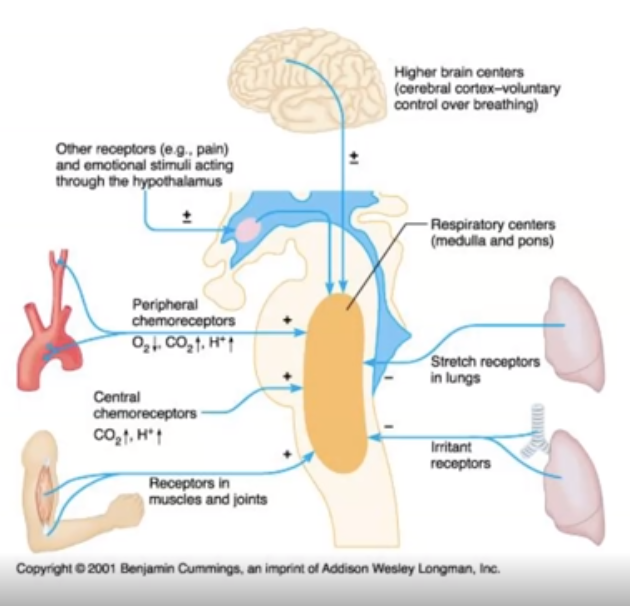
4.2c Chemical Control of ventilation
4.5(2)
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
1
New cards
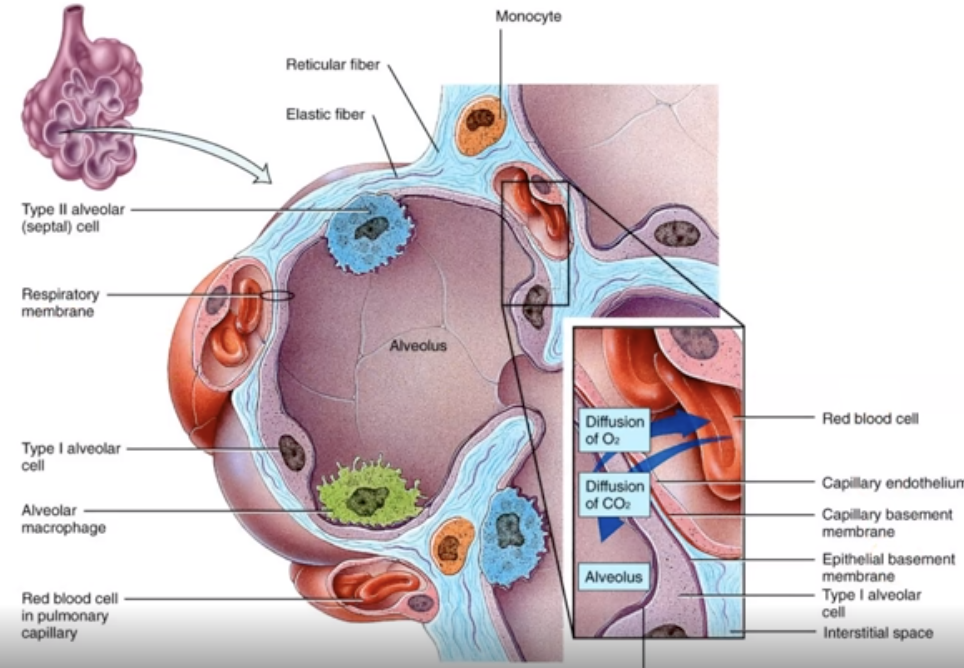
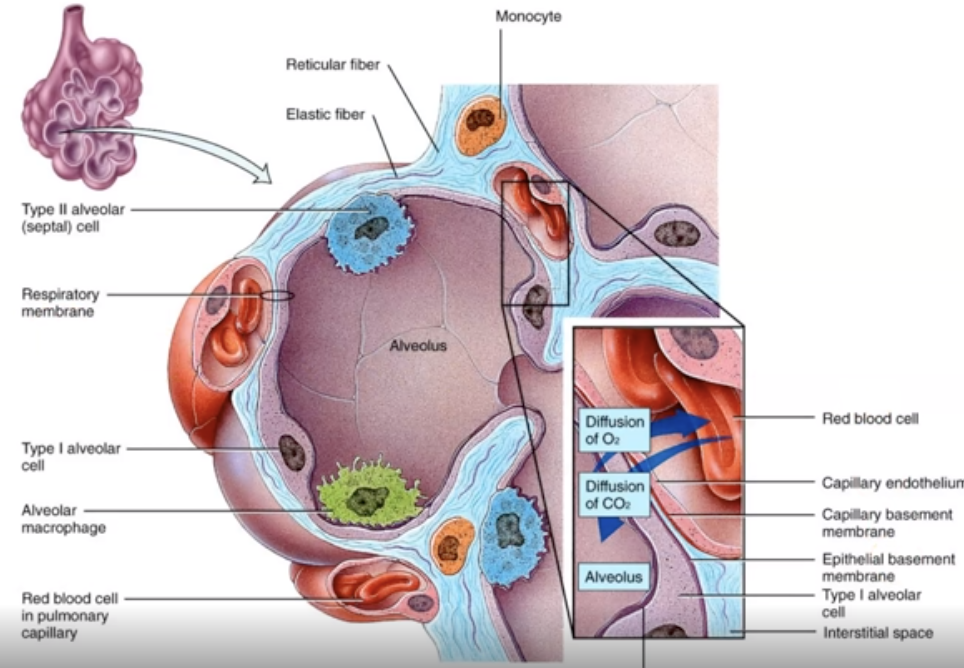
What is diffusion?
Gases move from high to low concentrations.
==REMEMBER: It’s caused by Type 1 alveolar cells==
==REMEMBER: It’s caused by Type 1 alveolar cells==
2
New cards
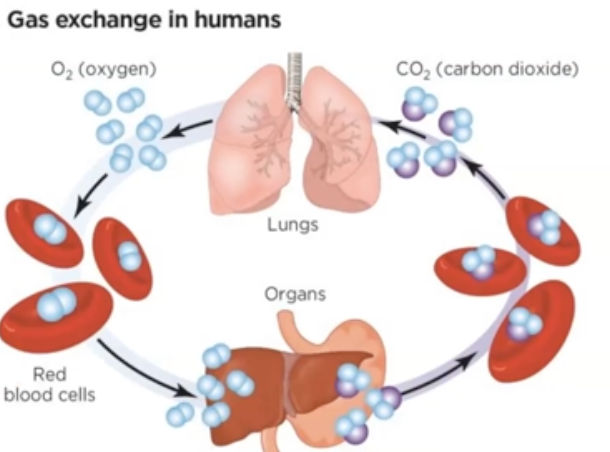
what is gas exchange?
Oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide enters the alveoli
3
New cards
What is macrophages?
A protective layer that surrounds alveoli.
4
New cards
What is surfactant?
