Chapter 5- Stereochemistry
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Enantiomers
Are mirror images of each other
Have four different substituents
Hence are not able to make a plane of symmetry.
This is also known as a chiral compound
Example of lactic acid as a chiral
Lactic acid exists in two forms
One is more active and more healthy
This is because one chiral might have different biological activity. Because for example it doesn’t fit in a receptor.
Imagine trying to shake a right with a left hand, doesn’t work
Most common cause of chirality
A carbon atom bonded to four different groups in an organic molecule.
Properties of chiral molecules
Different biological activity
Optical activity
Optical activity in chirals
Using a light source and a filter to make the light polarized and you shine this on an enantiomer
If the light is now angled left if will get a minus sign = levorotatory molecule
If the light is now angled right it will get a plus sign = dextrorotatory molecule
This is a property of an enantiomer
Two enantiomers will turn angle the light with the same value just in opposite directions so one will be + and one will be -
If you don’t have a chiral compound it won’t angle
RS system
R configuration = 123 clockwise
S configuration = 123 counterclockwise
Side note there is NO correlation between R and S and +/-
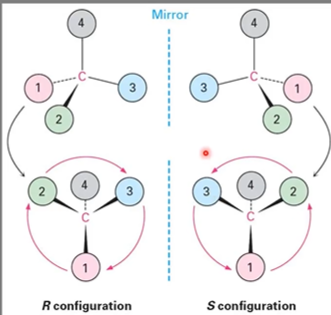
Sequence rules for specifying configuration (choosing between R and S)
Ranking: Look at the four atoms directly attached to the chirality center and assign priorities based on decreasing atomic number
If they atoms in the first atoms in the substituents are the same: look at the second, third or fourth atoms outward until a difference is found.
In case of double bonds: multiple bonded atoms are equivalent to the same number of single-bonded atoms. look at picture

Diastereomers
A molecule with multiple chiral atoms.
If a molecule has two chiral atoms, it means there will be four isomers.
formula = 2n where n is chirality centers.
Epimers
Diastereomers that differ in only 1 chiral center.
Meso compounds
2 chirality centers
When the top part of the carbon is the same as the bottom
They are identical → and so are not enantiomers
Meso compounds DO NOT give optical activity
Check configuration, if chiral centers have different configurations then they are meso if the configurations are the same they are not meso.
Allenes
When there is optical activity without chiral C atoms.