RA CH 9, 10 & 11 HELP ME
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
WE ALL GONNA DIE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Ear (Pinna) — Proportions
Length = 1/3 face length; width = 2/3 ear length.
Ear Placement
Vertical: along ramus of mandible
Middle: external auditory meatus/zygomatic arch
Lobe: anterior to mastoid process
Surface: superior = eyebrow/root of nose; inferior = base of nose.
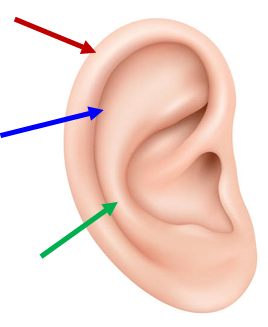
Helix (red)
Outer rim; question-mark shape.

Scapha (blue)
Shallowest depression; between helix & antihelix.
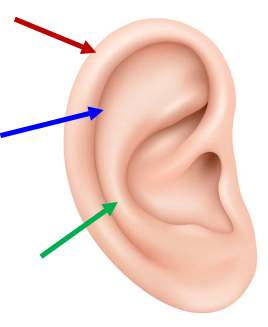
Antihelix (green)
Inner rim.
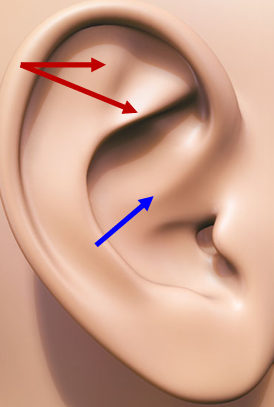
Crura of Antihelix (red)
Superior and anterior branches of the antihelix
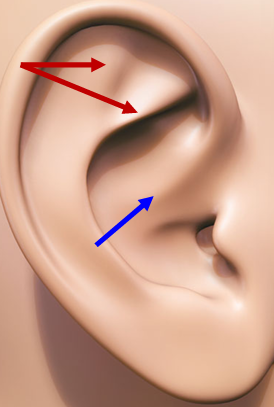
Crus of Helix (blue)
Origin; flattened in concha.
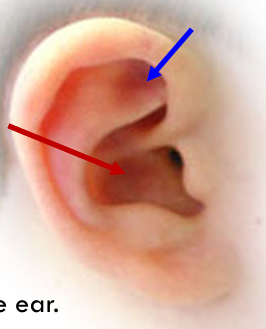
Concha (red)
Deepest depression. concave shell of the ear
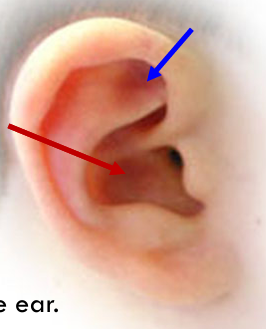
Triangular Fossa (blue)
Between crura; second deepest depression.
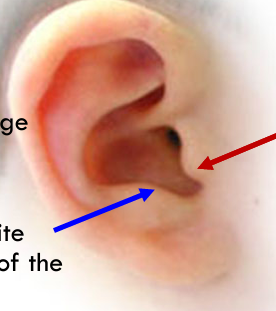
Tragus( red)
Elevation protecting external auditory meatus.
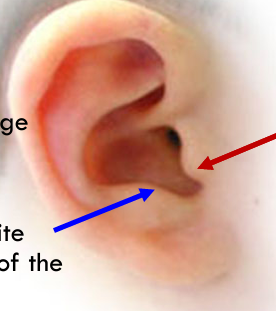
Antitragus (blue)
Opposite tragus, superior border of lobe
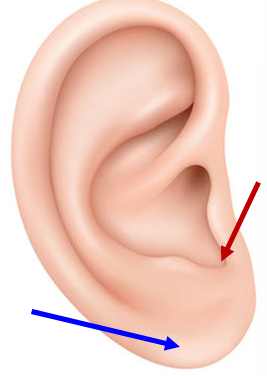
Intertragic Notch (red)
Between tragus & antitragus.
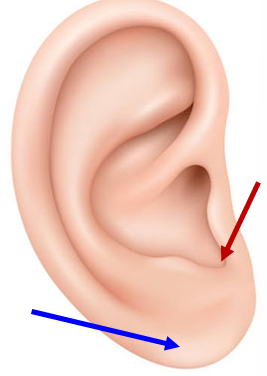
Lobe (blue)
Inferior fatty 1/3 of ear.
Nose — Proportions
Length = 1/3 face; width = 1/5 face.
