carbohydrates
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
macromolecules pt. 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is the difference between an anomer and an epimer?
An anomer differs at the anomeric carbon, while an epimer differs at only one position.
What are monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides have at least three carbons with the formula CH2On and hold an aldehyde or ketone.
What is the structure of glucose?
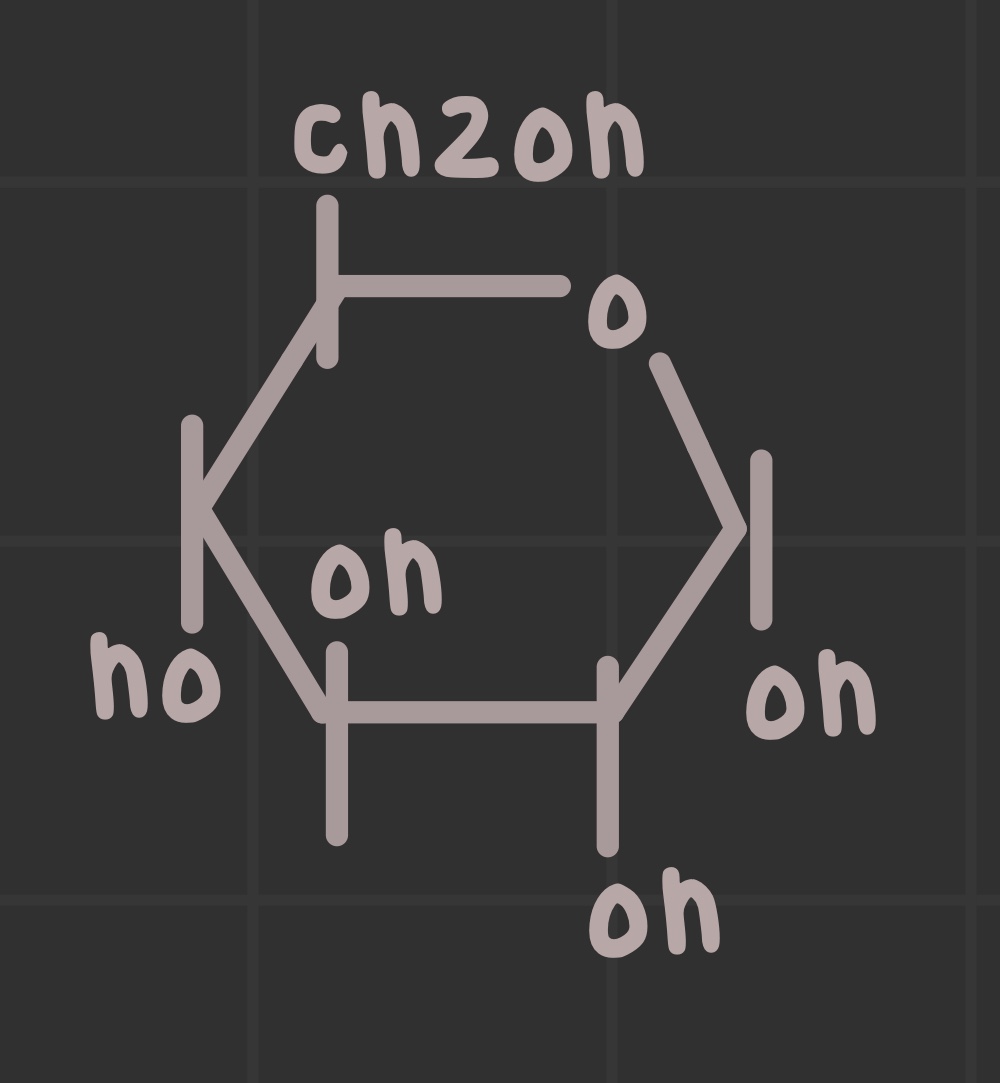
What is the structure of galactose?
