Organic Chemistry (Regents)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
addition
adding one or more atoms to an unsaturated hydrocarbon
clues: alkene or alkyne on reactant side, only one product
carbon can make ____________ bonds
4 covalent bonds
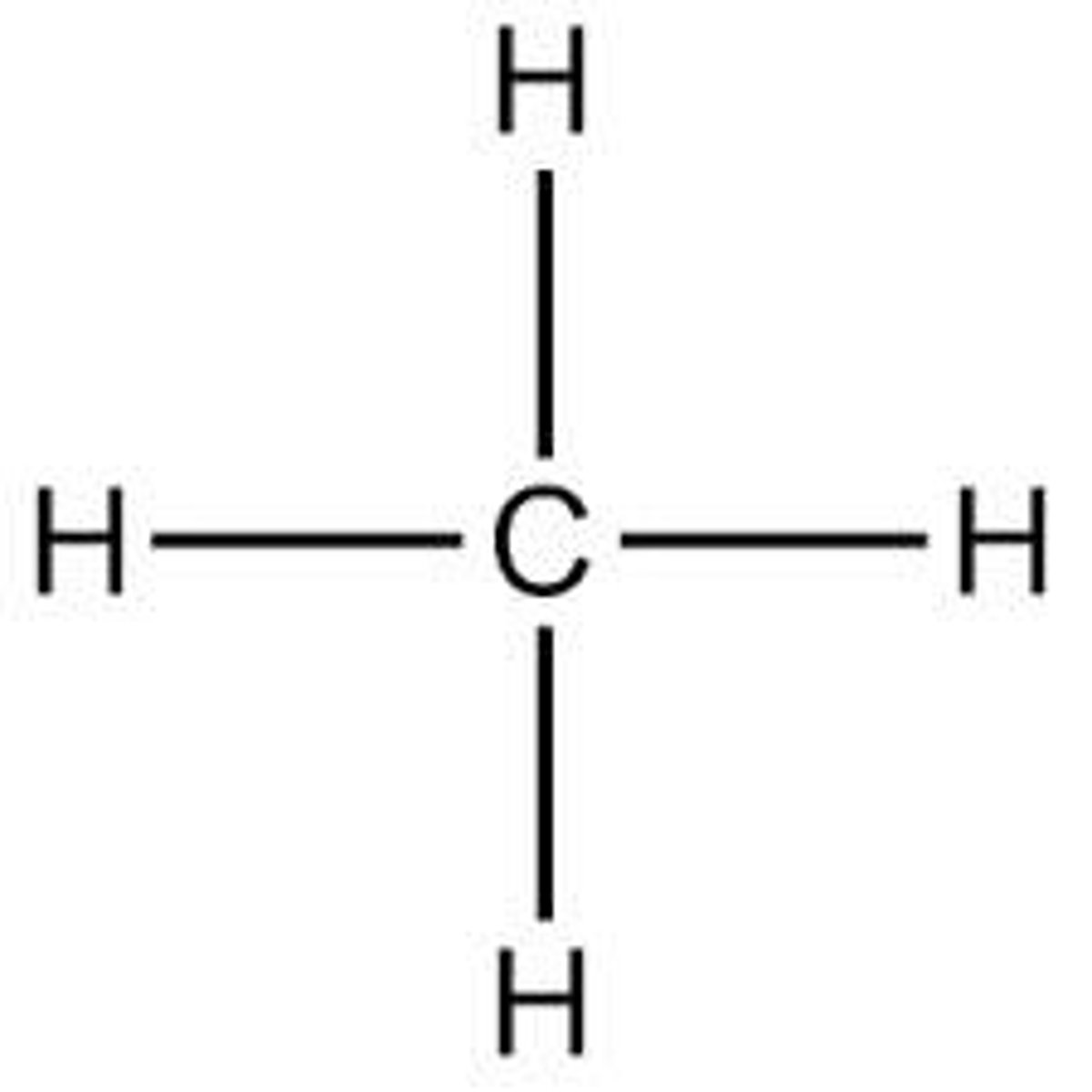
molecular formula
true formula: tells exactly how many of each type of atom there is present in a chemical, however does not tell the structure
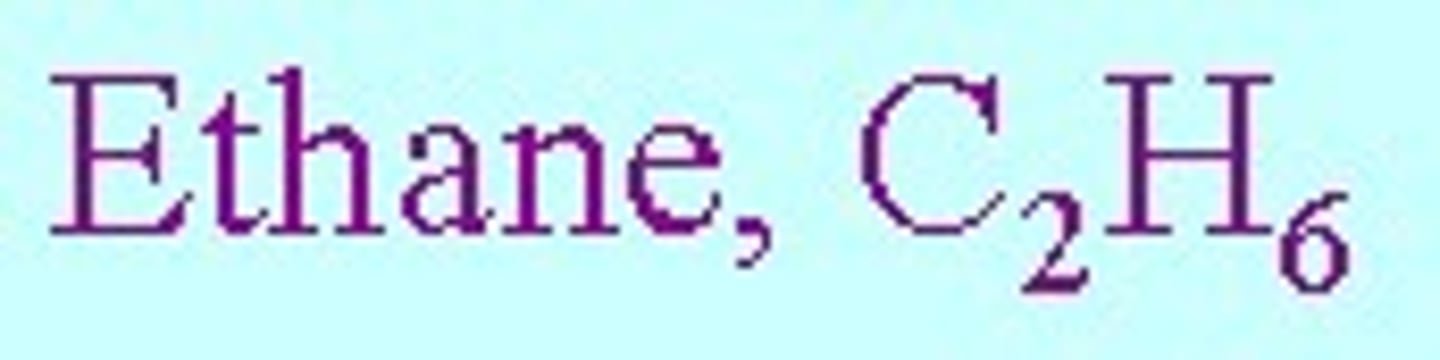
structural formula
shows arrangement of atoms
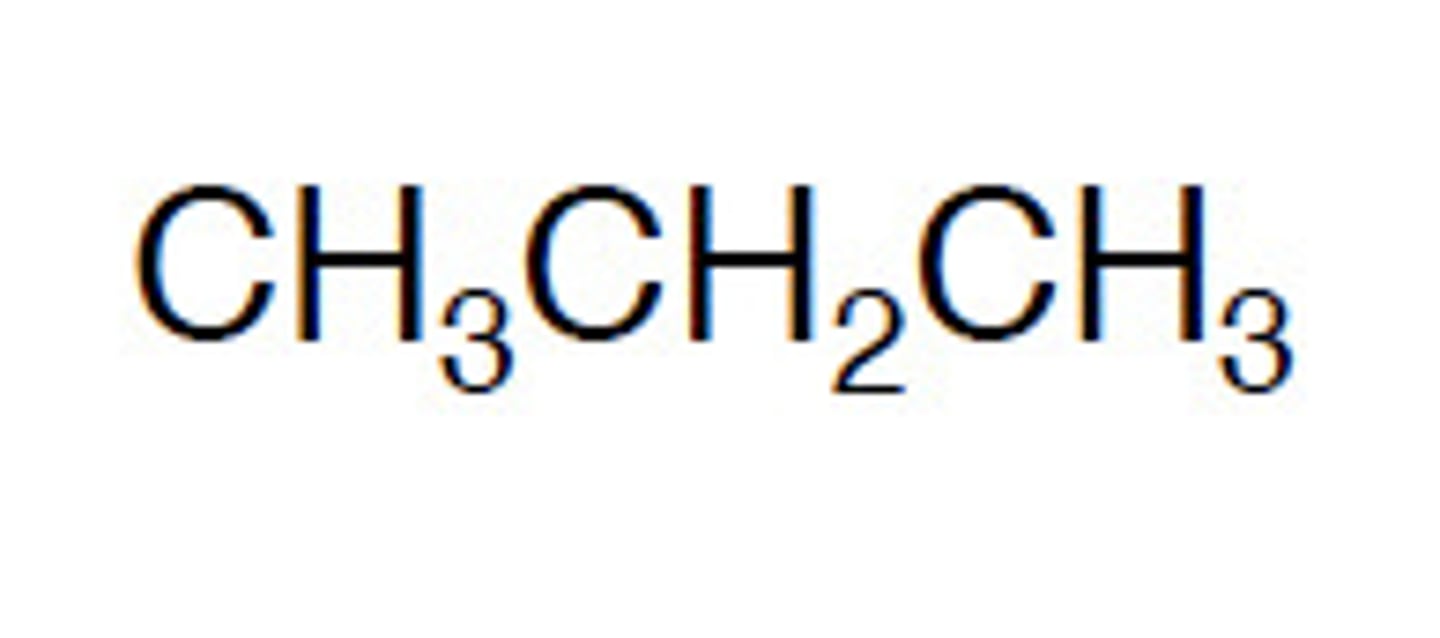
organic chemistry
study of compounds containing carbon
- carbon can make 4 covalent bonds, so long chains or rings can be formed
uses of organic compounds
fuel, medicines, construction, material, nutrients
properties of organic compounds (similar to covalent molecules)
- low melting point and boiling point
- usually react more slowly than ionic compounds
- weak intermolecular forces
- usually nonpolar
the longer the carbon chain, intermolecular forces are stronger and boiling points are higher
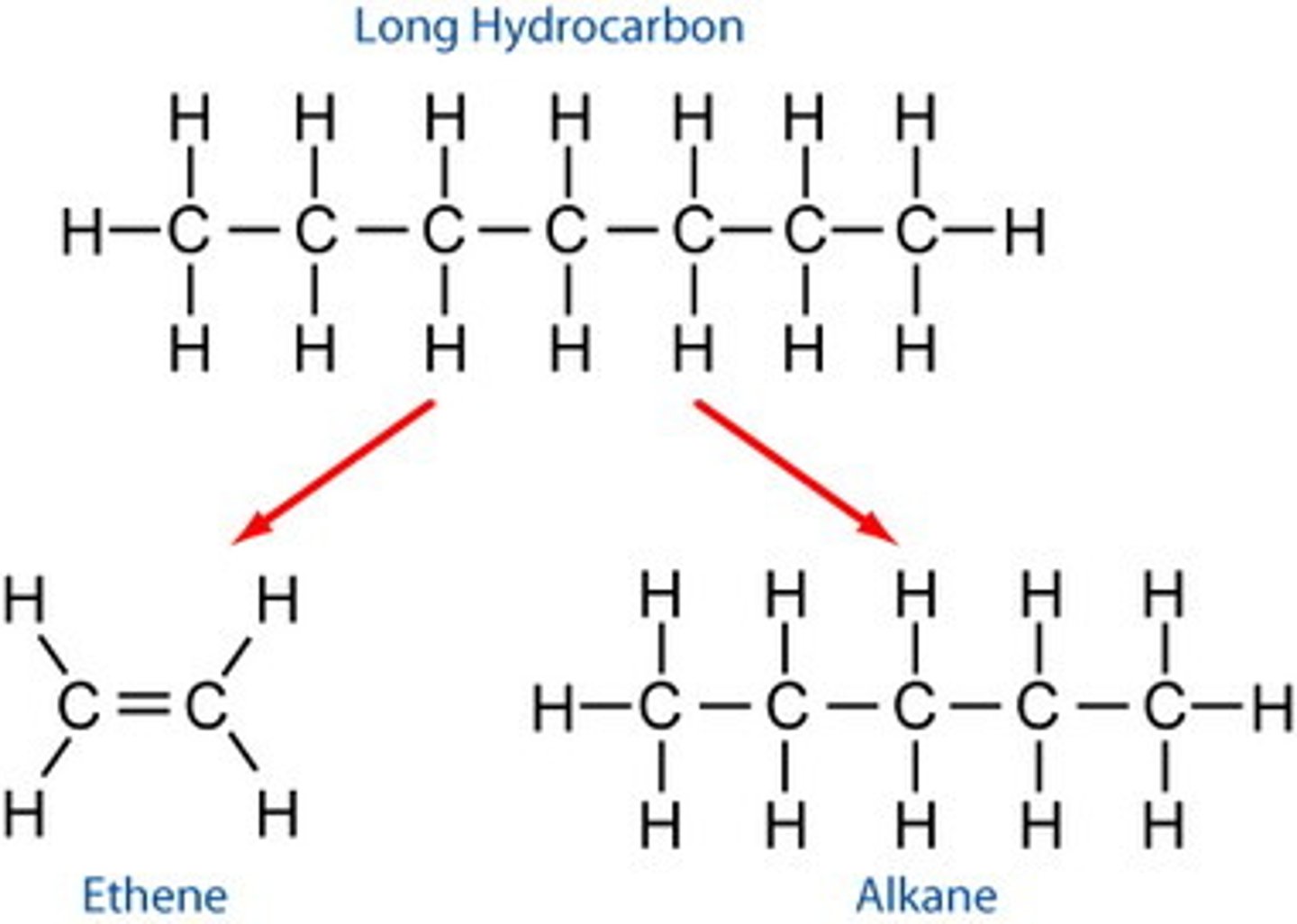
hydrocarbons
contain just carbon and hydrogen (usually used as fuels).