Nose Placement
Superior = glabella; inferior = plane of ear.
Nasal Index
Width ÷ Height × 100
(Classification) Leptorrhine
•A nasal index having a long, narrow, and high bridge.
•Nasal index of 70.0 or less
(Classification) Mesorrhine
A nasal index which is medium broad and medium-low bridged.
•Nasal index of 70.0 to 84.9
Classification: Platyrrhine
A nasal index which is short and broad and has the minimum of projection.
•Nasal index of 85.4 and above
Nose profile: Straight (Grecian)
•A nasal profile in which the dorsum exhibits a straight line from the root to the tip.
•The most common nasal profile
(Nose profile) Convex (Roman, Aquilin)
A nasal profile which exhibits a hump in its linear form.
Nasal Profiles
Straight (Grecian) — straight line root→tip
Convex (Roman) — hump
Concave (Infantine) — depressed/turned-up tip
Nose Anatomy
Nasal bones; nasal spine of maxilla; septum, • Vertical cartilage dividing nasal cavity into two chambers. • Responsible for asymmetry; lateral cartilages.
Dorsum Nasi Parts
• The anterior protruding ridge of the nose from the root to the tip of the lobe.
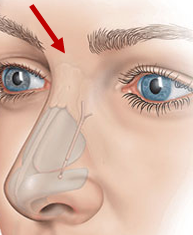
dorsum nasi: root
• The apex (top) of the pyramidal mass of the nose. • Directly inferior of the forehead. • Concave dip inferior to the forehead (profile view).
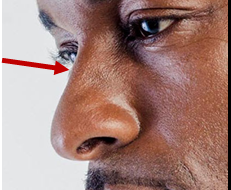
dorsum nasi: bridge
•A raised support. •The arched portion of the nose which is supported by the nasal bones
dorsum nasi: protuding lobe and tip
The rounded, anterior projection of the tip of the nose; tip, the termination of the forward projection of the nose.
Wings of the Nose
Lateral lobes.
Columna Nasi
Fleshy end of septum between nostrils. most inferior part of the nose.
Anterior Nares
External openings of nostrils.
Mouth — Proportions
Width = two eyes; 2/5 face; base of two noses.
Prognathism types (2)
Maxillary prognathism
Mandibular prognathism

Integumentary Lips
Skin portion of lips (upper and lower)
Mucous Membranes
Visible red portion.
Weather Lines
The line of color change at the junction of the wet and dry portions of each mucous membrane; point of lip-adhesive.
Medial Lobe
Prominence on midline of upper lip.
Line of Closure
Five arcs; "hunting bow."
Mouth Restoration
•Support for lips when part or all the teeth are missing.
• Filler
• Mouth former
Swollen Lips — Treatments
Electric spatula; channeling; chemical injection; aspiration; incising; surgical reduction.
electric spatula
An electrically-heated blade used to dry moist tissues, reduce swollen tissues, and restore contour to natural form.
channeling
Creation of dermal and subdermal passageway, through a single entry point in the tissues, in order to allow for the removal of watery fluids and gasses.
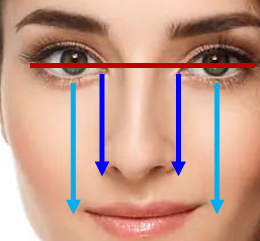
Eye — Proportions
Width = 1/5 face; ½ mouth; width of nose.
Eye Placement
Centered in orbit; inferior to supraorbital margin (red); medial canthi align with nasal wings (blue); vertical plane = mouth ends (celeste)
Eye Parts
Canthi (medial/lateral); cilia (eyelashes); supercilium (eyebrows)
Superior Palpebrum (Left and Right)
•Approximately 3x larger than inferior.
•Slightly wider than inferior.
•Greater projection than inferior.
•When naturally closed, it covers the cornea.
Line of closure
•Palpebrae adjacent but not overlapping.
•2/3 to 1/3 relationship
Eye Restorations
Sunken eyes; swollen eyelids; discoloration; wrinkled/lacerated eyelids; protrusion; separated lids; dehydrated canthus; enucleation care.
Modeling
Constructing a form with pliable material such as wax or clay.
Lip Wax
Soft, tinted, most adhesive; used on mucous membranes and lip separation.
Soft Wax
Very pliable; less adhesive; for razor burns, abrasions, suture incisions, punctures.
Medium Wax
Restorative wax; softer than firm; adheres well; holds shape.
Firm Wax
Most dense; putty-like; fills large cavities; wound filler; used for modeling features.
