OCR Gateway A GCSE Physics: P3 Electricity
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Charge
A property of something which experiences a force when placed in an electric field
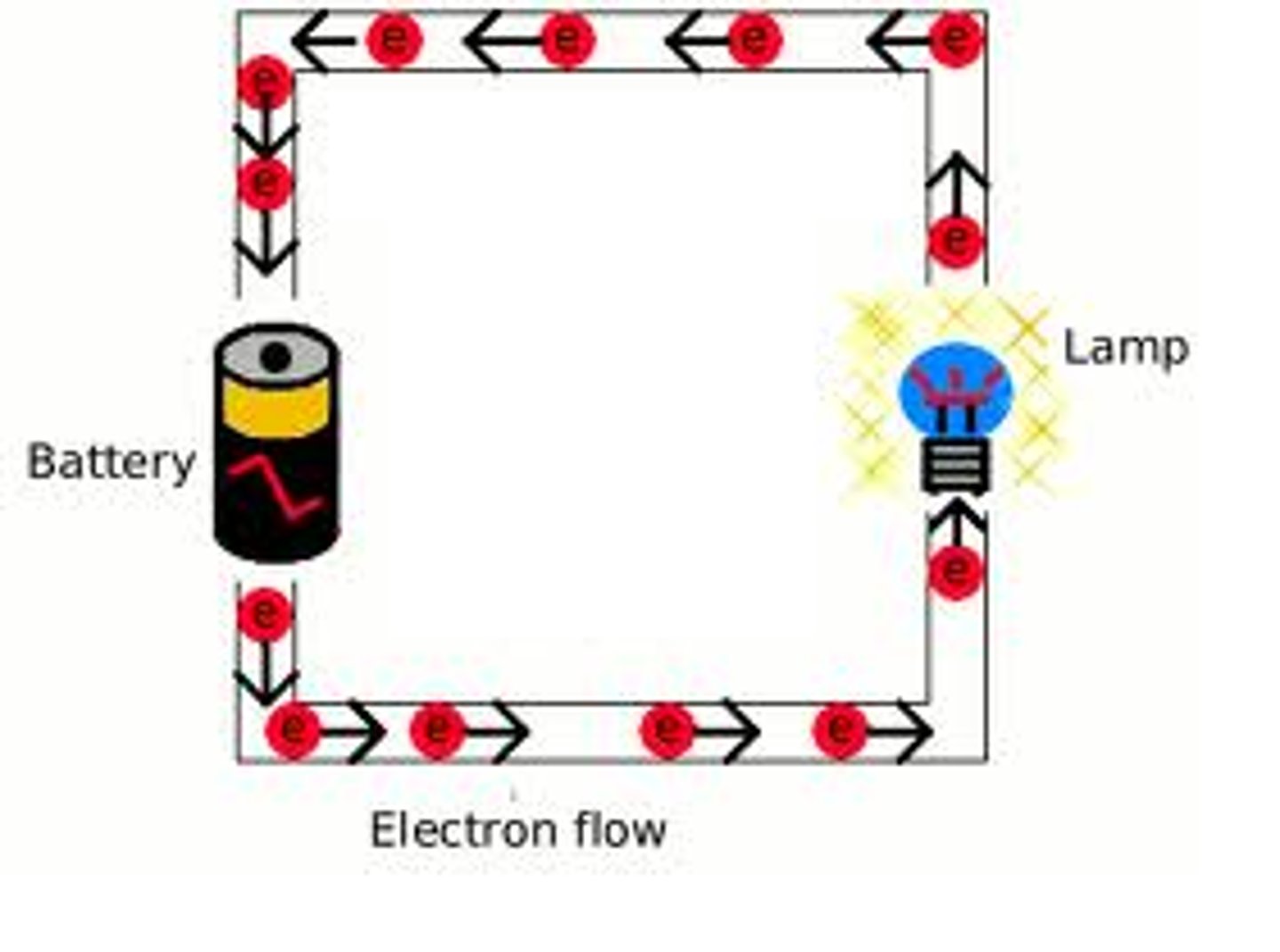
Electrons
Negatively charged particles that transfer energy through wires

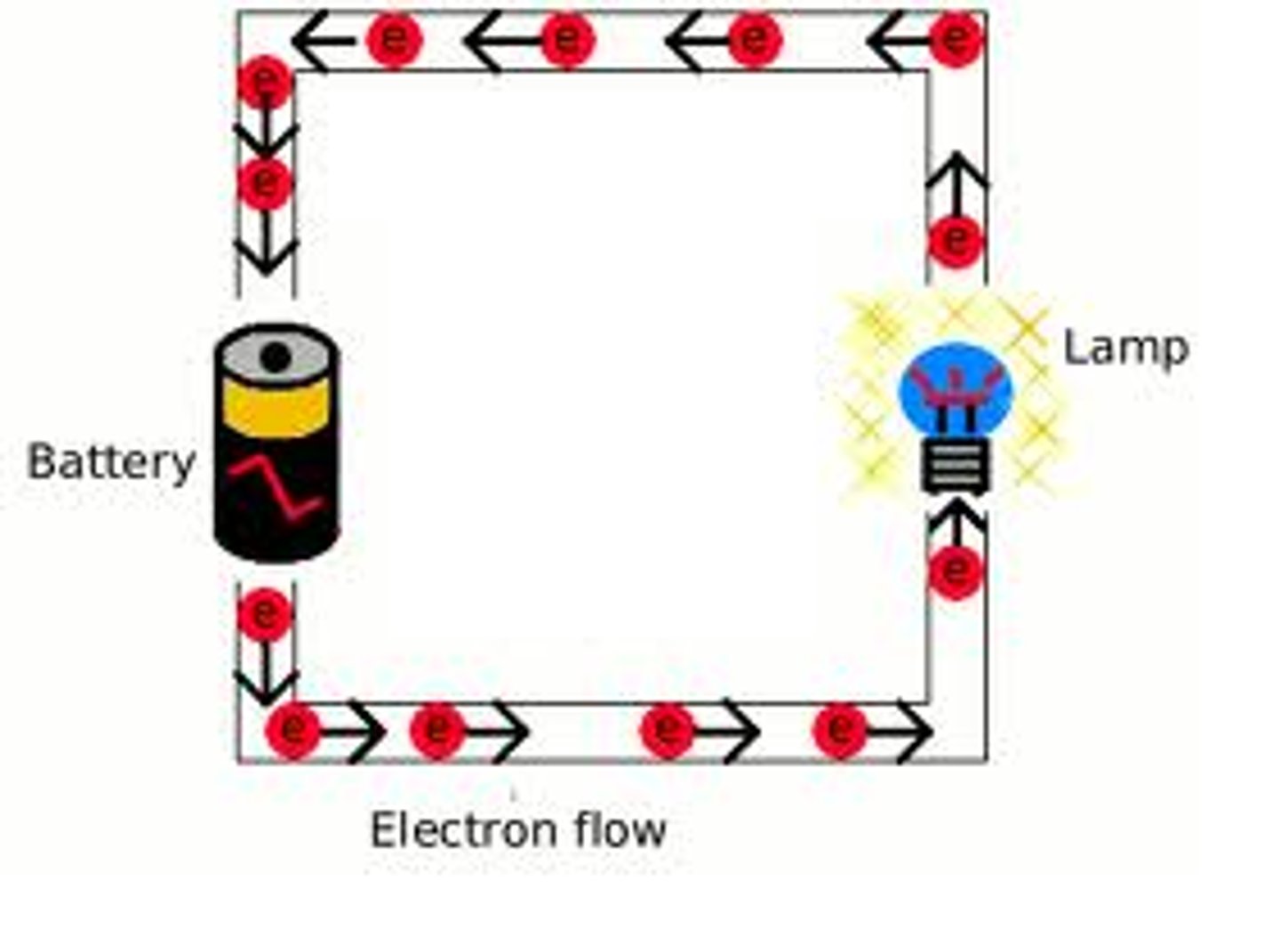
Current
The rate of flow of electric charge (electrons) around a circuit
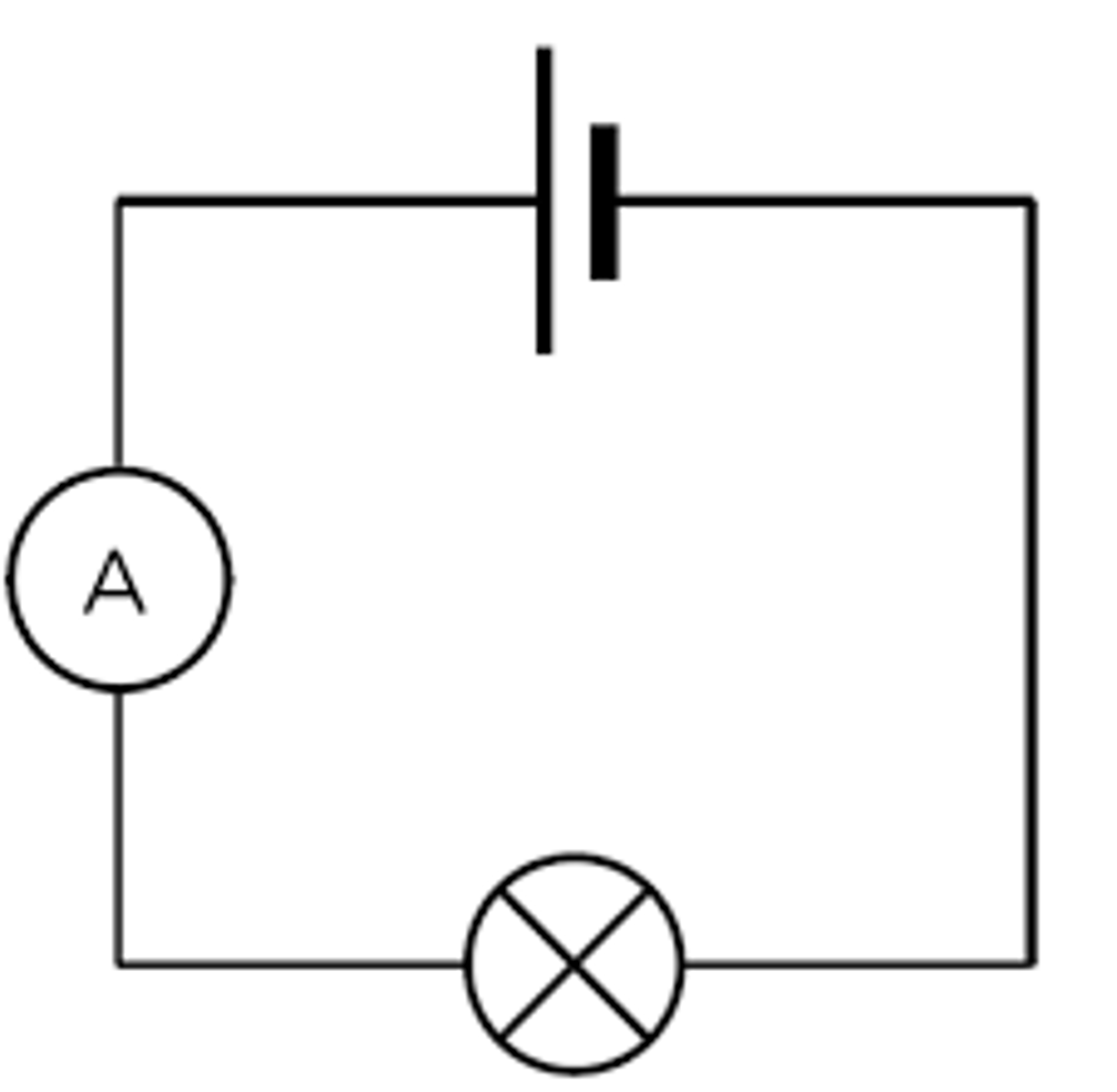
Ammeter (uses, ____ a component)
A device used to measure current through a component (must be placed in series with that component)
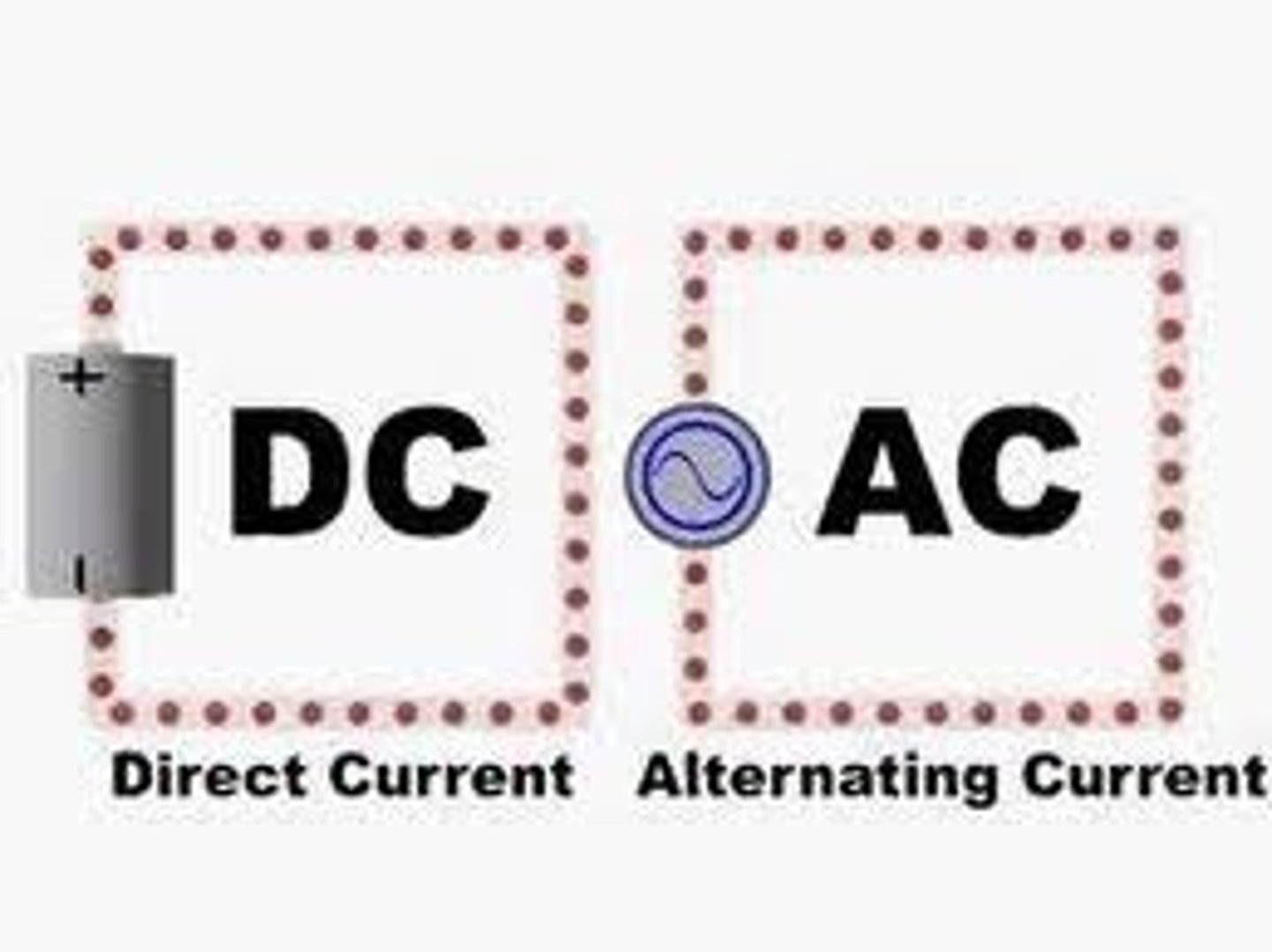
Direct current (dc)
An electric current which flows consistently in one direction around a circuit