there are thousands of different hydrocarbons known, they are placed in groups of similar structure and properties called homologous series (alkanes, alkenes, alkynes)
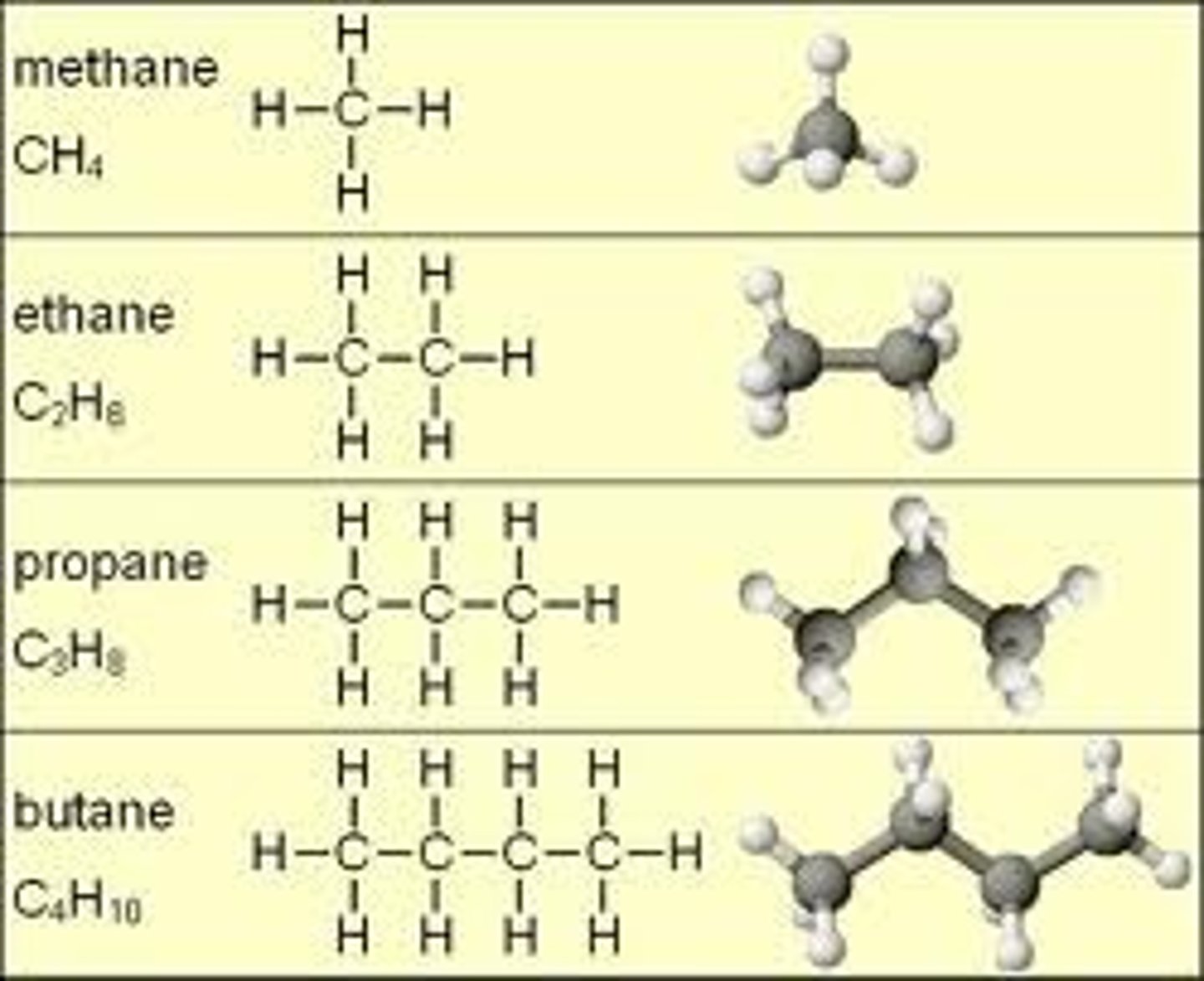
alkanes
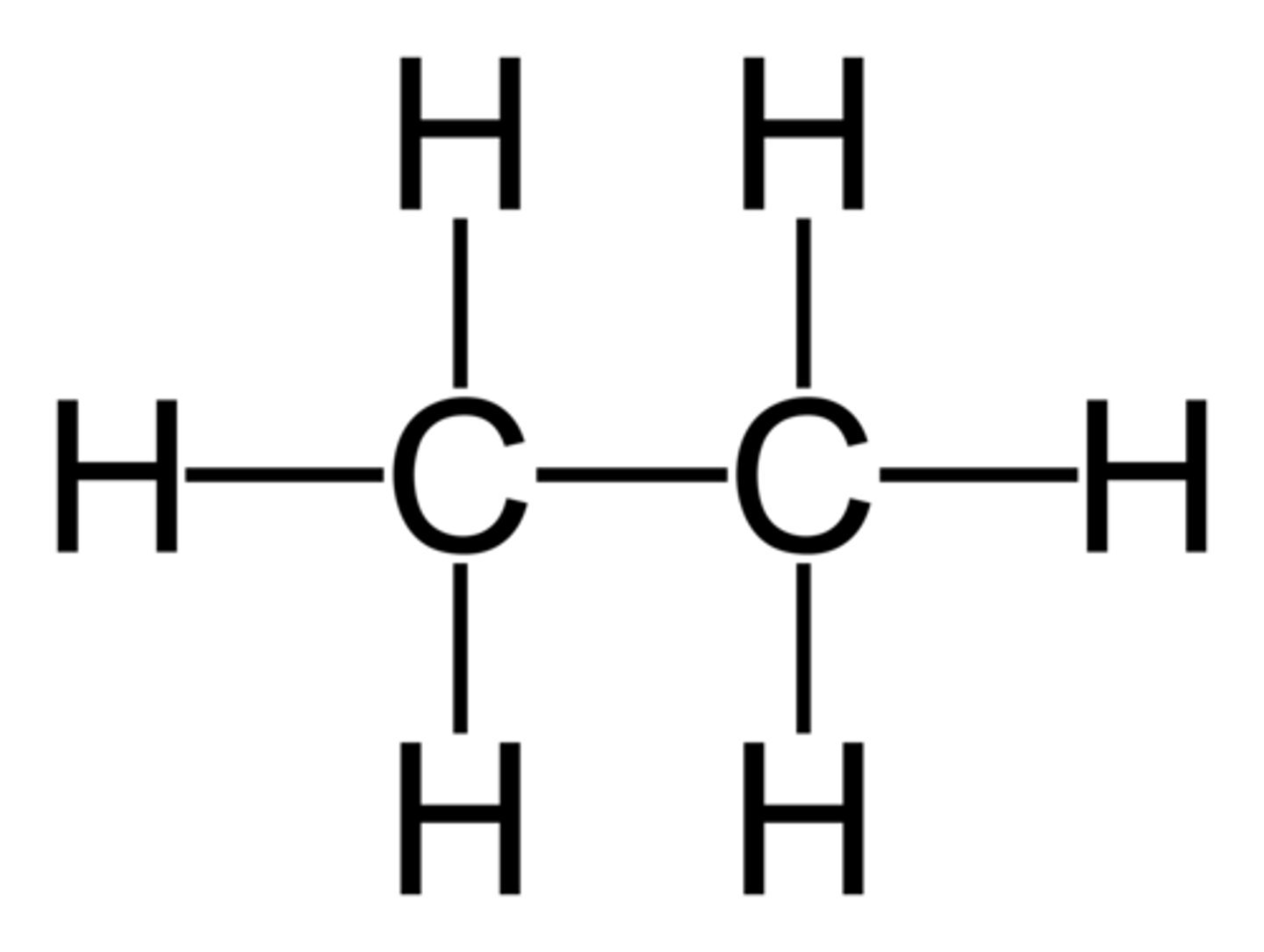
contain only single bonds, between carbons. due to the single bonds, they contain the maximum amount of hydrogen atoms per carbon atom and are called saturated hydrocarbons
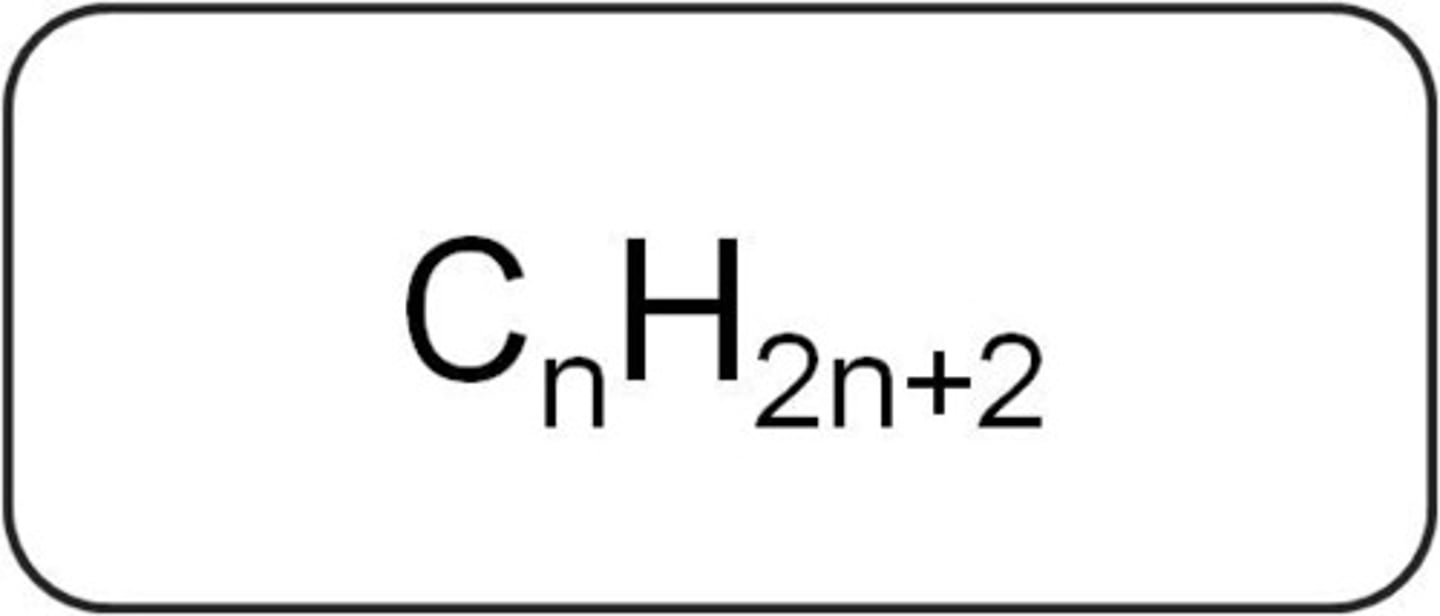
general formula of alkanes
where n = number of carbons, on Table Q
rules for naming simple alkanes/alkenes/alkynes (up to 3 carbons)
1. count the # of carbons, and choose appropriate prefix from Table P
2. end name with -ane/-ene/-yne depending on bond types
