Esri ArcGIS Pro Foundation Certification 2025
1/242
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Contains all material throughout the entire learning course of Esri ArcGIS Pro Foundation Certification 2025 training
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
243 Terms
What is created by default when making a new project?
Geodatabase, maps, styles, toolboxes, and layouts
What are The ArcGIS Pro user interface three main components?
ribbon, views, and dockable panes
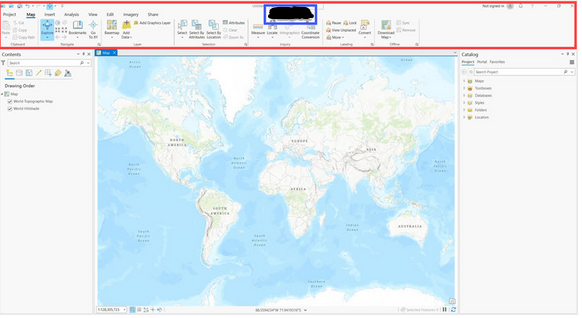
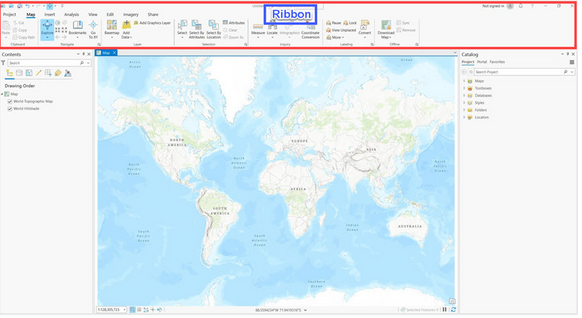
What is inside the red outline?
Ribbon
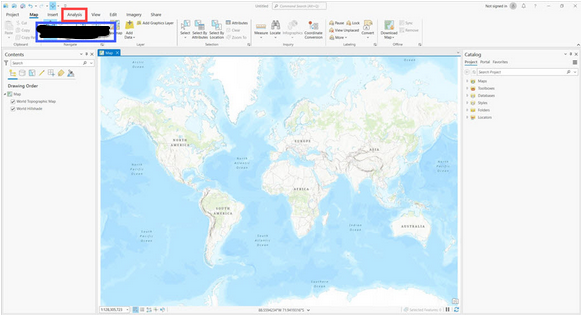
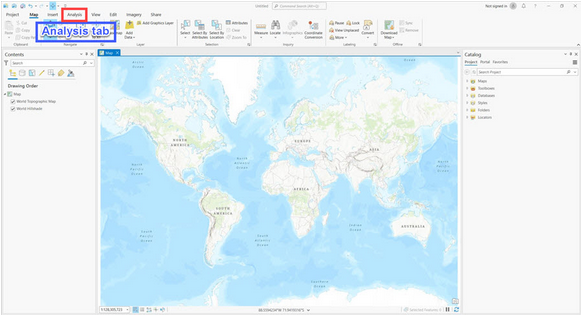
What is inside the red outline?
Tab
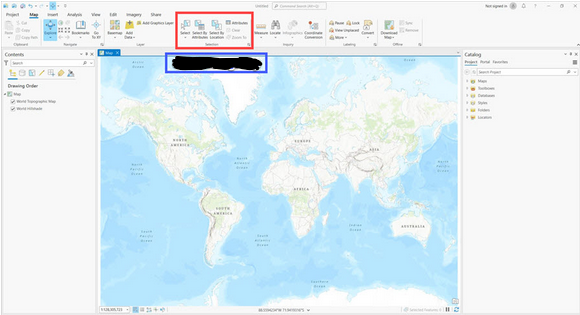
What is inside the red outline?
Group
What is inside the red outline?