a protective INNER layer of alveoli that prevents alveoli from sticking to themselves
5
New cards
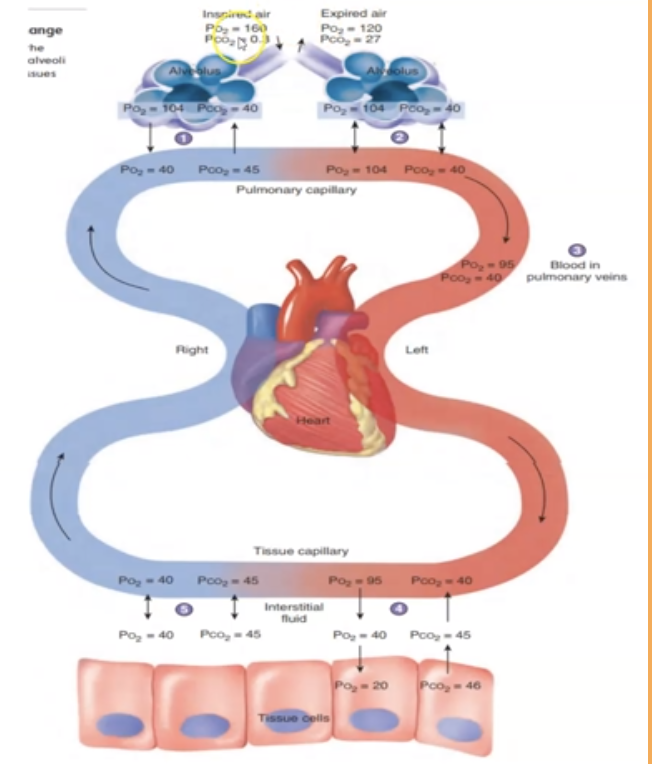
Partial pressure of oxygen ___ at it moves away from alveoli to tissue cells
decreases
6
New cards
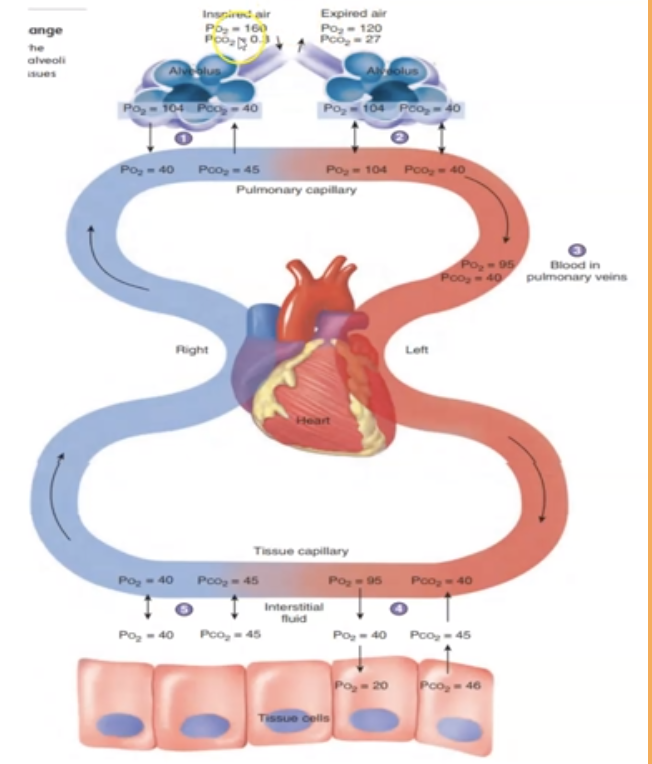
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide ___ as it moves from tissue cells to alveoli
increases
7
New cards
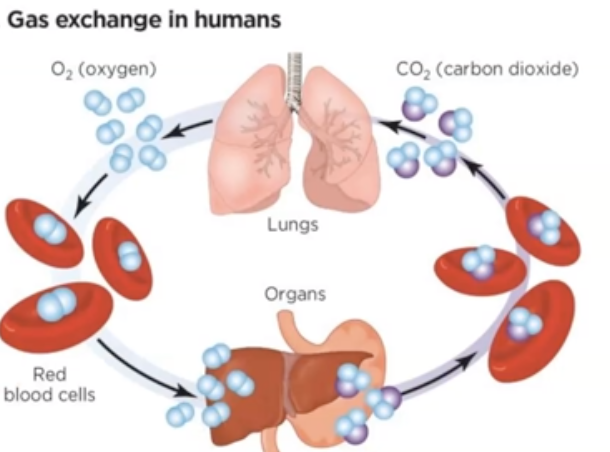
___ is only way Oyxgen can be carried throughout the body
Hemoglobin bonding