3. For alkenes and alkynes the number tells you which Carbon the double or triple bond is located
alkenes
contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. due to the fact that it cannot contain the maximum # of hydrogen per carbon they are considered unsaturated hydrocarbons
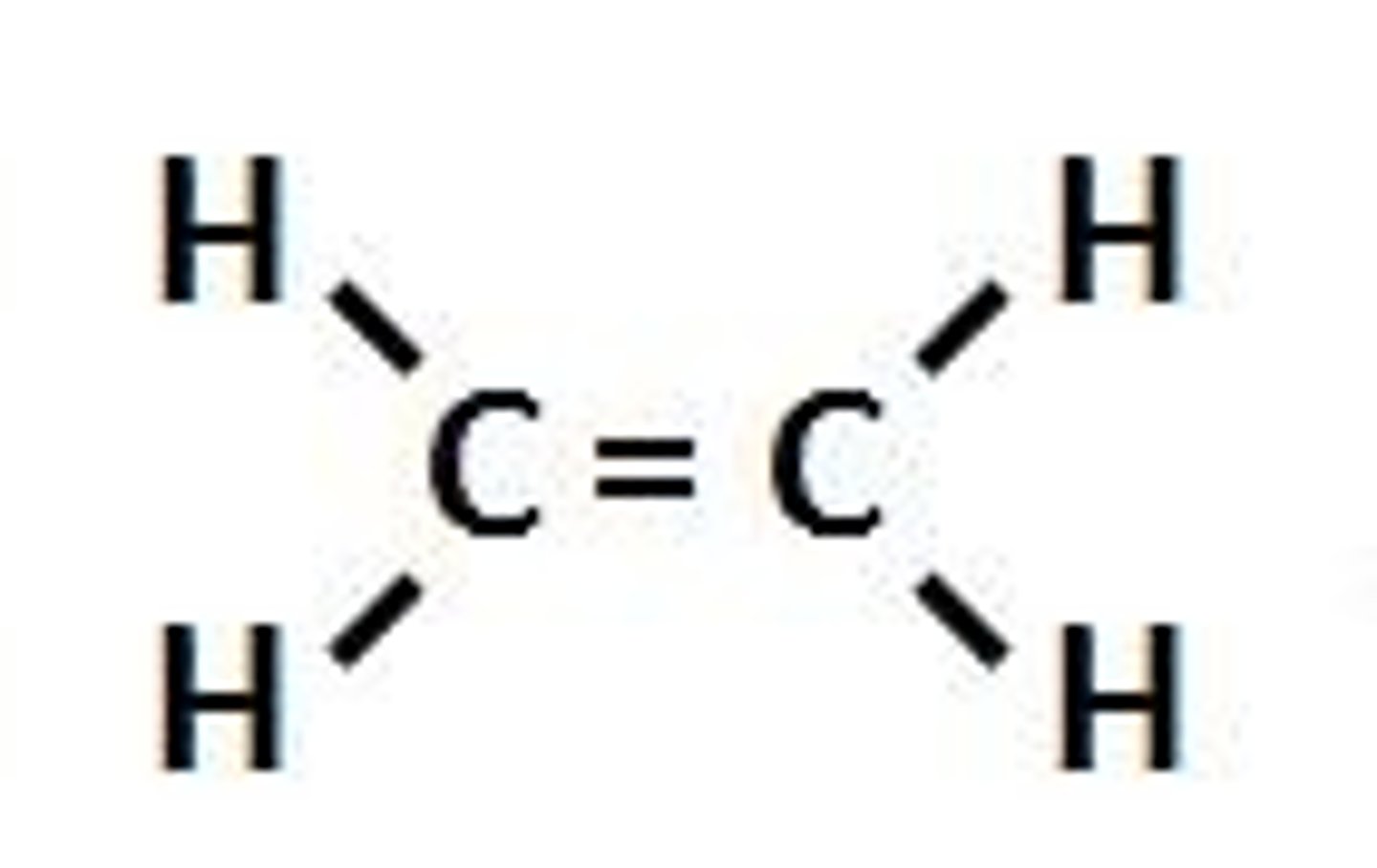
general formula of alkenes
n = # of carbons
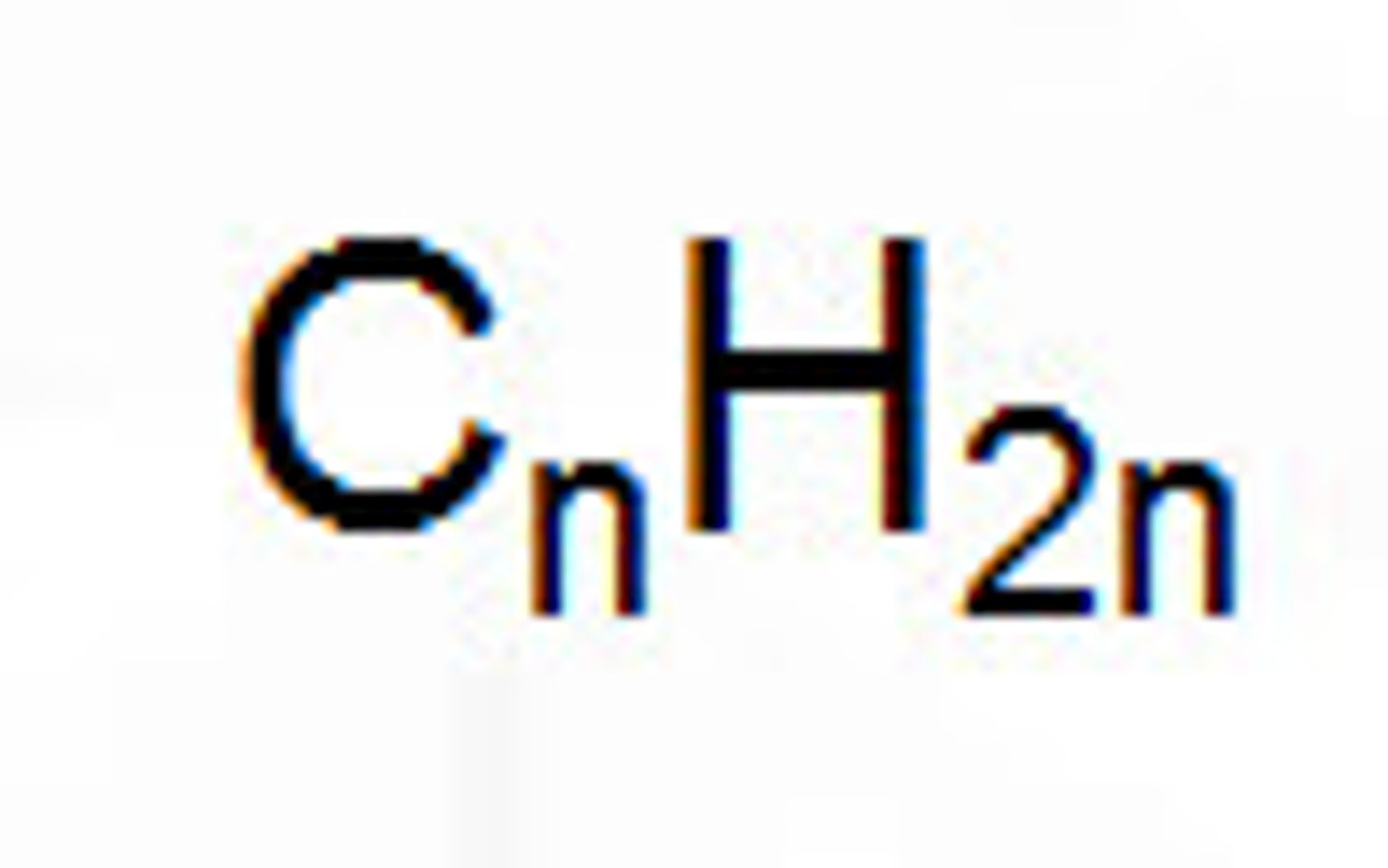
alkynes
contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. also considered unsaturated hydrocarbons
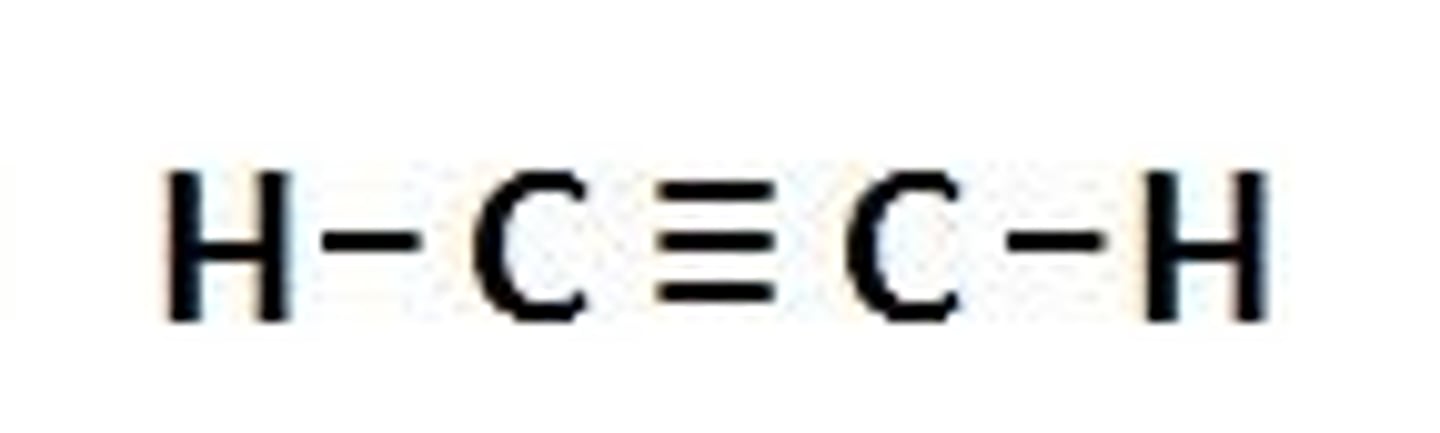
molecular formula of alkynes
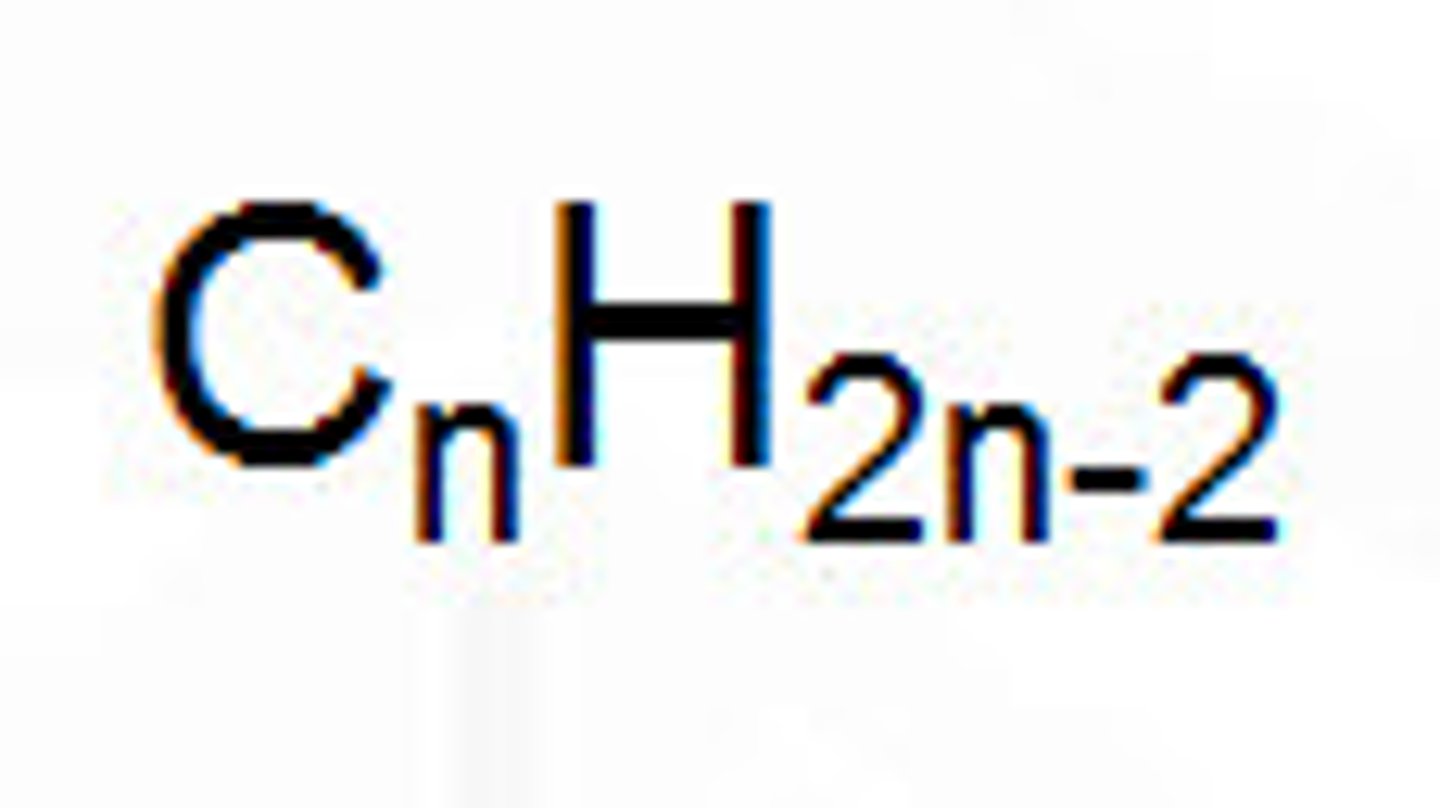
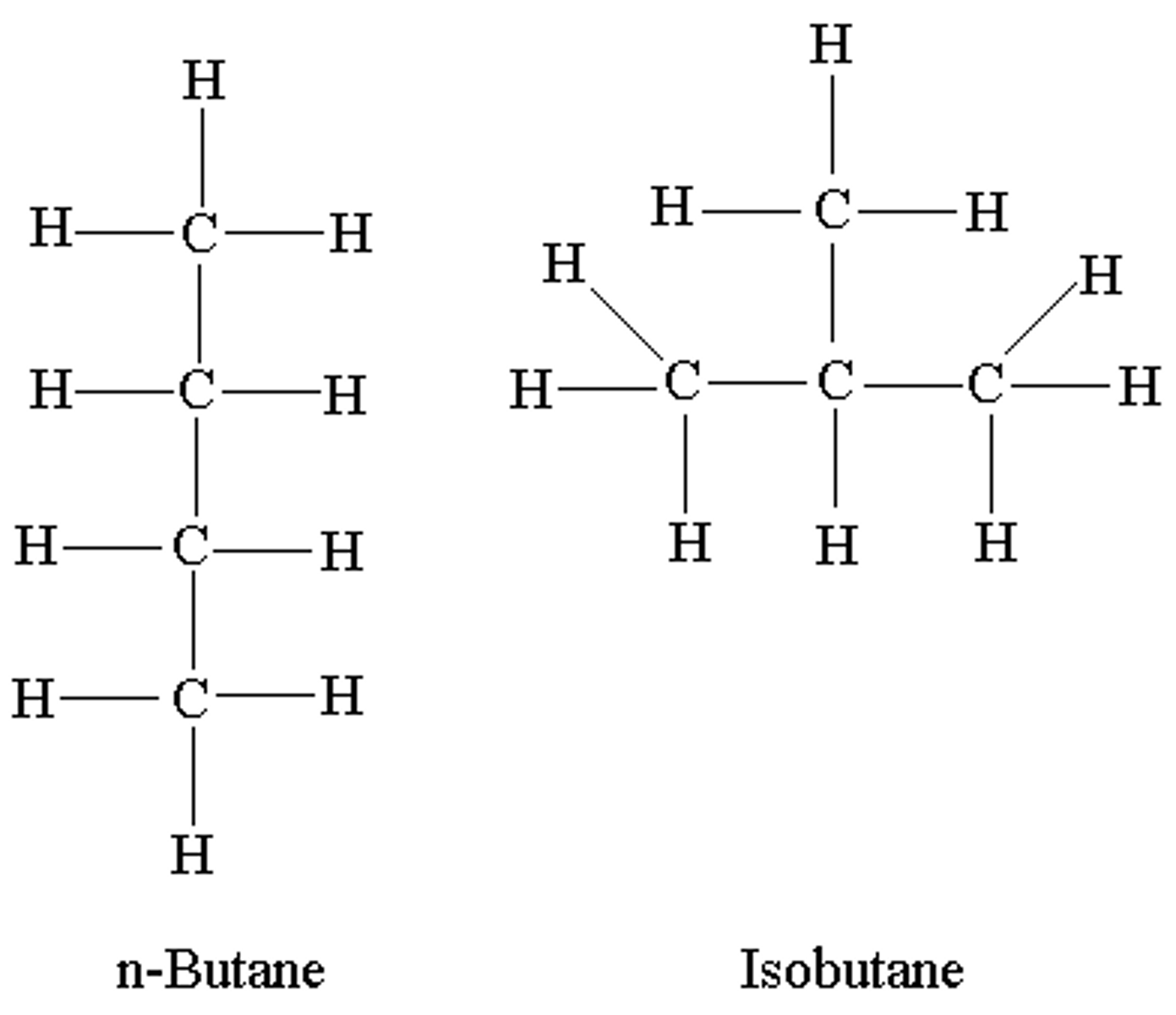
isomers
compounds that have the same molecular formula, but different structural formula.