Tool
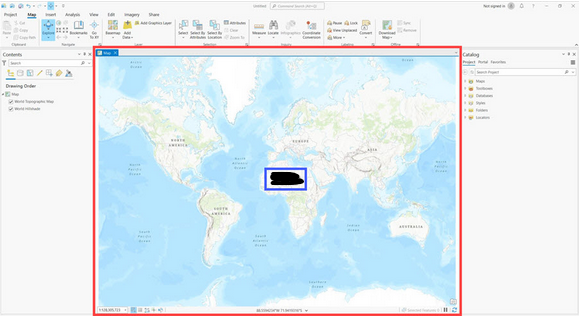
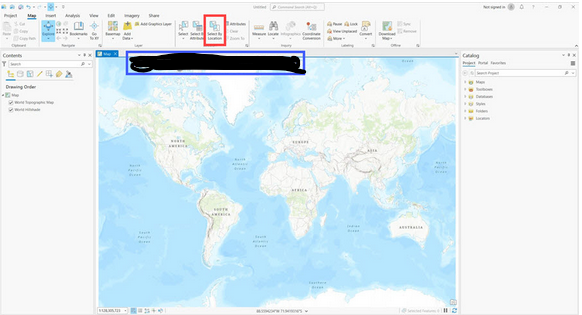
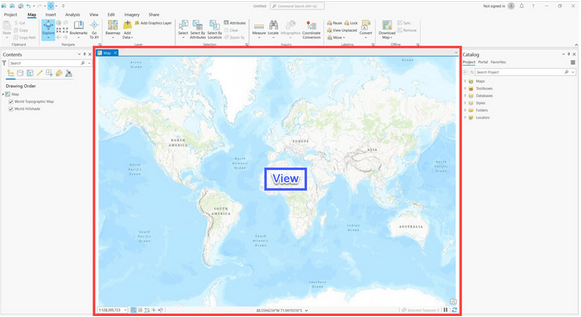
What is inside the red outline?
View
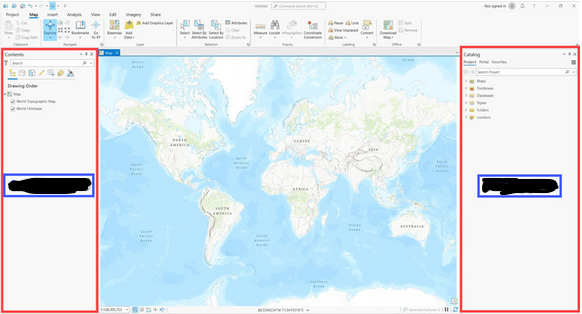
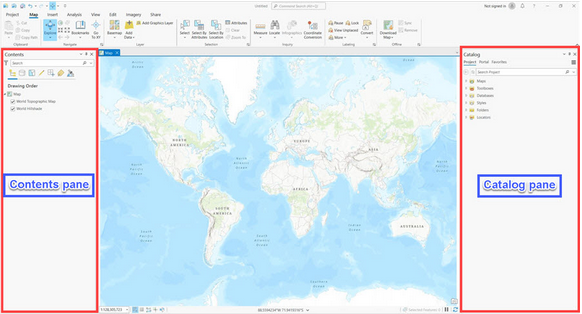
What is inside the red outline?
Contents Pane and Catalog Pane
Which two statements best describe ArcGIS Pro capabilities?
-Create 2D and 3D maps to visualize data.
-Perform link analysis to highlight connections in the data.
-View a dashboard that allows you to monitor data in real-time.
-Use artificial intelligence to recognize complex patterns.
Create 2D and 3D maps to visualize data & Use artificial intelligence to recognize complex patterns
Which element of the ArcGIS Pro user interface displays the contents of the active view?
Contents pane
Which option would be the best choice to view all the features of a specific layer on your map?
In the Contents pane, right-click the layer and choose Zoom To Layer.
Which statement best describes how to share a web layer in ArcGIS Pro?
Right-click the layer in the Contents pane
What is the difference between sharing as a “web layer” and sharing as a “web map”
Sharing as a web map contains data layers and basemaps while sharing as a web layer will only contain the data layers
What are packages used to share?
Contents of a map, project, or layer
What is the shape of the earth?
Oblate ellipsoid
Is the earth surface symmetrical?
No
Geographic coordinate systems
uses a three-dimensional spheroidal model to identify points or areas on the surface of the earth using a network of intersecting lines of latitude (parallels) and longitude (meridians) called the graticule.
Projected coordinate systems
transforms locations from the spheroidal earth to a flat map (converts latitude and longitude coordinates to planar coordinates (X,Y))
Which two statements best describe why maps need coordinate systems?