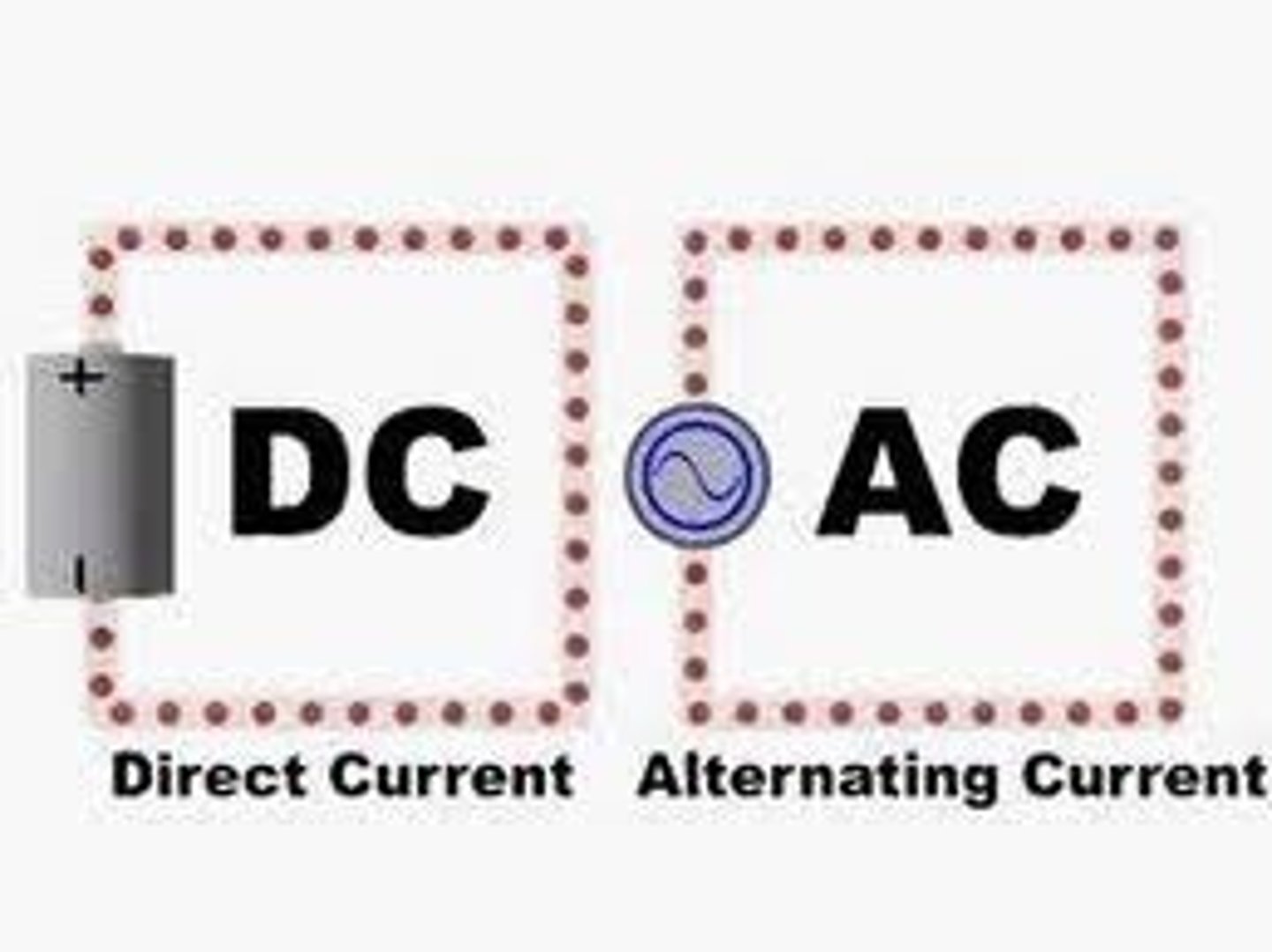
Alternating current (ac)
An electric current that continually reverses direction and changes size
Q = It
The equation linking charge flow, current and time
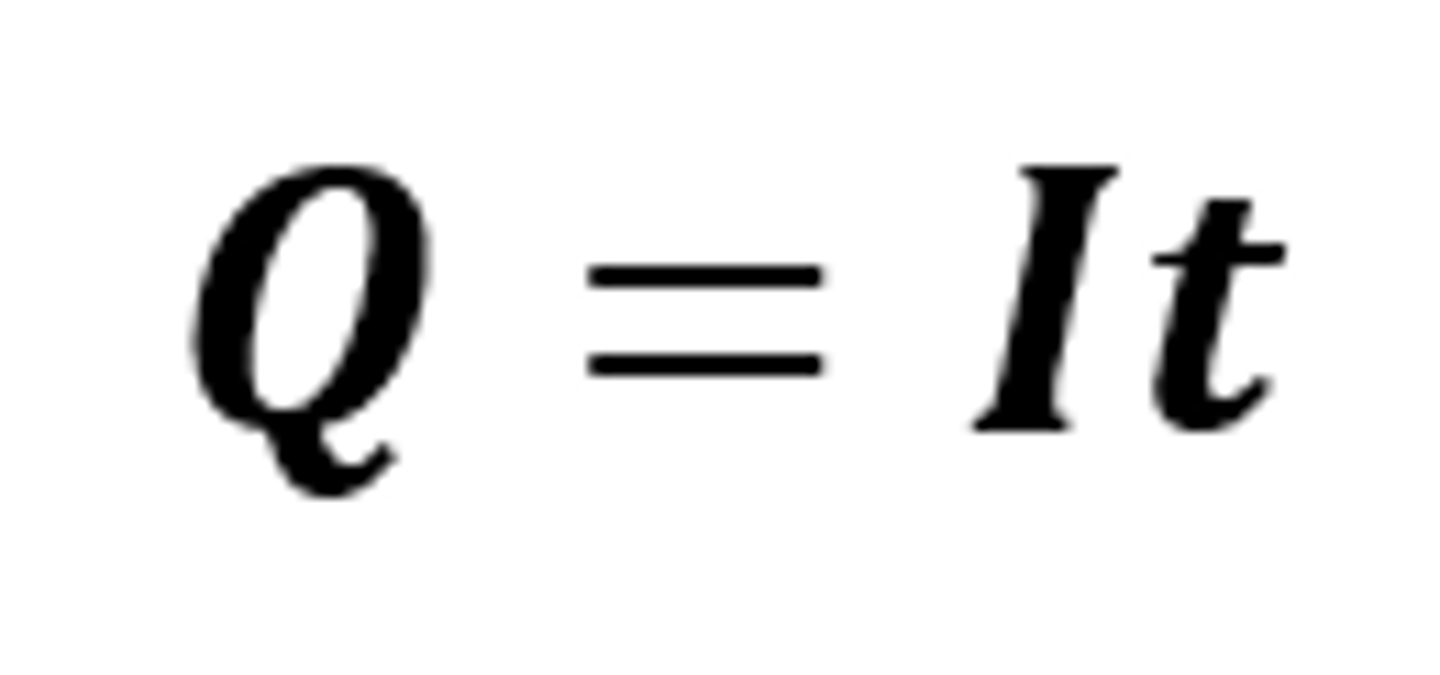
Q
The symbol for charge flow
I
The symbol for current
t
The symbol for time
Amps/amperes (A)
The SI unit for current

Coulombs (C)
The SI unit for charge flow

Seconds (s)
The SI unit for time

Series circuit
A circuit where electrical components are connected one after another in a single loop (a circuit that only has one path for the current to flow through)
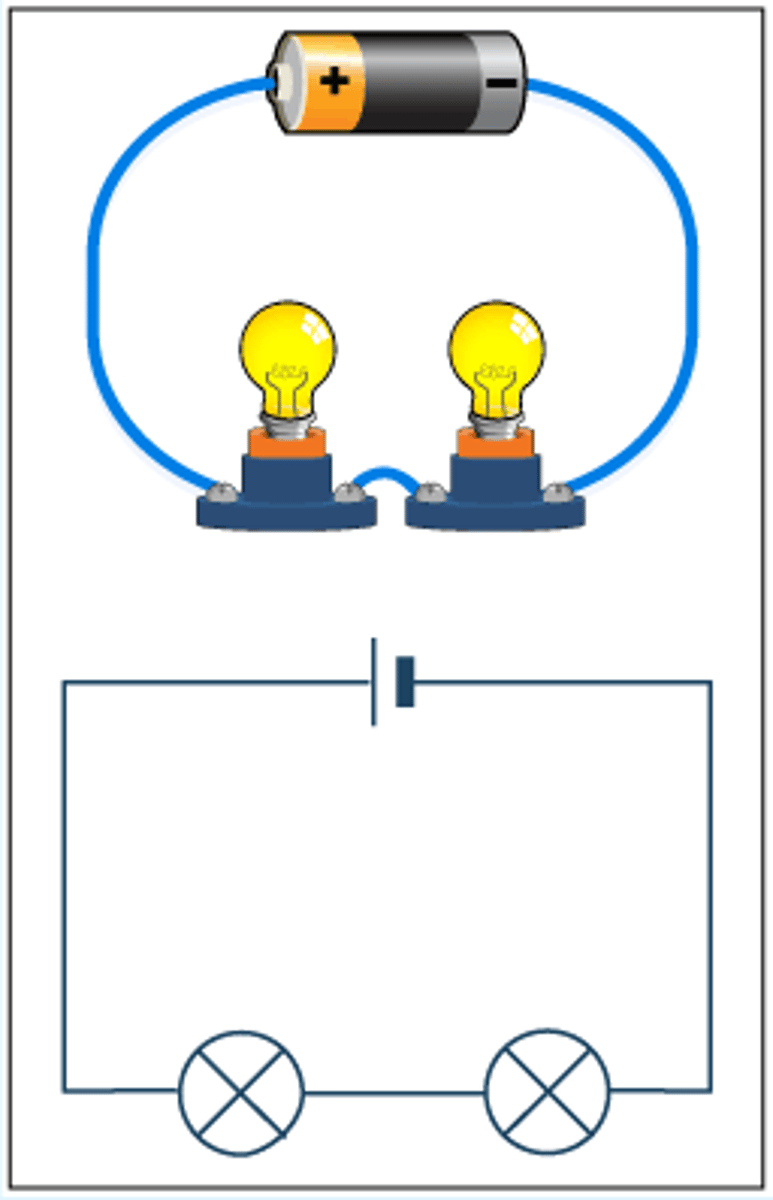
What happens when one component breaks in a series circuit?