- begin with a 4+ carbon chain
- more carbons = more possible isomers
- each one has a different chemical/physical properties
"branch"
any carbons that are not part of the longest continuous chain of carbons is called a branch
rules for naming branches compounds
1. find largest continuous chain of carbons. this is called the "parent chain" and is the last name of the compound
2. any carbons not part of parent chain are a branch. they are named by number of carbons and end in -yl
3. if necessary, the location of a branch (address) is given the lowest number possible
4. if more than one of the same type of branch is attached, a prefix is used to tell how many (di = 2, tri = 3, tetra = 4)
functional groups
atoms that replace one or more H's in a hydrocarbon that gives the compounds distinctive chemical and physical properties
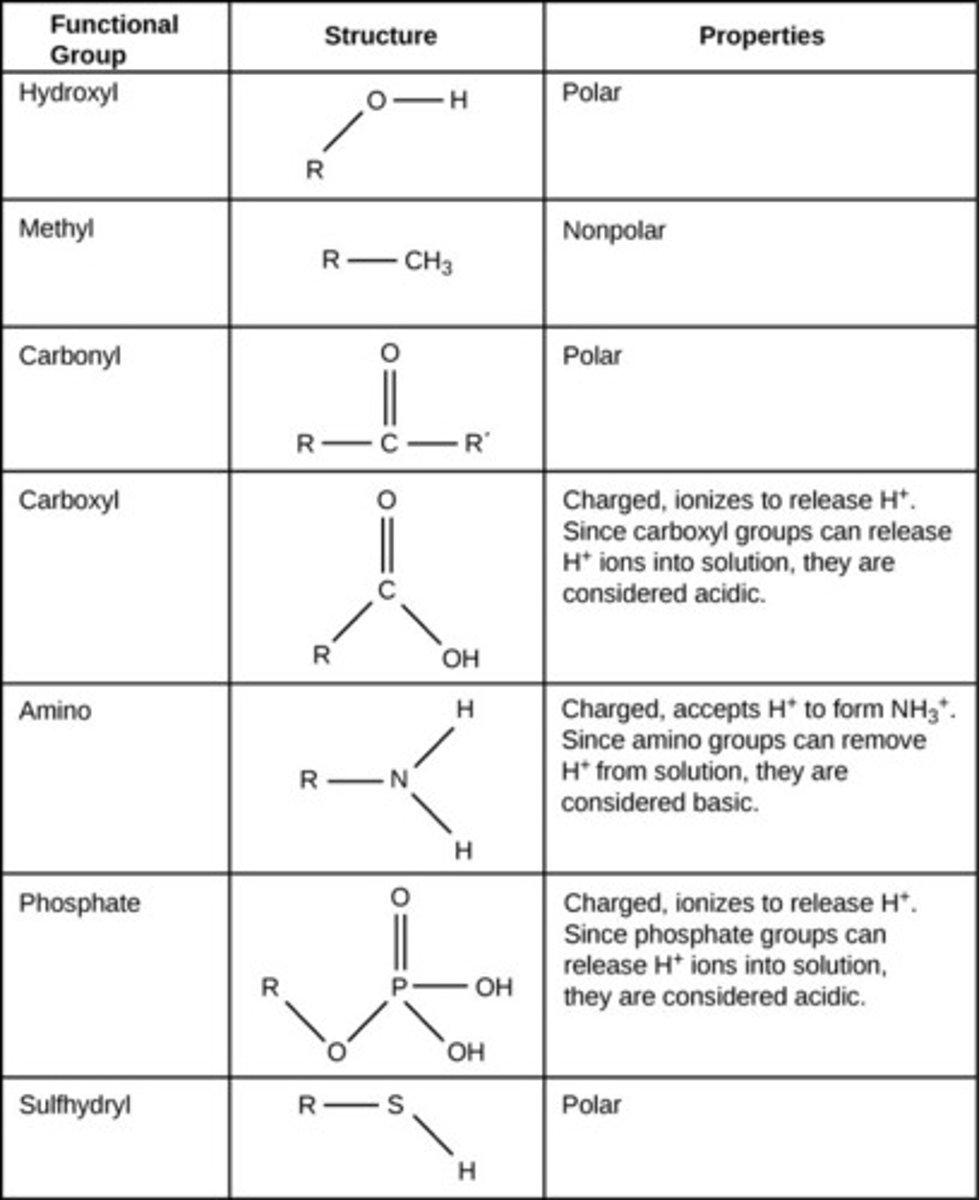
different classes of organic compounds have different
functional groups
Table R Regents Chemistry Reference Table
has a list of functional groups, and the class of compounds they belong to
compounds with functional groups could have
isomers with very few carbons (dont need 4 carbons to have an isomer like hydrocarbons)
halide (halocarbon)
have one or more halogen atoms attached to a hydrocarbon
to name: use tables P, Q, and R together. prefixes (fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, iodo-) then parent chain, might need address