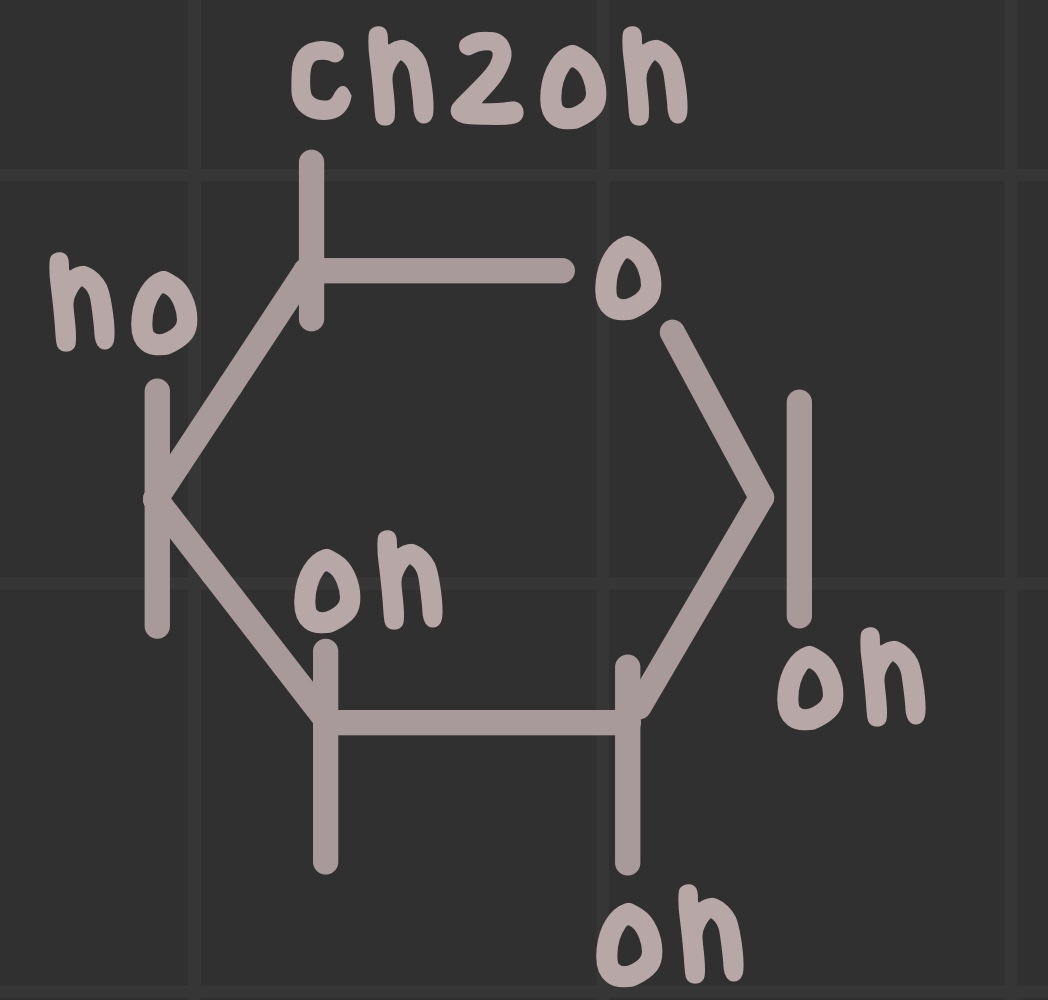
What is the structure of mannose?
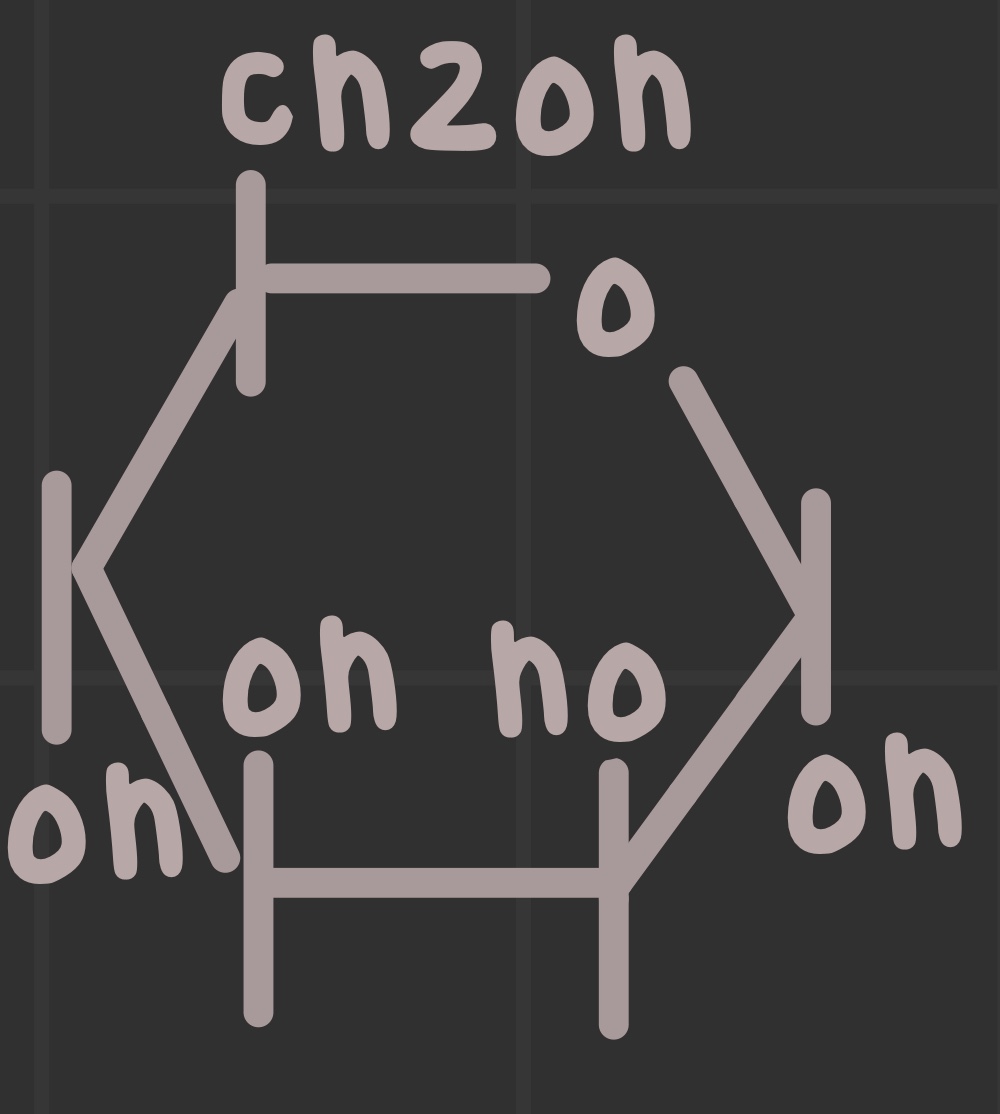
What is the structure of fructose?