8
New cards
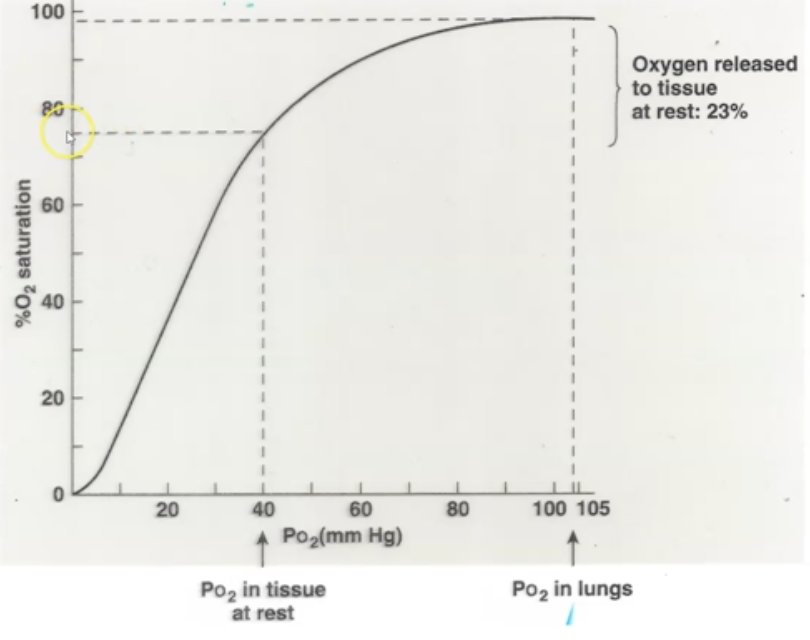
what is % saturation?
number of hemoglobin with an oxygen molecule attached to each heme group
9
New cards
What does 100% O2 saturation mean?
Each hemoglobin is bound to the maximum 4 oxygen molecules
10
New cards
What % saturation indicates that the cell is at rest?
when O2 saturation is at 77 - 75%
11
New cards
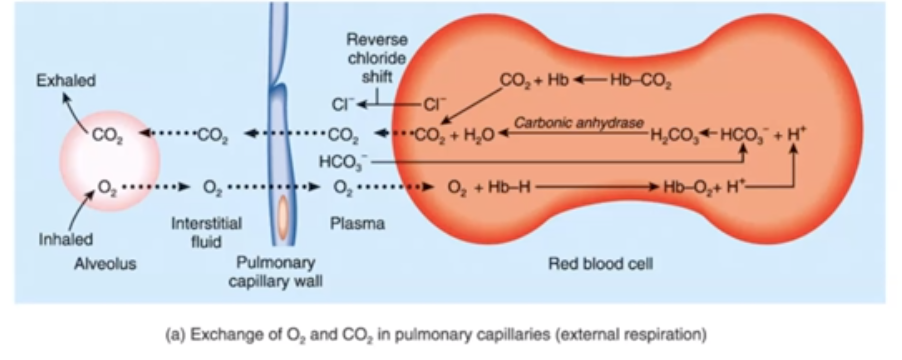
What are the 3 ways CO2 could be transported across the body?