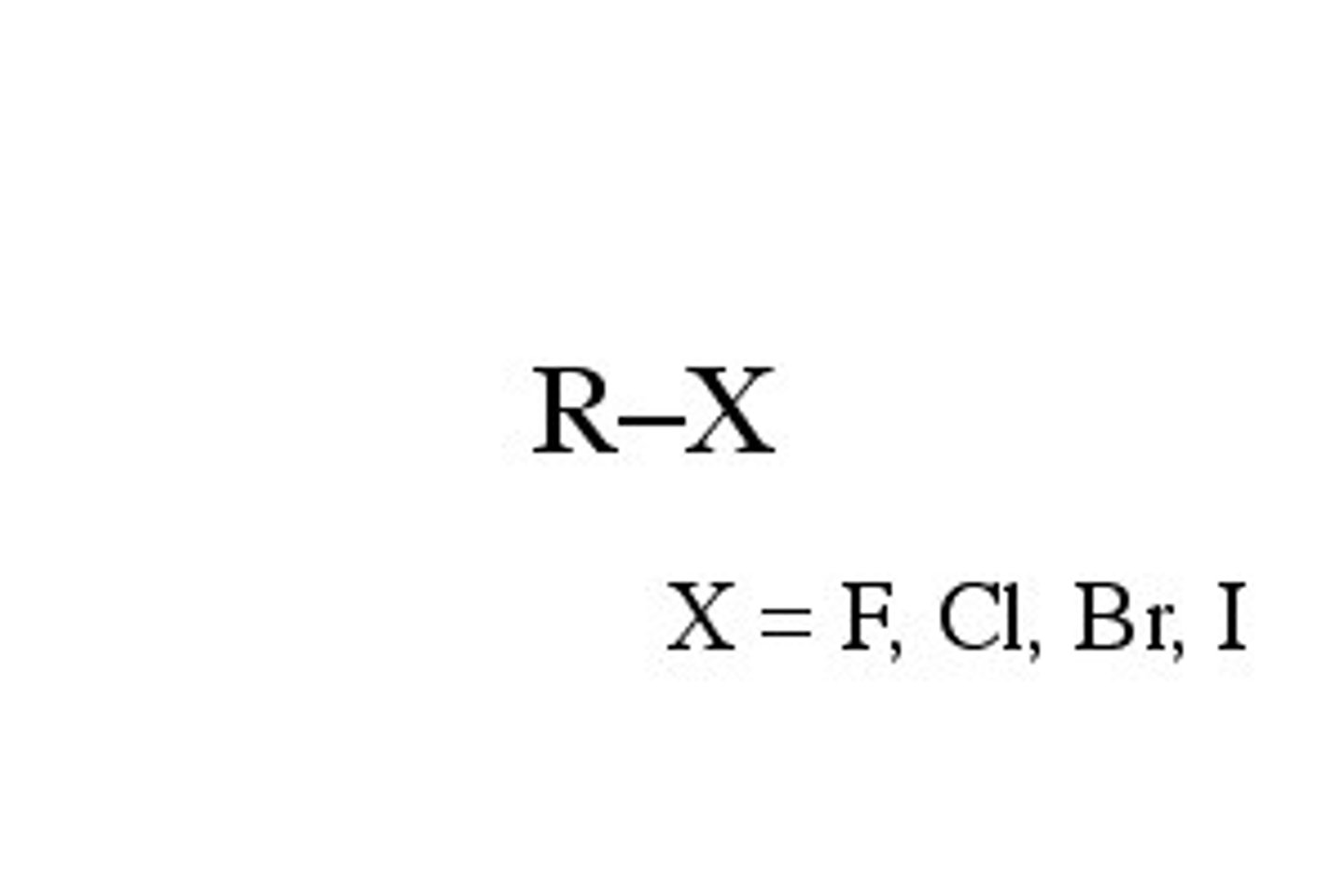
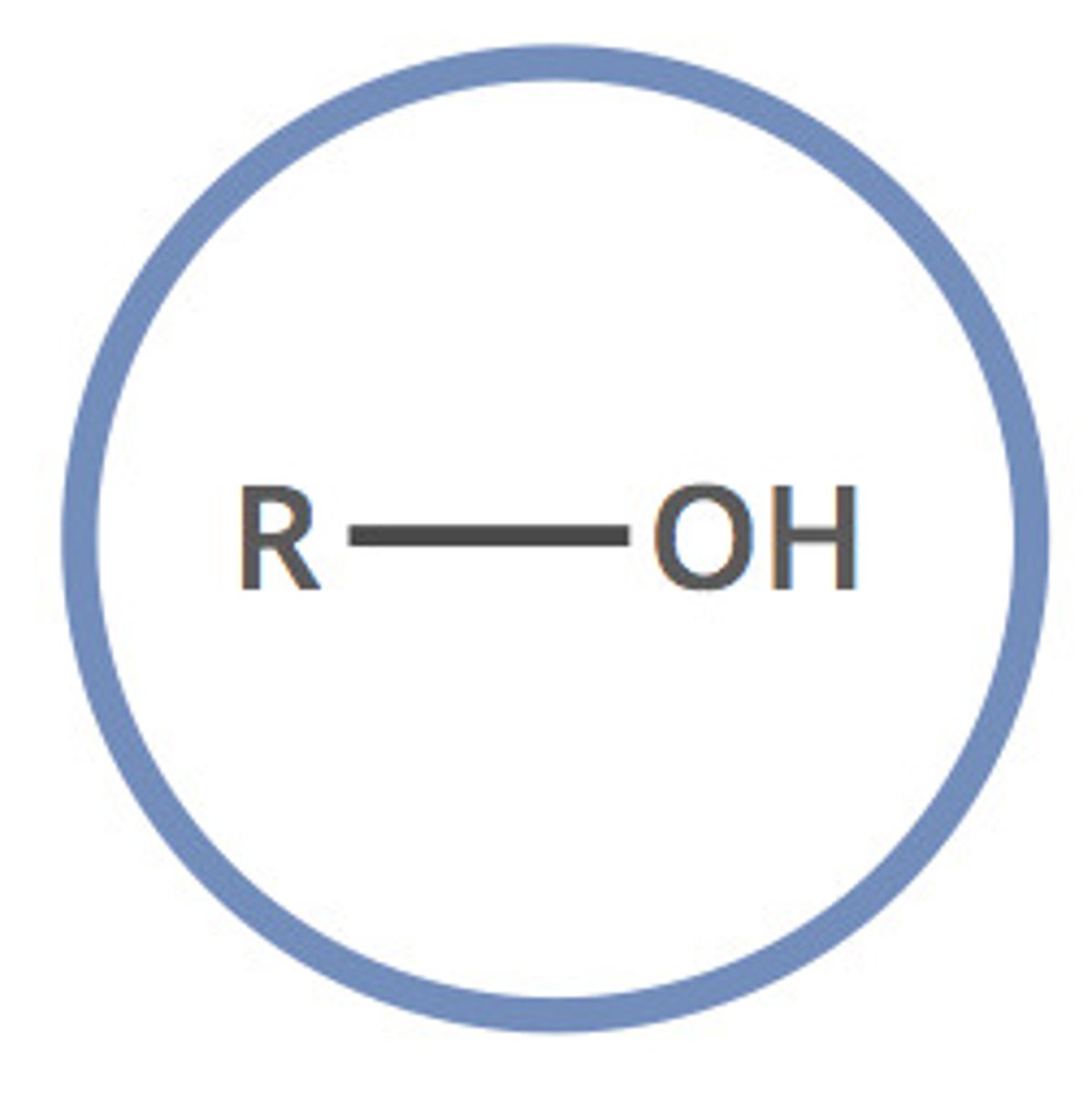
alcohols
when a hydroxyl group (-OH) is attached to a carbon chain.
to name: drop -e at end of parent chain and add (-ol), might need an address
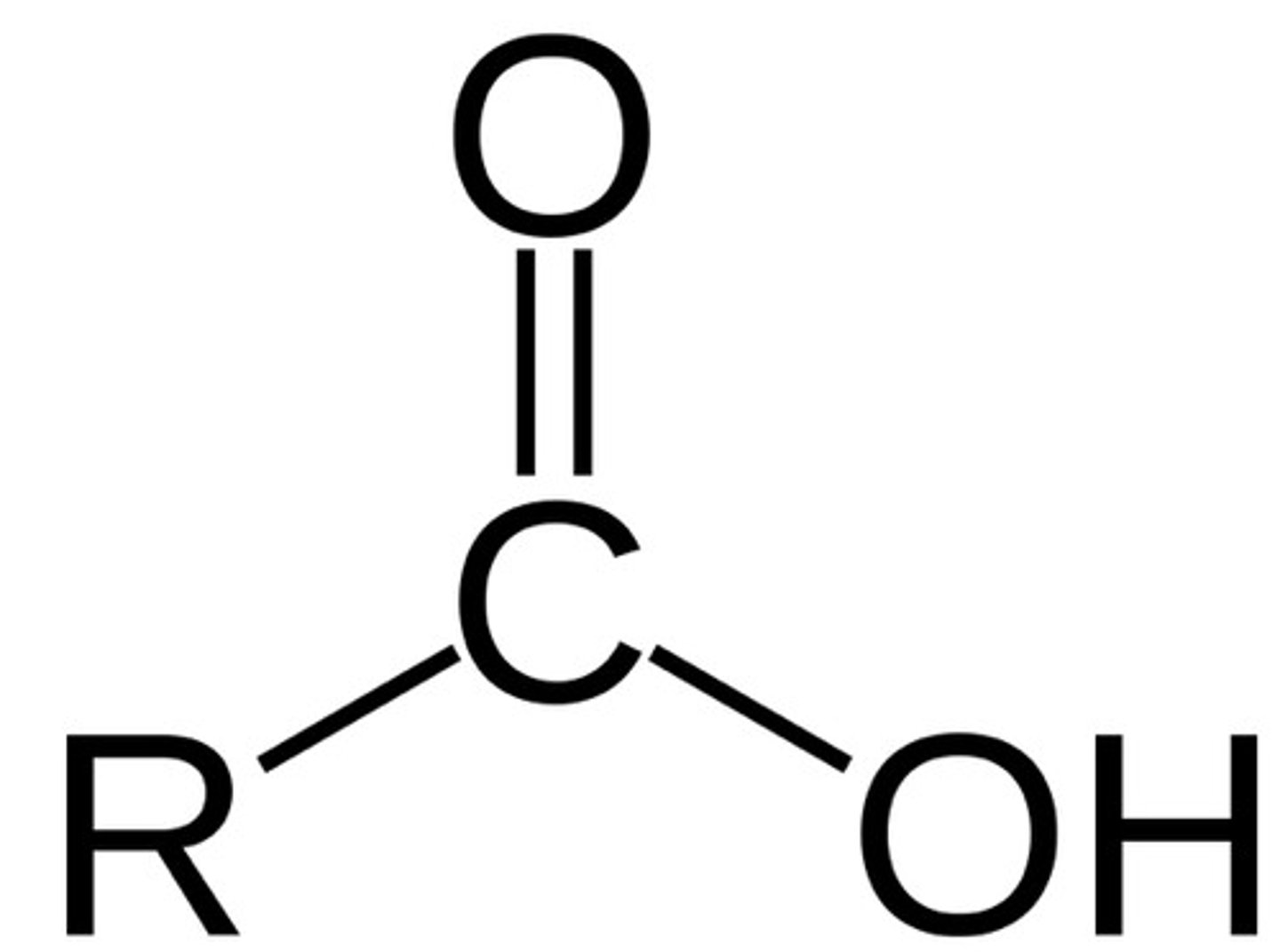
organic acids
functional group is a carboxyl group (-COOH)
to name: drop -e and add -oic acid to parent name, no address necessary bc -cooh always attached to carbon #1
aldehydes
have a carbonyl group (C=O) attached to end of molecule (-CHO)
to name: drop -e and add -al to parent chain, no address necessary bc attached to carbon #1
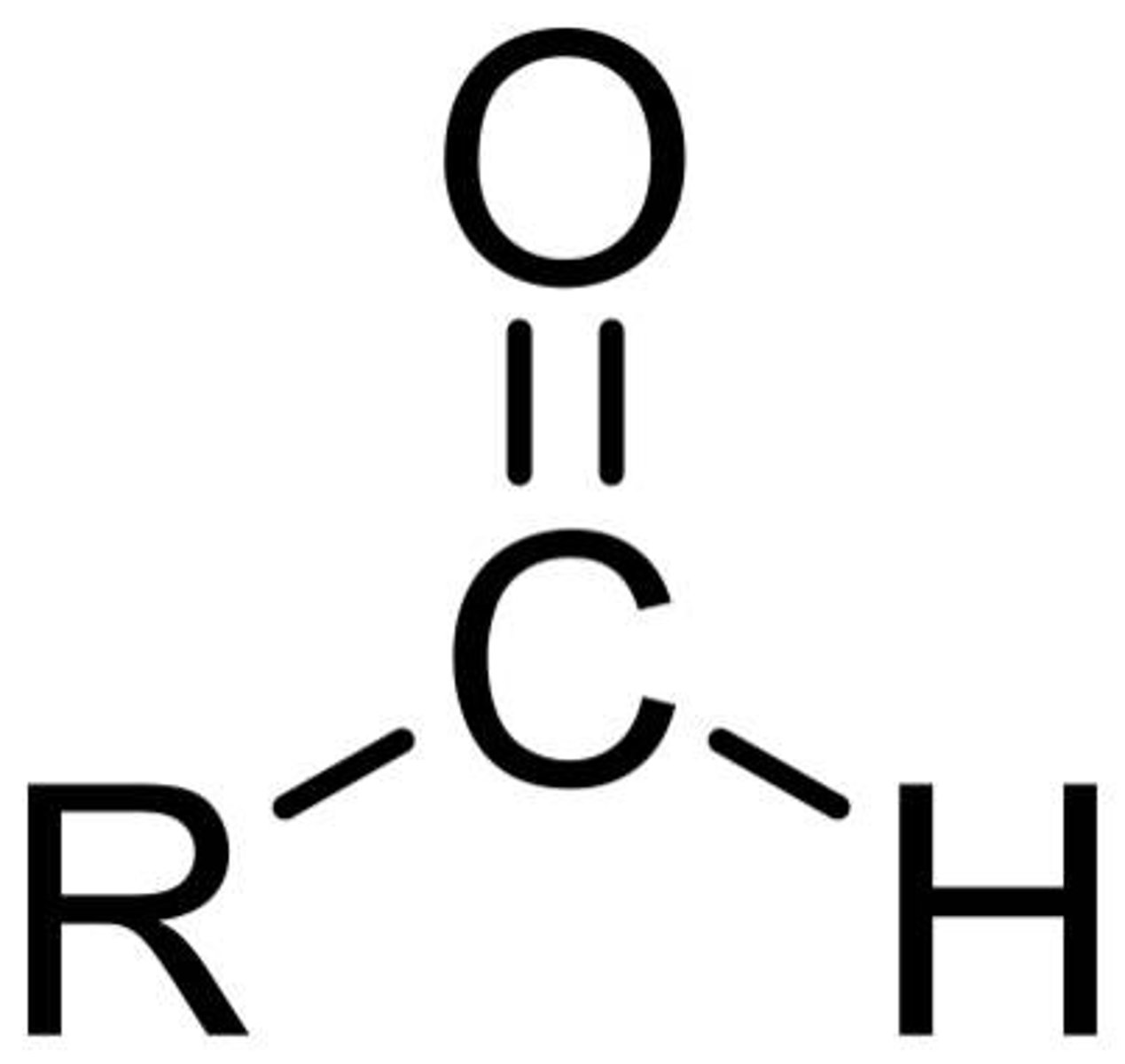
ketones
have a carbonyl group (C=O) located on an interior carbon of the parent chain, not first one
to name: drop -e and add -one to the parent chain, adding address may be necessary
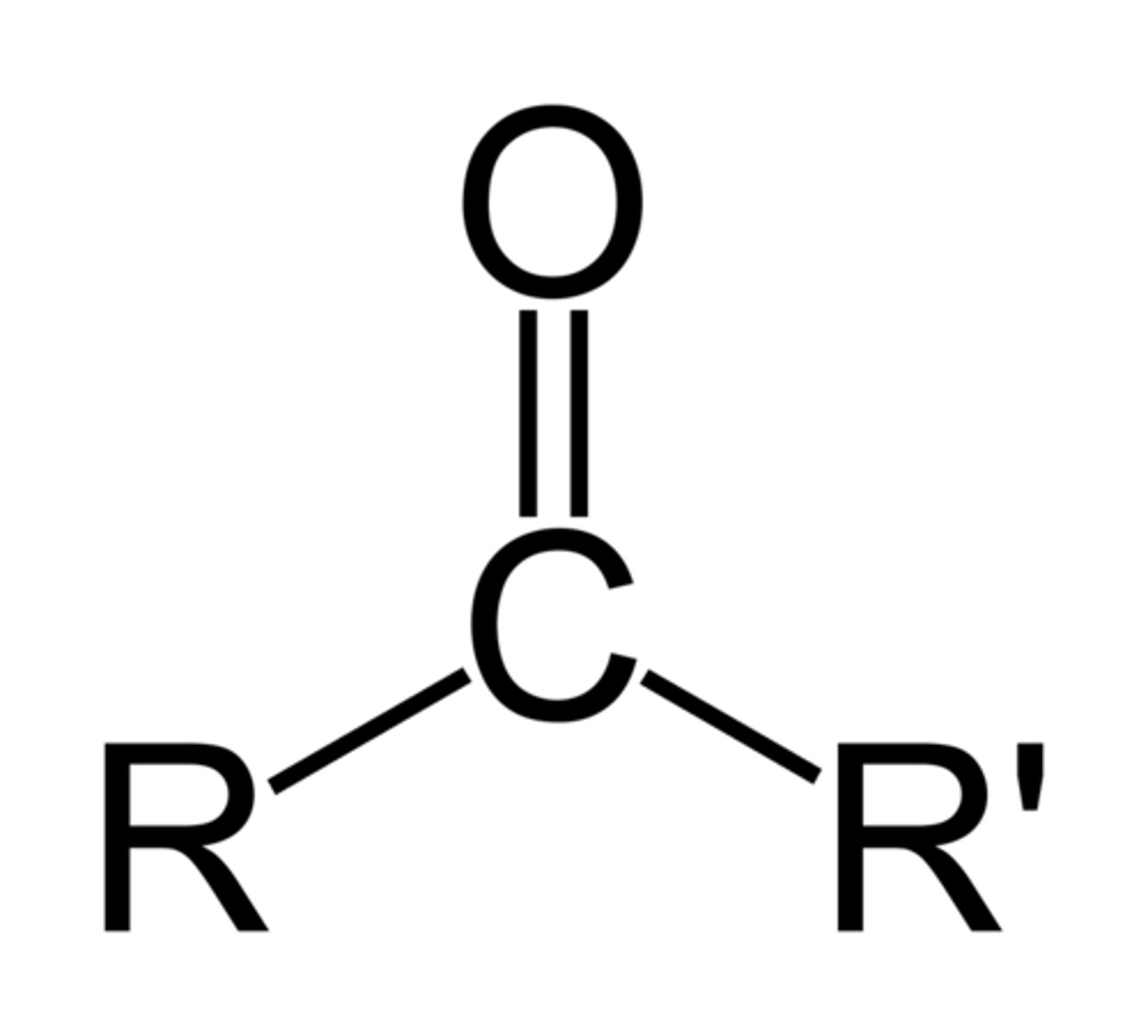
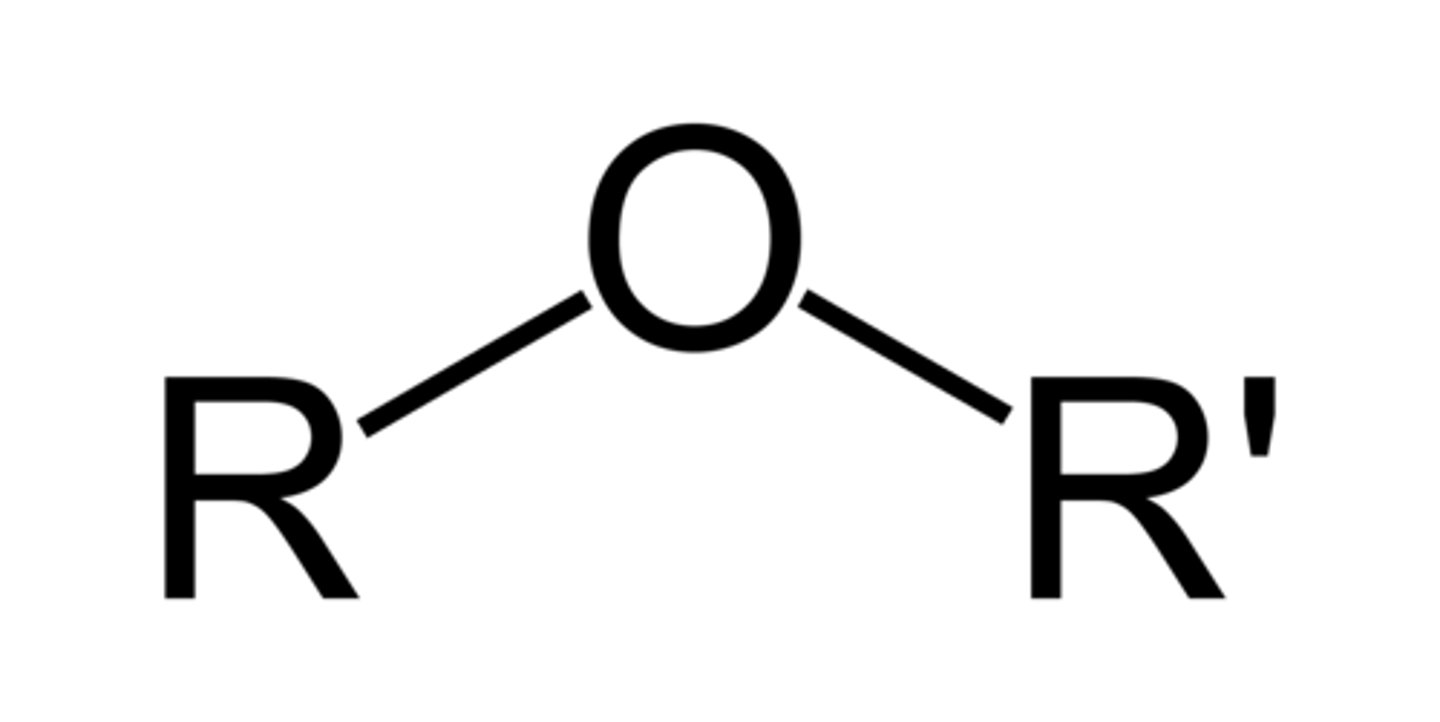
ethers
have a single bonded (C-O-C) interrupting a carbon chain
to name: use -yl to tell the branch length on either side of oxygen atom, end in "ether"
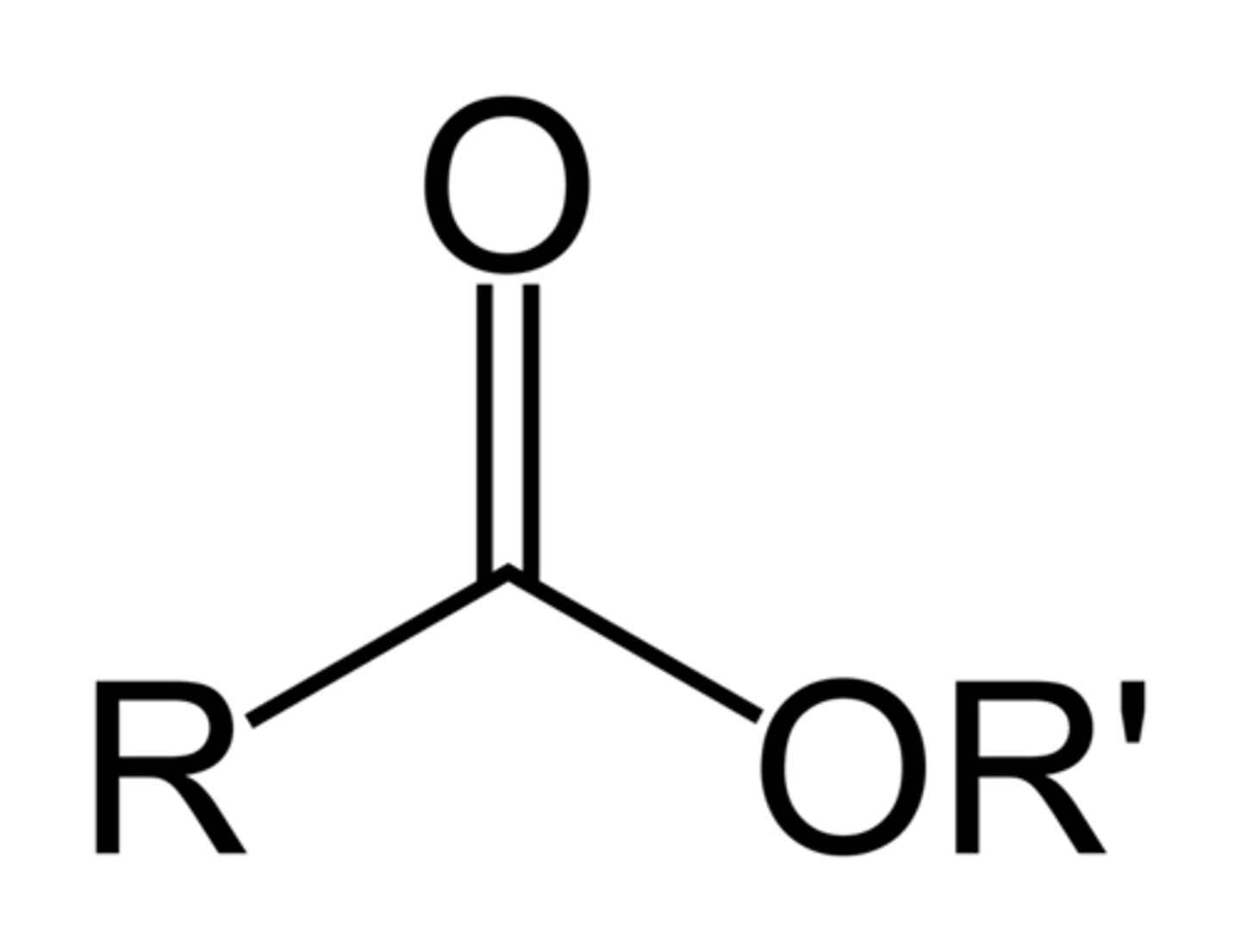
esters
have a -COOC- interrupting a carbon chain
to name: count the carbons attached to C=O and end in -oate, this is the last name, count the carbons attached to the O-C side, name this branch with -yl and use this as first name of molecule