-Coordinate systems help accurately match a location on the earth with a location on a map.
-Coordinate systems help accurately translate longitudes into y-values and latitudes into x-values.
--No matter which coordinate system you use, a specific location on the earth will have the same coordinate values.
-Coordinate systems ensure that geographic information is placed accurately on a map.
-Coordinate systems help accurately match a location on the earth with a location on a map. -Coordinate systems ensure that geographic information is placed accurately on a map.
Which two statements accurately define the types of coordinate systems that are used in a GIS?
-A geographic coordinate system converts locations from the spheroidal earth to a flat map based on a projected coordinate system.
-A projected coordinate system uses a 3D spheroidal model to identify locations on the surface of the earth.
-A geographic coordinate system uses a 3D spheroidal model to identify locations on the surface of the earth.
-A projected coordinate system converts locations from the spheroidal earth to a flat map based on a geographic coordinate system.
-A geographic coordinate system uses a 3D spheroidal model to identify locations on the surface of the earth. -A projected coordinate system converts locations from the spheroidal earth to a flat map based on a geographic coordinate system.
At which scale do differences in spheroids generally become visible?
1:5,000,000
Which two statements best explain why multiple spheroids are used to model the shape of the earth?
-Different spheroids provide refined accuracy for different regions of the earth due to deviations in the earth's shape.
-The earth’s symmetry allows for the use of multiple spheroids, which allows increased accuracy to model the earth’s shape.
-When a more accurate spheroid has been realized, all spatial geodatabases are updated to model the earth’s shape.
-Over time, improvements in measuring the earth result in spheroids with greater accuracy to model the earth’s shape.
-Different spheroids provide refined accuracy for different regions of the earth due to deviations in the earth's shape. -Over time, improvements in measuring the earth result in spheroids with greater accuracy to model the earth’s shape.
graticule
The imaginary grid created from the intersecting lines of latitude and longitude drawn onto globes
How are latitude and longitude measured?
angles measured from the earth's center to a point on the earth's surface commonly in degrees
prime meridian
zero value for longitude
equator
zero value for latitude
spheroid
the mathematical model that estimates the size and shape of the earth.
datum
defines the position of the spheroid relative to the center of the earth and provides a frame of reference for measuring locations on the surface of the earth.
Local Datum
a spheroid that is only accurate at a specific location where it aligns with the earths surface
To create a map to compare global data, which type of spatial reference should be used?
Earth-centered datum
What option best describes the impact of using multiple geographic coordinate systems?
Using multiple geographic coordinate systems contributes to data misalignment.
Using multiple geographic coordinate systems in a GIS project contributes to greater accuracy when using coordinate data from multiple countries.
Using multiple geographic coordinate systems helps improve data alignment.
Using multiple geographic coordinate systems in a GIS project helps more accurately display the area of interest.
Using multiple geographic coordinate systems contributes to data misalignment.
Which three statements about geographic coordinate systems are true?
A geographic coordinate system's coordinates are based on latitude and longitude values.
A geographic coordinate system uses a three-dimensional spheroidal model to identify specific locations on the earth.
A geographic coordinate system gives linear measurements on a planar surface from a predefined starting point.
A geographic coordinate system's coordinates are measured in linear units, such as feet or meters.
A geographic coordinate system is represented by a graticule of intersecting parallels (latitude) and meridians (longitude).
A geographic coordinate system's coordinates are based on latitude and longitude values.
A geographic coordinate system uses a three-dimensional spheroidal model to identify specific locations on the earth.
A geographic coordinate system is represented by a graticule of intersecting parallels (latitude) and meridians (longitude).
Which two statements explain why geographic coordinate systems provide a foundation for GIS functionality?
The presence of a geographic coordinate system is necessary for your GIS to properly interpret coordinate values.
The purpose of a geographic coordinate system is to identify a location on the globe using linear measurements.
A geographic coordinate system enables your GIS to accurately display spatial data on a map.
The presence of a geographic coordinate system is necessary for your GIS to store coordinate values in an attribute table.
The presence of a geographic coordinate system is necessary for your GIS to properly interpret coordinate values.
