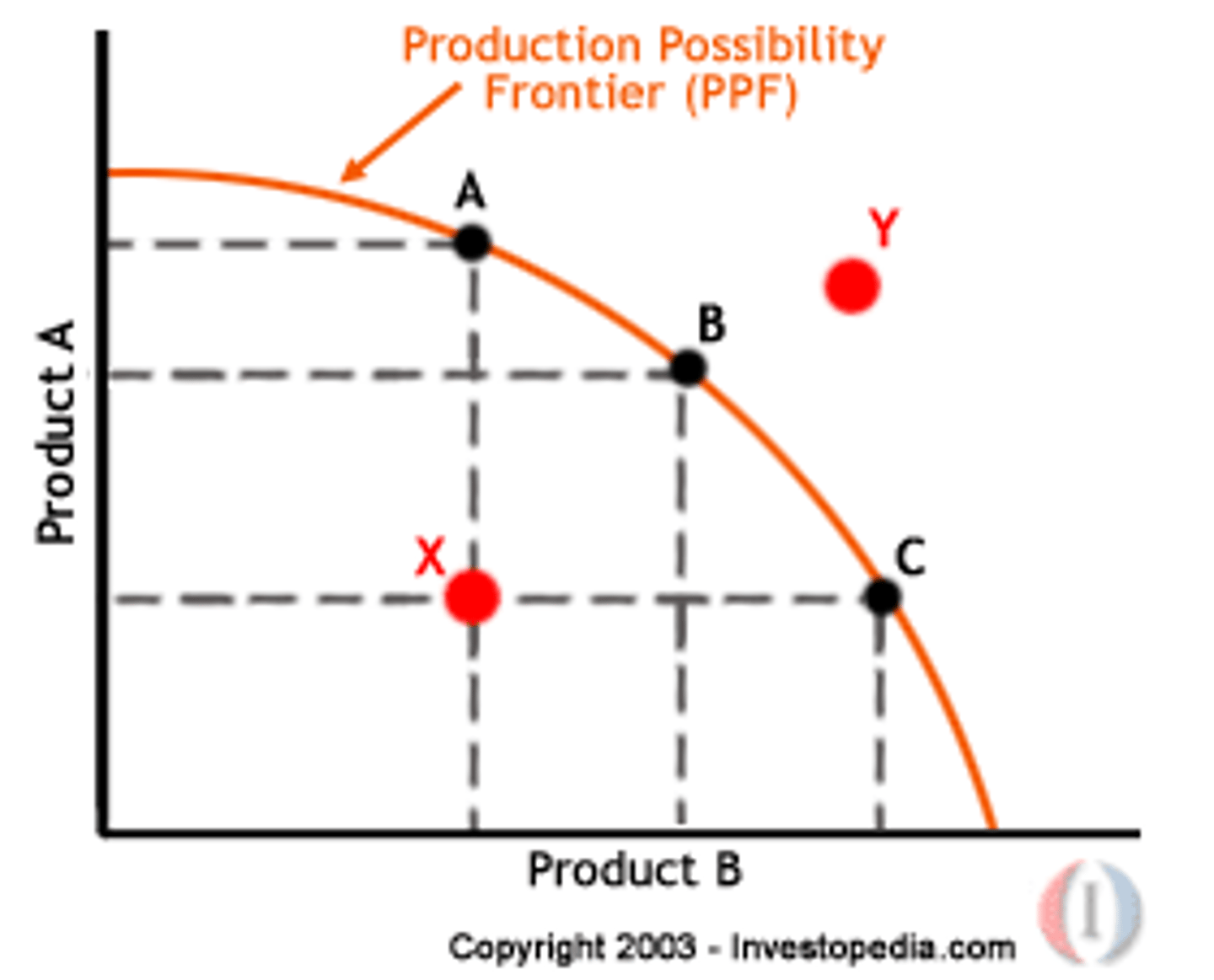
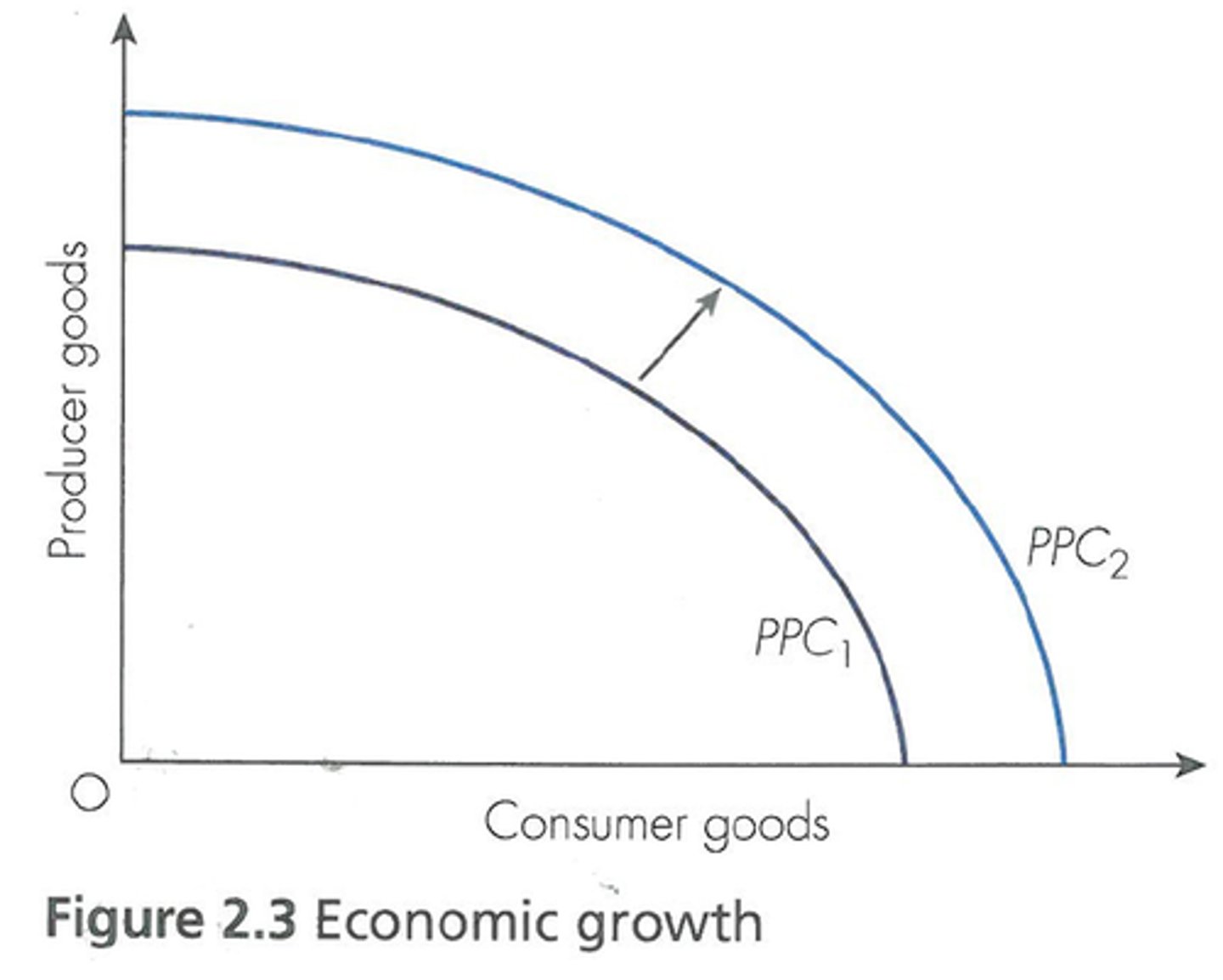
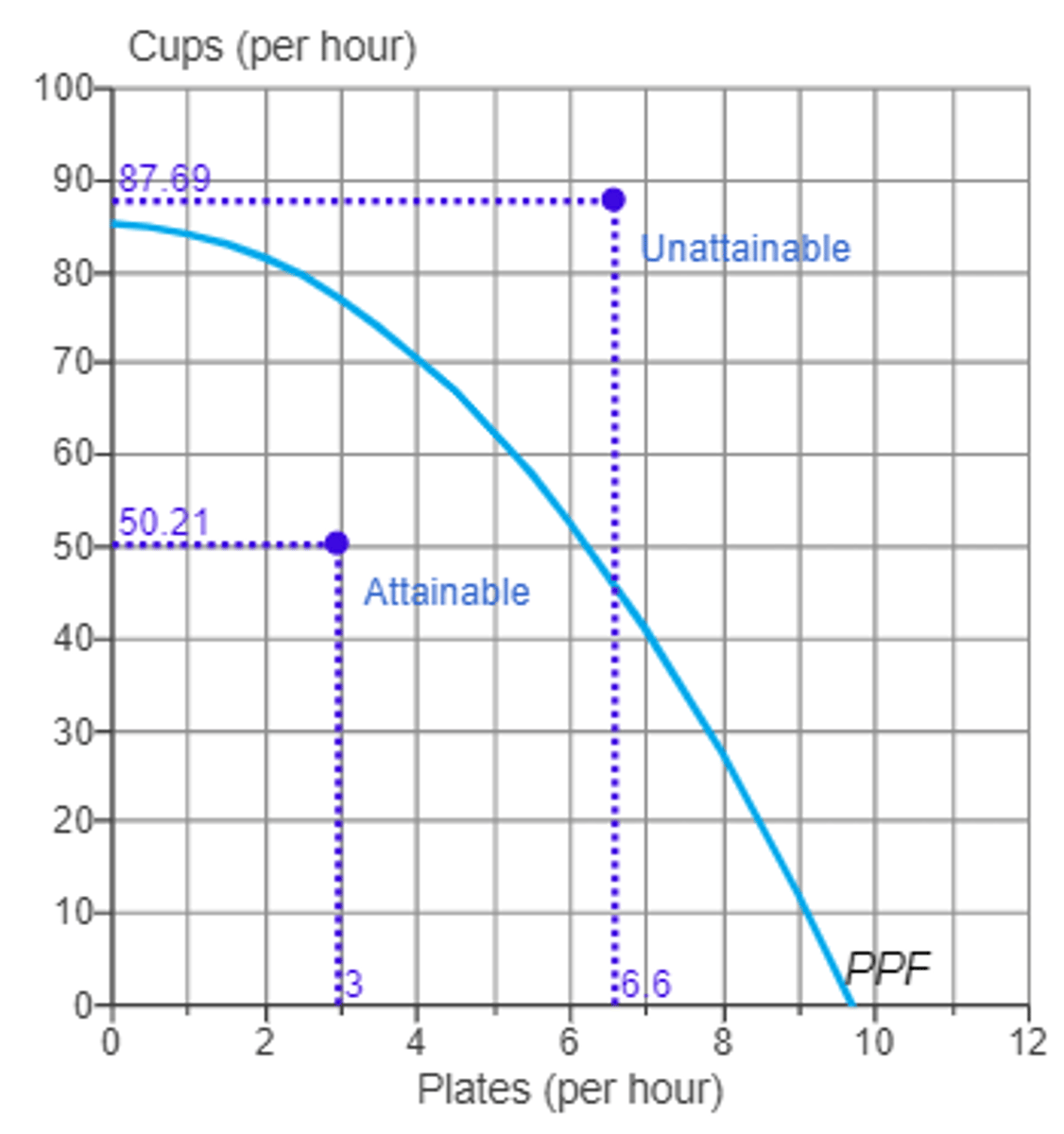
Production possibilities frontier
the combinations of two goods that can be produced if the economy is efficient (concave to the origin because of law of increasing costs)
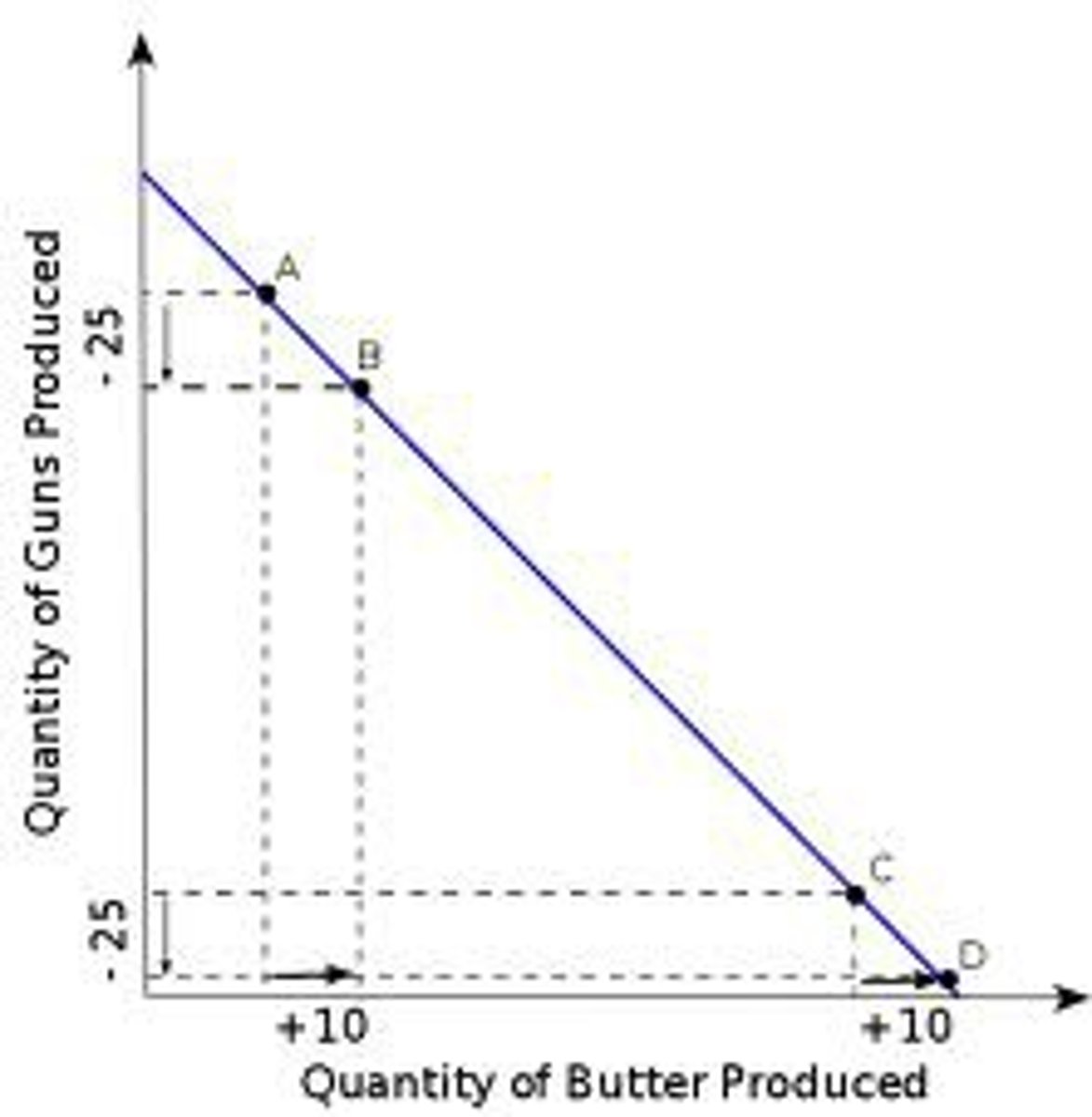
Constant Opportunity Cost
Require similar resources
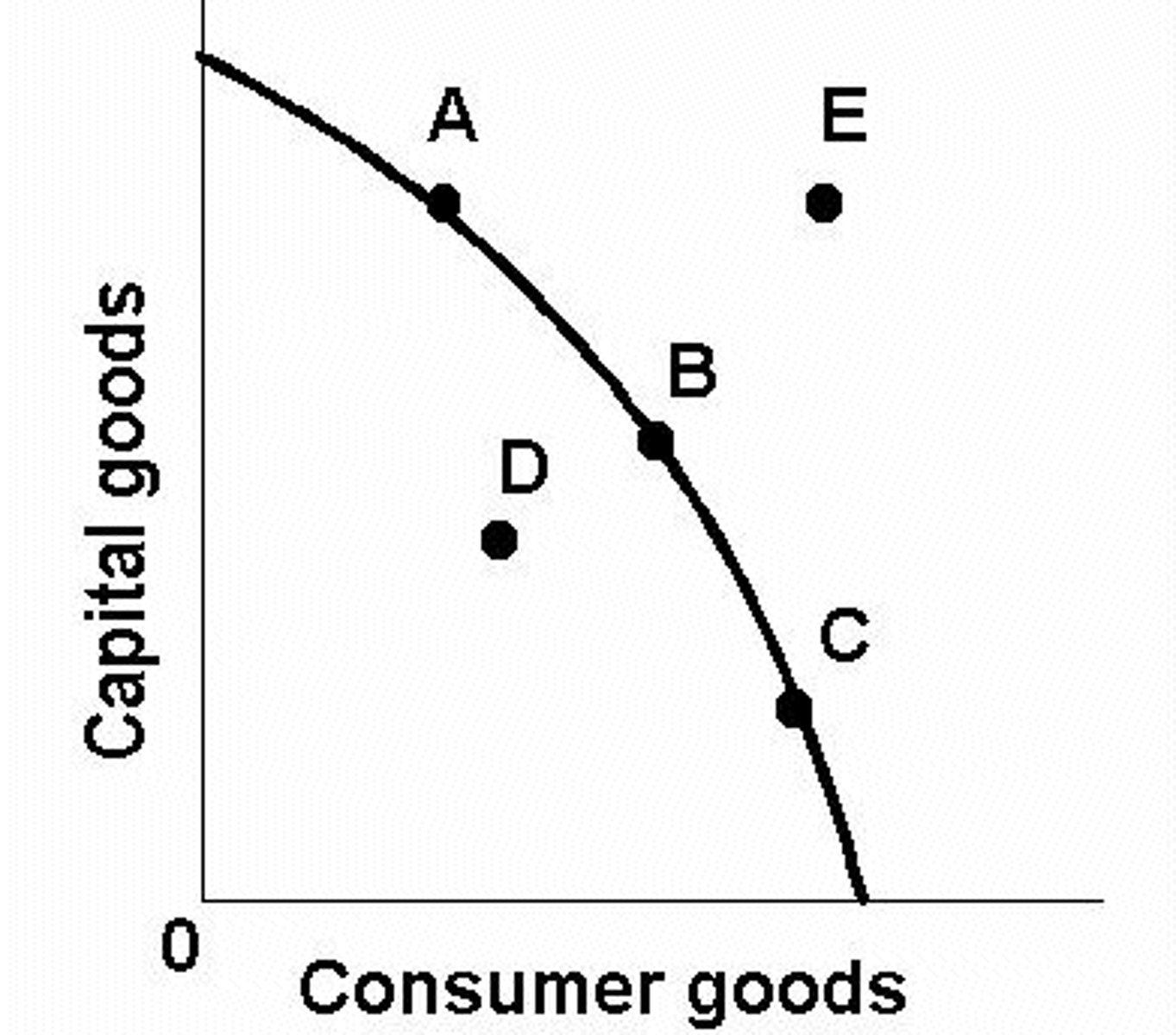
Increasing Opportunity Cost
Require very different resources
comparative advantage
the ability to produce something with lower opportunity cost
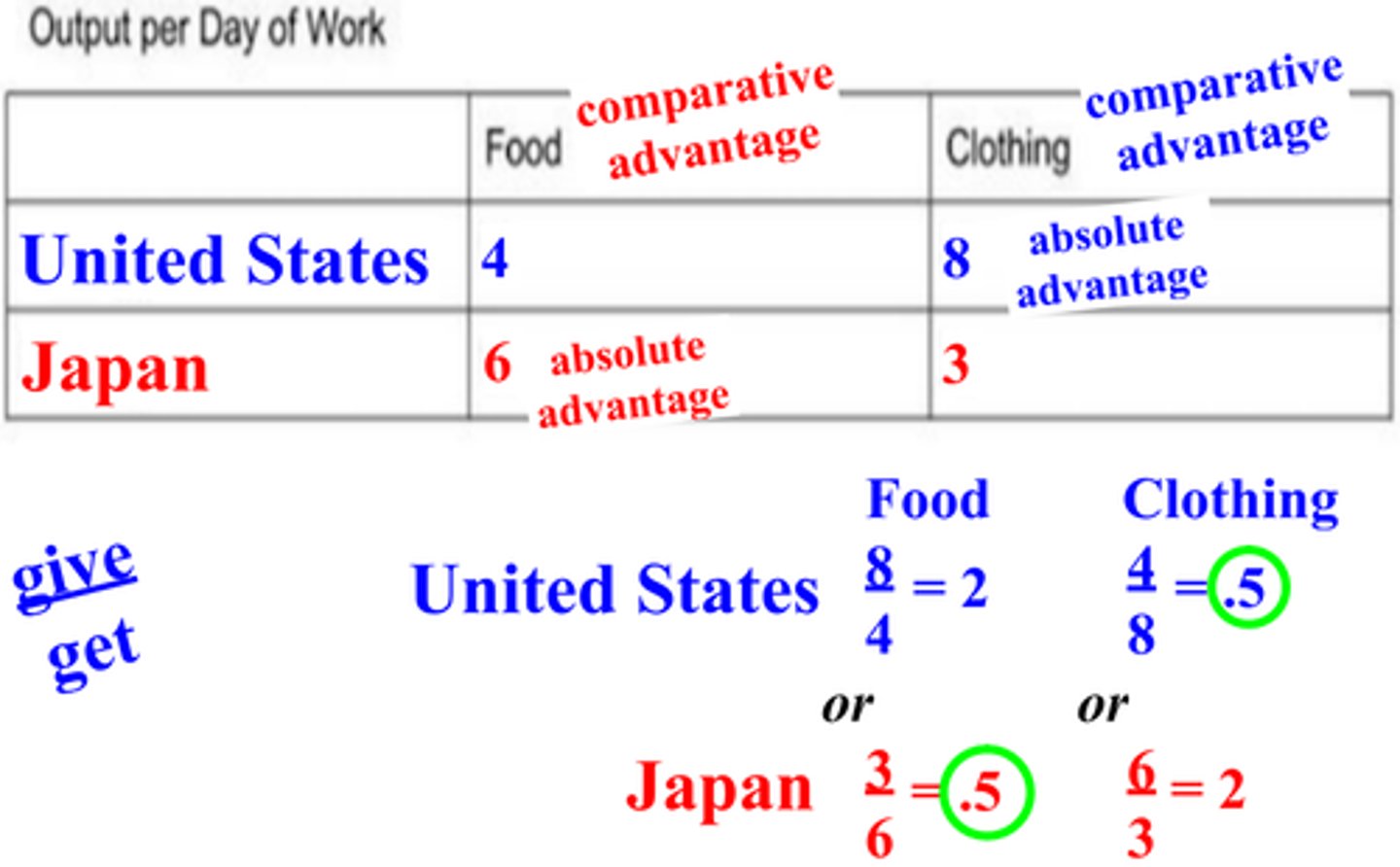
absolute advantage
the ability to produce something more efficiently