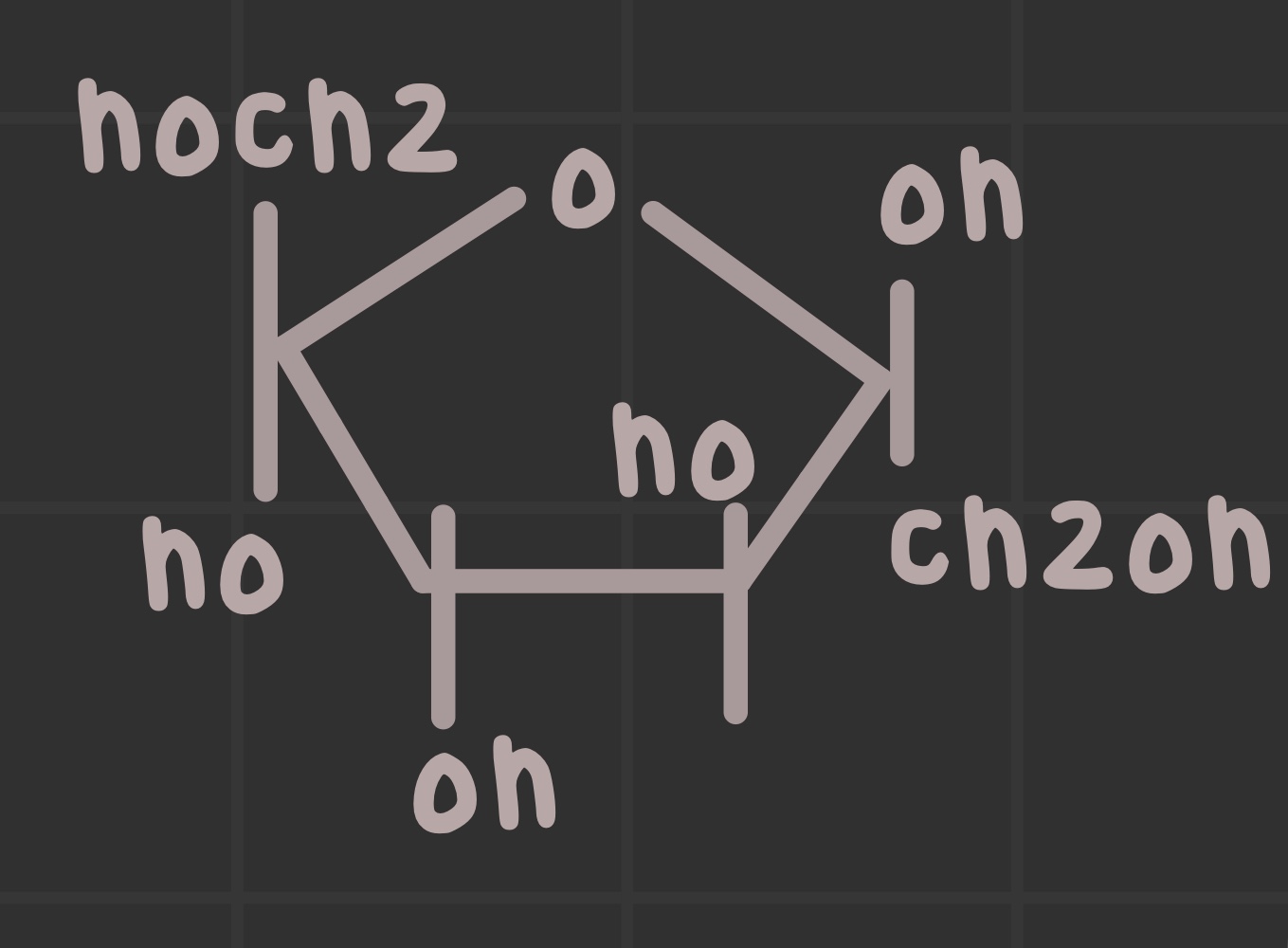
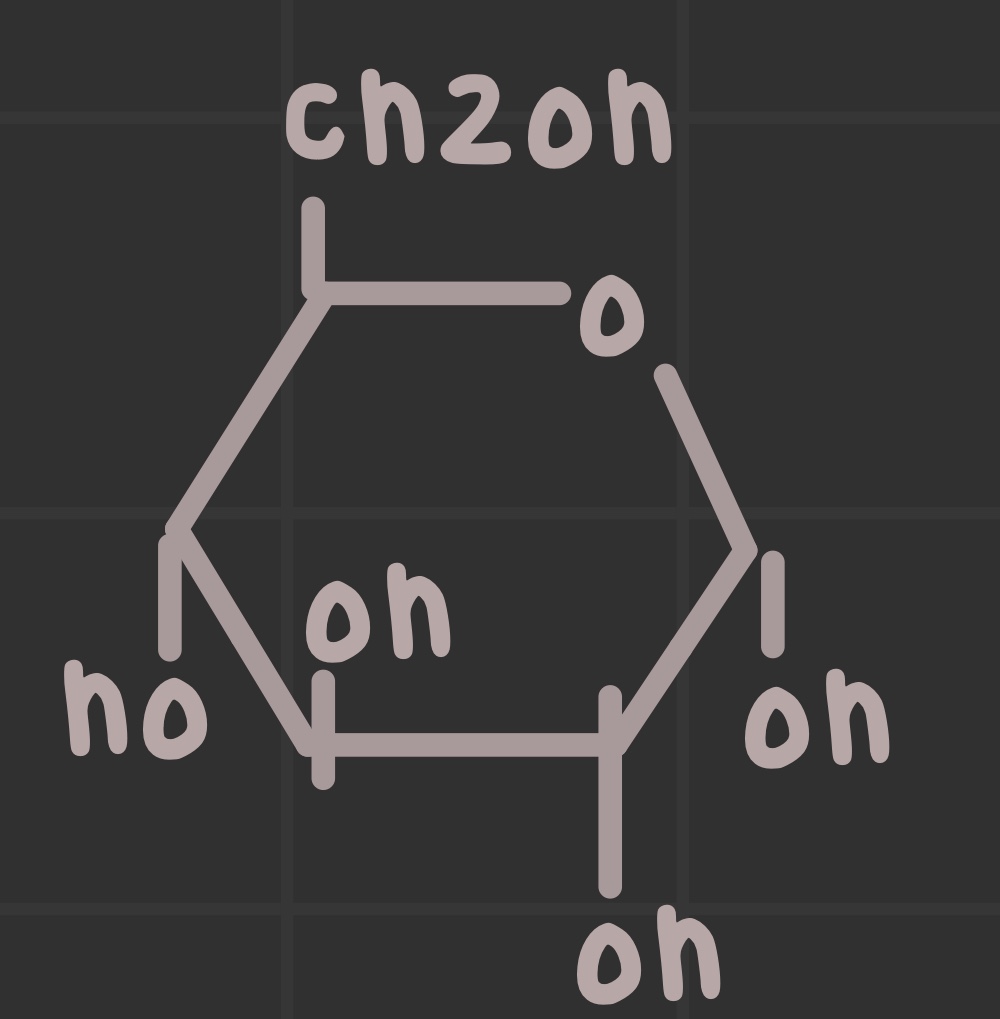
What is an anomeric carbon?
The carbon with two bonds to oxygen; it is the aldehyde or ketone in the linear form.
Identify where the anomeric carbon is.

What are aldolases?
Monosaccharides with an aldehyde; their anomeric carbon is C1.
What are ketoses?
Monosaccharides with a ketone; their anomeric carbon is C2.
What is a furanose?
A five-membered ring monosaccharide (e.g., ribose and fructose).
What is a pyranose?
A six-membered ring monosaccharide (e.g., glucose, galactose, and mannose).
What are deoxysugars?
Sugars where a hydroxyl group is replaced by a hydrogen via a redox reaction.
What are aldonic sugars?