A geographic coordinate system enables your GIS to accurately display spatial data on a map.
What causes the difference between projected types?
Their projected surface
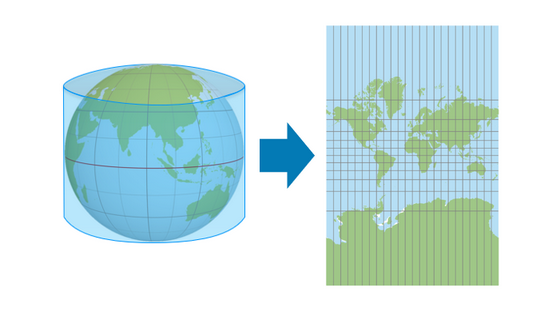
cylindrical projections
represent meridians as straight, evenly spaced, vertical lines; they represent parallels as straight, horizontal lines. Meridians and parallels intersect at right angles, as they do on the globe.
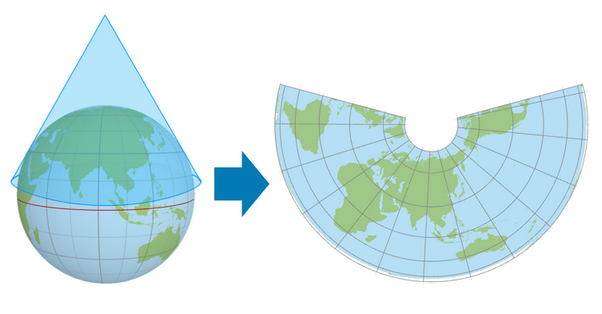
Conic projections
A projection that contacts the globe along a single latitude line called the standard parallel. In general, distortion increases north and south of the standard parallel.
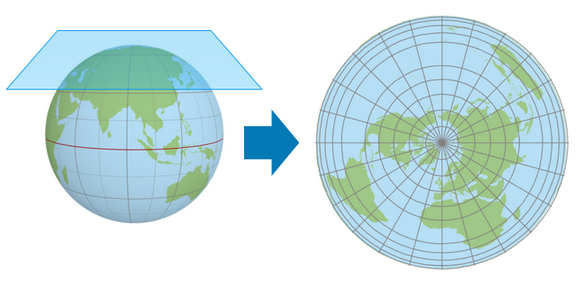
Azimuthal projections
A map projection where a point is tangent to the globe with longitude lines radiating outward from said point. Latitude lines appear as a series of concentric circles (most often map the polar regions).
what projection type should you use when your map area extends north–south
cylindrical projection
what projection type should you use when your map area extends east–west
conic projection
what projection type should you use when your map has equal extent in all directions
azimuthal projection
Every projection type causes distortion in a minimum of how many map properties?
Two
What are the four map properties that at least two will be distorted in every projection?
shape, area, distance, or direction
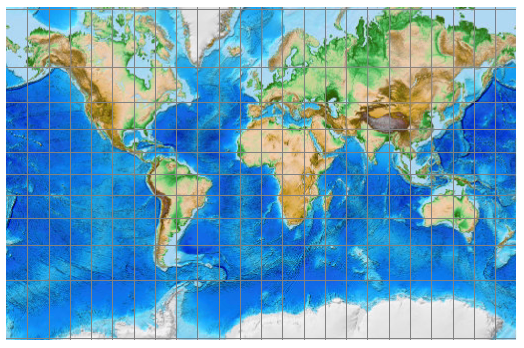
what does Conformal projections preserve and distort?
preserve shape but not area
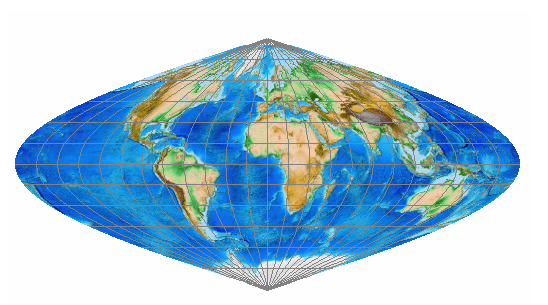
what does Equal-area projections preserve and distort?