efficiency
using resources to maximum potential
Economic Resources
Land, labor, Capital, and Entrepreneurship
labor
all productive human activity
Command economy
the government decides what, and how much is produced, and who receives the goods
Law of demand
when the price of a product increases, the quantity demanded decreases
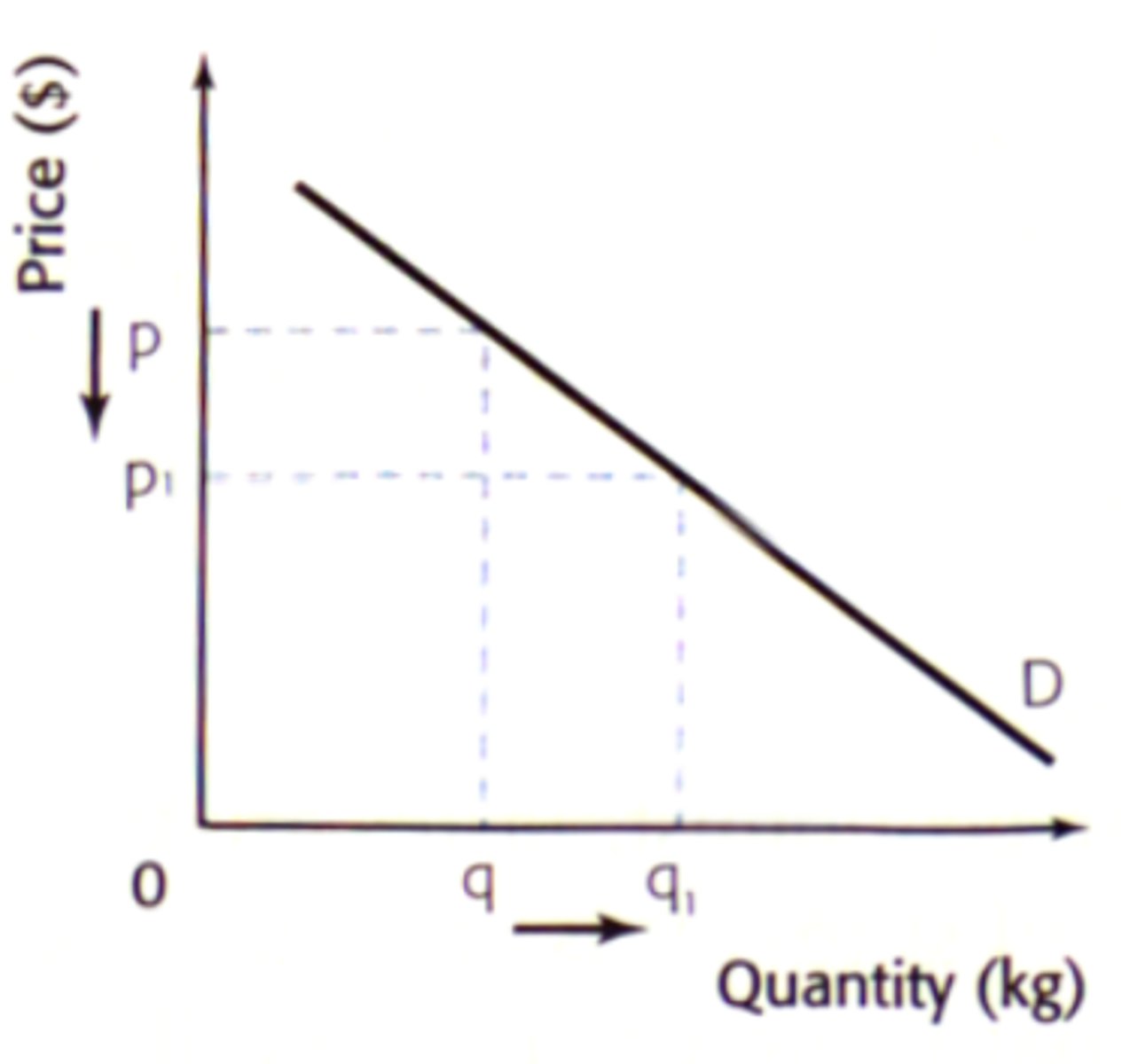
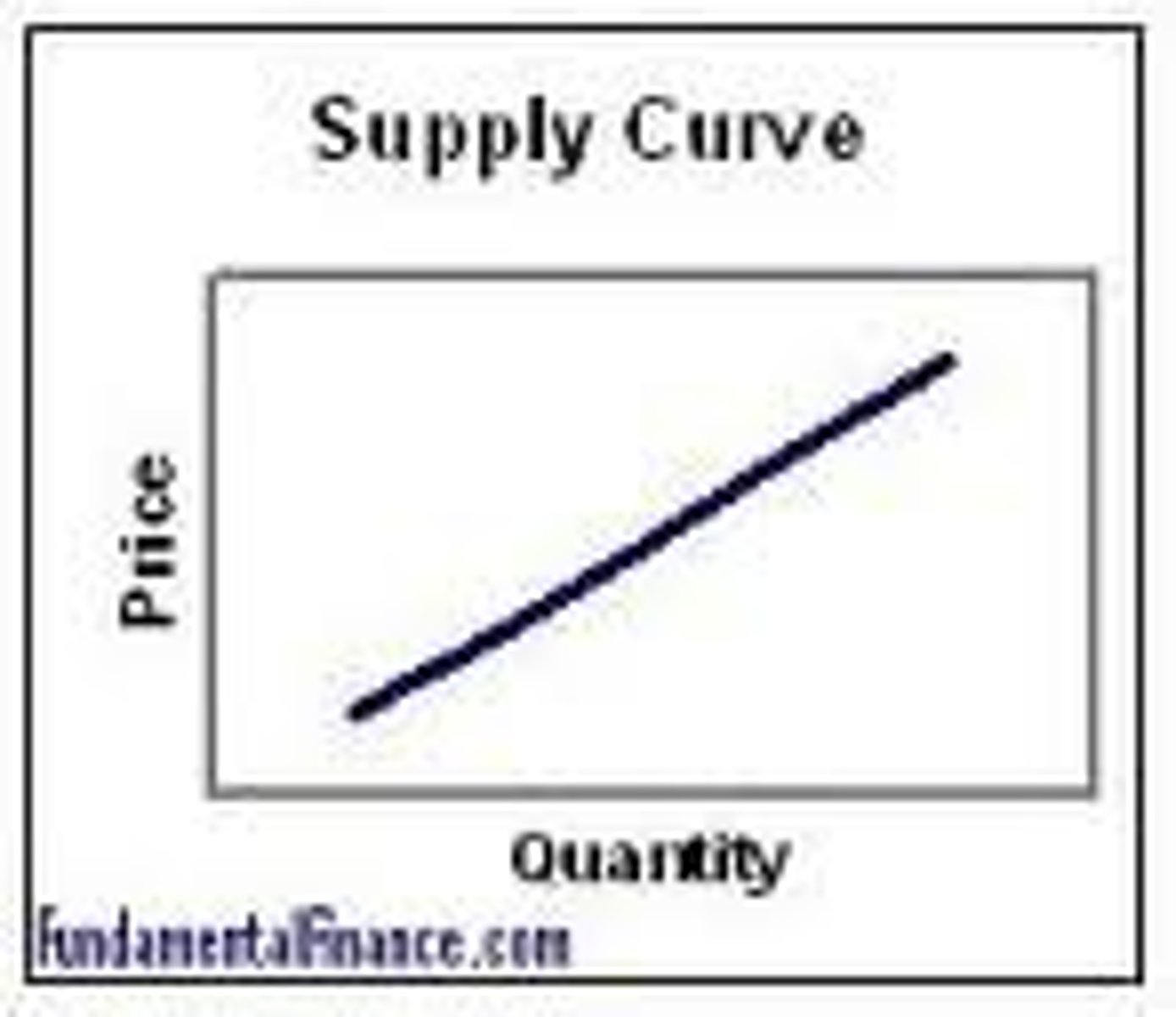
Law of supply
when the price increases, the supplied quantity increases
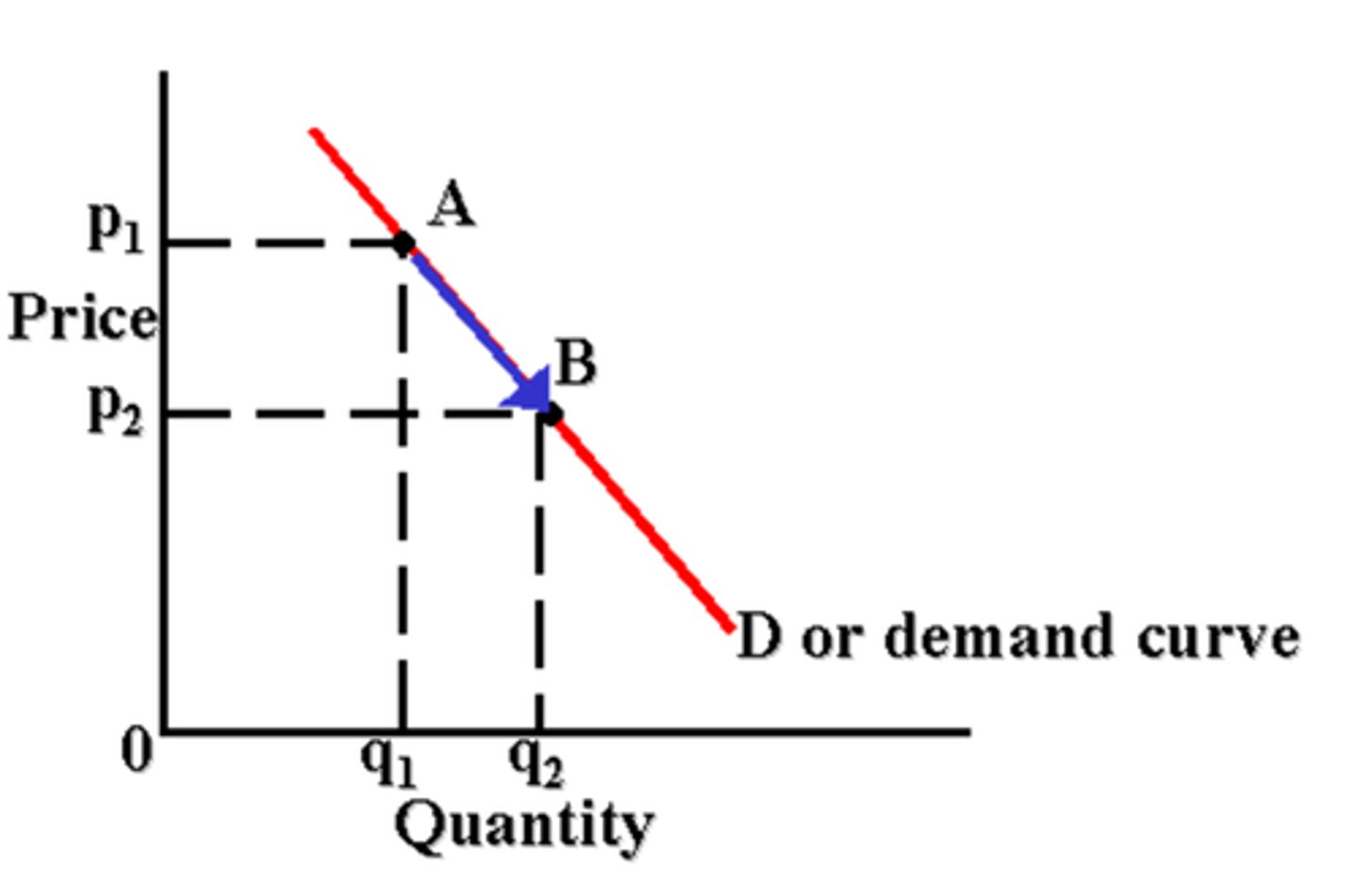
change in quantity demanded
occurs when the price of a good changes, no shift in curve, just a movement along the curve (inverse relationship with changes in price of good)