Coloring Wax
Under-wax (liquid, spray, water-base); mixed with wax (liquid/cream); over-wax (most common).
Softening Wax
Kneading; adding cream cosmetics; petroleum jelly; warm water; blow-dryer.
Firming Wax
Refrigeration; add cornstarch or talcum/pigment powder.
Other Modeling Media
Clay, latex, silicone, plaster of Paris, cotton, collodion.
Prerequisites for Wax Restoration
Firm, dry tissue; moist/unembalmed tissue prevents adhesion.
Firming Tissue Methods
Hypodermic injection; cavity-fluid compress.
Modeling Techniques
Correct feature location/size/form; profile consideration; distance viewing; work in stages; use correct measurements.
Pores
Smooth = negative appearance; poorly simulated = major fault.
Simulating Pores
Stipple brush; moist paper towel; lintless gauze.
Wrinkles/Furrows
Made with blunt instruments, ligature, or thin plastic.
Classification of Cases Requiring Restorative Art
Injury; Disease; Post-mortem tissue changes; Post-embalming changes; Natural age progression.
Incision
A clean cut into tissue or skin.
Discoloration
Any abnormal color in or on the body; may be removed by arterial injection; includes livor mortis (intravascular red-blue due to hypostasis).
Stain
Discoloration caused by external/foreign matter.
Bleaching
Act of lightening a discoloration using chemical bleaching agents.
what are surface Stain Removers?
Agents that remove or lessen external discolorations; includes mortuary solvents, cavity fluid, phenol & alcohol, preservative gel, special bleaching fluid.
First-Degree Burn
Redness of skin caused by heat.
Second-Degree Burn
Acute inflammation and blisters.
Third-Degree Burn
Destruction of cutaneous + subcutaneous tissues; seared/charred tissue.
Fourth-Degree Burn
Total absence of tissue; not appropriate for reconstruction.
Excising
Removal of tissue by cutting; performed pre-embalming or post-embalming.
Decapitation Types
Complete; Partial; Internal (skull base separated from spine).
Decapitation Reattachment (checklist)
Use wood splints/metal rods/spinal canal/foramen magnum; suture; apply mastic, cotton, sealer; wax; cosmetics.
Distention
Abnormal swelling caused by embalming, decomposition, trauma, or pathology.
Types of Distention
Liquid, Solid, Semi-solid, Gaseous.
Distention Treatments
External pressure; wet compress; collar; aspiration; channeling; incisions.
Desquamation (Skin Slip)
Separation of epidermis from dermis.
Causes Before Death (desquamation)
Excess heat/cold, radioactive agents, chemicals, kidney failure, edema.
Causes After Death (desquamation)
Decomposition
After Embalming Causes (desquamation)
Weak solution, inadequate volume/distribution.
Simple (Closed) Fracture
Bone broken but does not pierce skin.
Compound (Open) Fracture
Bone pierces the skin; always requires treatment.
Fracture Treatment – Simple
May require before & after embalming restoration.
Fracture Treatment – Compound
Attention needed for jagged bone, leakage, distorted features, vascular disruption, trauma.
Hair Restoration – Preparation
Trim; shampoo; rinse; style; correct direction/density.
where can you get hair from?
Endogenous, hairpieces, salons, camel-hair brush bristles.
Attachment Methods (hair)
Imbedding (wax, needle fork), cementing (adhesive), or covering (scarf, hat, bandage, etc.).
Facial Hair Areas
Sideburns, eyebrows, eyelashes, moustache, beard.
Equipment (Hypodermic Tissue Building)
Syringe (various types/sizes; Luer-Lok), needles (5/4–3 in; 16–24 gauge; beveled)
Cautions (hypodermic tissue building)
Always post-embalming; avoid altering expression; better too little than too much.
technique (hypodermic tissue building)
Concealed site; inject while withdrawing; radiate needle; compress; assess.
Common Points of Entry (tissue building)
Eyes, temples, nose, cheeks, lips, ears, forehead, neck, hands.
Cranial Autopsy Treatment
Brain preparation; fill cavity with putty-material, embalming powder, cotton.
Ligature Types
Waxed or unwaxed.
Needle Types
Postmortem double-curved; 3/8 curved; half curved; back curved.
Type of suture and ligature is determined by
• Location of the wound
• Size of the wound
• Purpose of the suture
Baseball Stitch
Strong closure; made from beneath; tighten after each stitch.
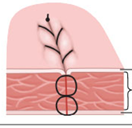
Draw Stitch
Draws incision edges together; ligature exposed.