properties of esters
sweet smell, component of natural fruit smells and perfumes
amines contain
nitrogen
amides contain
nitrogen and =O on same carbon
amino acids
contain amine group on one end and -COOH on other
combustion
when sufficient oxygen is present, hydrocarbons will burn and produce water and carbon dioxide
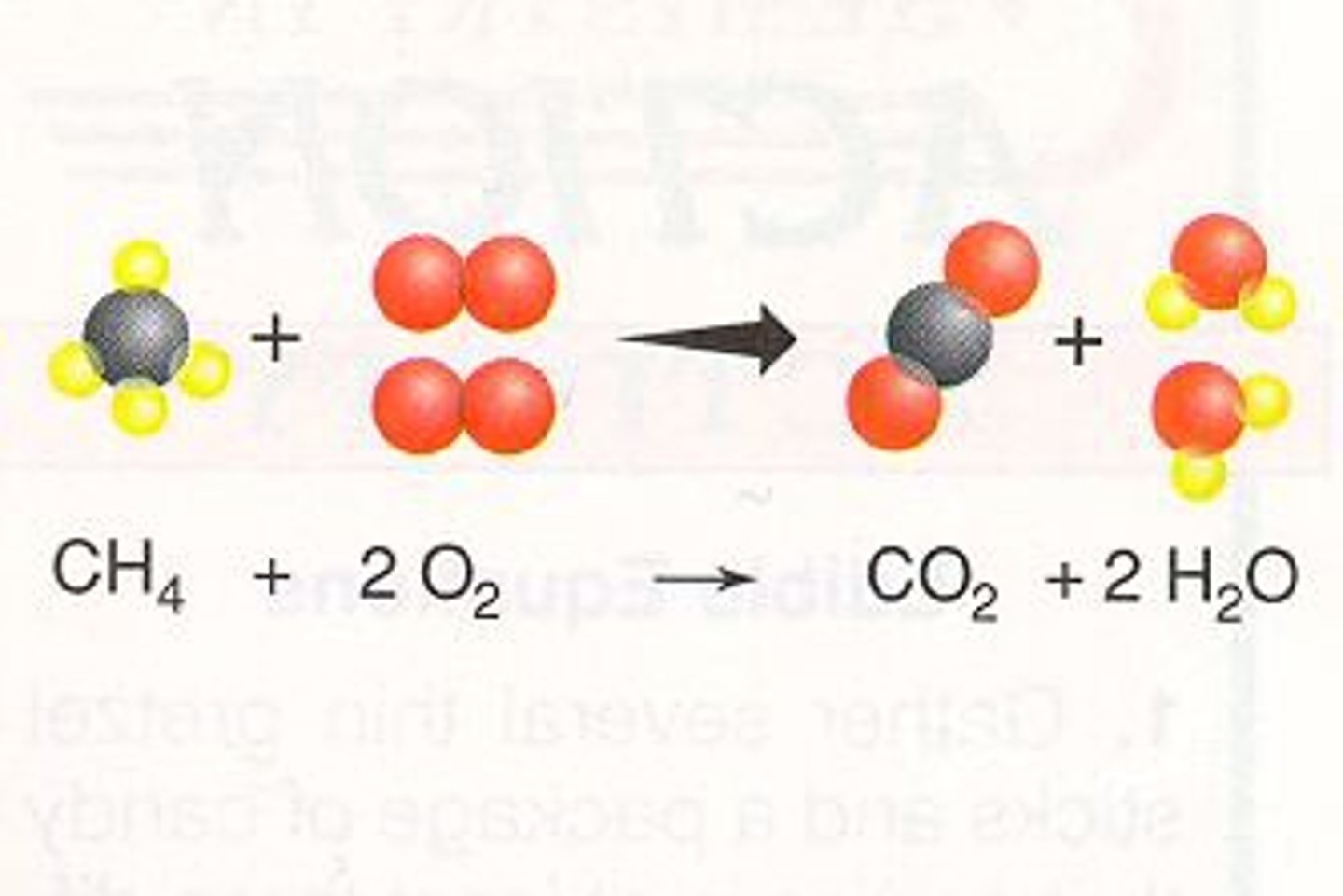
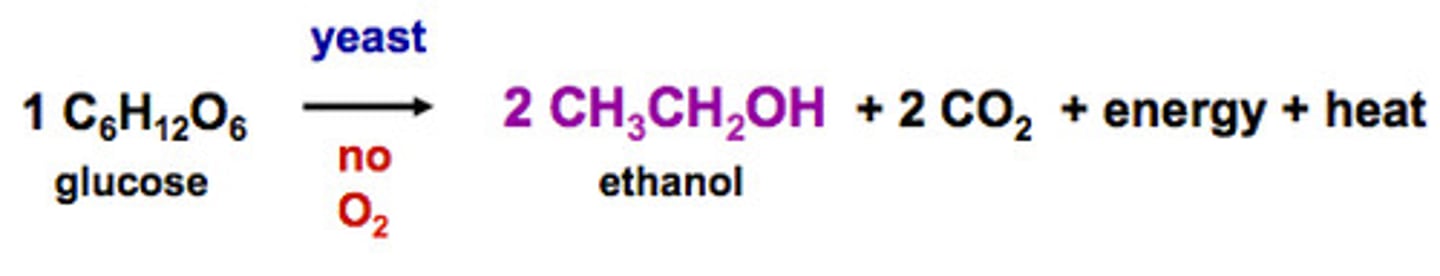
fermentation
when a sugar is broken down into alcohol and carbon dioxide, without o2 present
substitution
switching a hydrogen atom on an alkane with a different atom
clues: alkane on reactant side, hydrogen with another element on product side
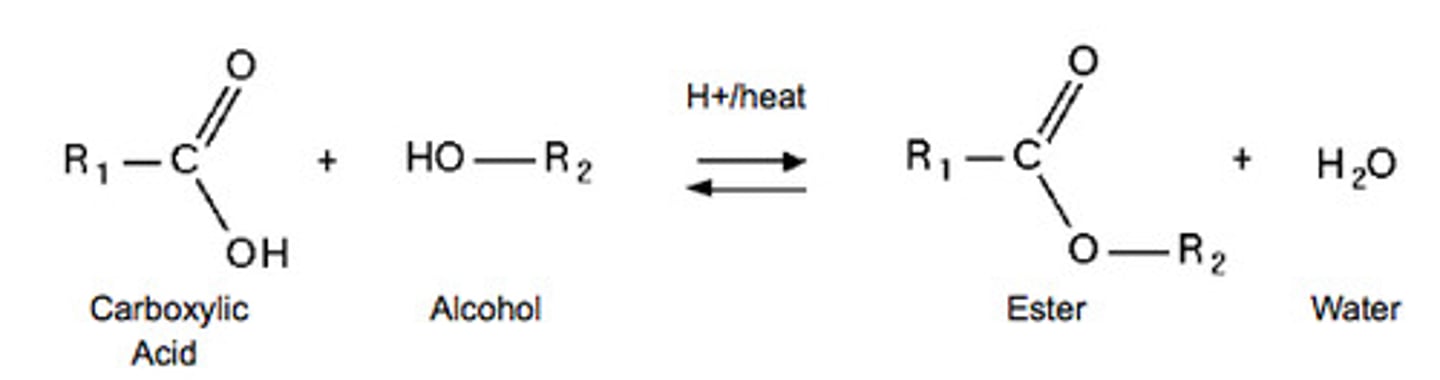
esterification
making esters by reacting an acid with an alcohol
clues: acid and alcohol are reactants, ester is product
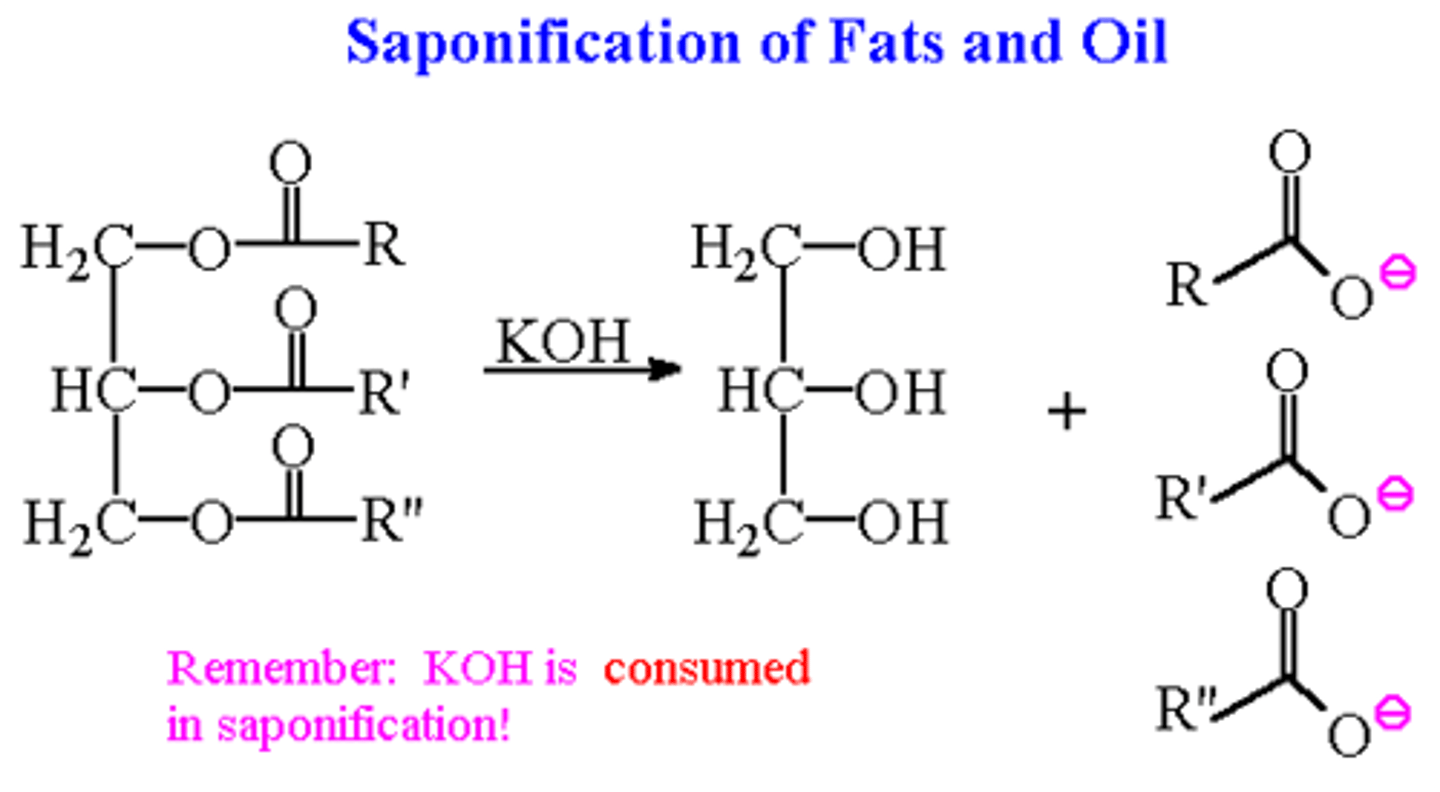
saponification
making soap by reacting fats with strong bases, clue: a base will be reactant use table l
fat + base = glycerol + soap
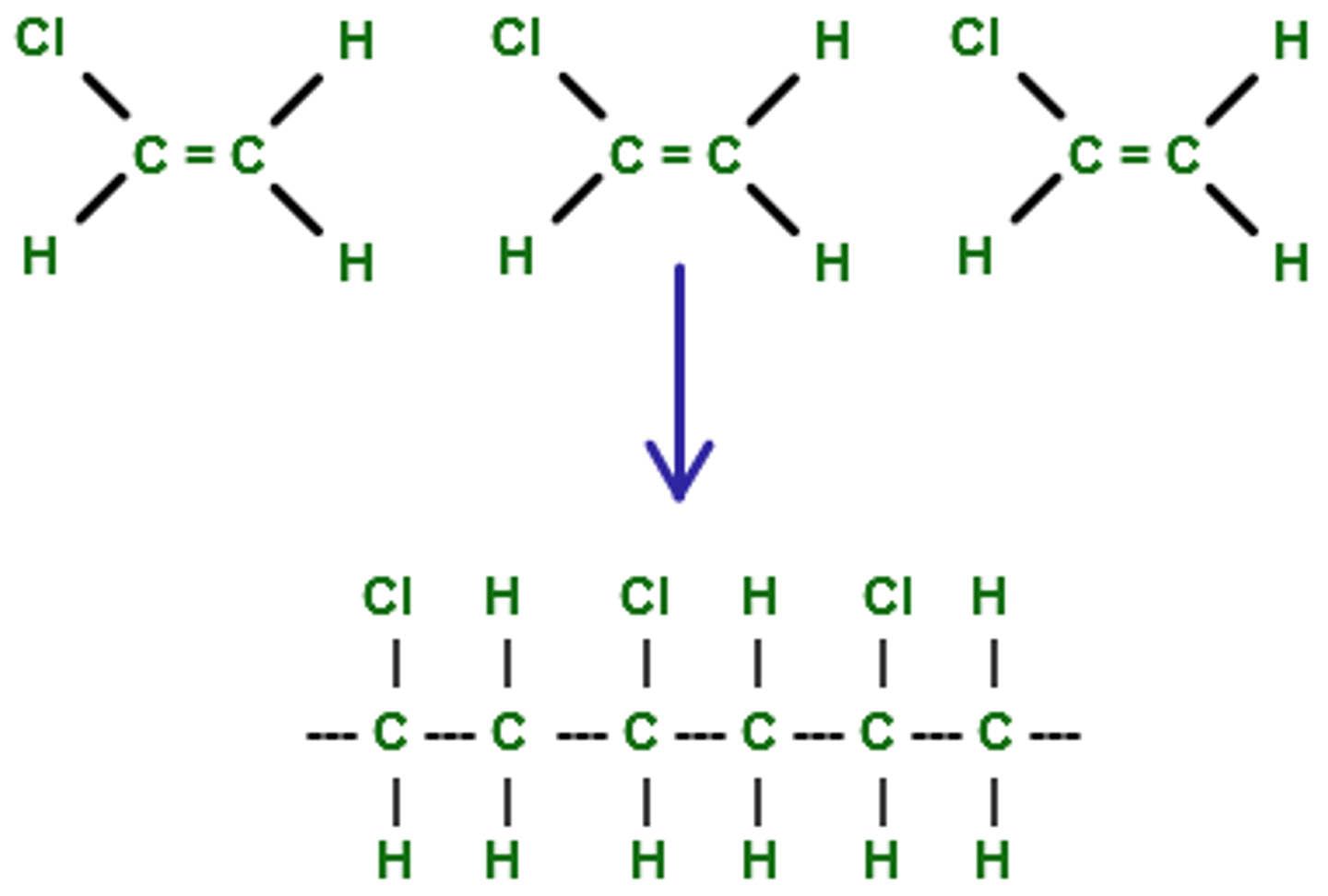
polymerization
making a large molecule by putting together many monomers
addition: breaking double or triple bonds
condensation: removing water
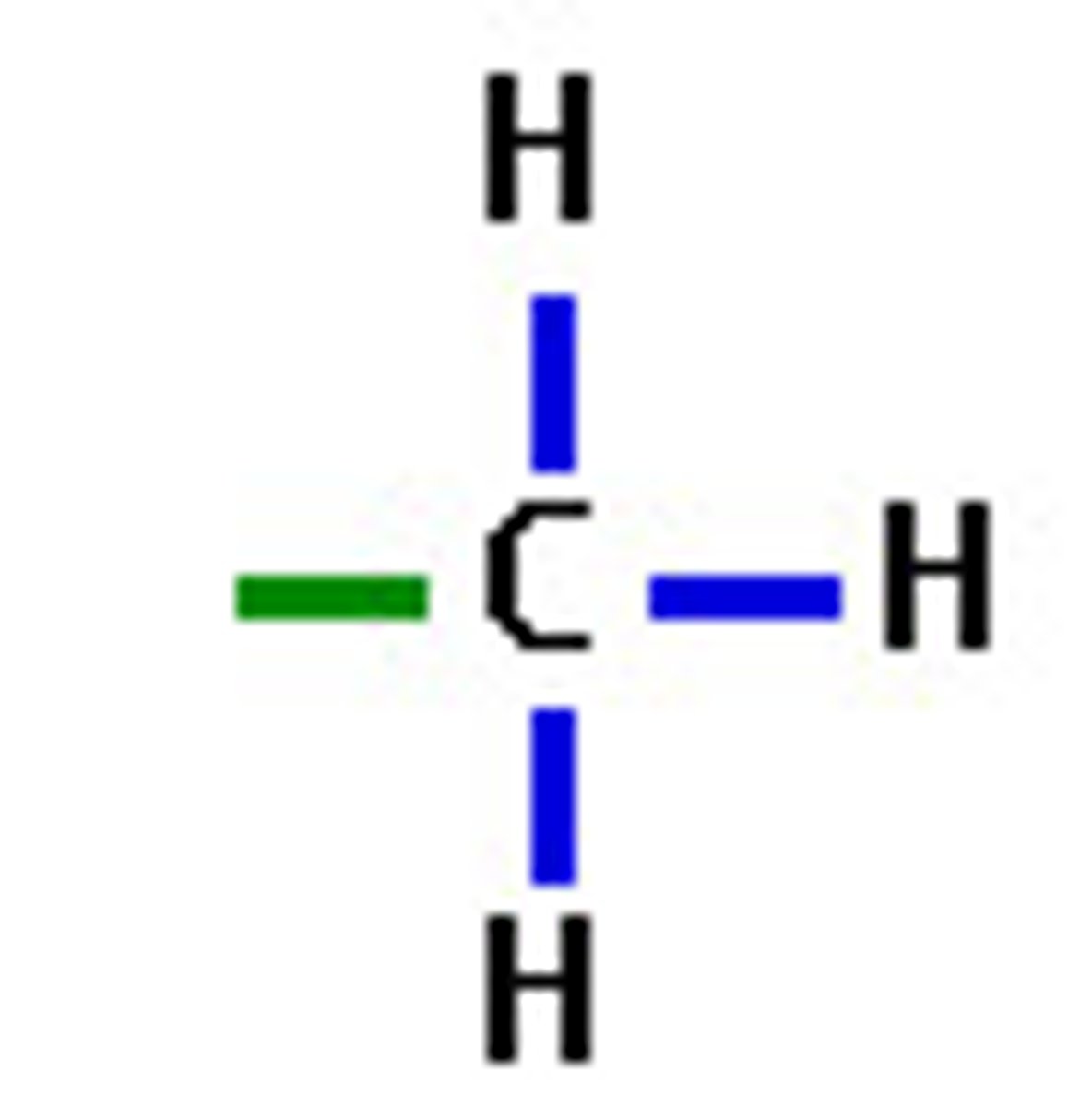
METHYL
common "Branch" or side chain in a hydrocarbon that has 1 carbon. Name from prefix on Table P + "yl"
if there are more than 1 present must use a prefix: di, tri, tetra, etc.