Determinants of demand (SPICE)
S-ubstitute goods, P-references and population, I-ncome, C-omplementary goods, E-xpectations
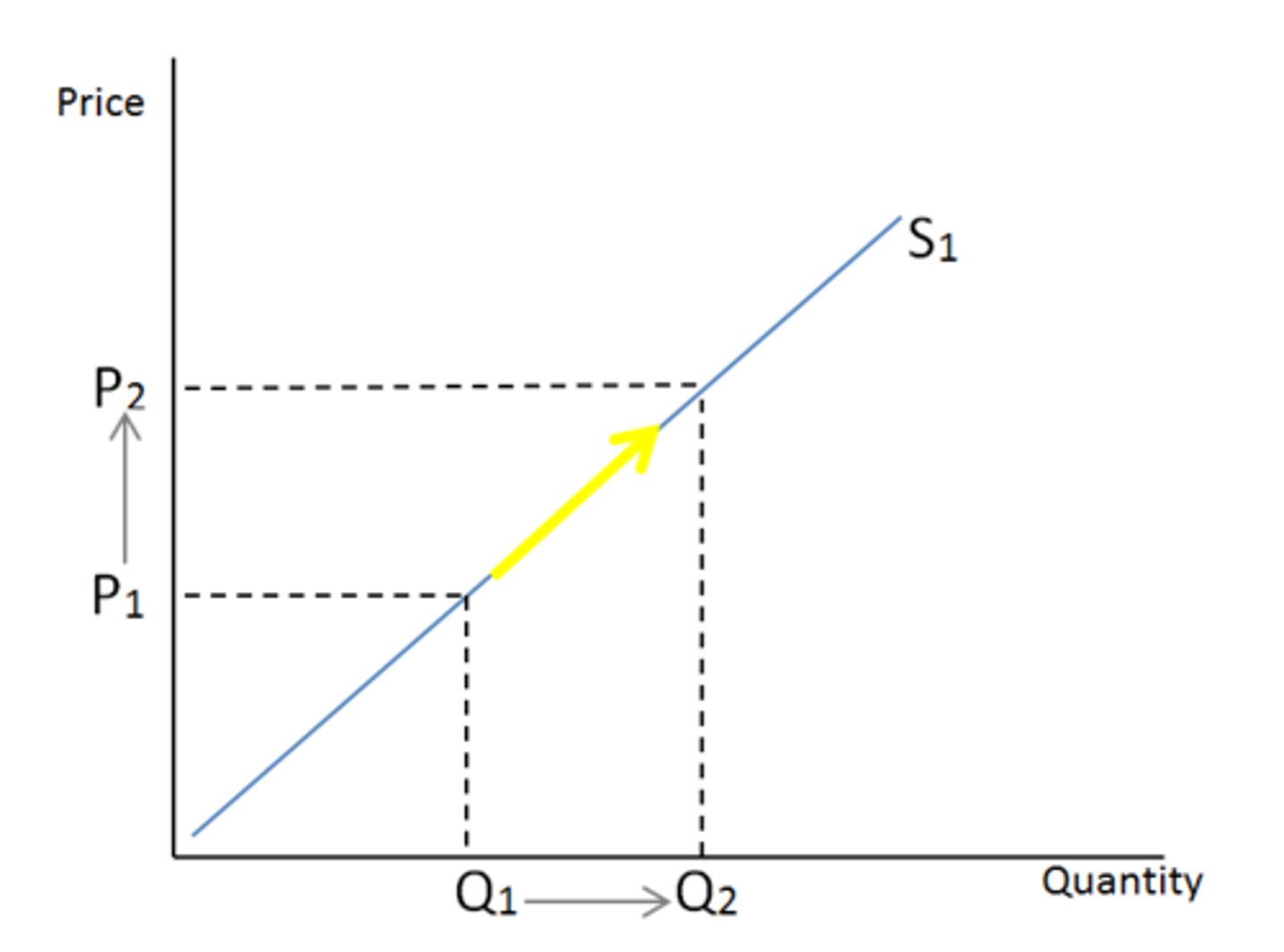
change in quantity supplied
occurs after a price change, no shift in supply curve (direct relationship with changes in price of good)
Determinants of supply (COTTEN)
C-ost of inputs, O-pportunity cost of alternative production, T-echnology, T-axes/ subsidies, E-xpectations, N-umber of sellers
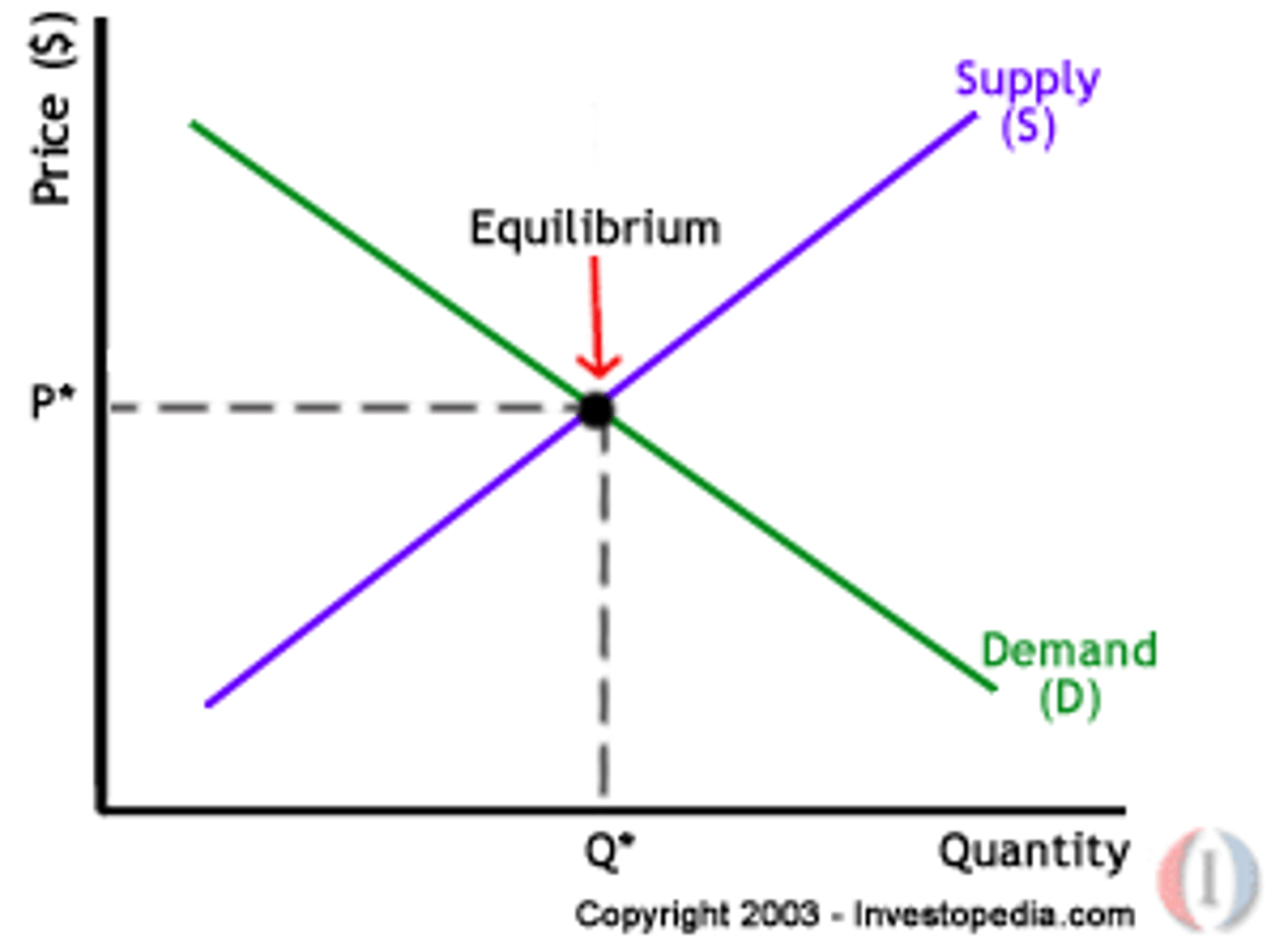
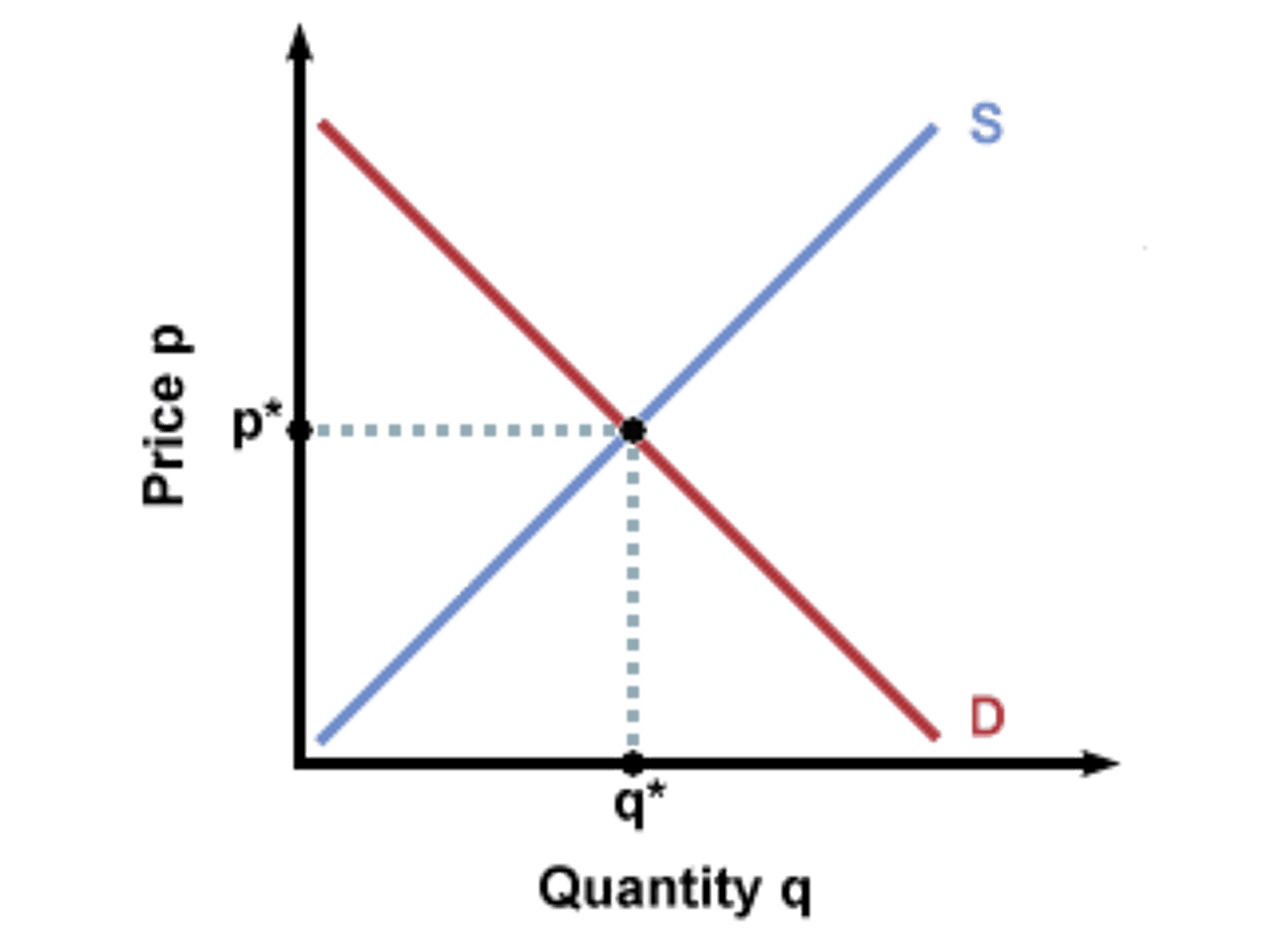
Equilibrium price
price at which quantity supplied equals quantity demanded
Income effect
