Mid term for Microeconomics
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
Scarcity
A condition that arises from the conflict between unlimited human wants and limited resources available to fulfill those wants
Economics
A social science that studies how individuals, businesses, governments, and societies allocate scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants and needs.
Microeconomics
the study of the economic behavior in individual markets, industries, or sectors, such as that for computers or unskilled labor.
Macroeconomics
the study of economic behavior of entire economies, as measured, for example, by total production and employment
economic theory
a simplification of reality used to make conjectures about cause and effect in the real world
Economic model
A simplification of reality used to make conjectures about cause and effect in the real world.
Scientific method
systematic approach scientists use to study and understand the world through observation, hypothesis formulation, experimentation, data analysis, and conclusion drawing.
Other-things-constant assumption
The assumption, when focusing on the relation among key economic variables, that other variables remain unchanged
Behavioral assumptions
an assumption that describes the expected behavior of economic decision makers- what motivates them
Hypothesis
A theory about how key variables relate
Positive economic statement
a statement that can be proved or disproved by reference to facts
Normative economic statement
a statement that reflects an opinion, which cannot be proved or disproved by reference to the facts
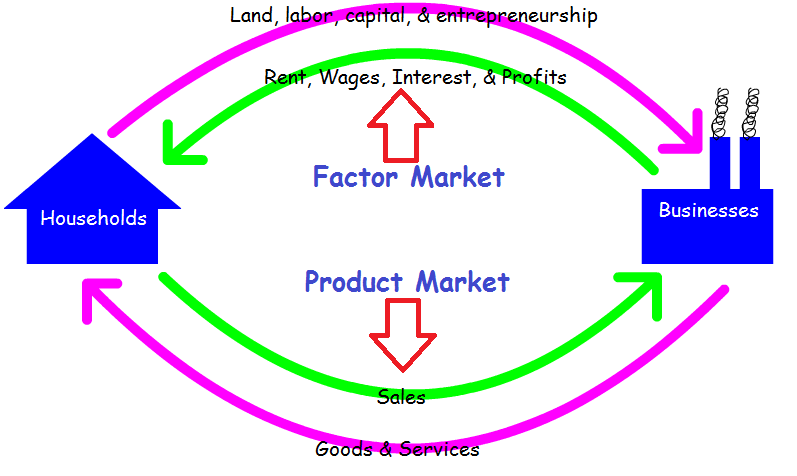
Circular-flow model
A diagram that traces the flow of resources, products, income, and revenue among economic decision makers
resources
the inputs, or factors of production, used to produce the goods and services that people want; consist of labor, capital, natural resources, and entrepreneurial ability
Labor
The physical and mental effort used to produce goods and services
Capital
the buildings, equipment, tools, utensils, appliances, and machinery used to produce goods and services
Human capital
The knowledge, skills, abilities, and other attributes that individuals possess, which can be used to produce goods and services and generate economic value.
entrepreneurial ability
the imagination required to develop a new product or process, the skill needed to organize production, and the willingness to take the risk of profit or loss
entrepreneur
A profit-seeking decision maker who starts with an idea, organizes an enterprise to bring that idea to life, and assumes the risk of the operation
Natural resources
All gifts of nature used to produce goods and services; includes renewable and exhaustible resources
good
a tangible product used to satisfy human wants
service
an activity, or intangible product, used to satisfy human wants
wages
payment to resource owners for the use of their capital
interest
payment to resource owners for the use of their capital
rent
payment to resource owners for the use of their natural resources
Profit
reward for entrepreneurial ability; sales revenue minus resource cost
markets
a set of arrangements by which buyers and sellers carry out exchange at mutually agreeable terms
Product markets
a market in which a good or service is bought and sold
resource markets
a market in which a resource is bought and sold
rational self-interest
each individual tries to maximize the expected benefit achieved with a given cost or to minimize the expected cost of achieving a given benefit
marginal
incremental, additional, or extra; used to describe a change in an economic variable
association-is-causation fallacy
the incorrect idea that if two variables are associated or correlated in time, one must necessarily cause the other
fallacy of composition
the incorrect belief that what is true for the individual, or part, must necessarily be true for the group, or the whole
secondary effects
unintended consequences of economic actions that may develop slowly over time as people react to events
economic theory or economic model
a simplification of reality used to make conjectures about cause and effect in the real world
positive/direct/relation
it occurs when two variables increase or decrease together; the two variables move in the same direction
negative/inverse
It occurs when two variables move in opposite directions; when one increases, the other decreases
slope of a line
a measure of how much the vertical variable changes for a give change in the horizontal variable
tangent
a straight line that touches a curve at a point but does not cut or cross the curve; used to measure the slope of a curve at a point
positive relation/direct relation
it occurs when two variables increase or decrease together
negative relation/inverse relation
it occurs when two variables move in opposite directions; when one increases, the other decreases
opportunity cost
the value of the best alternative forgone when an item or activity is chosen
sunk cost
a cost that has already been incurred, cannot be recovered, and thus is irrelevant for present and future economic decisions.