preserve area but not shape
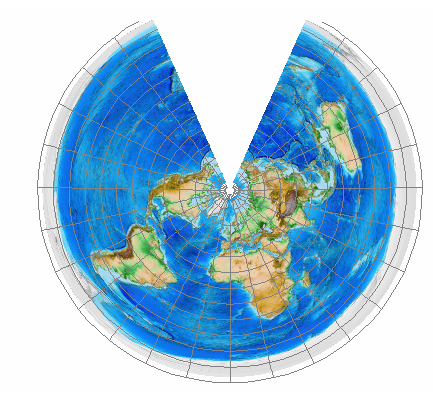
what does Equidistant projections preserve and distort?
preserve true scale between one or two points to every other point on the map, or along every meridian. there is no shape, area, or scale distortion along the standard parallels, however the further away from these standard parallels, the greater the distortion.
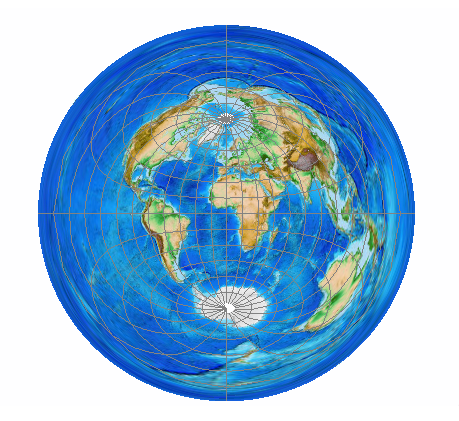
what does Azimuthal projections preserve and distort?
preserve direction from one or two points to every other point.
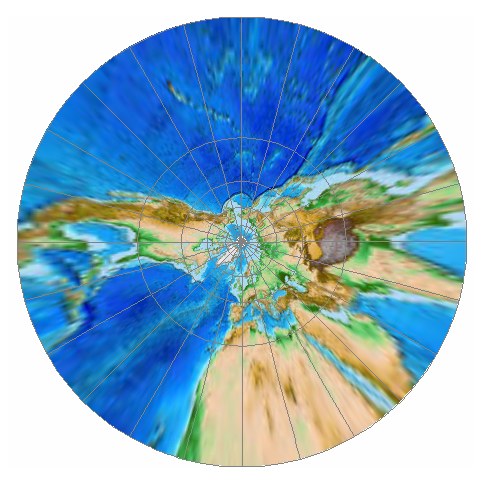
what does Gnomonic projections preserve and distort?
preserve the shortest route (distance and direction) but cannot preserve area
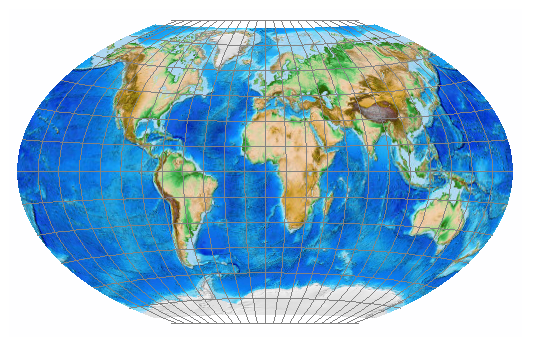
what does Compromise projections preserve and distort?
Preserve none but distorts all slightly
Which two statements about projected coordinate systems are true?
A projected coordinate system gives linear measurements on a planar surface from a predefined starting point.
A projected coordinate system is represented by a graticule of intersecting parallels (latitude) and meridians (longitude).
A projected coordinate system's coordinates are measured in linear units, such as feet or meters.
A projected coordinate system uses a three-dimensional spheroidal model to identify specific locations on the earth.
A projected coordinate system gives linear measurements on a planar surface from a predefined starting point.
A projected coordinate system's coordinates are measured in linear units, such as feet or meters.
To create a map that has minimal distortion but does not perfectly preserve any of the four spatial properties, which type of projection should be used?
Compromise
What three surfaces are developable surfaces for creating map projections?
Cylinder, cone, plane
To create a map for measuring how much total land is part of a national park, which spatial property should be preserved?
Area
Which two statements identify map distortions introduced by projections?