purchasing power of income is inversely related to product price; as price decreases, consumer may buy more because of increased buying power of income
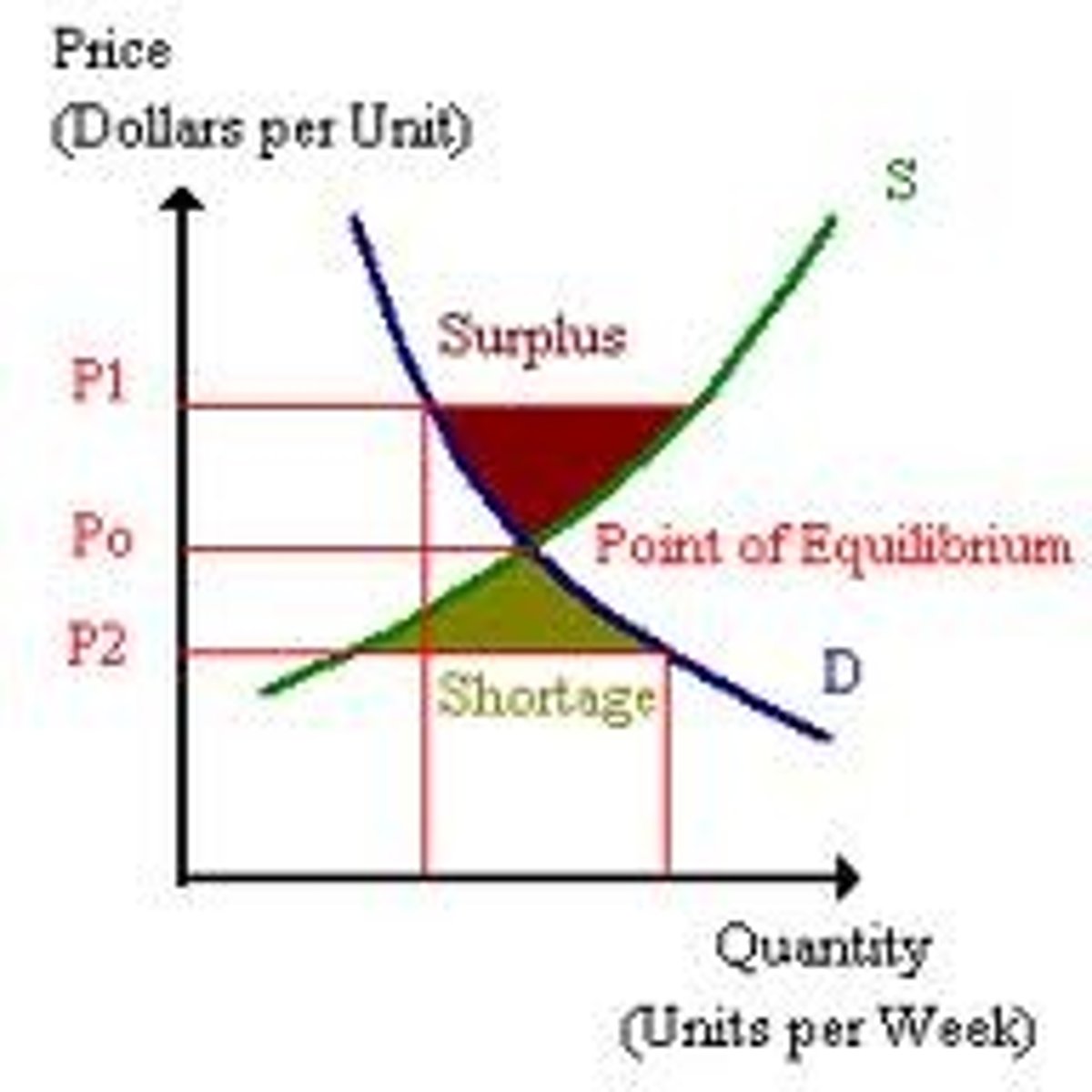
shortage
when quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied
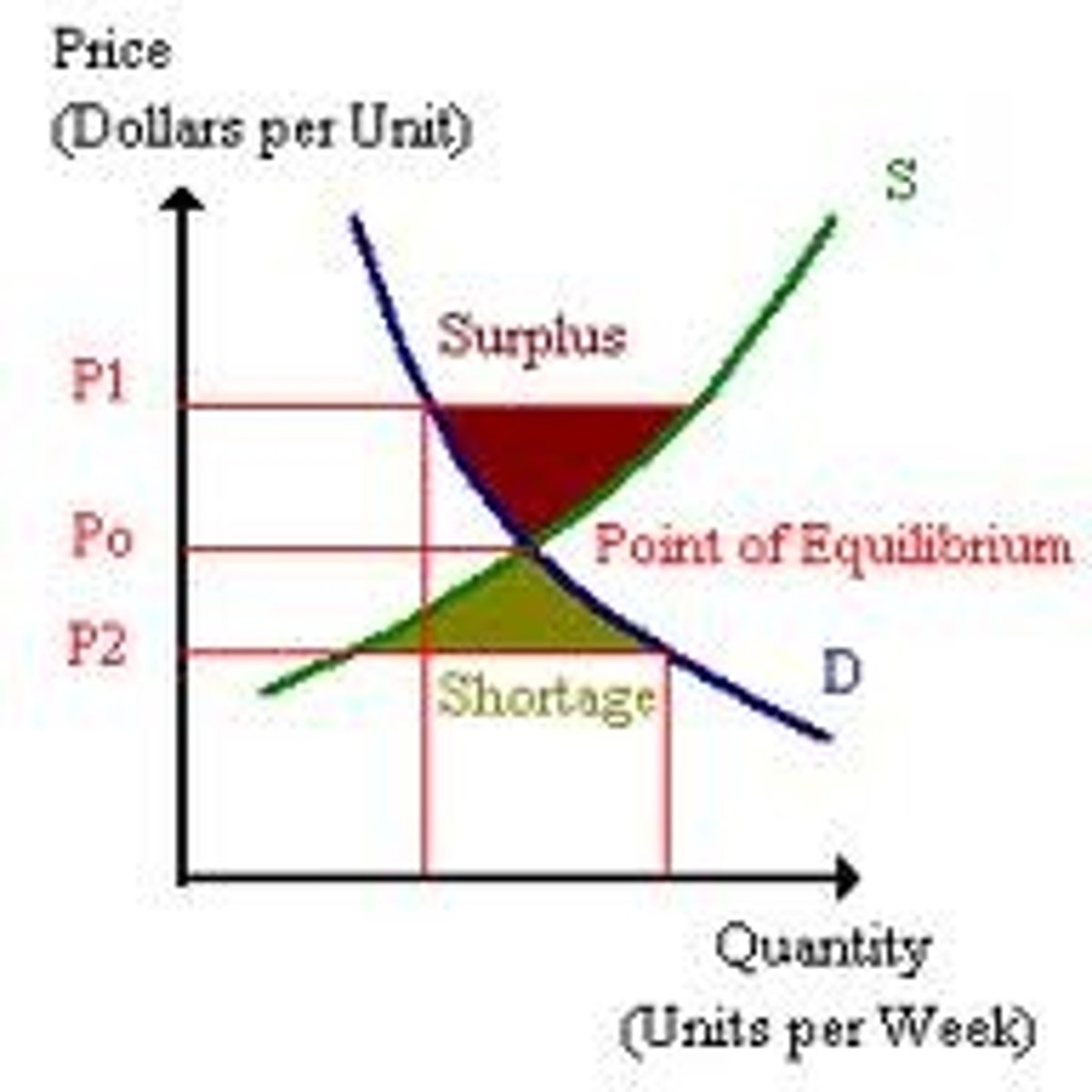
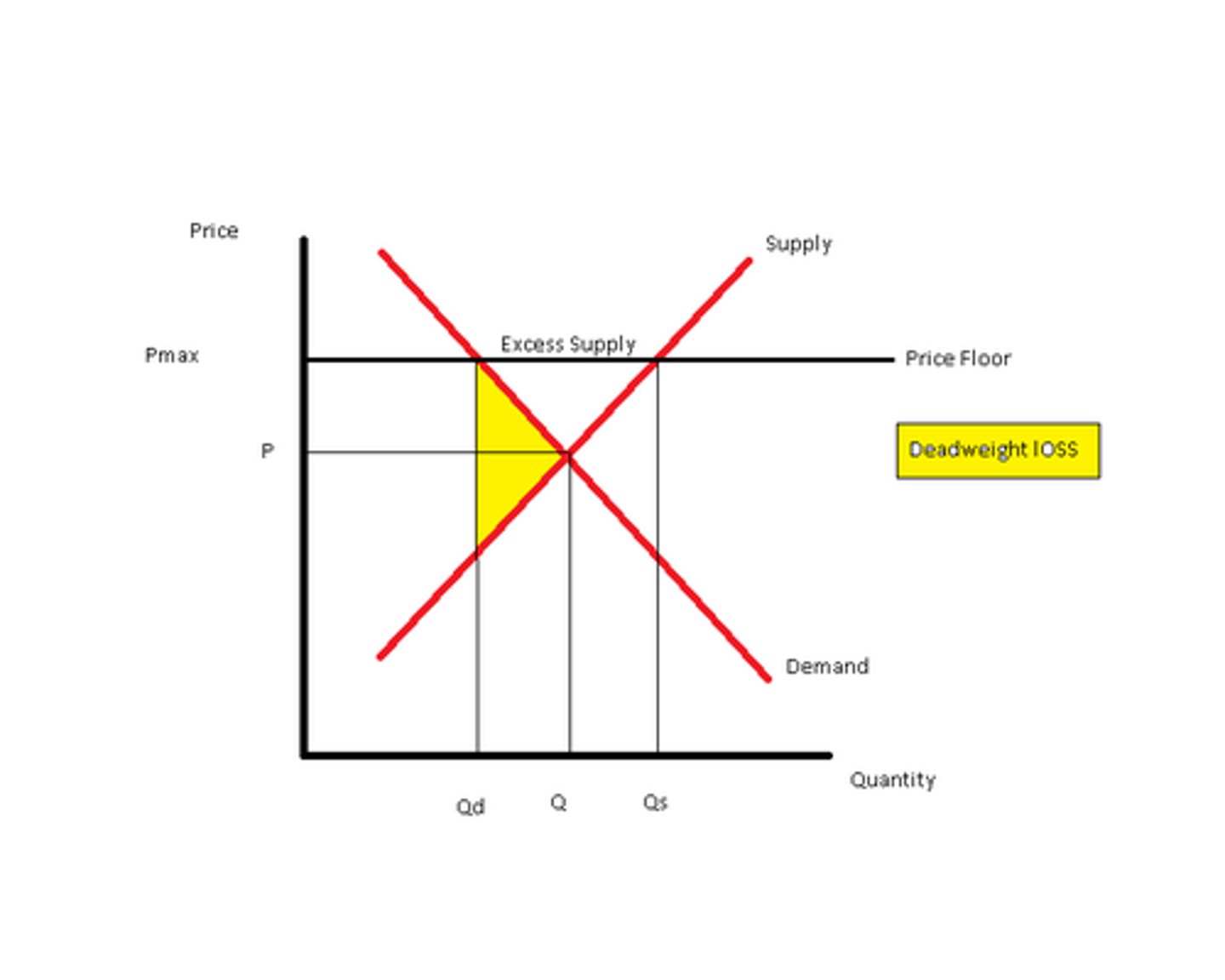
surplus
when quantity demanded is less than quantity supplied
Substitution effect
as the price of a good decreases, a consumer buys more of this good relative to other, more expensive goods (as apples rise, buy oranges (ceteris paribus))
Substitute Goods
goods are substitutes if CPED X increases and Y increases (positive sign on ratio)