Sugars that form via aldehyde oxidation on the aldose anomeric carbon.
What are amino sugars?
Sugars where a hydroxyl group on a monosaccharide is replaced with an amino group.
How is sugar configuration determined?
Based on the second to last carbon on the linear structure.
What are D sugars?
Sugars with an R absolute configuration at the last chiral center.
What are L sugars?
Sugars with an S absolute configuration at the last chiral center.
What is mutarotation?
Cyclic interconverting between a chiral and achiral form.
What two forms arise from mutarotation?
a- and b-anomers (isomers).
a-anomer arises from an upward attack, the b-anomer arises from a below attack
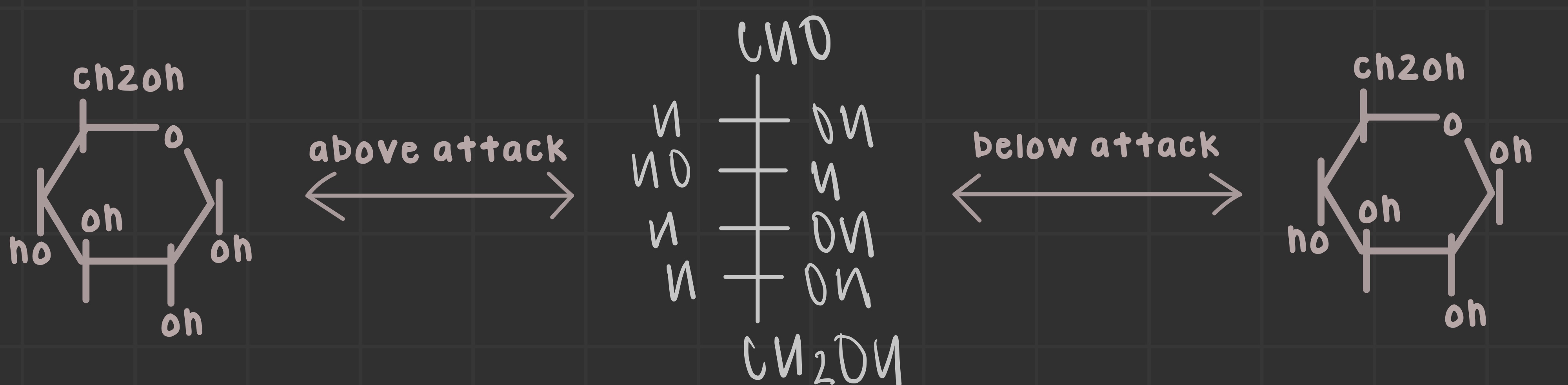
What is an alpha anomer?