The current will not be able to flow round the circuit; if one component breaks, then all of the other components stop working
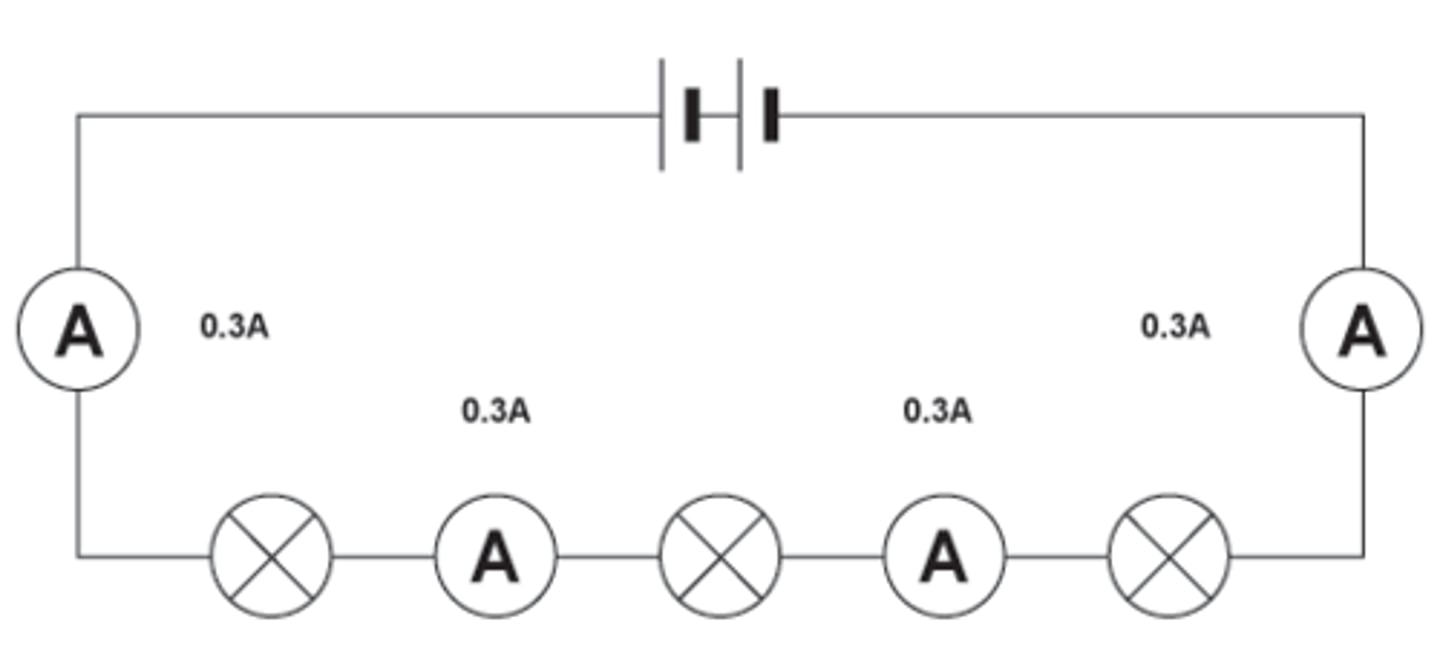
Rule for current in series
The same current passes through each component connected in series
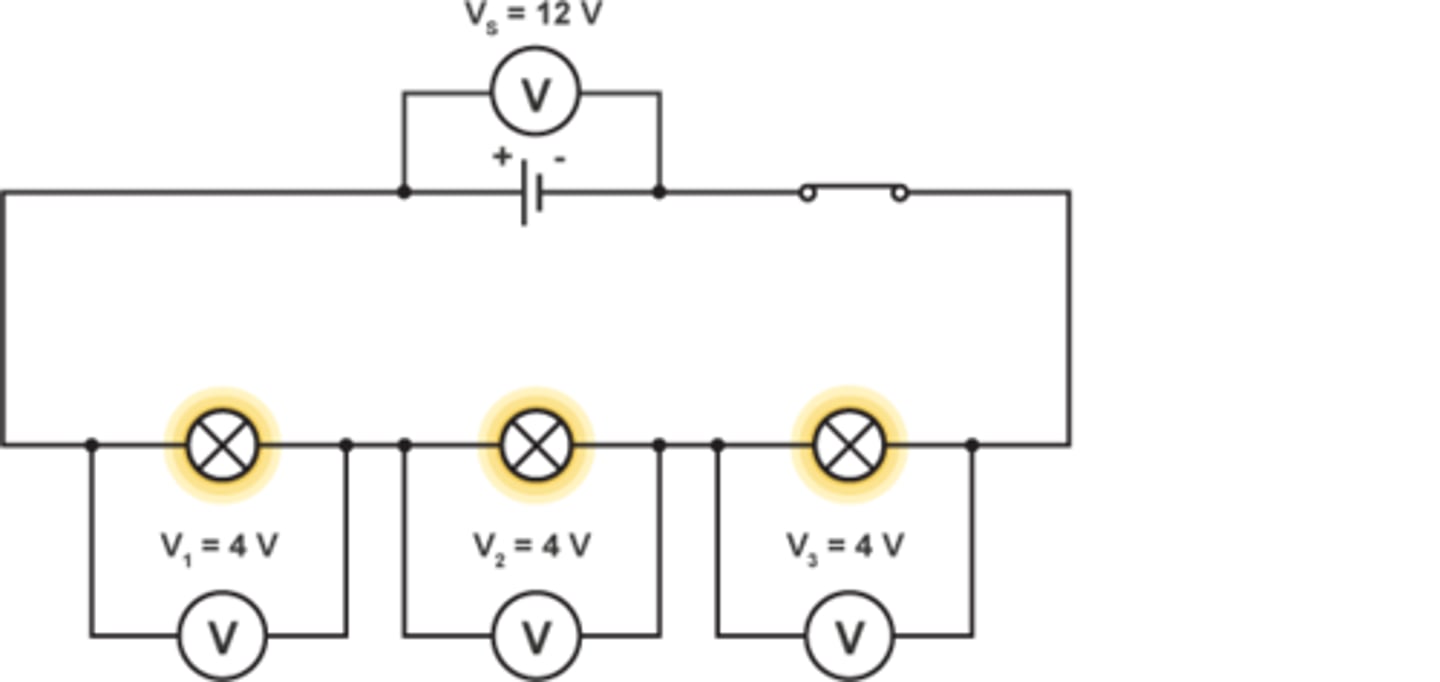
Rule for potential difference in series
The total potential difference of the power supply is shared between components connected in series
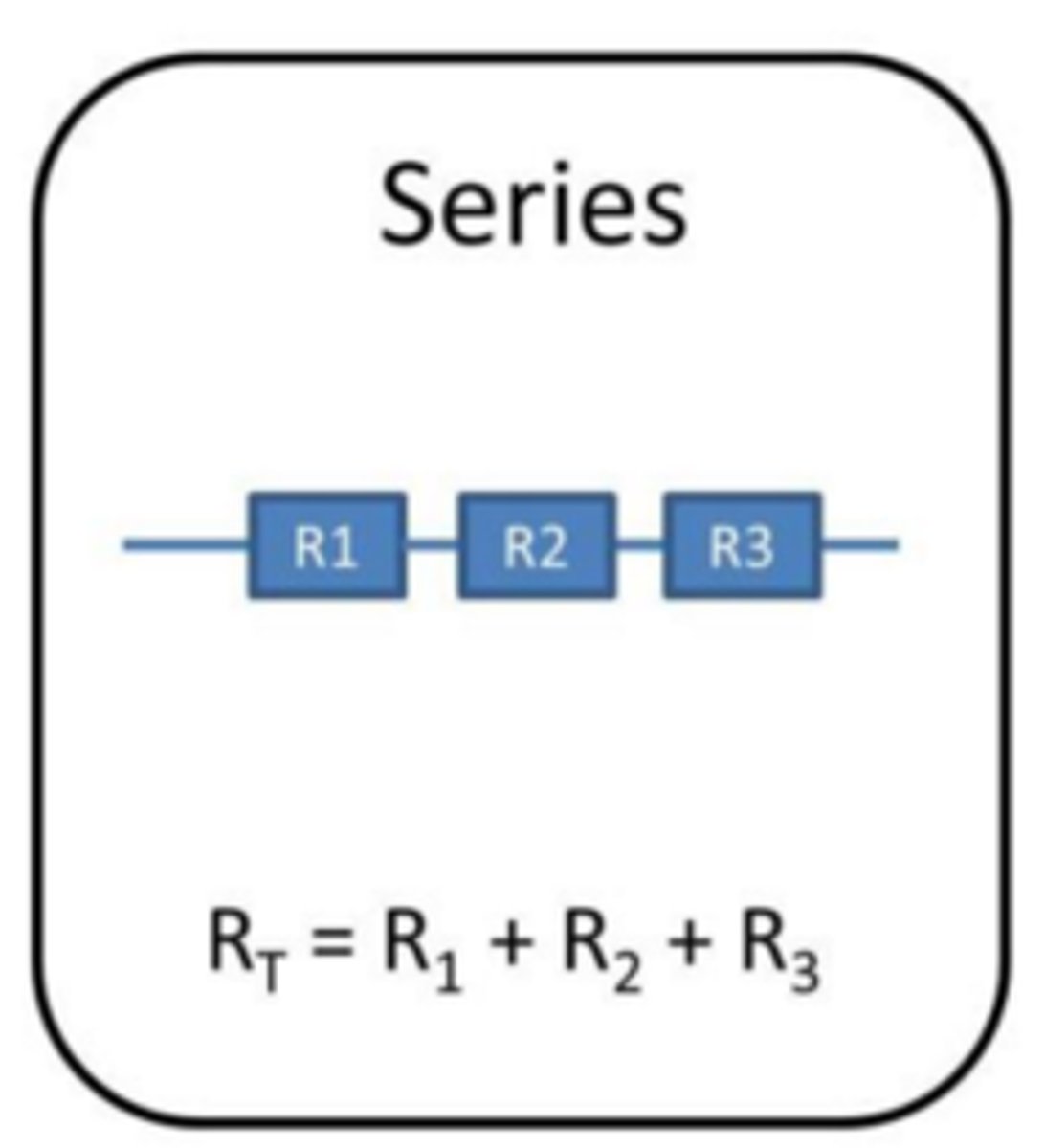
Rule for resistance in series
The total resistance of two components connected in series is the sum of the resistance of each component
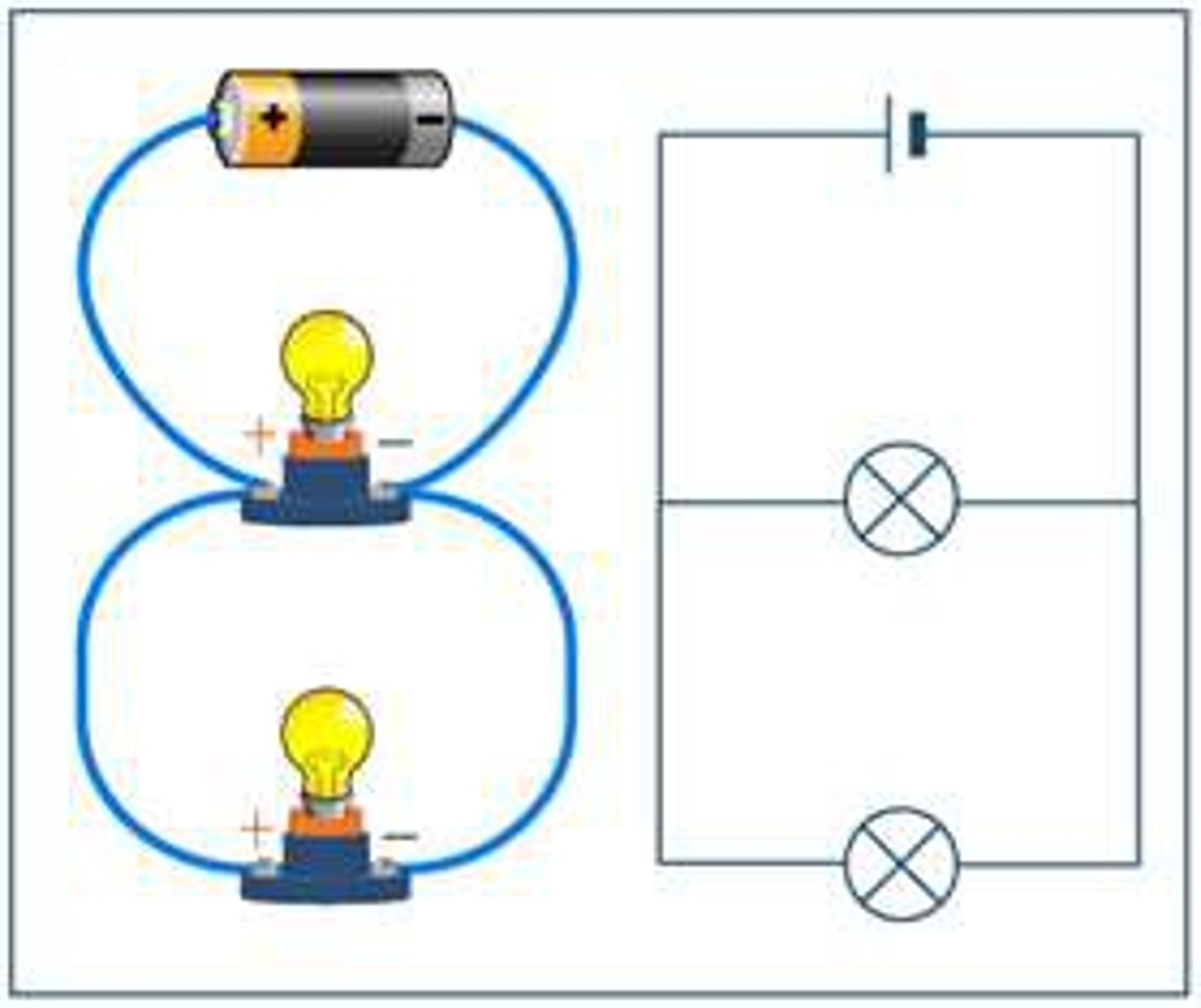
Parallel circuit
a circuit that has multiple paths for the current to flow through
What happens if one component breaks in a parallel circuit?
The current can still flow round the circuit through one of the other paths; if one component breaks, the other components still work
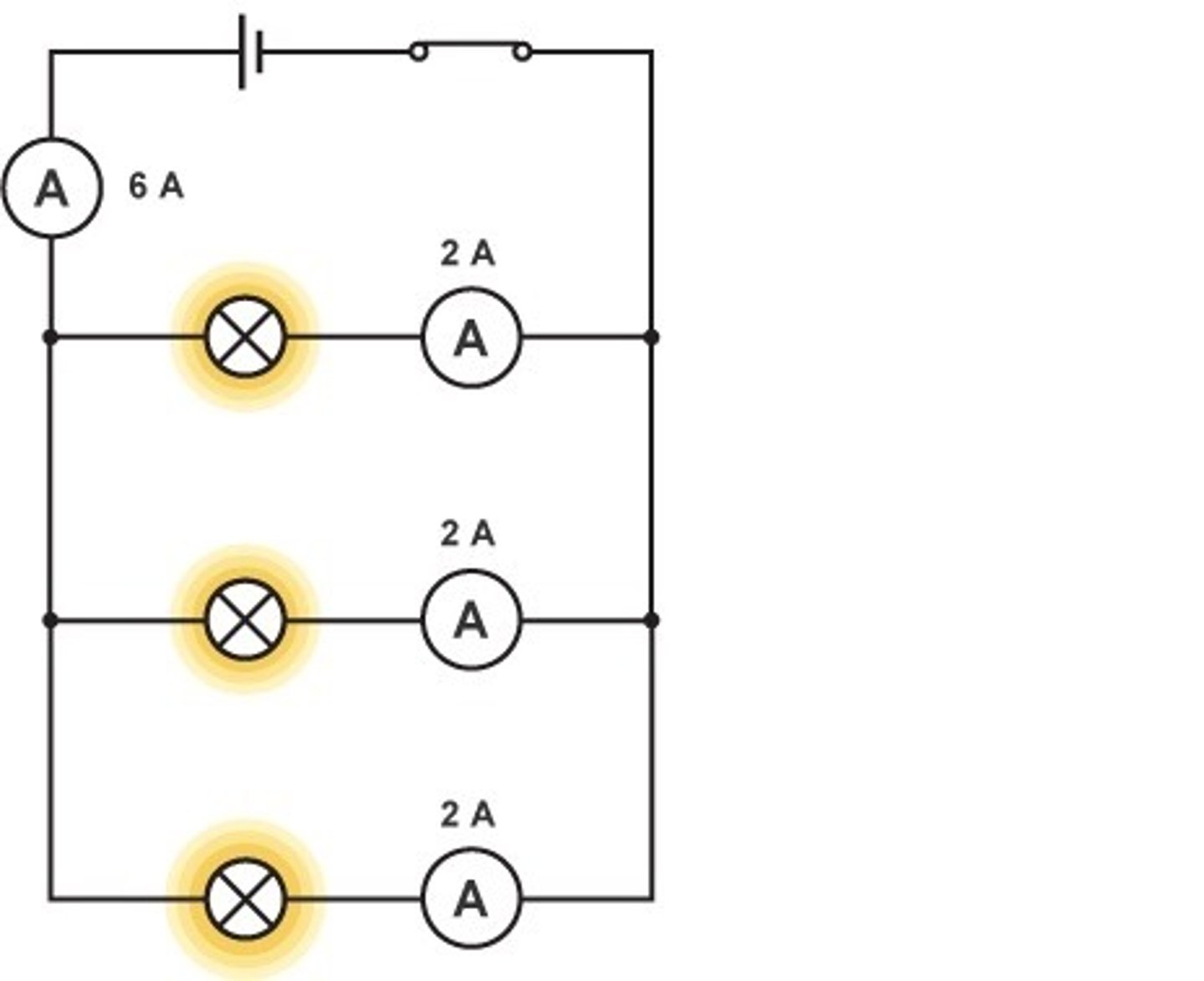
Rule for current in parallel
