Chapter 2: Energy and the First Law of Thermodynamics
energy can be stored within systems in three forms: internal energy, kinetic energy, and gravitaional potential energy
energy can be transferred to and from closed systems only by work and heat transfer
energy transfer by heat to and from a system is due to a temperature difference between the system and its surroundings
types of heat transfer
conduction - transfer of energy from more energetic particles of a substance to adjacent less energetic particles
radiation - energy transported by electromagnetic waves (does not need contact)
convection - energy transfer between a solid surface at a temperature and and adjacent gas or liquid at another temperature
sign conventions for work and heat transfer

First law of thermodynamics - energy is conserved
energy balance
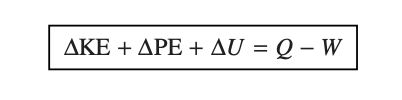
energy rate balance
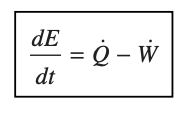
Key Terms and Concepts
internal energy - all other energy of a system which is not related to position (potential) or motion (kinetic)
adiabatic process - a system undergoes a process involving no heat transfer with its surroundings
heat and energy are not properties (not only reliant on the initial and final states of a process)
thermodynamic cycle - a sequence of processes that begins and ends at the same state