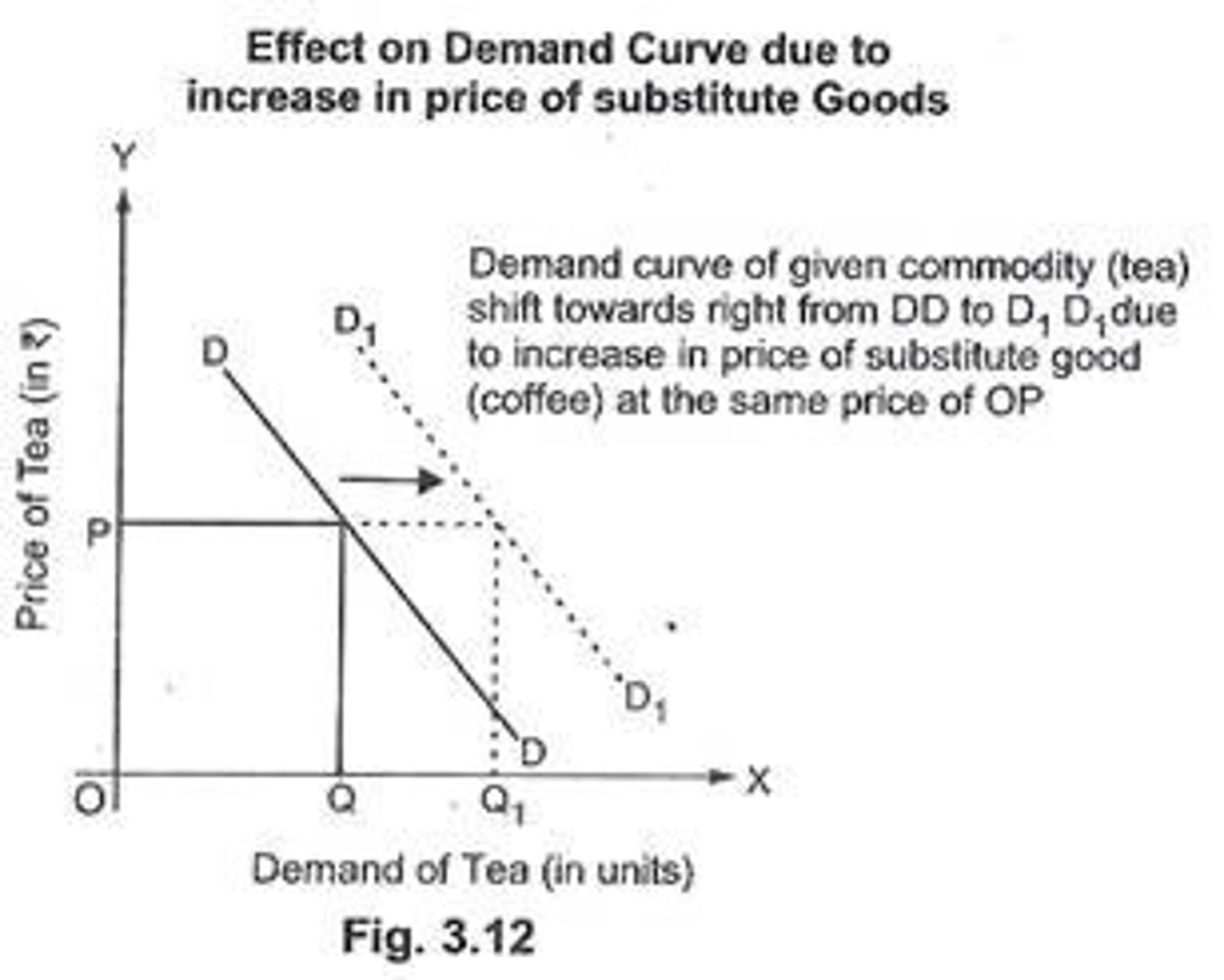
Compliment Goods
goods are compliments if CPED X increases and Y decreases (negative sign on ratio)

Shifters of the PPC
Production Method, Technology, and New Resources
Shortage
Qd > Qs
Surplus
Qd < Qs
Equilibrium
Qd = Qs
Price Floor
Go over equilibrium and result in Surplus
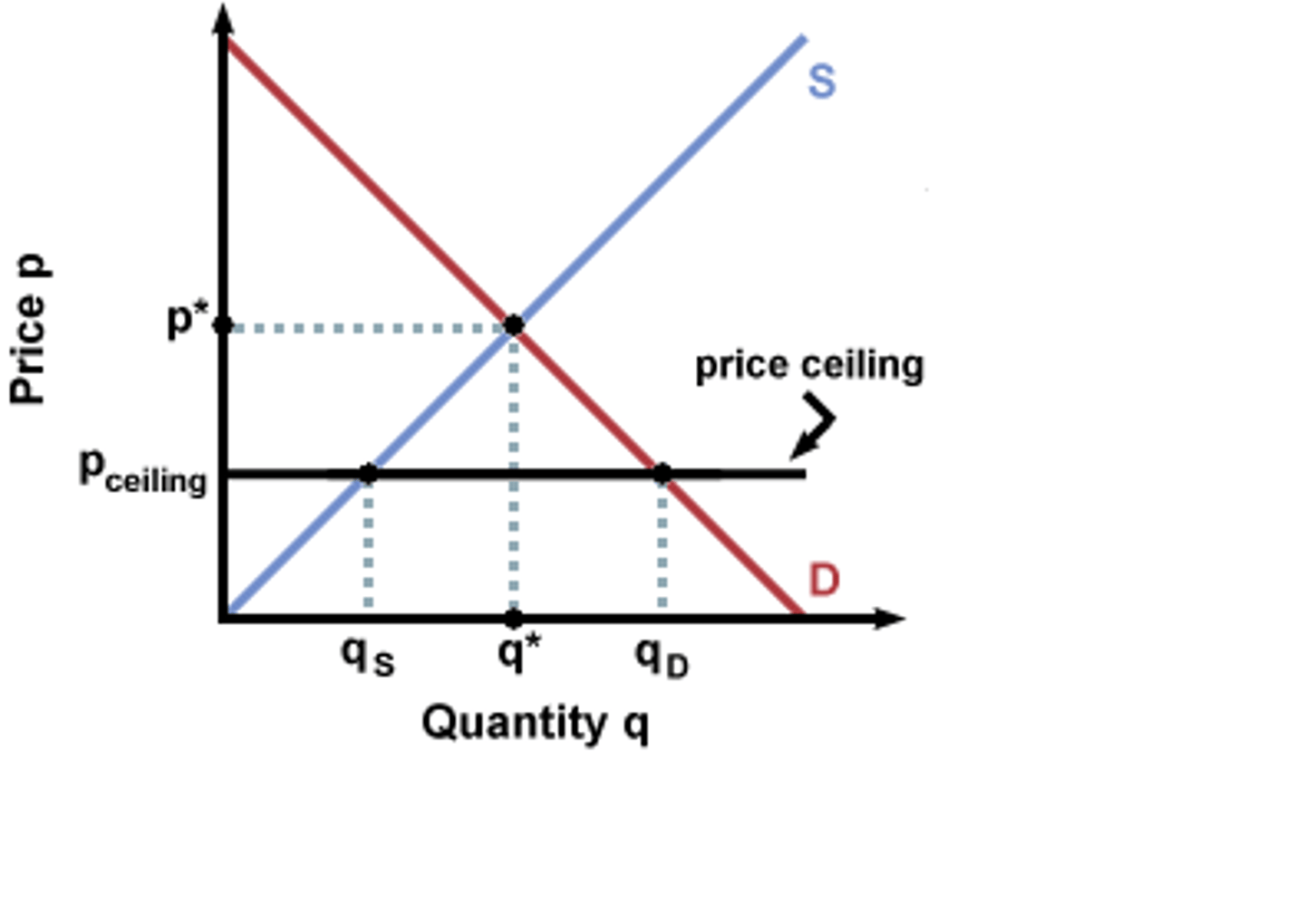
price ceiling
Go under equilibrium and result in Shortage
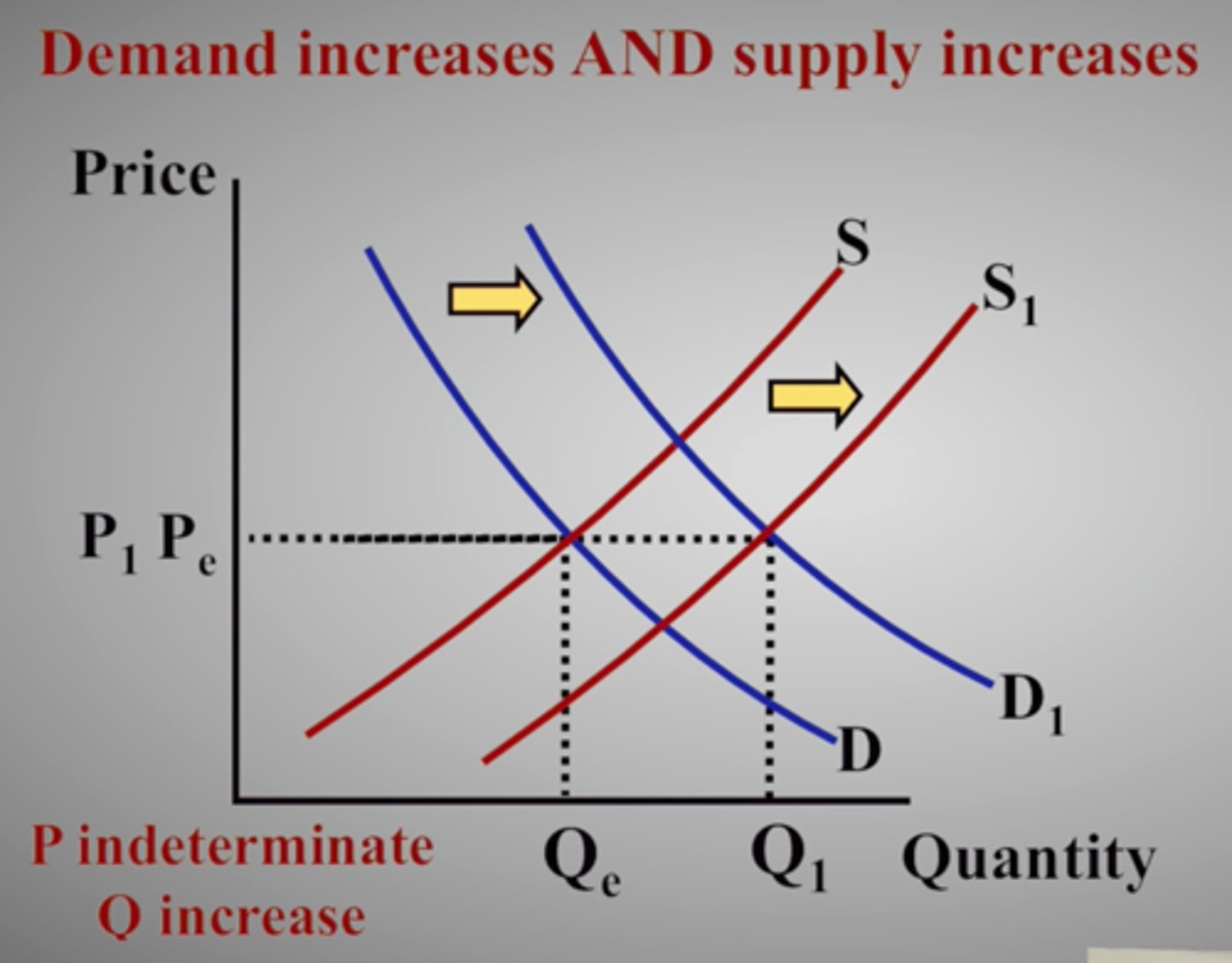
Increase/Decrease of both supply and demand
may result in an indeterminate value
A point outside of the production possibilities frontier is unattainable
True
A person has an absolute advantage in an activity if the person can perform the activity at a lower opportunity cost than every else