The total current through the whole circuit is the sum of the currents through the separate components
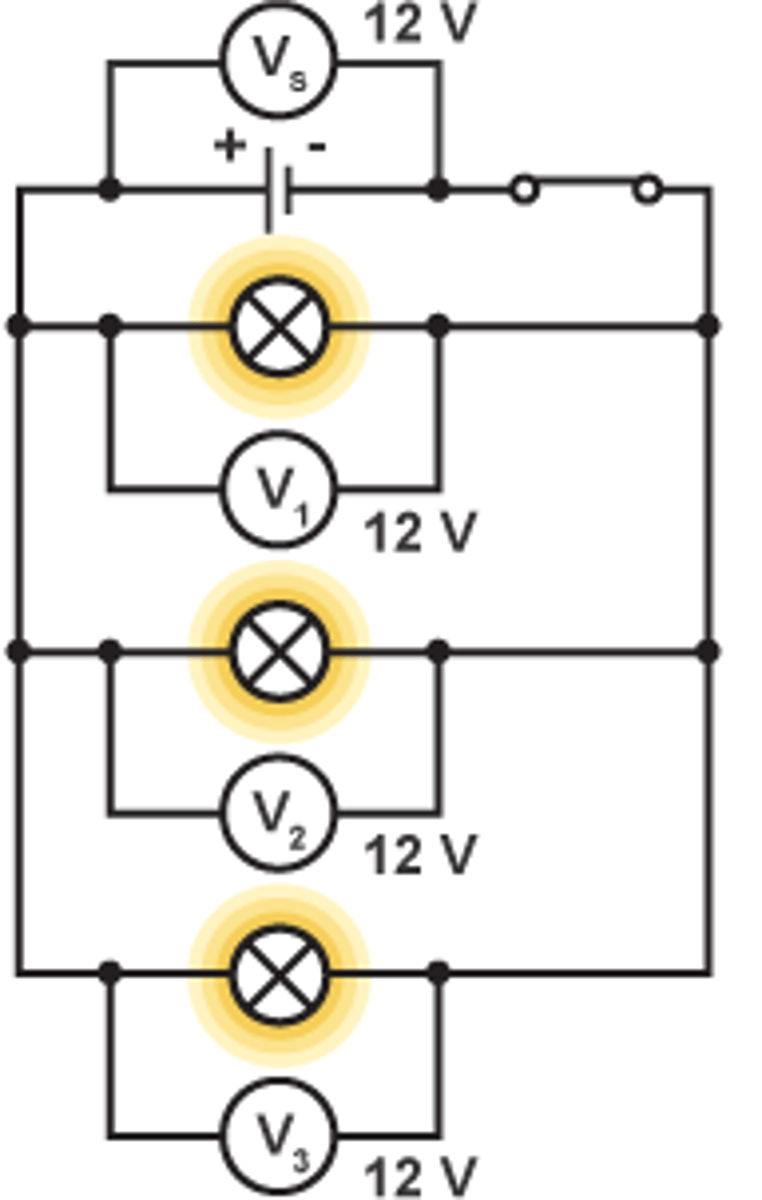
Rule for potential difference in parallel
The potential difference across each component is the same
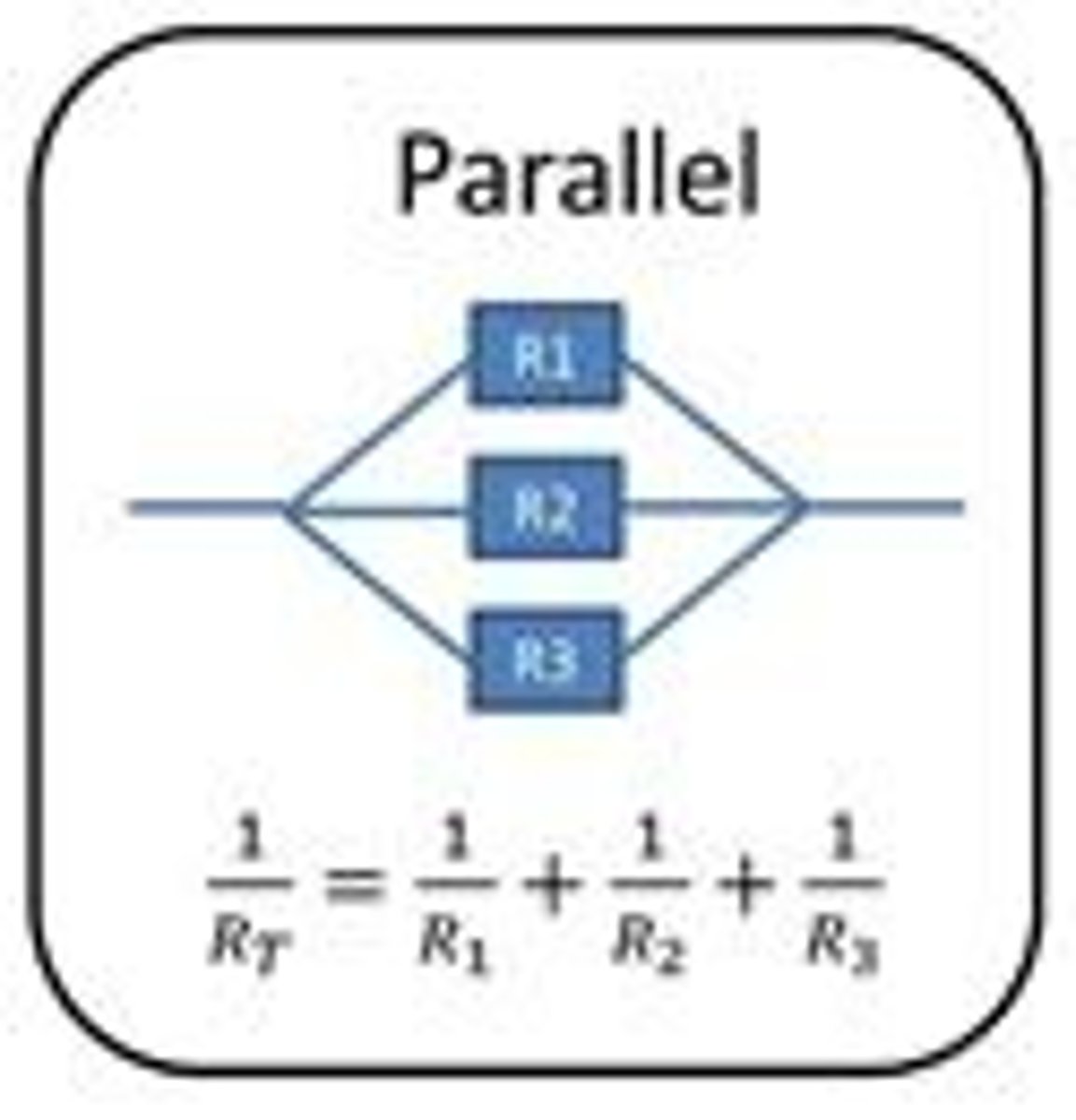
Rule for resistance in parallel
The total resistance of two resistors is less than the resistance of the smallest individual resistor
I(1) = I(2) = I(3)
The mathematical relationship for the current through components connected in series
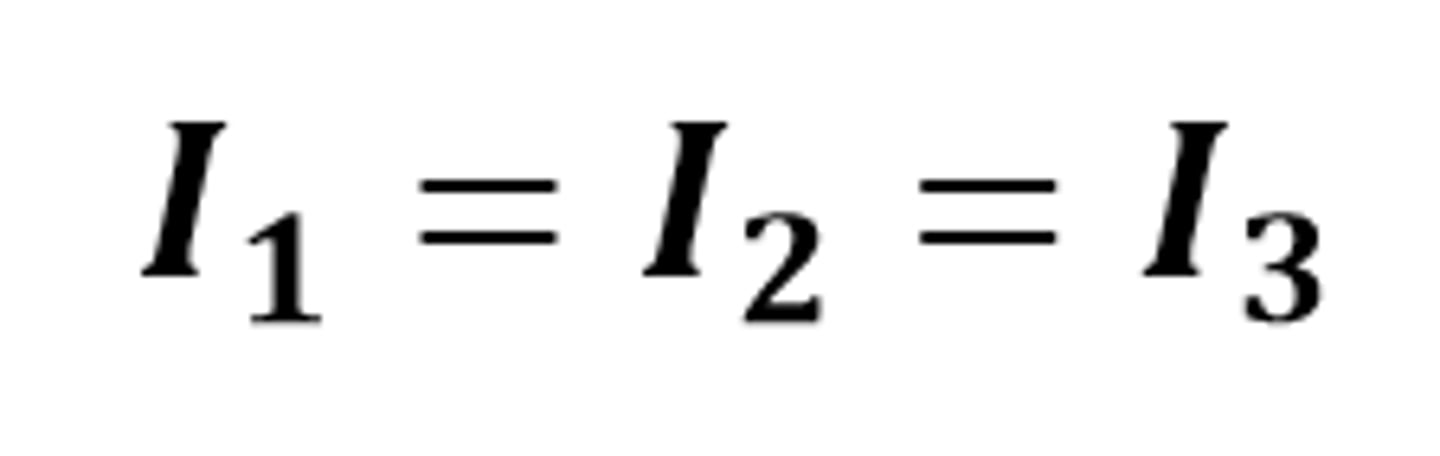
V(total) = V(1) + V(2)
The mathematical relationship for the total potential difference in a circuit when components are connected in series
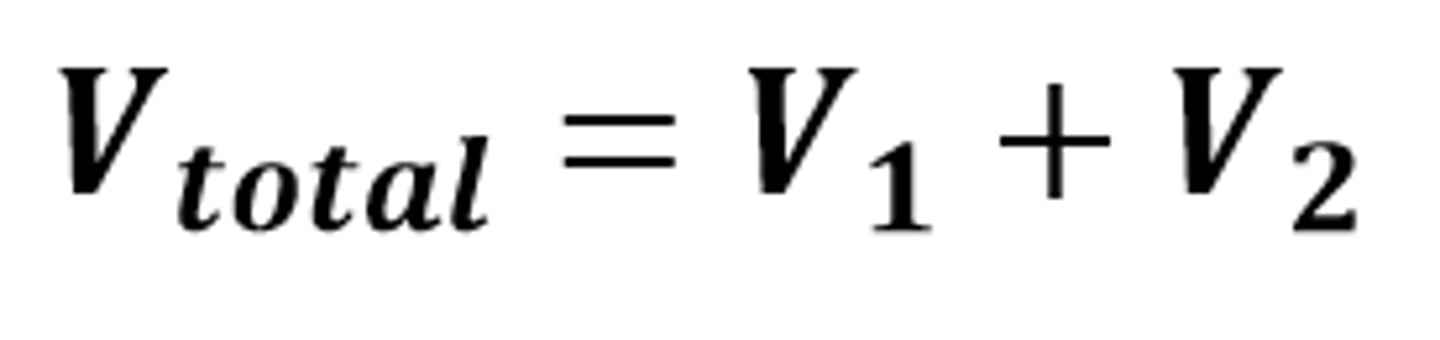
R(total) = R(1) + R(2)
The mathematical relationship for the total resistance in a circuit when components are connected in series
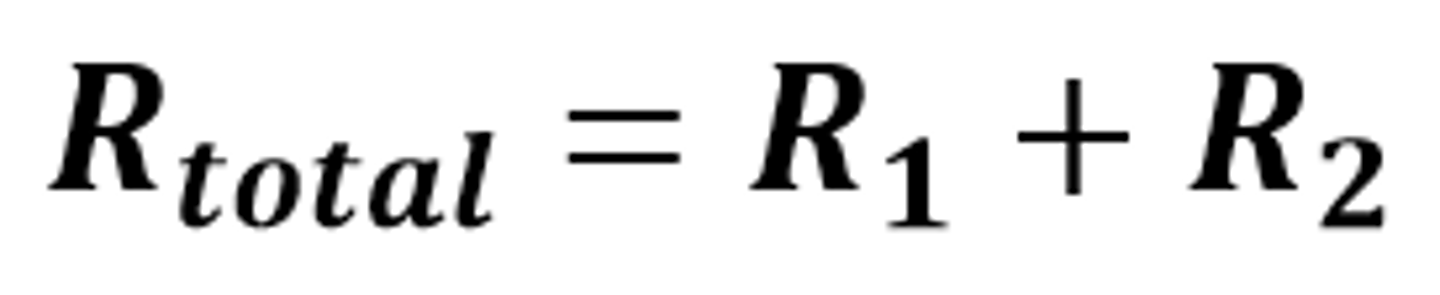
I(total) = I(1) + I(2)
The mathematical relationship for the total current in a circuit when components are connected in parallel