* Dissolved CO2
* Bound to Hemoglobin
* HCO3 (bicarbonate)
* Bound to Hemoglobin
* HCO3 (bicarbonate)
12
New cards
CO2 reacts with water to form ____
Carbonic acid (H2CO3)
13
New cards
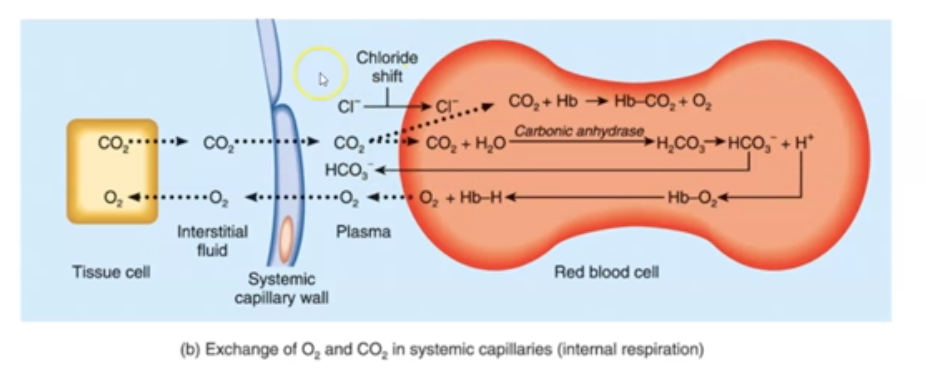
Explain how bicarbonate transport carbon dioxide
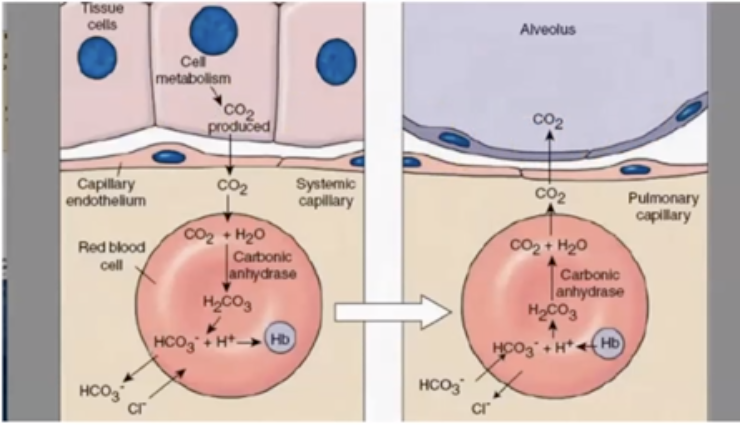
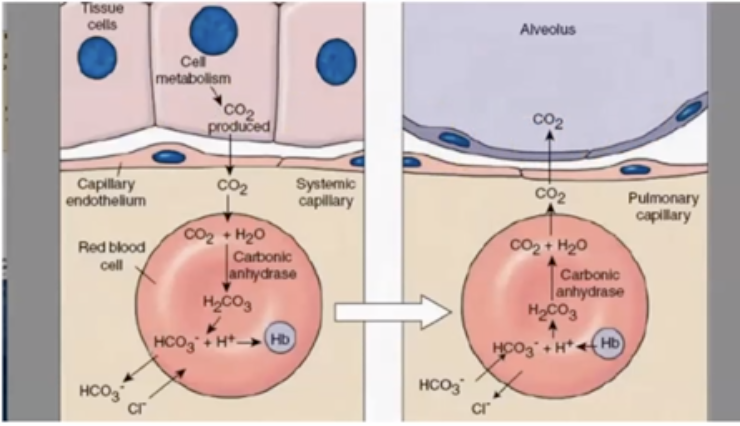
* Carbonic Acid (H2CO3) dissociates into H+ (Hydrogen ions) & HCO3 (bicarbonate ions)
* Electrical neutrality is maintained by moving CI- ion into RBC when HCO3 moves out; “chloride shift.”
* Increases in CO2 decrease the pH of blood (making it more acidic)
* HCO3 converts back to CO2, and you exhale it
* Process reverses when blood reaches alveoli
* Electrical neutrality is maintained by moving CI- ion into RBC when HCO3 moves out; “chloride shift.”
* Increases in CO2 decrease the pH of blood (making it more acidic)
* HCO3 converts back to CO2, and you exhale it
* Process reverses when blood reaches alveoli
14
New cards
What do chemoreceptors in blood vessels measure?
Chemoreceptors measure changes in:
* Blood pH
* PO2
* PCO2
* Blood pH
* PO2
* PCO2