Functional groups are trans to each other; points down on Haworth projection (dash).
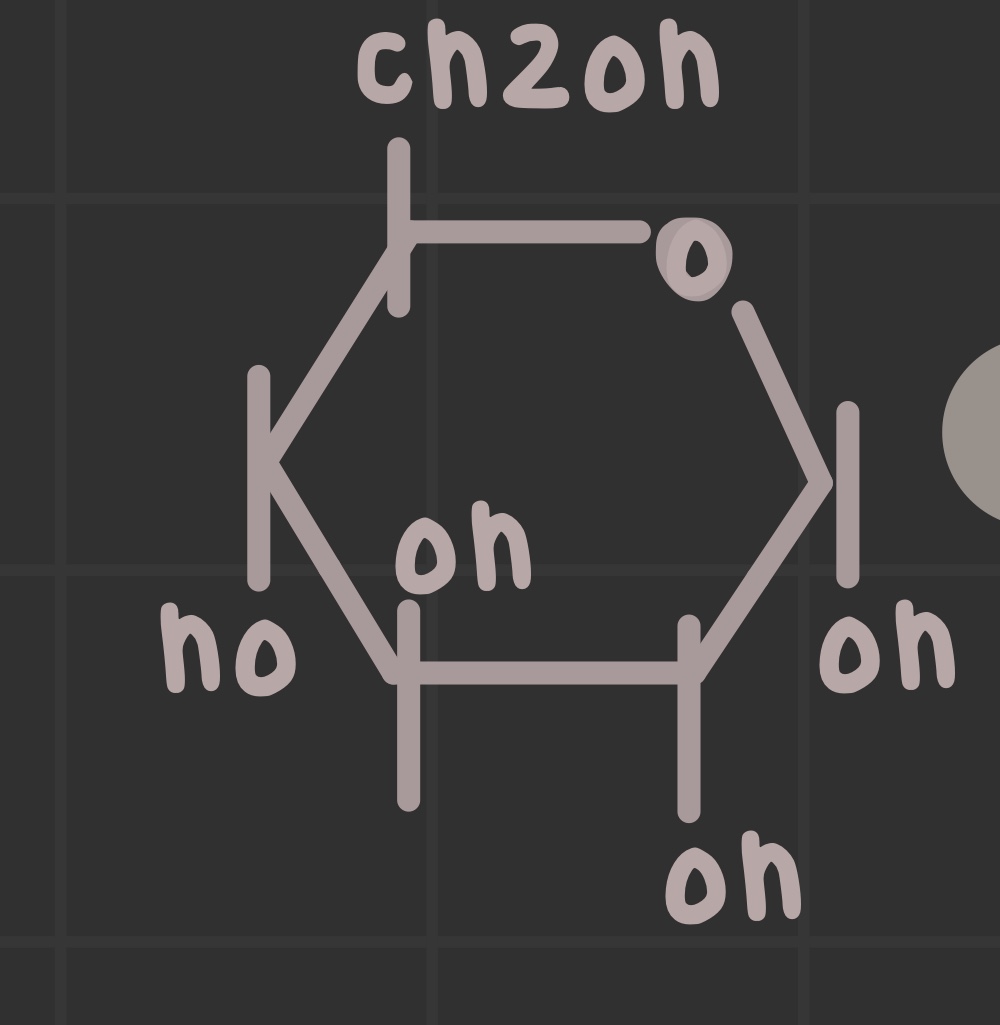
What is a reducing sugar?
A sugar with free anomeric carbons that can reduce silver ions to silver metals.
What is a beta anomer?
Functional groups are cis to each other; points up on Haworth projection (wedge).