False
A person has an comparative advantage in an activity if the person can perform the activity at a lower opportunity cost than every else
True
If the quantity of ice cream demanded at each price increases, there is a movement along the demand curve for ice cream
False
If the quantity of ice cream demanded at each price increases, there is a shift of demand for ice cream
True
When Sue's income increases, her demand for movies increases. For Sue, movies are a normal good.
True
If people's incomes fall and all other influences on buying plans remain the same, the demand for computers will decrease and there will be movement along the demand curve.
False
If people's incomes fall and all other influences on buying plans remain the same, the demand for computers will decrease and there will be a shift of the demand curve.
True
If the price of coffee is expected to rise next month, the supply of coffee this month will decrease
True
The supply of a good will increase and there will be a movement up along the supply curve of a good if the price of one of its substitutes in production falls
False
The supply of a good will increase and there will be a shift of the supply curve of a good if the price of one of its substitutes in production falls
True
If the price of asparagus is below the equilibrium price, there're a shortage of asparagus and the price of asparagus will rise until the shortage disappears
True
When the demand for skateboards decreases and the supply of skateboards remains unchanged, the quantity supplied of skateboards decreases as the price rises
False
When the demand for skateboards decreases and the supply of skateboards remains unchanged, the quantity supplied of skateboards decreases as the price falls
True
Gasoline refiners expect the price of oil will fall next month. If the supply of oil does not change, the equilibrium price of oil today falls and the equilibrium quantity today decreases (ep decrease and eq decrease)
True