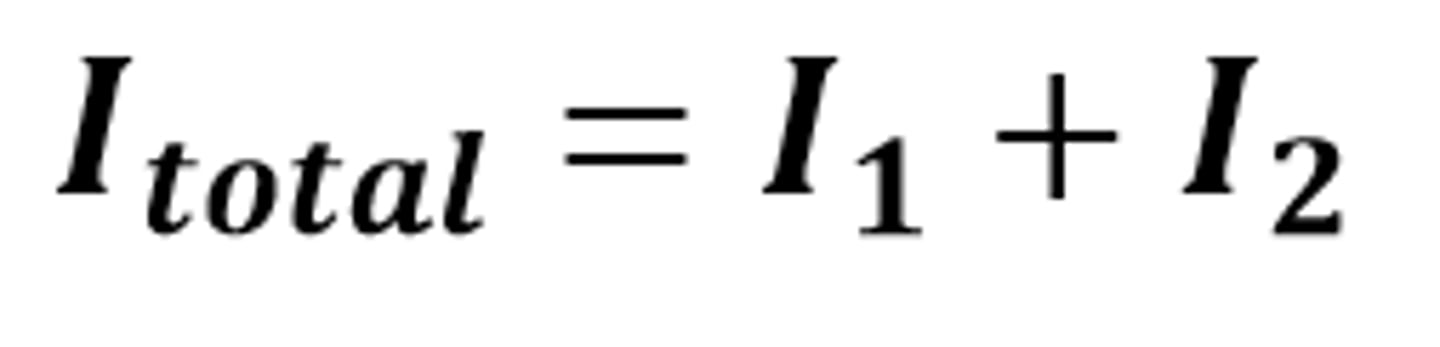
V(1) = V(2) = V(3)
The mathematical relationship for the potential difference across components connected in parallel
Potential difference (voltage)
A measure of the amount of energy given to the charge carriers (electrons) in a circuit

E = QV
The equation linking energy transferred, charge flow and potential difference
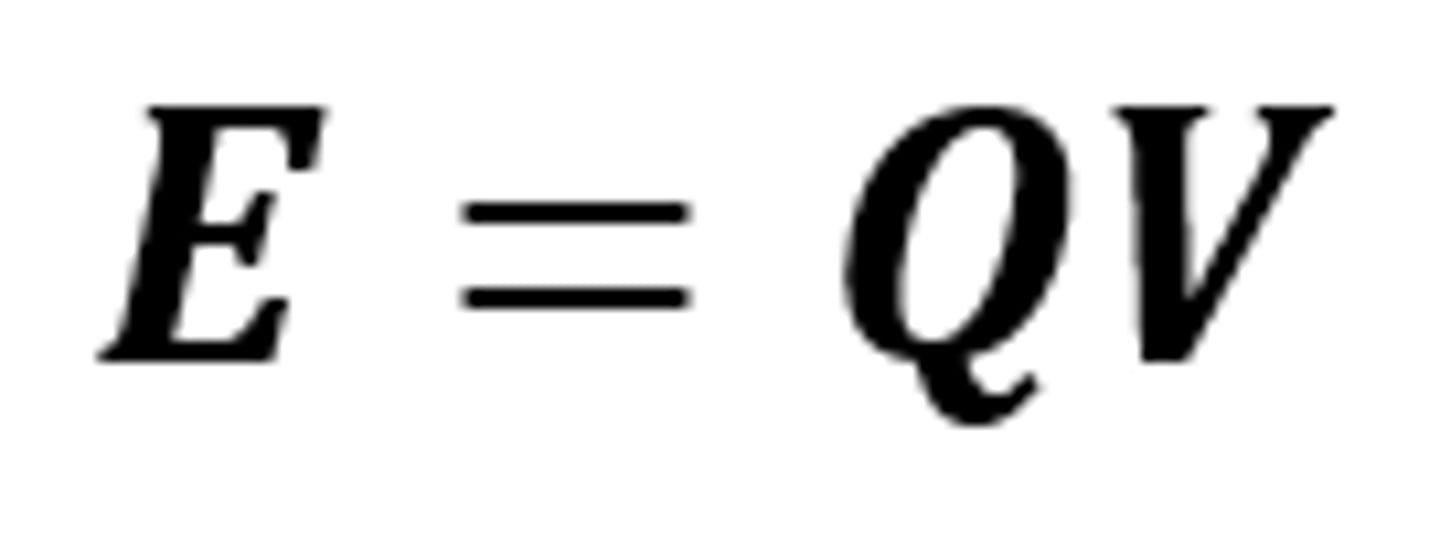
E
The symbol for energy transferred
Q
The symbol for charge flow
V
The symbol for potential difference
Joules (J)
The SI unit for energy and work

Coulombs (C)
The SI unit for charge flow

Volts (V)
The SI unit for potential difference

1 volt is equal to
The potential difference when one coulomb of charge transfers one joule of energy (1 V = 1 J/C)
V = IR
The equation linking potential difference, current and resistance; also known as Ohm's Law
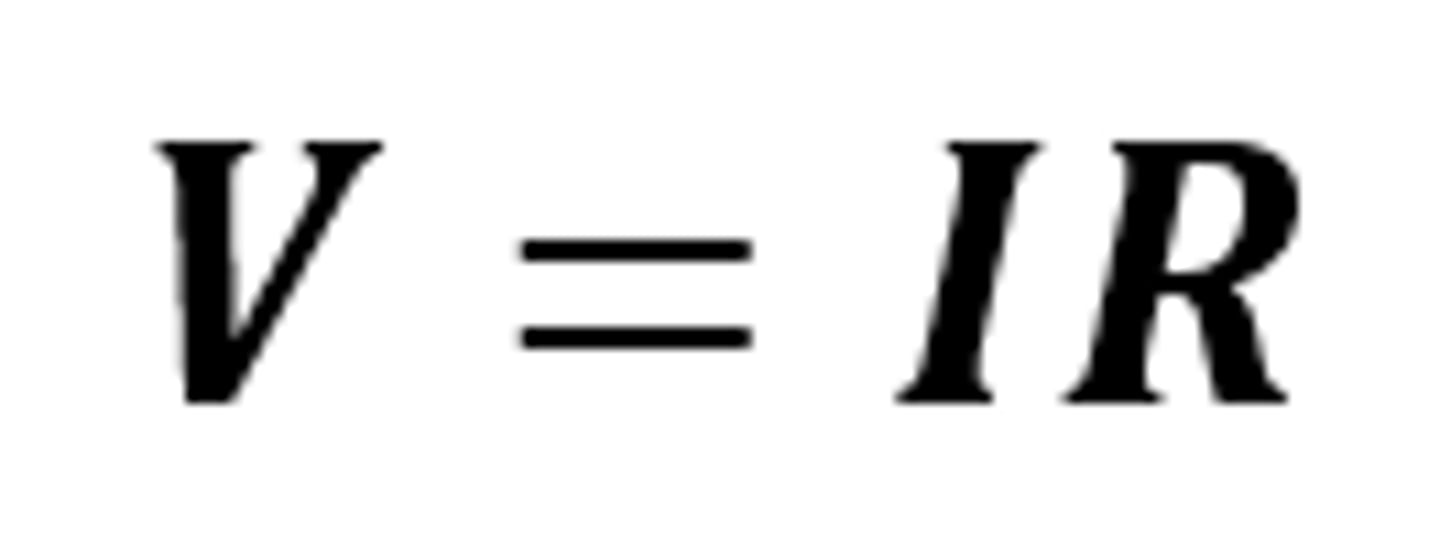
Current
The rate of flow of electric charge (electrons) around a circuit
Resistance