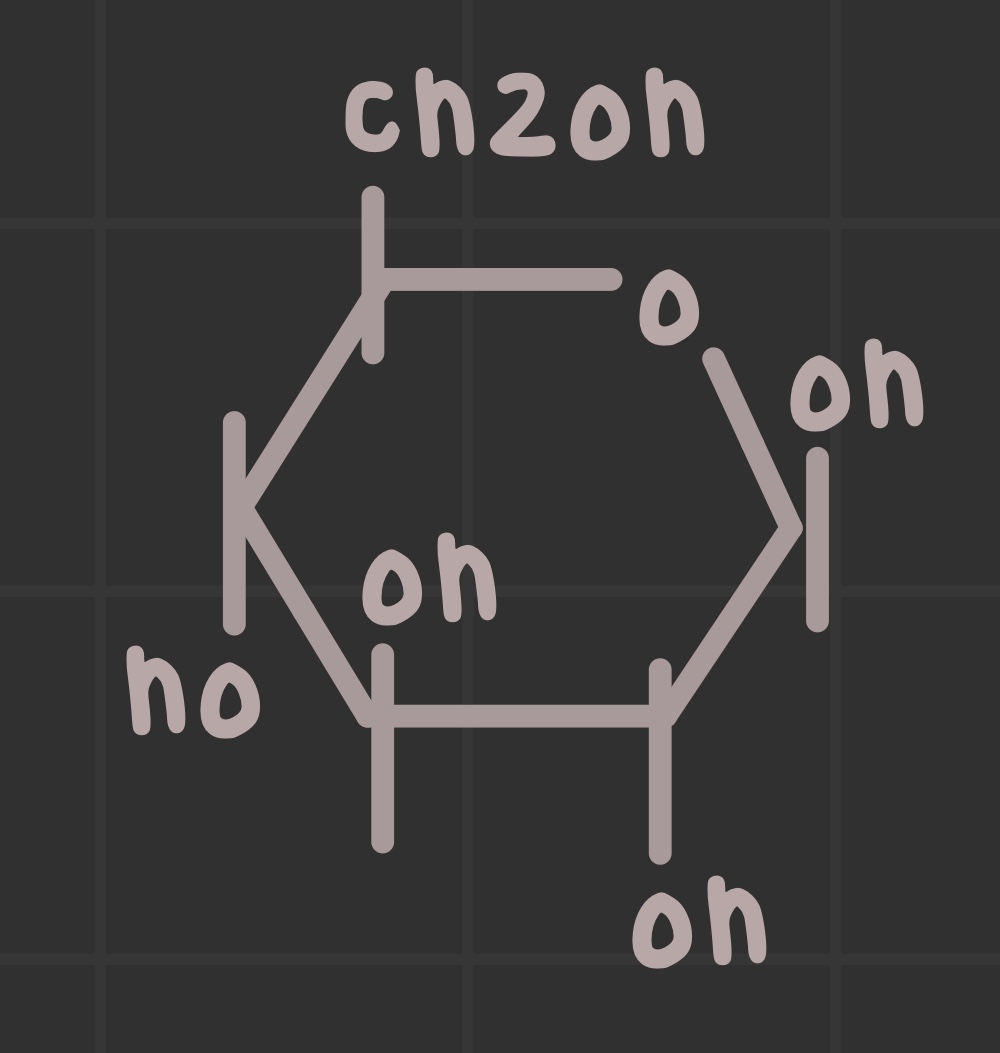
What are glycosidic bonds?
Links the anomeric carbon of a carbohydrate and the nucleophilic atom of another molecule.
How are glycosidic bonds formed?
Via a reversible condensation reaction.
How are glycosidic bonds broken?
Via a reversible hydrolysis reaction.
What is cellulose?
Glucose linked by β-1,4 glycosidic bonds in plant cell walls.
What are disaccharides?
Two monosaccharides linked via a glycosidic bond (CH2On-1).
Describe the formation of disaccharides
They form when the hemiacetal/hemiketal carbon of one monosaccharide condenses with a hydroxyl group on the other.
What are polysaccharides?
Multiple monosaccharides; decrease glucose molarity and total cellular molarity.
What is amylose?
The simplest starch with α-1,4 glycosidic bonds; it is broken down into maltose, which can be further degraded to glucose.
What is amylopectin?
Has α-1,4 glycosidic linkages and α-1,6 branches (~25 units); used by plants and has a reducing end.
What is glycogenin?
A protein that links glycogen chains by a glycogen bond to tyrosine.
What happens when a hemiacetal/hemiketal is converted to an acetal/ketal?
It cannot linearize or mutarotate.
What is starch?
The simplest glucose polysaccharide.
What is glycogen?
Animal storage with α-1,4 glycosidic linkages and α-1,6 branch points; it lacks a reducing end for glucose addition/removal.
What is aldose reduction?
The aldehyde group of a linear monosaccharide donates electrons to silver ions, and the aldehyde becomes a carbohydrate.
What is ketose reduction?
Acts as a reducing sugar since they tautomerize into aldoses; unable to be further oxidized.
What is a reducing end?
The end that terminates with an anomeric carbon.
What is a nonreducing sugar?
A carbohydrate that lacks anomeric carbons (sucrose).
What is a nonreducing end?
The end that has no free anomeric carbons.
What is maltose?
A disaccharide sugar composed of two glucose units in an a-1,4 linkage
Identify the structure of maltose.