**when naming place the number of the carbon it is attached to infant of it. When multiple place the numbers in order separated by a comma. (2,2 dimethyl, 3,2 tri-ethyl, or 2,3 diethyl 2 methyl)
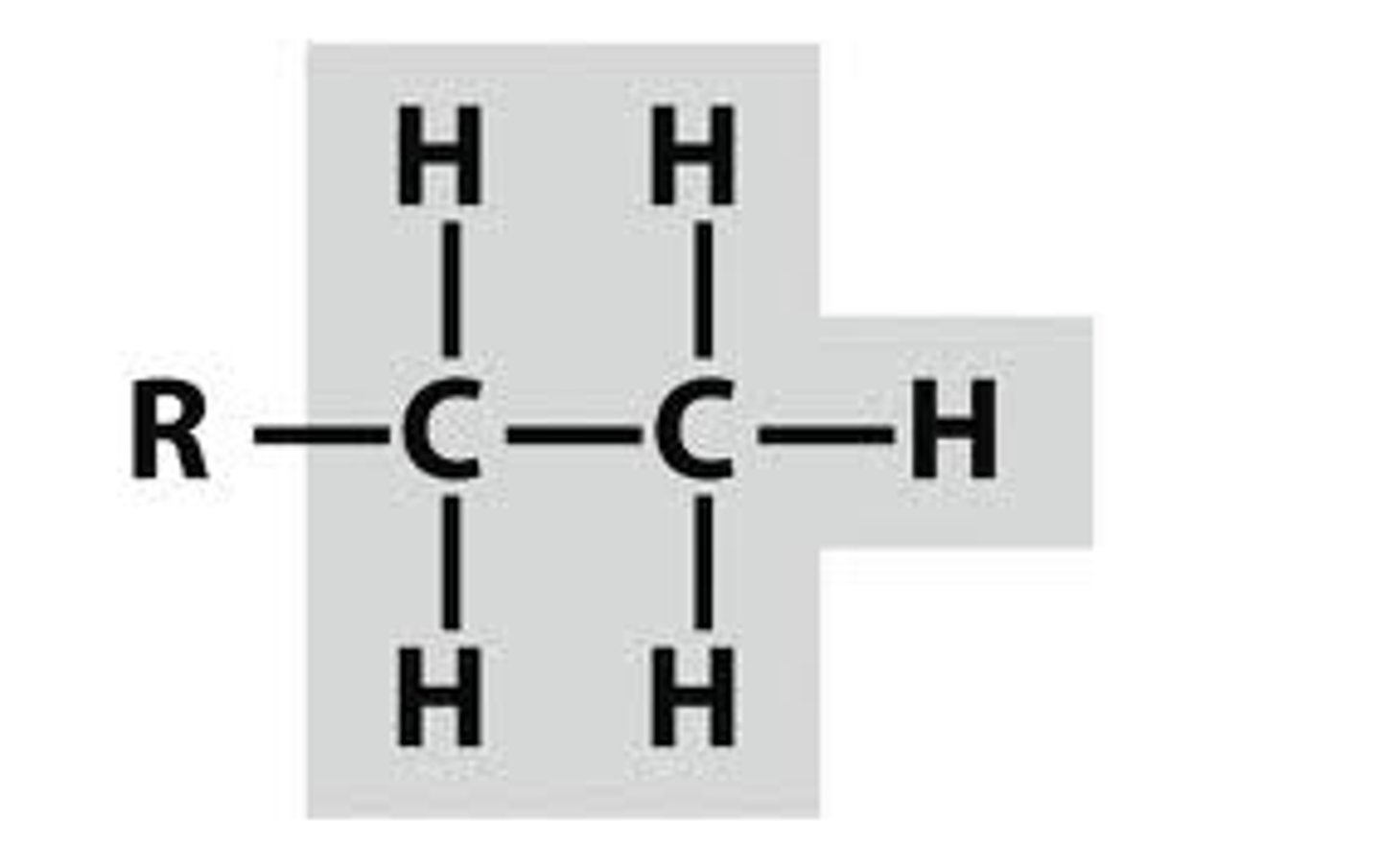
ETHYL
common "Branch" or side chain in a hydrocarbon that has 2 carbons. Name from prefix on Table P + "yl"
if there are more than 1 present must use a prefix: di, tri, tetra, etc.
**when naming place the number of the carbon it is attached to infant of it. When multiple place the numbers in order separated by a comma. (2,2 dimethyl, 3,2 tri-ethyl, or even 2,3 diethyl 2 methyl)
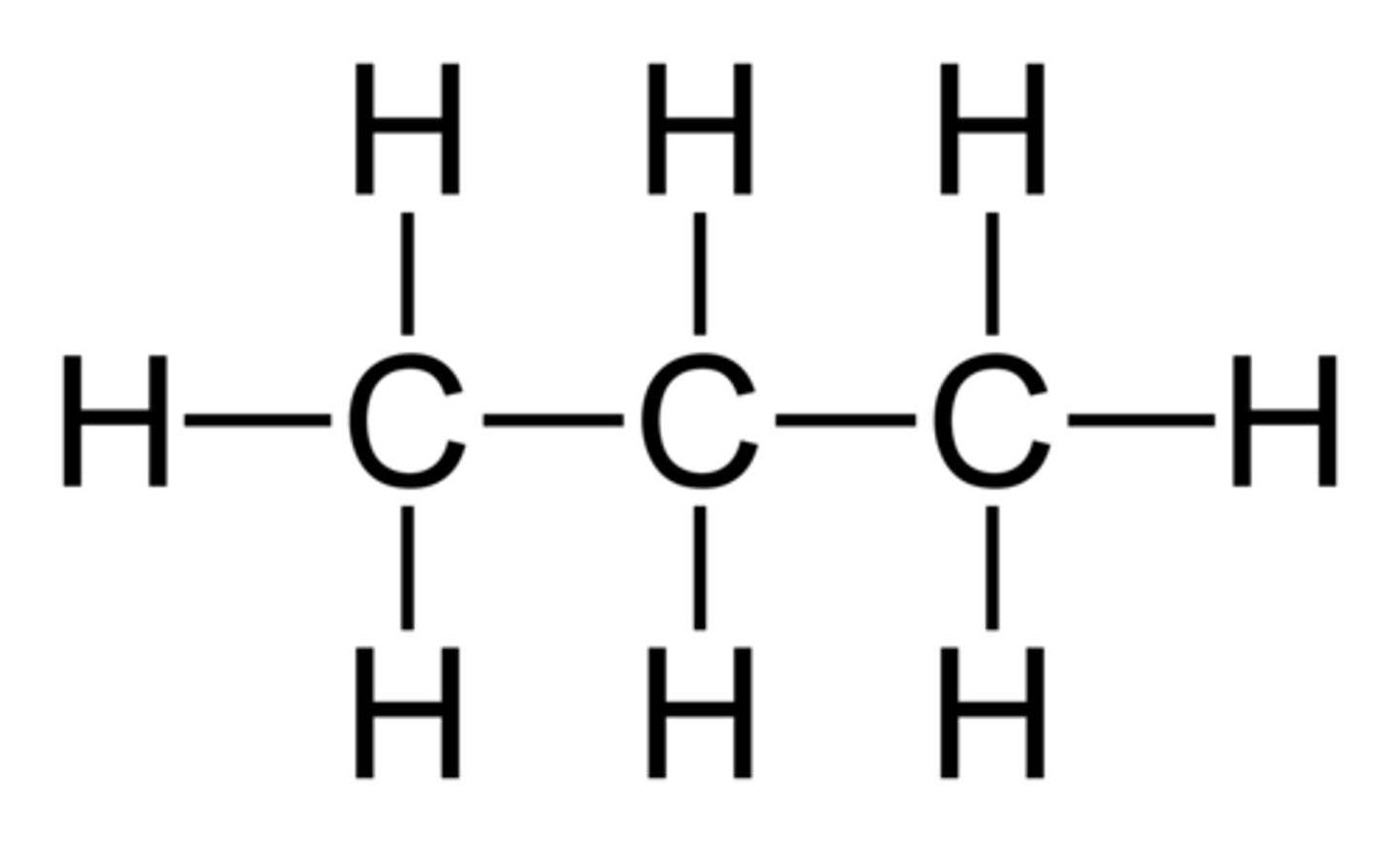
Propane
common hydrocarbon with 3 carbons.
Name from prefix on Table P + "ane" because there are only single bonds present, aka it is an alkane
Butane
common hydrocarbon with 4 carbons.
Name from prefix on Table P + "ane" because there are only single bonds present, aka it is an alkane
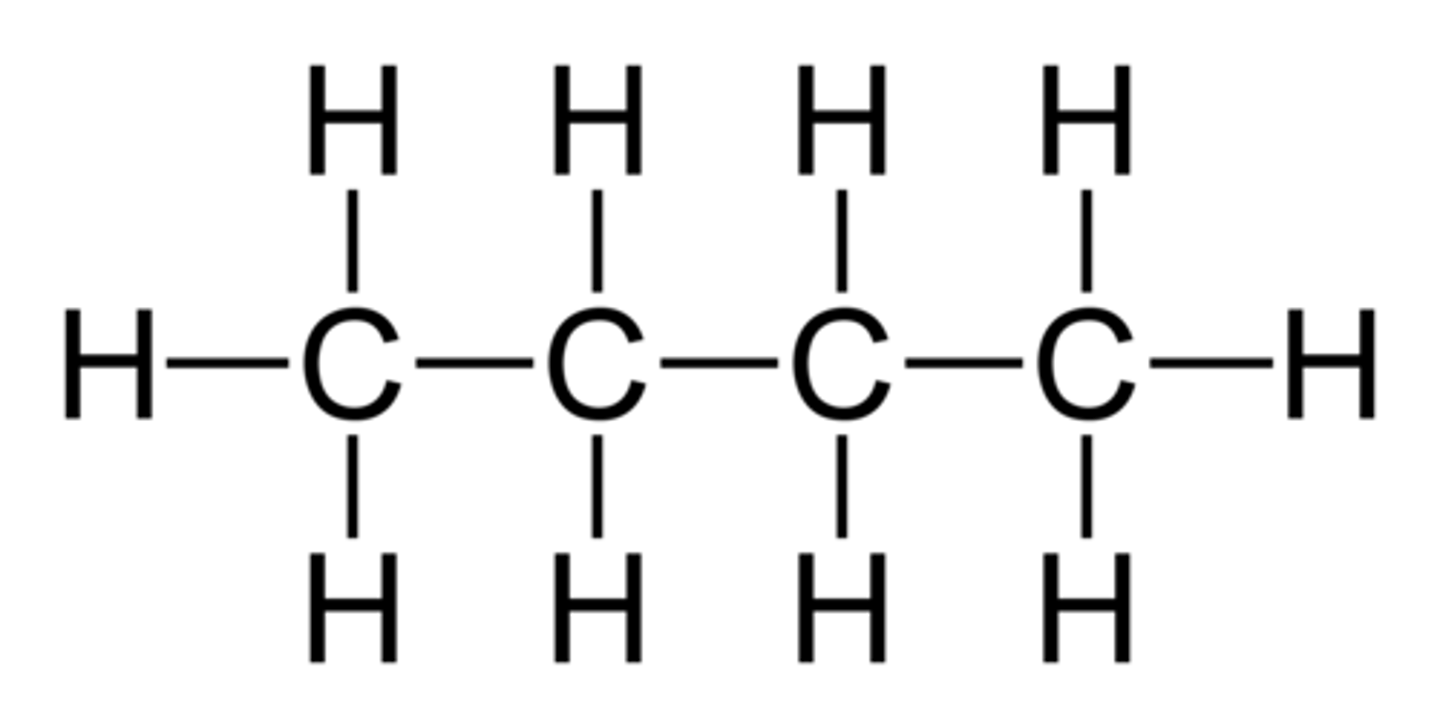
Pentane
common hydrocarbon with 5 carbons.