Production possibility frontier (PPF)
a curve showing alternative combinations of goods that can be produced when available resources are used efficiently; a boundary line between inefficient and unattainable combinations
law of comparative advantage
the individual, firm, region, or country with the lowest opportunity cost of producing a particular good should specialize in that good
Absolute advantage
the ability to make something using fewer resources than other producers use
Comparative advantage
The ability to make something at a lower opportunity cost than other producers face
Barter
The direct exchange of one product for another without using money
division of labor
breaking down the production of a good into separate tasks
specialization of labor
focusing work effort on a particular product or a single task
efficiency
the condition that exists when there is no way resources can be reallocated to increase the production of one good without decreasing the production of another; getting the most from available resources
constant opportunity costs
where the trade-off between producing different goods or services remains constant, meaning that the resources sacrificed to produce one unit of a particular good or service are the same for each additional unit produced
law of increasing opportunity cost
to produce more of one good, a successively larger amount of the other good must be sacrificed
economic growth
an increase in the economy’s ability to produce goods and services; reflected by an outward shift of the economy’s production possibilities frontier
rules of the game
the formal and informal institutions that support the economy- the laws, customs, manners, conventions, and other institutional underpinnings that encourage people to pursue productive activity
economic system
the set of mechanisms and institutions that resolve the what, how, and for whom questions
pure capitalism
An economic system characterized by the private ownership of resources and the use of prices to coordinate economic activity in unregulated markets
Private property rights
an owner’s right to use, rent, or sell resources or property
pure command system
pure command system, an economic system characterized by the public ownership of resources and centralized planning
mixed system
An economic system characterized by the private ownership of some resources and public ownership of other resources; some markets are regulated by the government
production possibilities frontier (PPF)
A curve showing alternative combinations of goods that can be produced when available resources are used efficiently; a boundary line between inefficient and unattainable combinations
utility
the satisfaction received from consumption; sense of well-being
transfer payments
cash or in-kind benefits given to individuals by the government
industrial revolution
development of large-scale factory production that began in Great Britain around 1750 and spread to the rest of Europe, North America, and Australia
firms
economic units formed by profit-seeking entrepreneurs who employ resources to produce goods and services for sale
sole proprietorship
a firm with a single owner who has the right to all profits but who also bears unlimited liability for the firm’s losses and debts
partnership
a firm with multiple owners who share the profits and bear unlimited liability for the firm’s losses and debts
corporation
a legal entity owned by stockholders whose liability is limited to the value of their stock ownership
cooperative
An organization consisting of people who pool their resources to buy and sell more efficiently than they could individually
nonprofit organizations
groups that do not pursue profit as a goal; they engage in charitable. educational, humanitarian, cultural, professional, or other activities, often with a social purpose
information revolution
technological change spawned by the microchip and the internet that enhanced the acquisition, analysis, and transmission of information
market failure
A condition that arises when the unregulated operation of markets yields socially undesirable results
antitrust laws
prohibition against price fixing and other anticompetitive practices
monopoly
a sole supplier of the product with no close substitutes
natural monopoly
One firm that can supply the entire market at a lower per-unit cost than could two or more firms
private goods
a good, such as pizza, that is both rival in consumption and exclusive
public goods
a good that, once produced, is available for all to consume, regardless of who pays and who doesn’t; such a good is nonrival and nonexclusive, such as a safer community
externality
a cost or a benefit that affects neither the buyer nor seller, but instead affects people not involved in the market transaction
fiscal policy
The use of government purchases, transfer payments, taxes, subsidies, and borrowing to influence economy-wide variables such as inflation, employment, and economic growth
Monetary policy
regulation of the money supply and interest rates to influence economy-wide variables such as inflation, employment, and economic growth
mandatory spending
Federal mandatory spending refers to government spending that is mandated by laws and does not require annual congressional approval through the appropriations process. This spending includes entitlement programs like Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid.
discretionary spending
Federal discretionary spending refers to government spending that is determined through the annual appropriations process and is subject to limits set by Congress. This spending includes funding for various federal agencies, programs, and initiatives such as national defense, education, infrastructure, and research and development.
ability-to-pay tax principle
Those with a greater ability to pay, such as those earning higher incomes or those owning more property, should pay more taxes
benefits-received tax principle
Those who get more benefits from government programs should pay more taxes.
tax incidence
The incidence of a tax refers to the distribution of the tax burden between buyers and sellers in a market
proportional taxation
the tax as a percentage of income remains constant as income increases; as called a flat tax
progressive taxation
The tax as a percentage of income increases as income increases
marginal tax rate
the percentage of each additional dollar of income that goes to the tax
regressive taxation
The tax as a percentage of income decreases as income increases
trade balance
The value during a given period of a country’s exported goods minus the value of its imported goods
ne exports
The value during a given period of a country’s exported goods minus the value of its imported goods
balance of payments
a record of all economic transactions during a given period between residents of one country and residents of the rest of the world
foreign exchange
foreign money needed to carry out international transactions
tariffs
a tax on imported goods
quota(s)
a legal limit on the quantity of a particular product that can be imported or exported
demand
a relation between the price of a good and the quantity that consumers are willing and able to buy per period, other things constant
law of demand
The quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to buy per period relates inversely, or negatively, to the price, other things constant
demand curve
a curve showing the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity consumers are willing and able to buy per period, other things constant
quantity demanded
The amount of goods that consumers are willing and able to buy per period at a particular price, as reflected by a point on a demand curve