The opposition to the movement of electric current through a material
I
The symbol for current
R
The symbol for resistance
Amps/amperes (A)
The SI unit for current

Ohms (Ω)
The SI unit for resistance

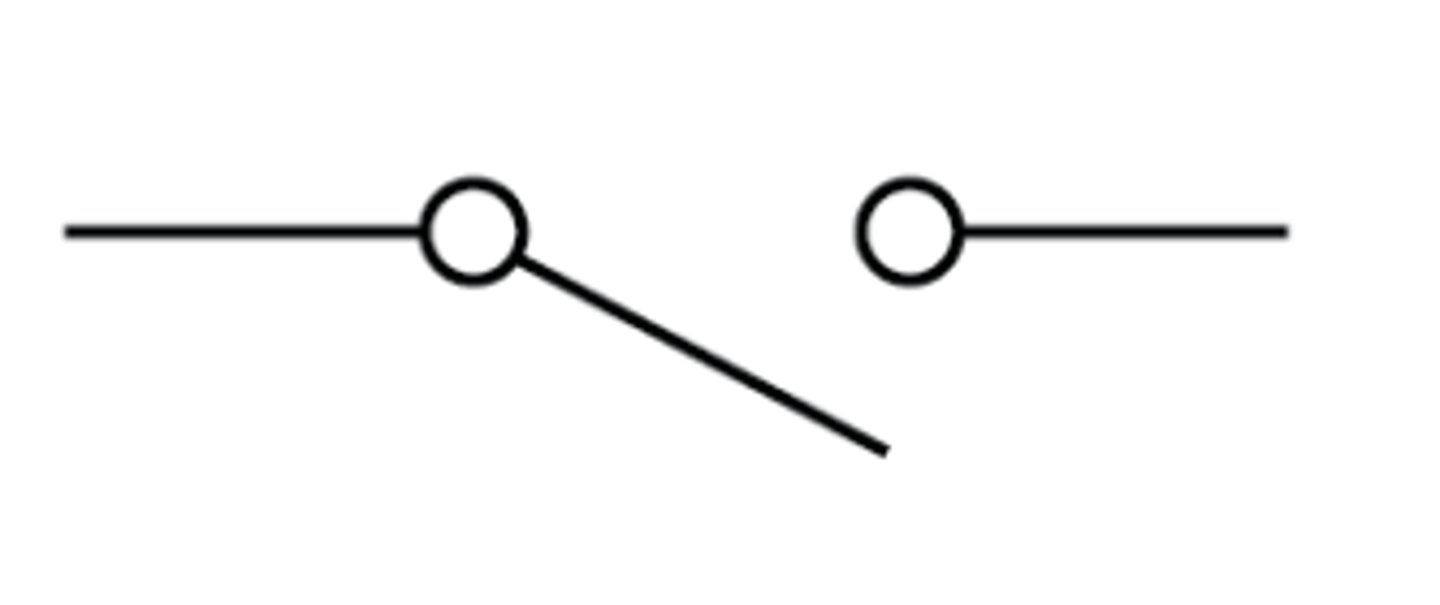
Switch (open)
Used to turn a circuit off
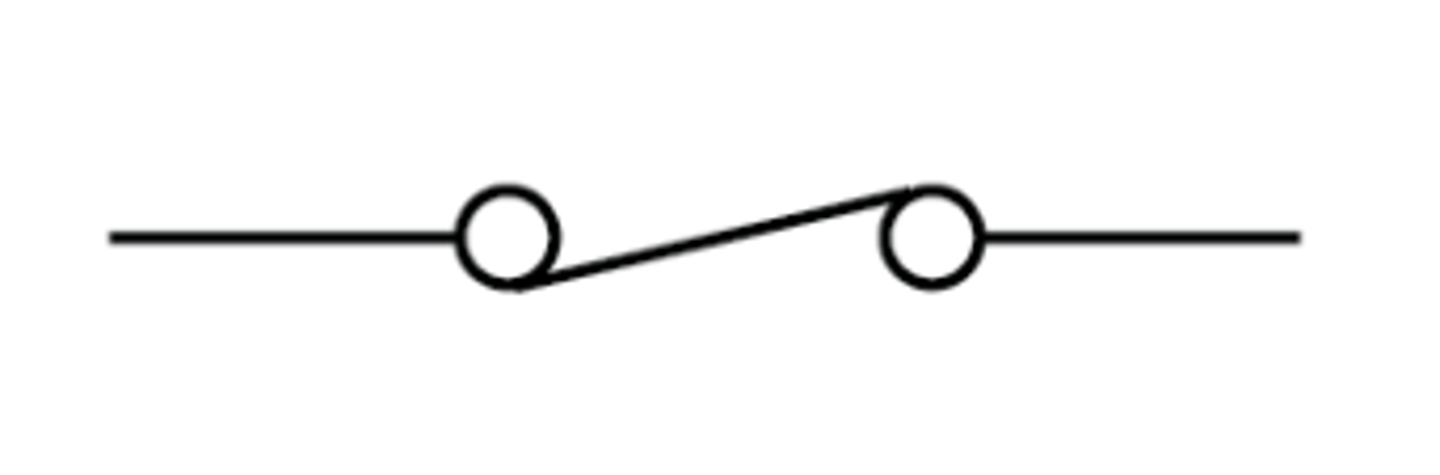
Switch (closed)
Used to turn a circuit on
Cell (electrical) what does it supply?
Provides the energy for a circuit
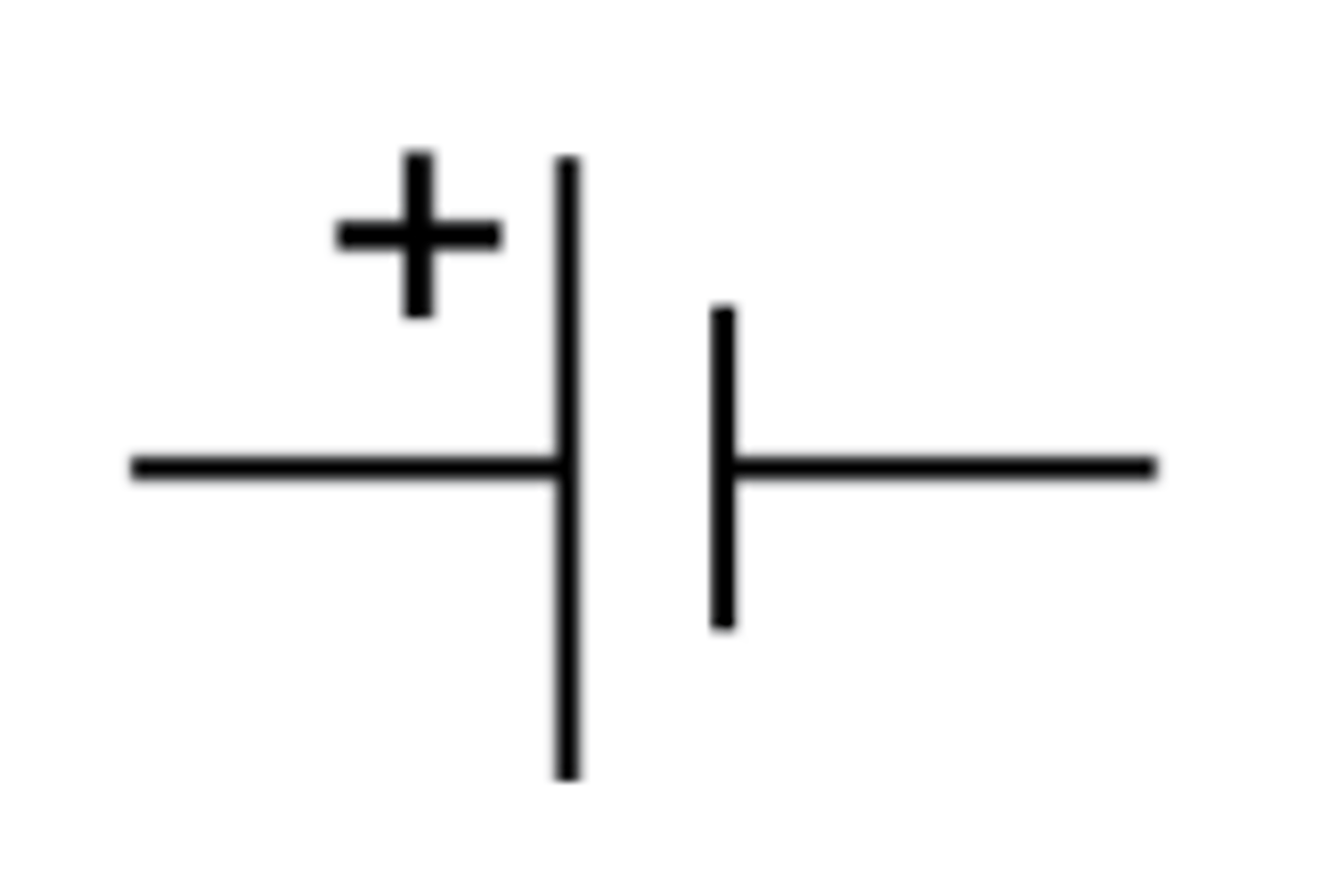
Battery
Two or more cells connected together
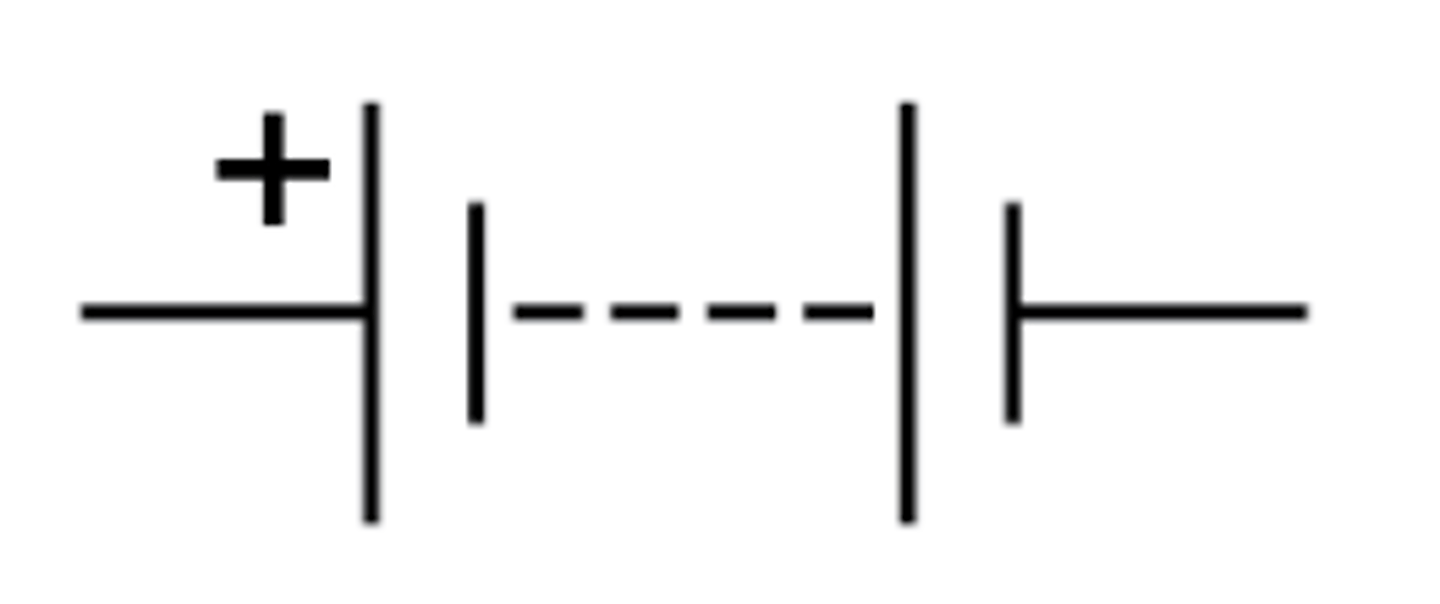
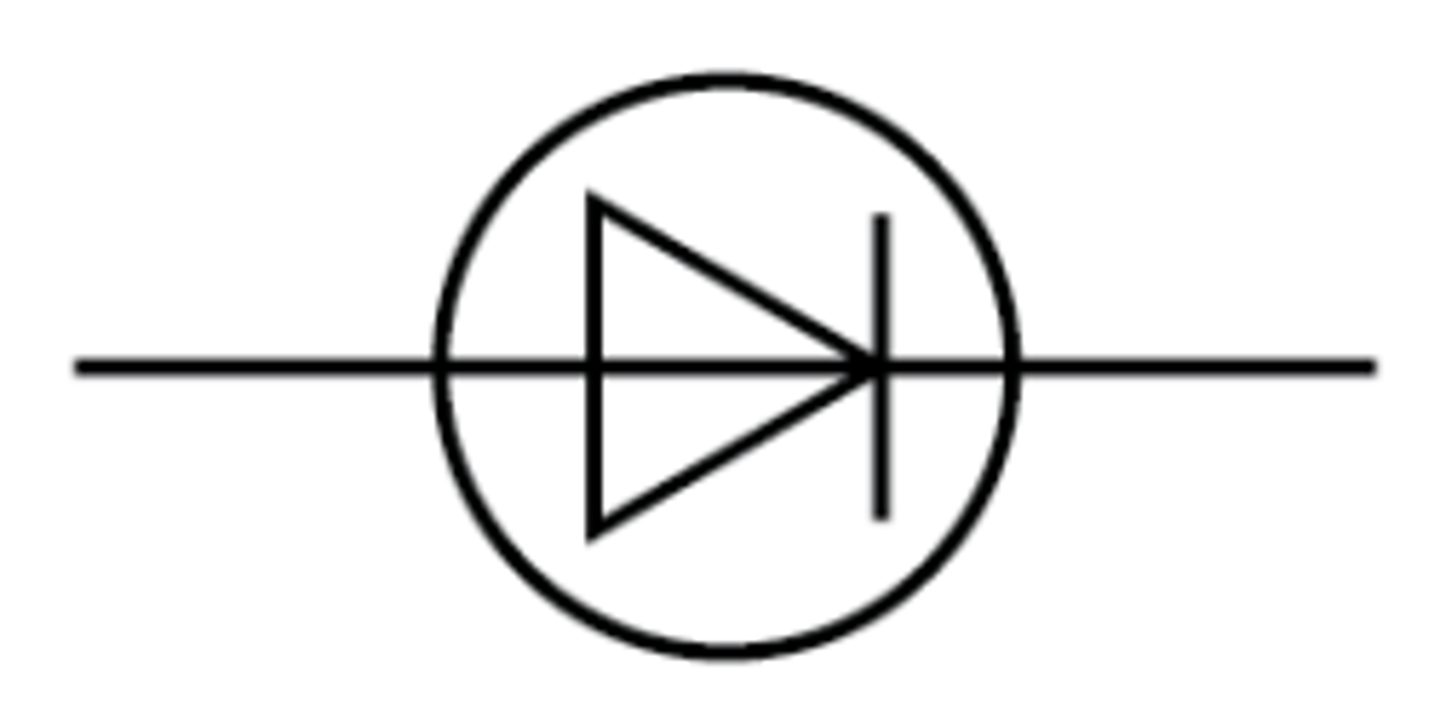
Diode
A device that allows current to flow in one direction only
Resistor (fixed)
A device that restricts or limits the flow of current

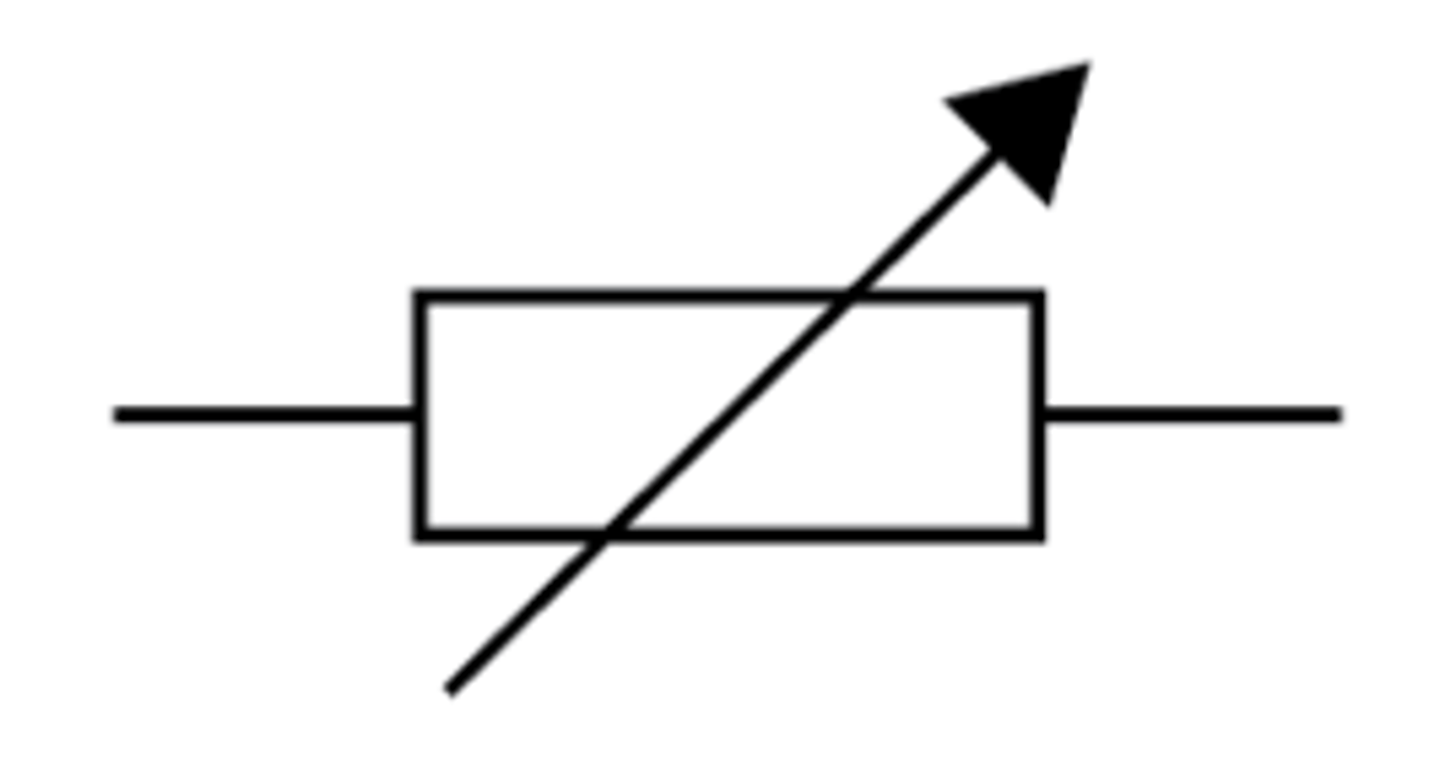
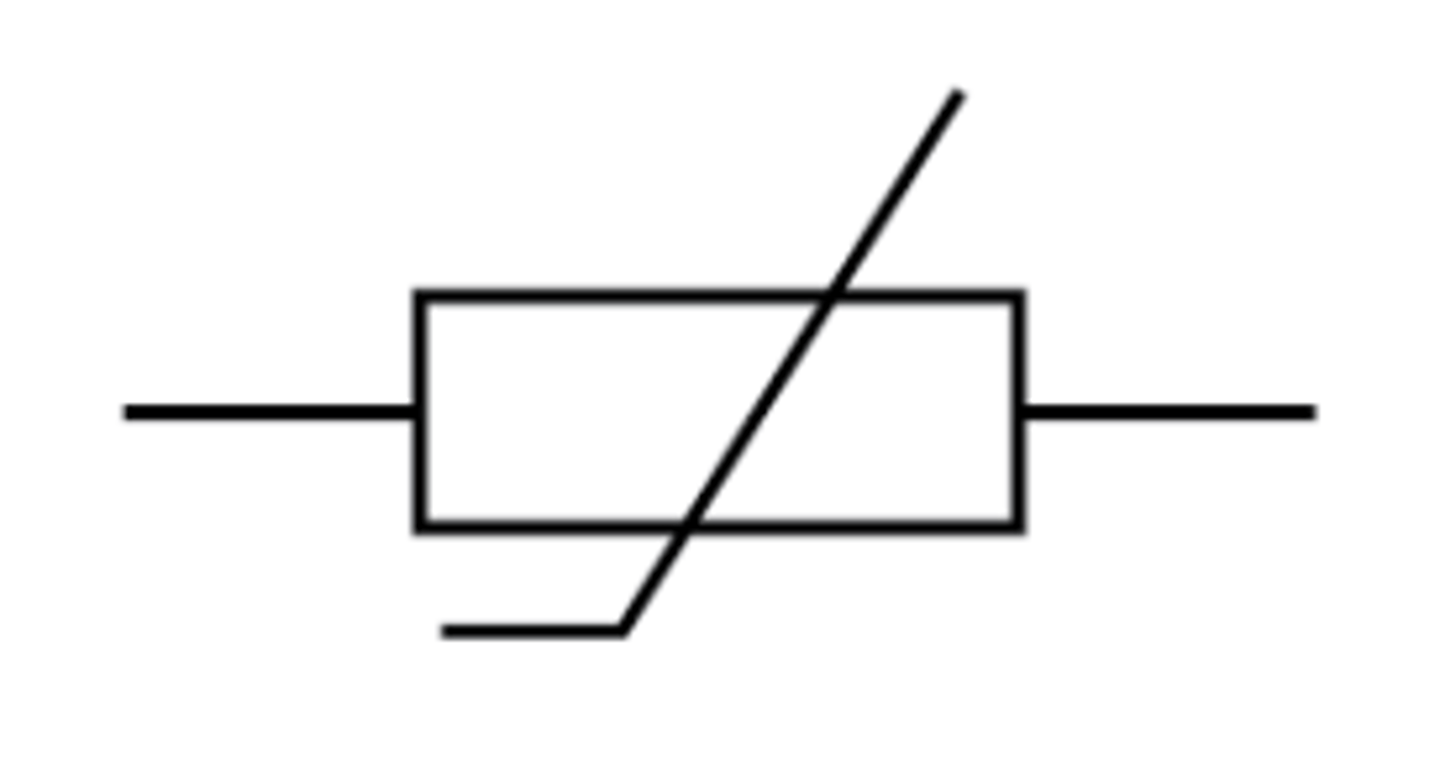
Variable resistor
A device that has a slider which can be moved to change the resistance
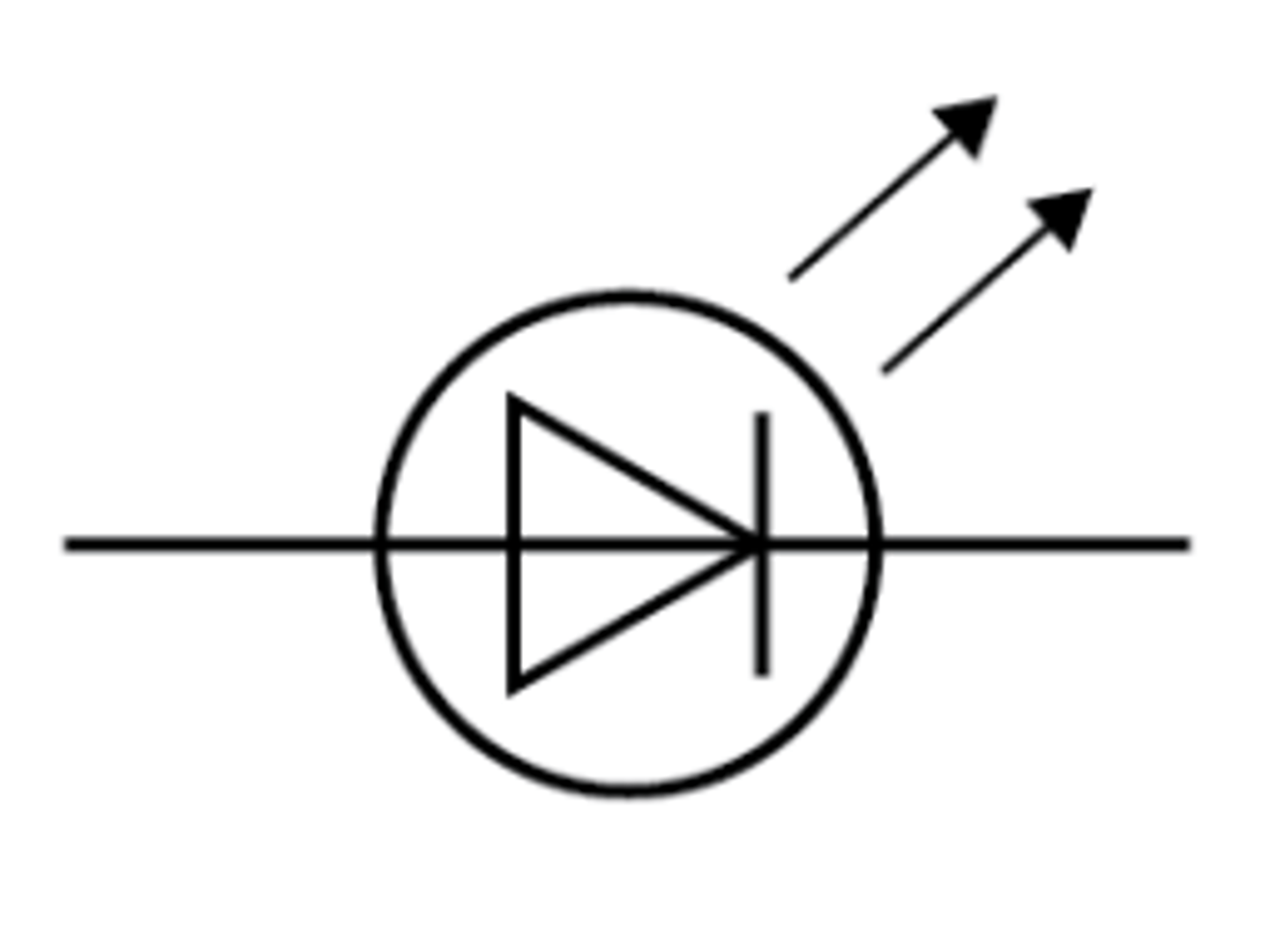
LED (light-emitting diode)