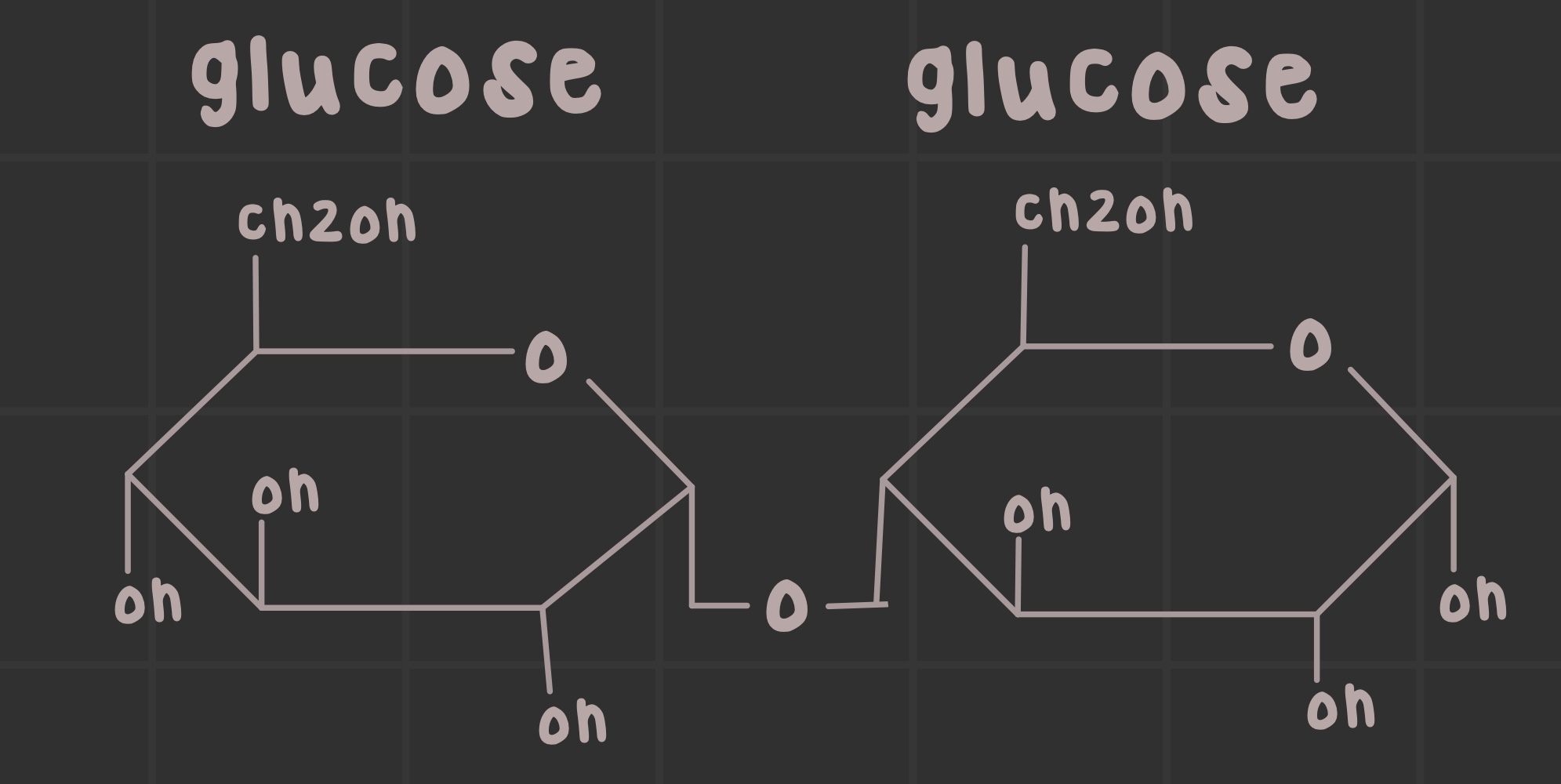
What is sucrose?
A disaccharide formed by an a-1,2 linkage of glucose and fructose
Identify the structure of sucrose.
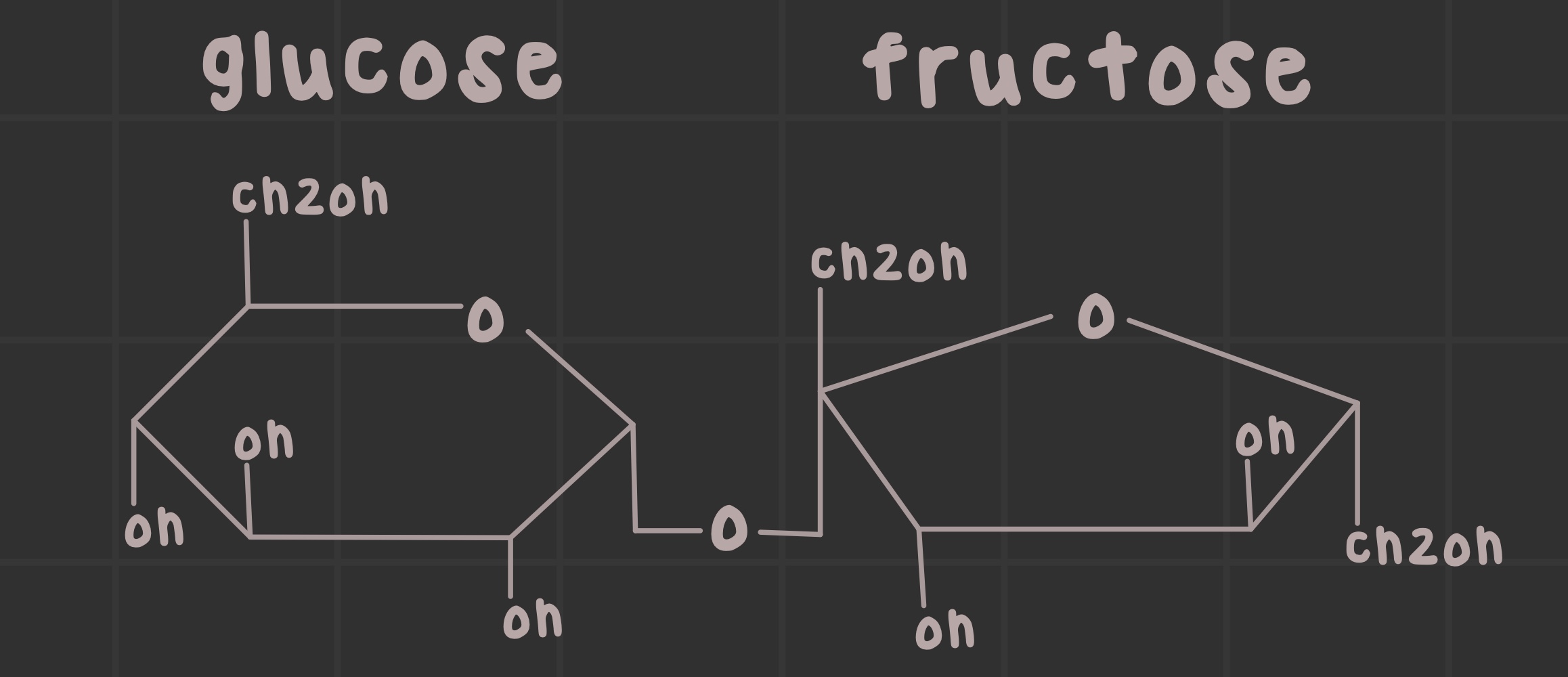
What is lactose?