Name from prefix on Table P + "ane" because there are only single bonds present, aka it is an alkane
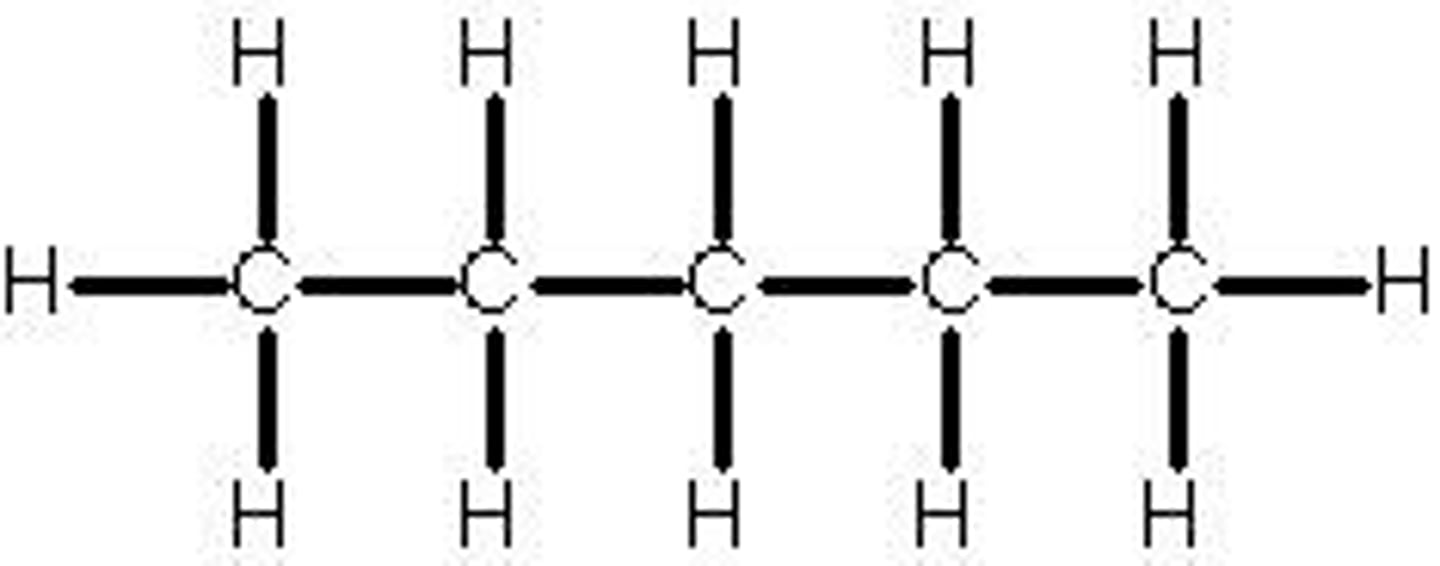
Hexane
common hydrocarbon with 6 carbons.
Name from prefix on Table P + "ane" because there are only single bonds present, aka it is an alkane
Names of "branches" added to make isomers (based on the number of carbons in the branch)
Name from prefix on Table P + "yl"
if there are more than 1 present must use a prefix: di, tri, tetra, etc.
**when naming place the number of the carbon it is attached to infant of it. When multiple place the numbers in order separated by a comma. (2,2 dimethyl, 3,2 tri-ethyl, or even 2,3 diethyl 2 methyl)
Saturated
Has only SINGLE bonds (Alkanes!)
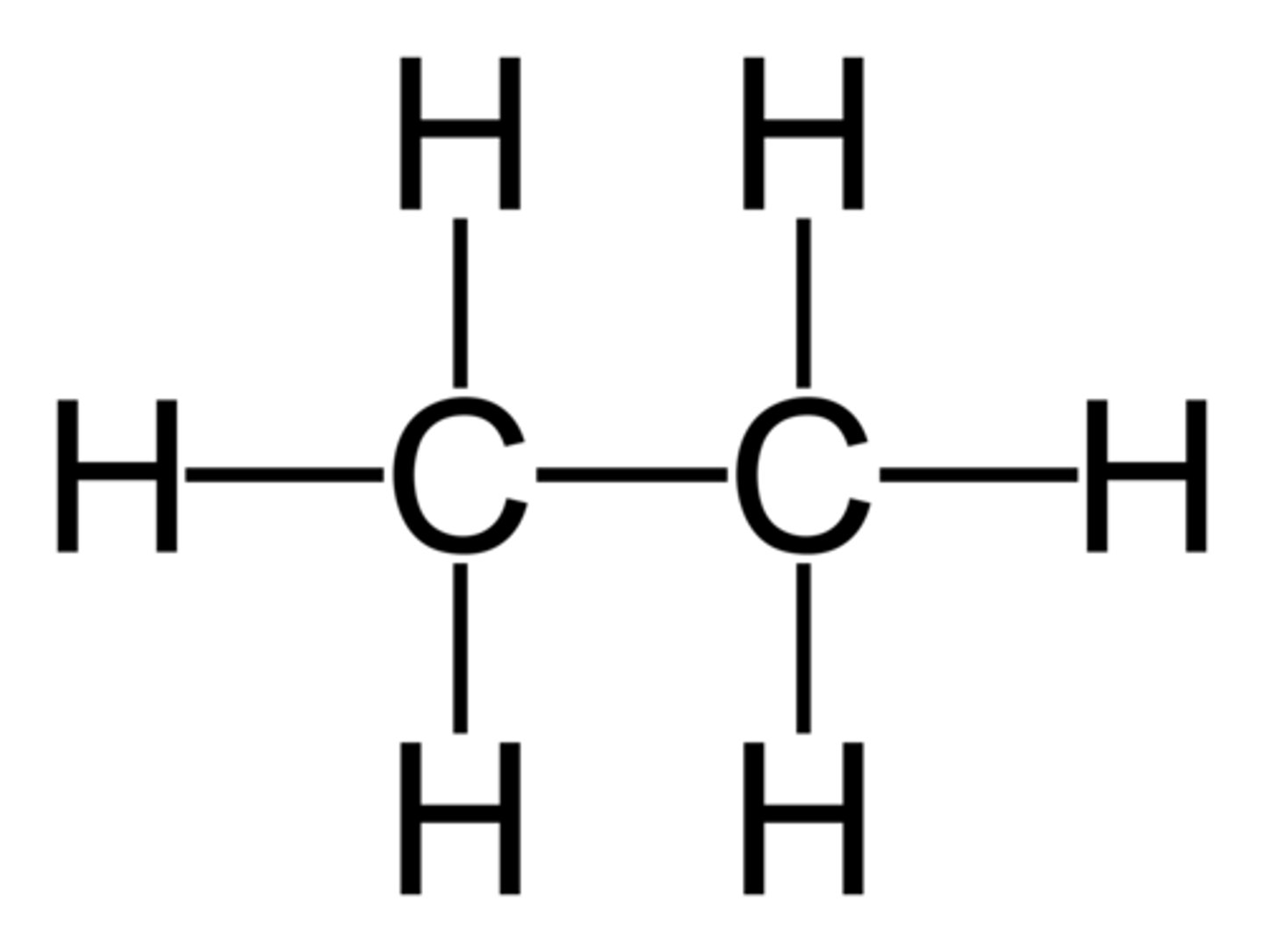
Fermentation
Fermentation: The anaerobic (without oxygen) respiration of simple sugars by yeast to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Enzymatic reaction (zymase)
Glucose ==> ethanol + CO2
C6H12O6 ==> C2H5OH + CO2
Unsaturated
Has DOUBLE or TRIPLE bonds present (Alkenes and Alkyne's
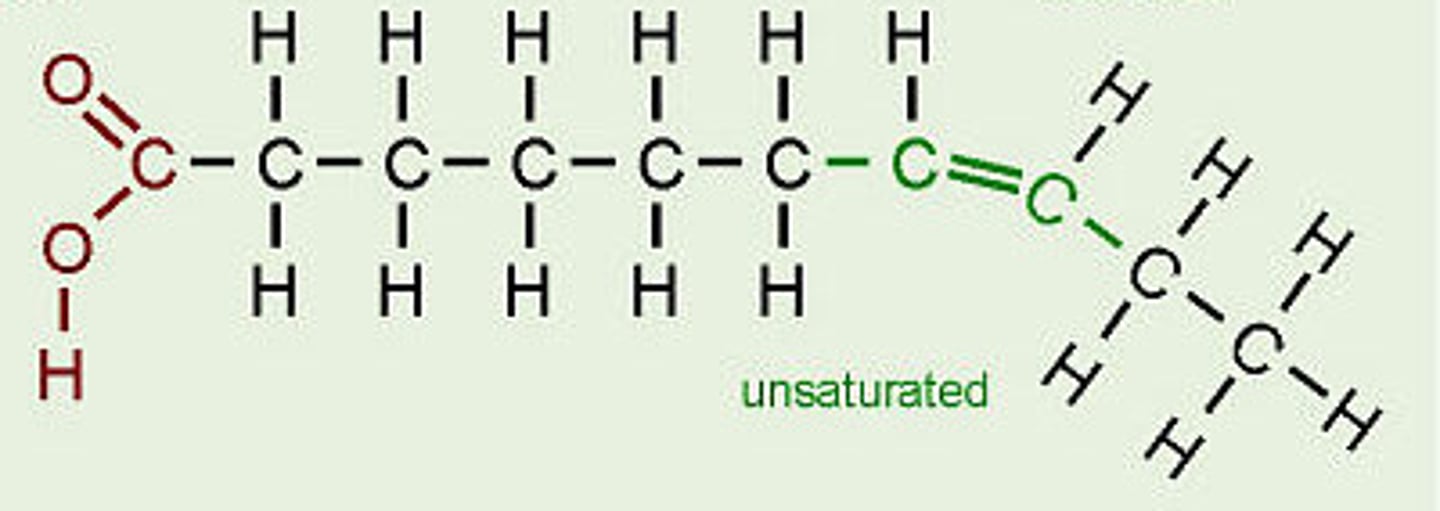
Polymers
olymer: A long chain of connected monomer units. A few examples include: rayon, silk, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic, and polystyrene (plastic).
Synthetic: nylon, polyethylene
Natural : cellulose, starch, proteins
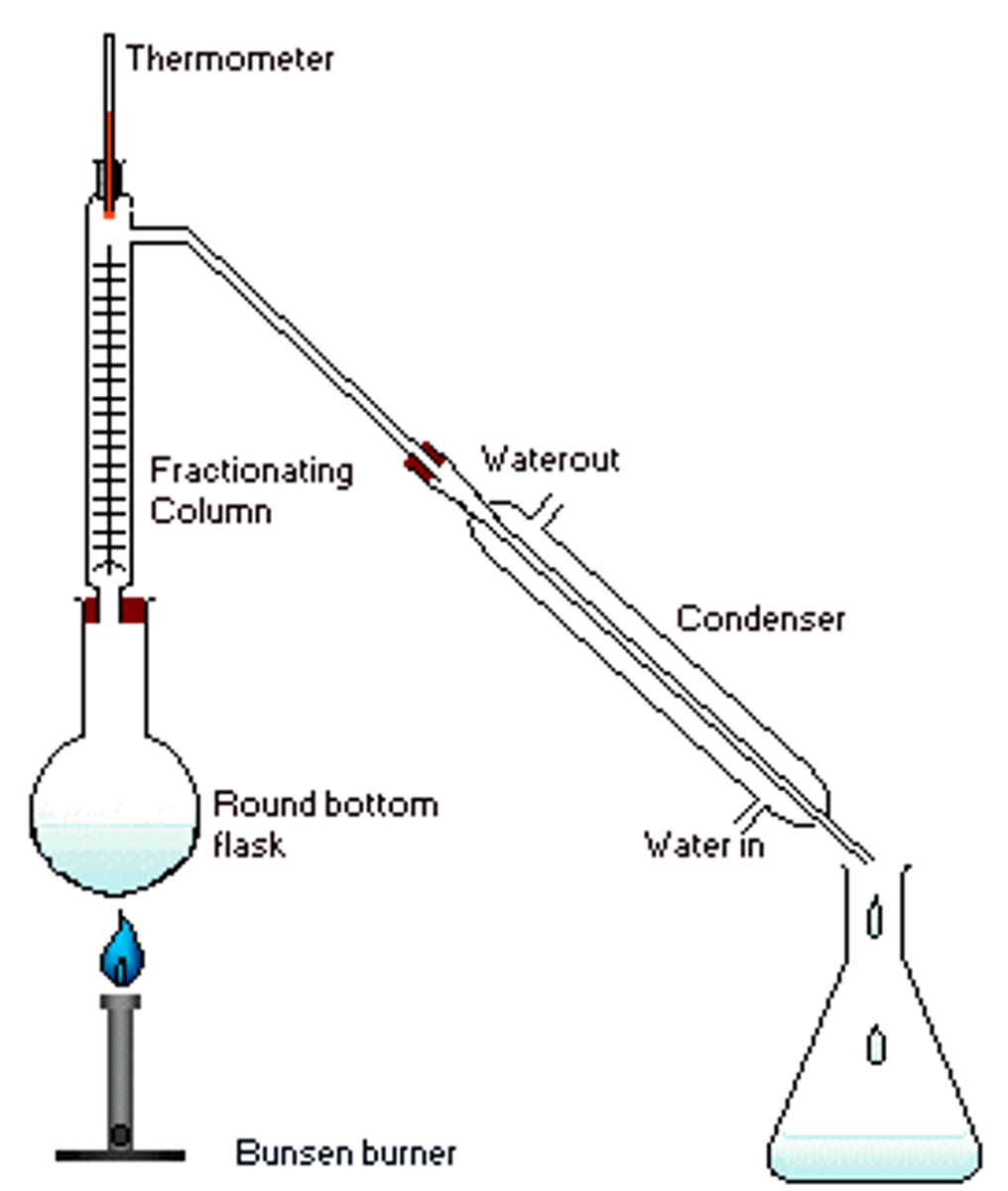
Fractional Distillation
A process used to separate liquids with different B.P.'s (which is boiled to produce a vapor that's then condensed into a liquid).
Cracking
A controlled process by which hydrocarbons are broken down or rearranged into smaller, more useful molecules.