A diode which emits light and is much more efficient than a filament bulb
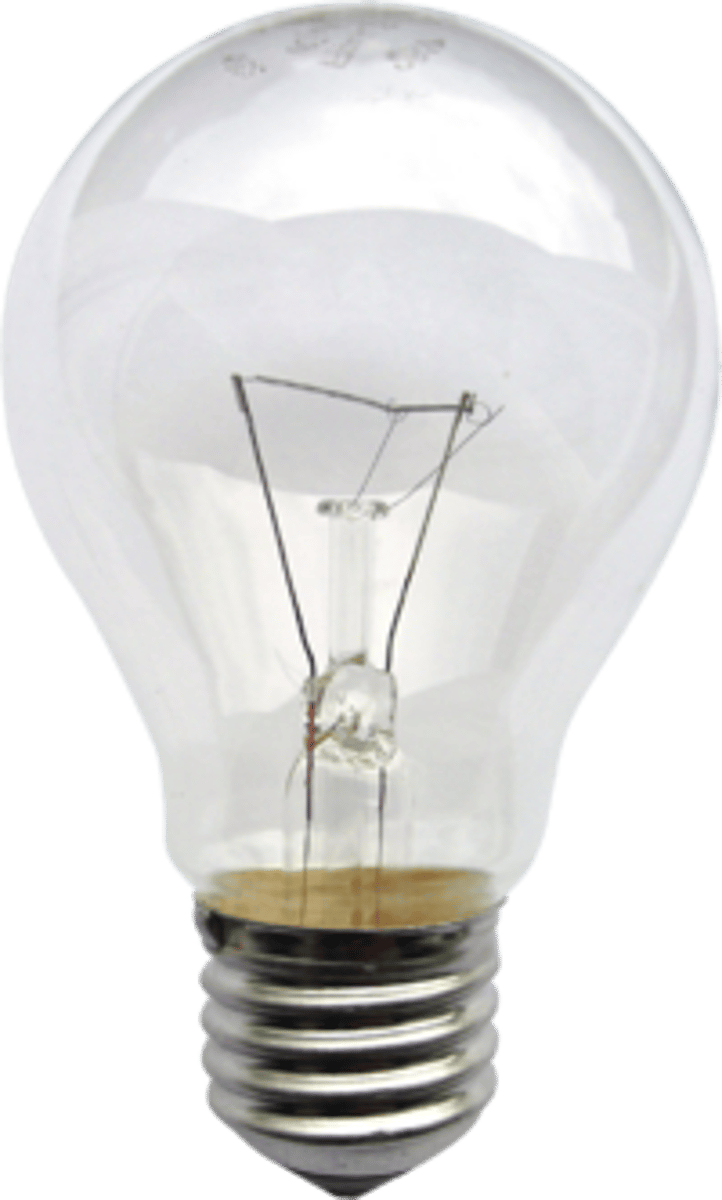
Lamp (filament bulb)
A device containing a filament in a bulb that heats up when a current flows so that it emits light
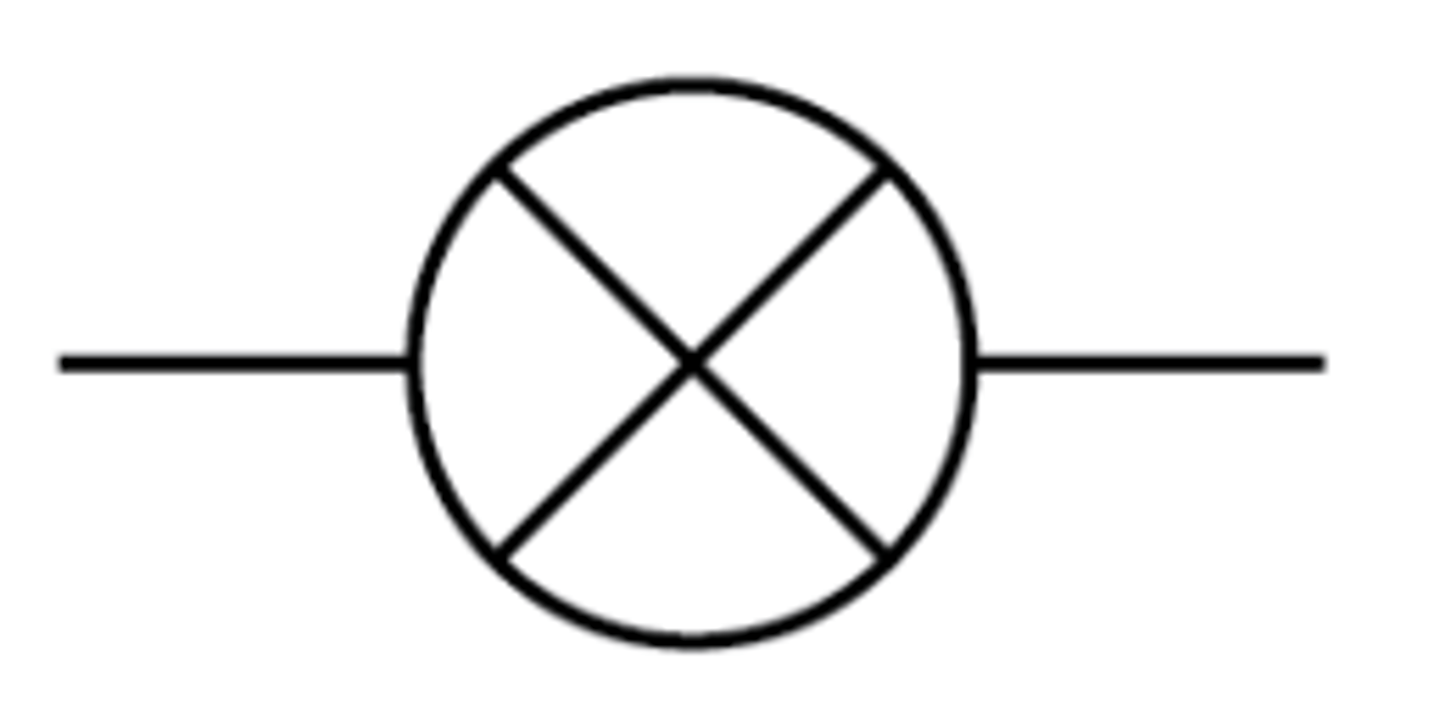
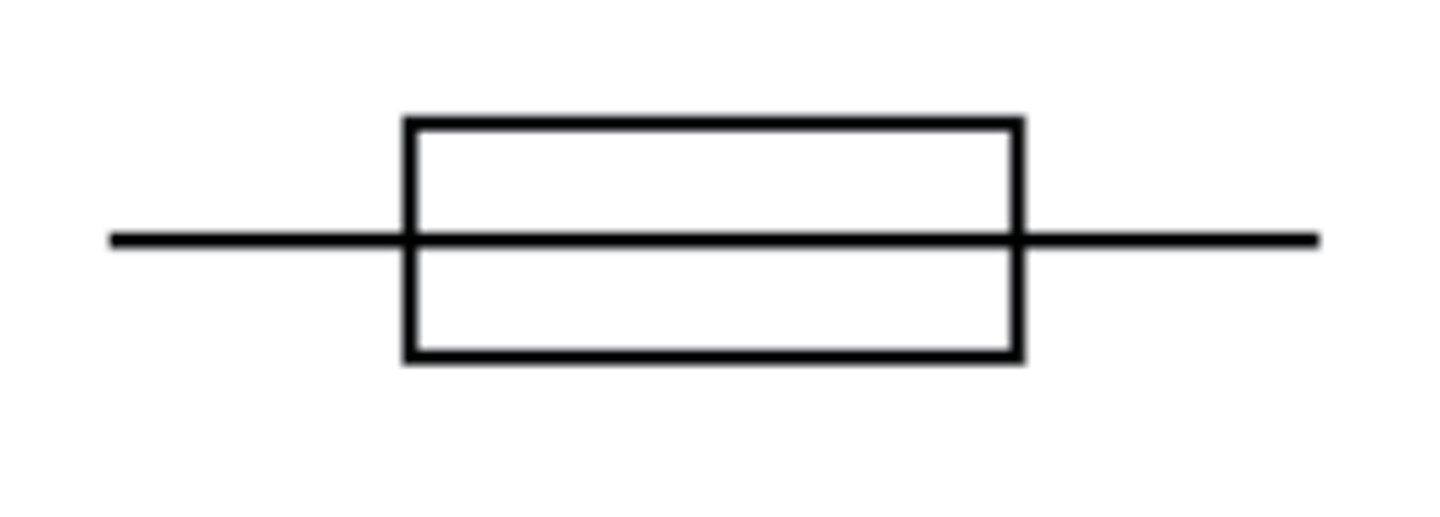
Fuse
A safety device consisting of a strip of wire that melts, breaking an electric circuit, if too much current passes through it

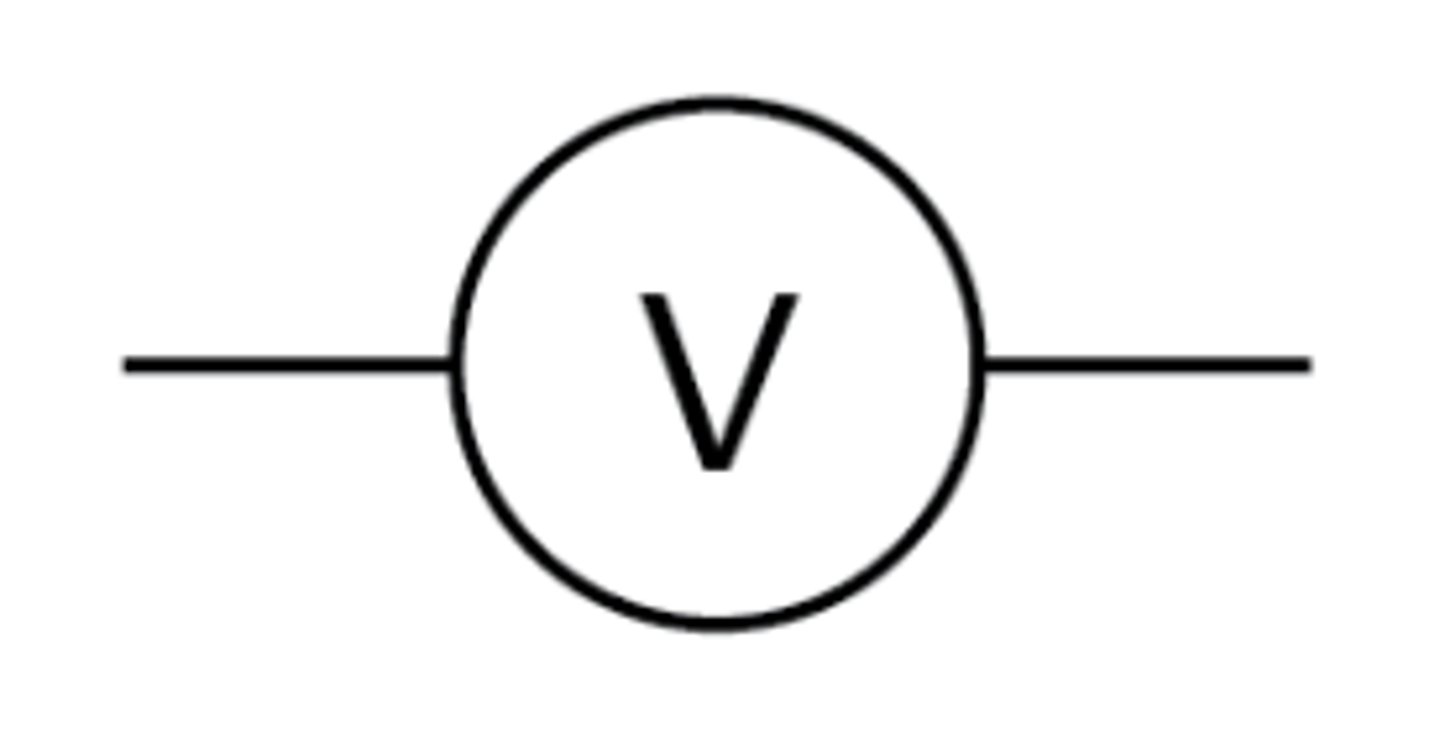
Voltmeter
A device placed in parallel with a component to measure the potential difference (voltage) across it
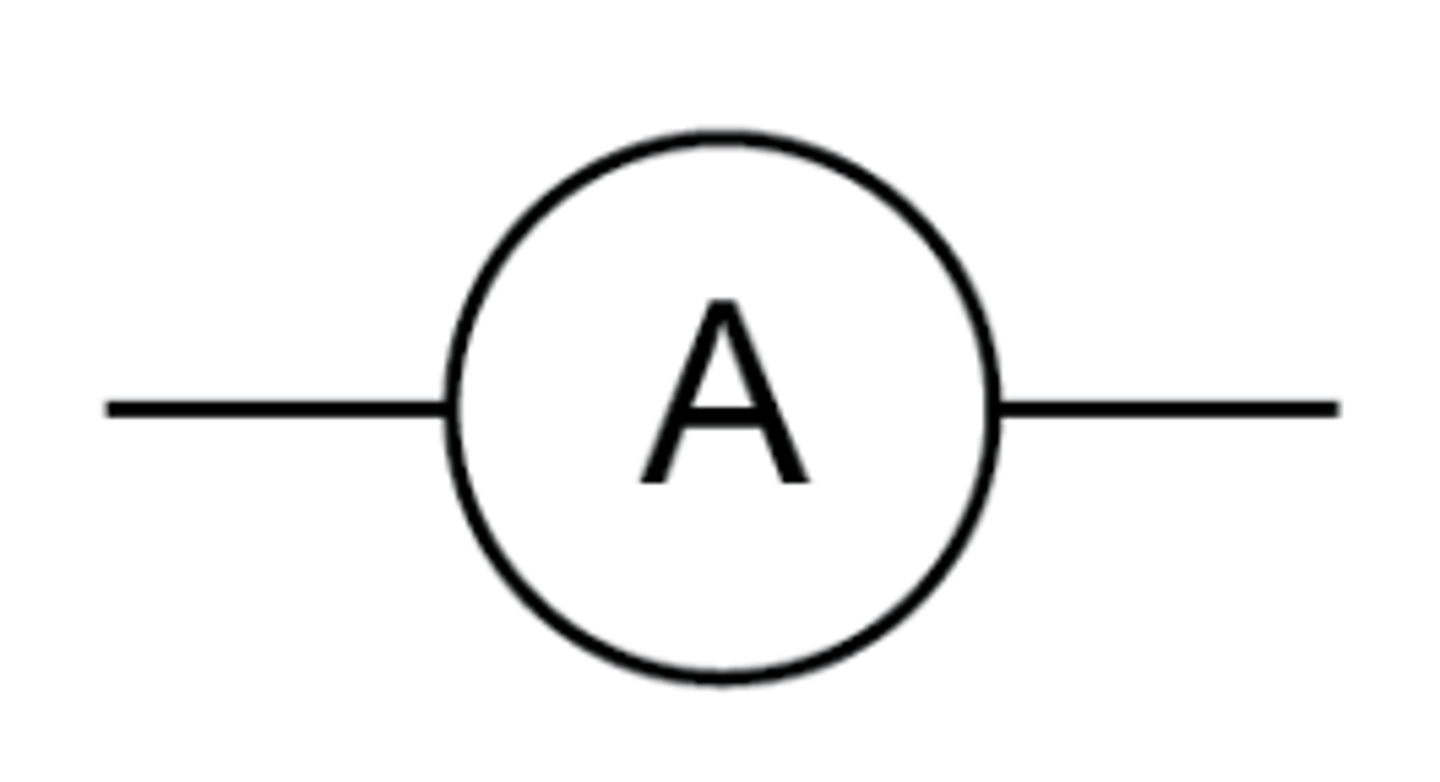
Ammeter
A device placed in series with a component to measure the current through it
Themistor
A device whose resistance decreases as the surrounding temperature increases
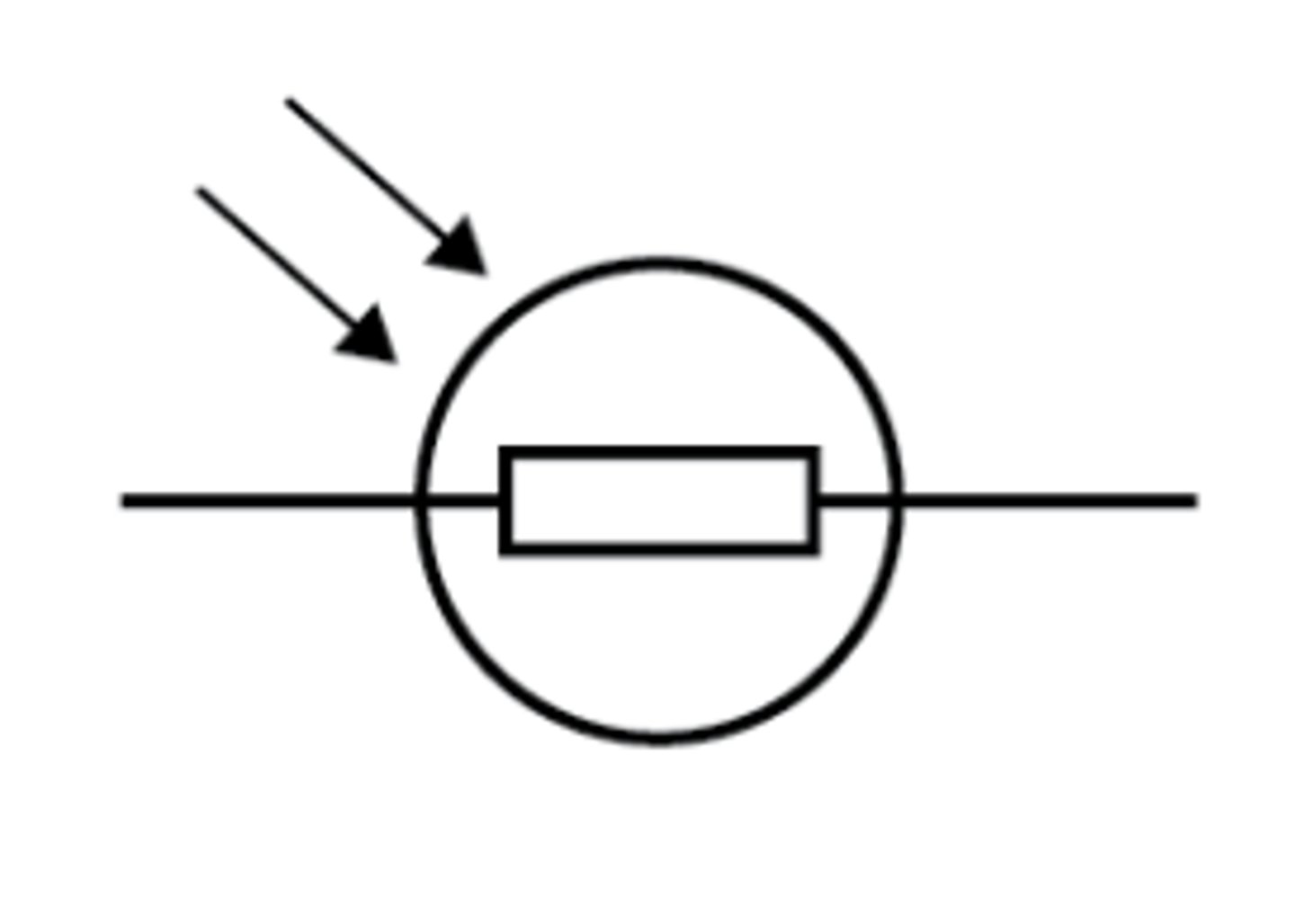
LDR (light-dependent resistor)
A device whose resistance decreases as the surrounding light intensity increases
Ohm's Law (V = IR) (include proportion ideas)