A disaccharide formed by a b-1,4 linkage of galactose and glucose
Identify the structure of lactose.
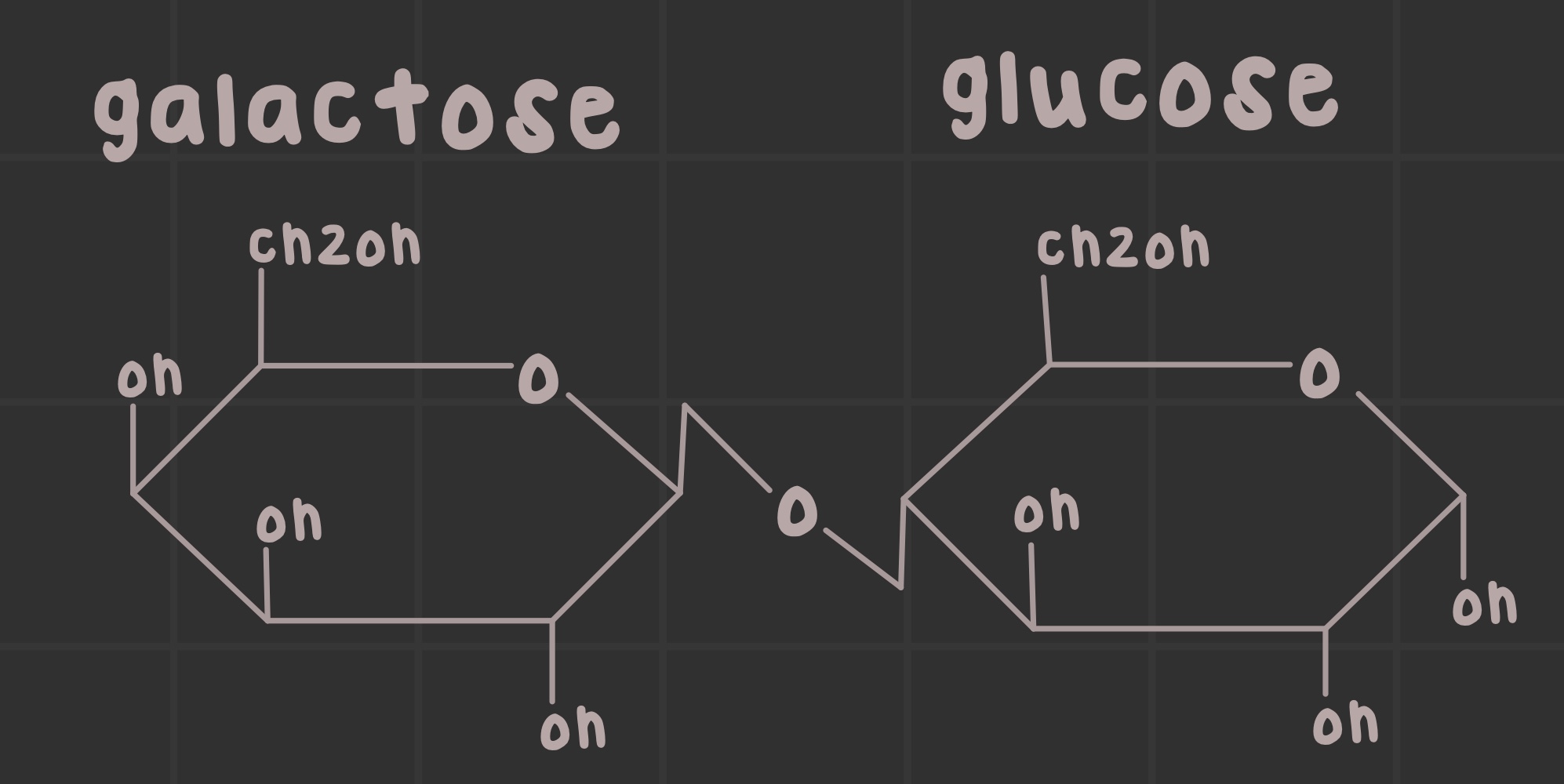
What is the tollen’s test?
A chemical test that distinguishes between reducing and non-reducing sugars by producing a silver ion when a reducing sugar, such as glucose, is oxidized.