Projections introduce distortions to at least two properties of a map: shape, area distance, or direction.
Projections preserve at minimum the shape and area while distorting other properties of the map.
Projections preserve at minimum two map properties of either shape, area, distance, or direction.
Projections introduce distortions to some areas of the map while preserving map properties in other parts of the map.
Projections introduce distortions to at least two properties of a map: shape, area distance, or direction.
Projections introduce distortions to some areas of the map while preserving map properties in other parts of the map.
geocoding
transforms a location's description (coordinates, an address, a place-name, or other attribute) onto the earth's surface, as represented by map
What is input data?
data you are trying to place on a map
What are the two geocoding types?
Location descriptions and tables with multiple plottatble points
reference data
geometry and attributes used to locate a feature
The quality of the geocoding results depends on what?
the quality of the input and reference data.
Locators
tools that use reference data to place input data on a map, you can create or use an existing published
What is meant by geocoding?
Transforming a location into location description attributes
Transforming a location description into a location on the earth's surface
Finding a location using a map
Locating a feature through spatial analysis
Transforming a location description into a location on the earth's surface
Which two scenarios are examples of when enabling location on nonspatial data would be important?
Following an analysis workflow on crime density using a crime incident locations feature class
Identifying where houses are located in relation to waste facilities using street address data
Analyzing nonspatial relationships such as income-to-debt ratios using a spreadsheet
Answering questions involving median income in different locations using tabular data
Identifying where houses are located in relation to waste facilities using street address data
Answering questions involving median income in different locations using tabular data
True or False? Geocoding can be used to map the location of a local fitness club with only street address data.
true
Which two attributes could be used when applying the place-name method to enable location on nonspatial data?
Category field
Coordinates field
Description field
Title field
Description field
Title field
three main components of geocoding
input data, a locator, and reference data
What does Input data contain?
contains the location description and is provided by the user.
locator
a tool that ties the location descriptions in the input data to geographic coordinates to place features on a map
reference data
Data the locator finds matches between the input data and places features on a map.
three main types of locators
free, paid, local (created by you)
What would be changed in order to specify how a locator would identify location?
Components
composite locator
locator made of other locators (instead of a table of reference data)
What does having different types of reference data allow you to do?
Provide different input fields to the user
Which item do you need to create a locator for geocoding?
Reference data
What is meant by the address component called street type?
The street suffix, such as Avenue or Boulevard
Which method is the best way to get accurate search results from your address locator?
Have the most precise reference and input data
To create a place-name locator, which attribute is needed?
Reference data with a name field
If a locator provides multiple results, which action would help locate the correct feature on a map?
Use an attribute query
Which of these examples is not a place that could be located on a map by its name?
Pine Avenue and Main Street
The location of a feature that has a street address will also have Name as an attribute, appropriate for a place-name locator.
False
Which sources are used to create a composite locator?
Other locators
Coordinate data
a value or pair of values that denotes the location of a feature on the earth (x,y)
How is x,y data used to locate a feature on a map?
The x value represents the east-west location and the y value represents the north-south location.
attribute table
provides descriptive information about the features
feature
the location of an object on a map
object identifiers
unique ID for each row in an attribute table
Short and Long field types represent what?
whole numbers
Float and Double field types represent what?
decimal numbers
attribute query
query features based on their attributes
Attribute query operator
the measurement that you will use to query a selection of features (less than, equal to, includes values, etc.)
Vector data is composed of
points, lines, and polygons (geometry and attributes)
Raster data is composed of
grids of cells
Metadata
specific information describing data that makes it easier to search for and discover
Complete metadata typically indicates that
the source data or content is high quality
Attribute Table Domains
constrain valid values for a particular field to a set
Attribute Table Subtypes
subset of features that share the same attributes (automatically set attribute value)
Topology
Connectedness, adjacency, and proximity between features
Archiving data
allows you to record and access changes to data
Which three statements describe common editing tasks with spatial data?
Modify an existing feature.
Create a new feature.
Delete a feature.
How is location identified in a GIS?
x,y coordinates
When people say that metadata is "data about data," what do they mean?
Metadata is data that describes data.
With GIS data, which format is appropriate for recording a geographic location?
42.944, -122.172