The current flowing through a device is directly proportional to the potential difference across the it (providing the temperature remains constant)
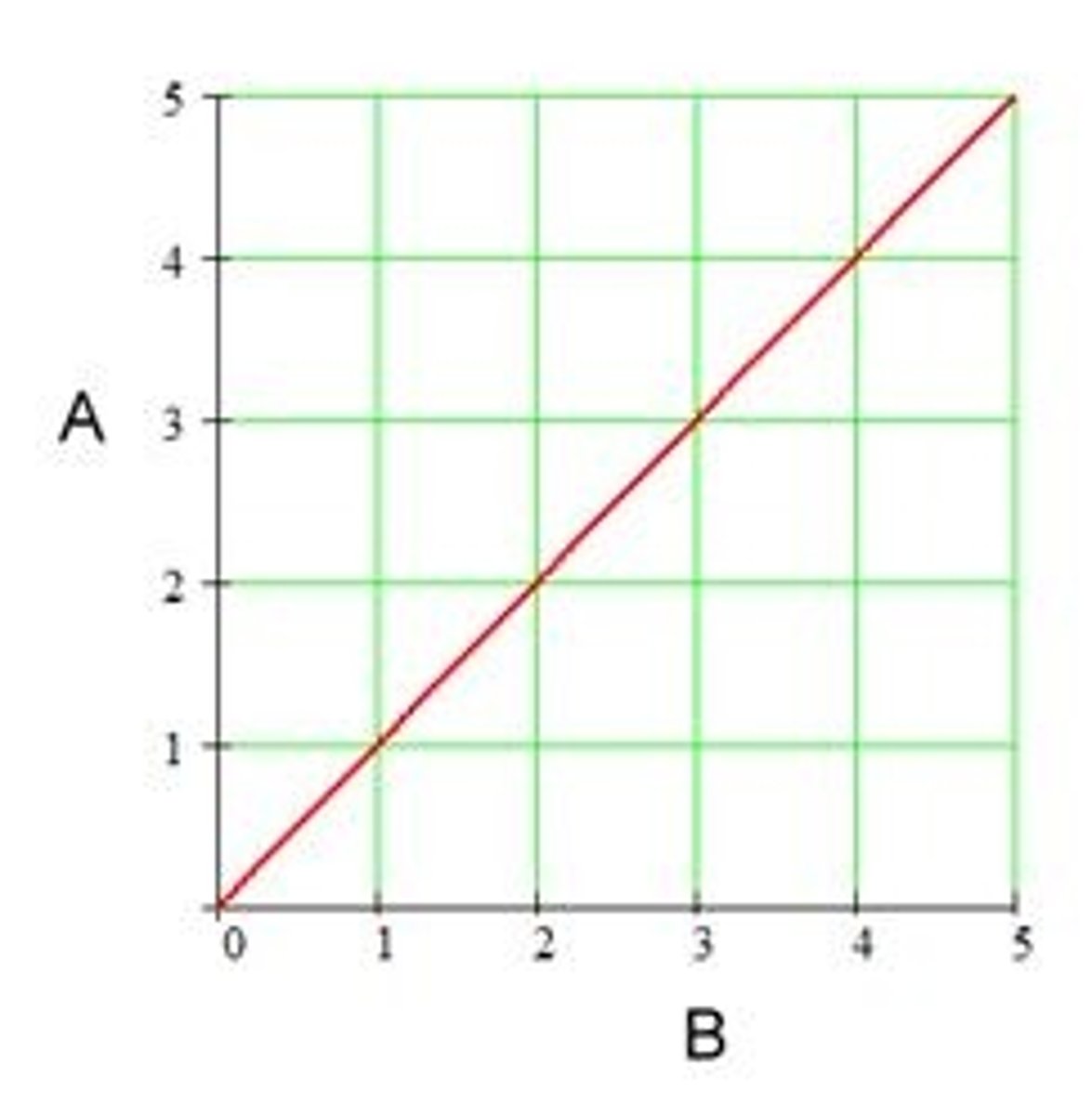
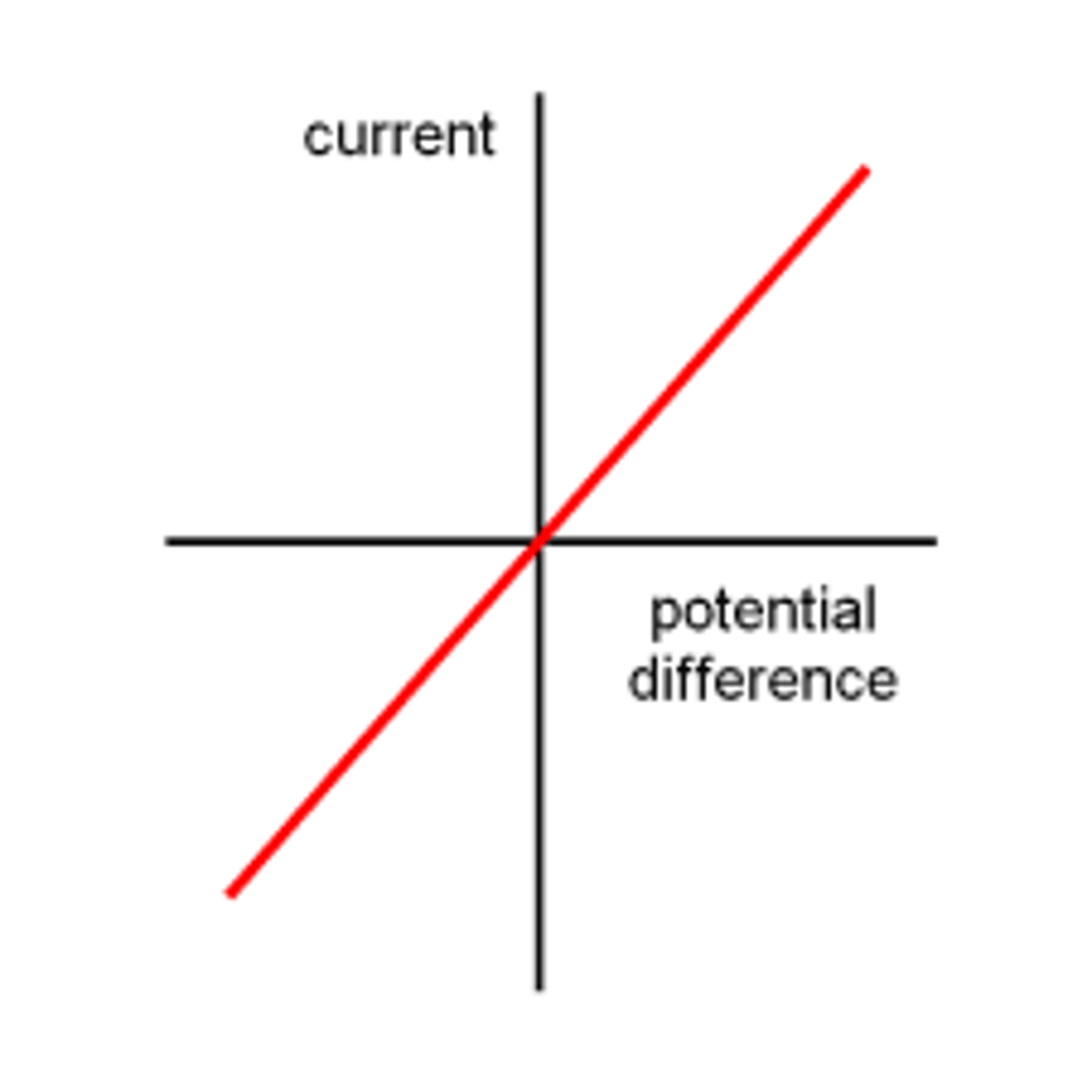
Directly proportional
When a graph of two variables is a straight line that passes through the origin (0,0)
Ohmic conductor
A device that obeys Ohm's Law
Fixed resistor
An ohmic conductor that obeys Ohm's Law because its resistance is fixed

Filament bulb
Not an ohmic conductor because it doesn't obey Ohm's Law

Diode
Not an ohmic conductor because it doesn't obey Ohm's Law
Reason why a filament bulb is not an ohmic conductor
The filament gets hot which causes its resistance to increase
Reason why a diode is not an ohmic conductor
Its resistance changes depending on which direction the current flows through it
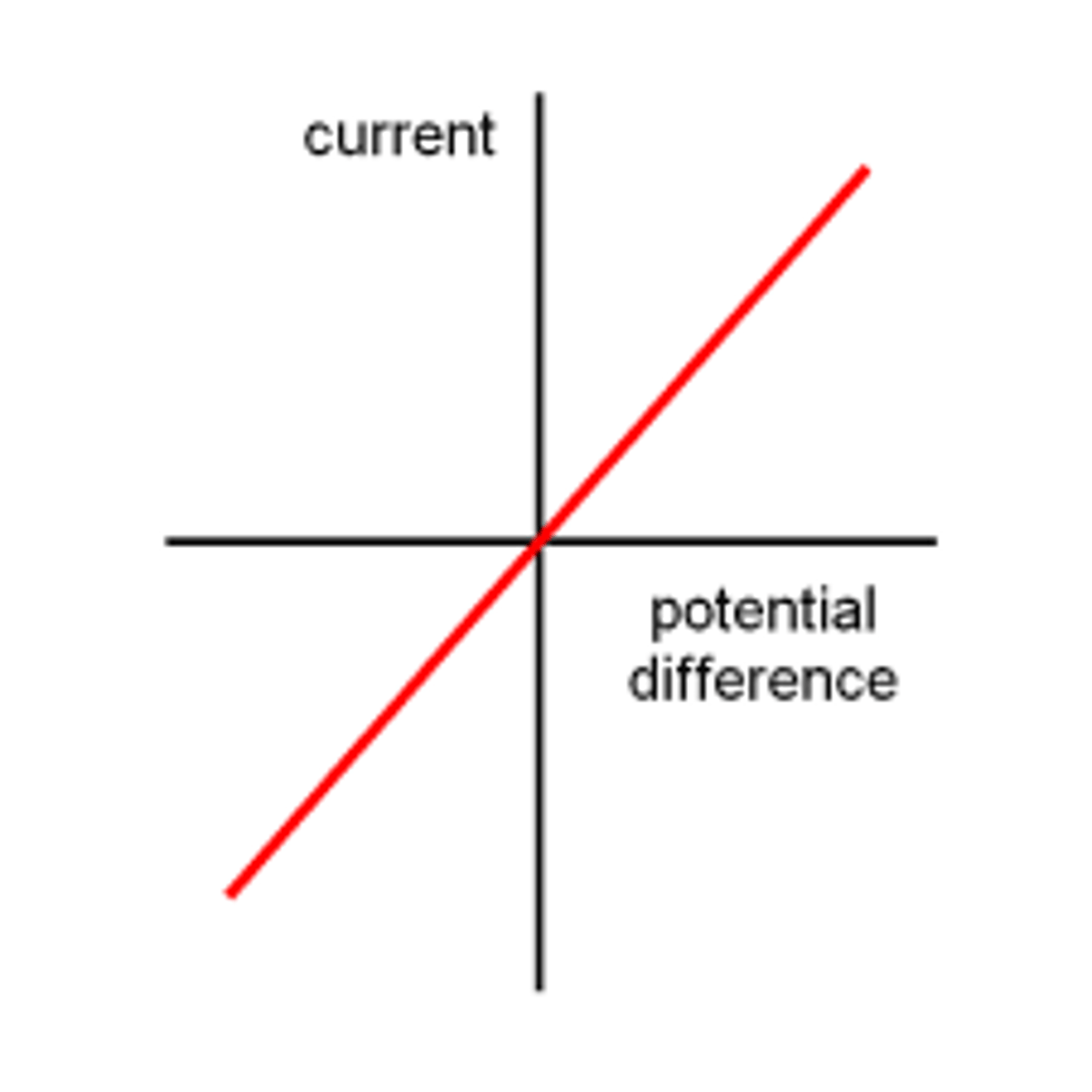
IV (current-potential difference) graph
a graph used to show how the current through a component varies as the potential difference across it changes
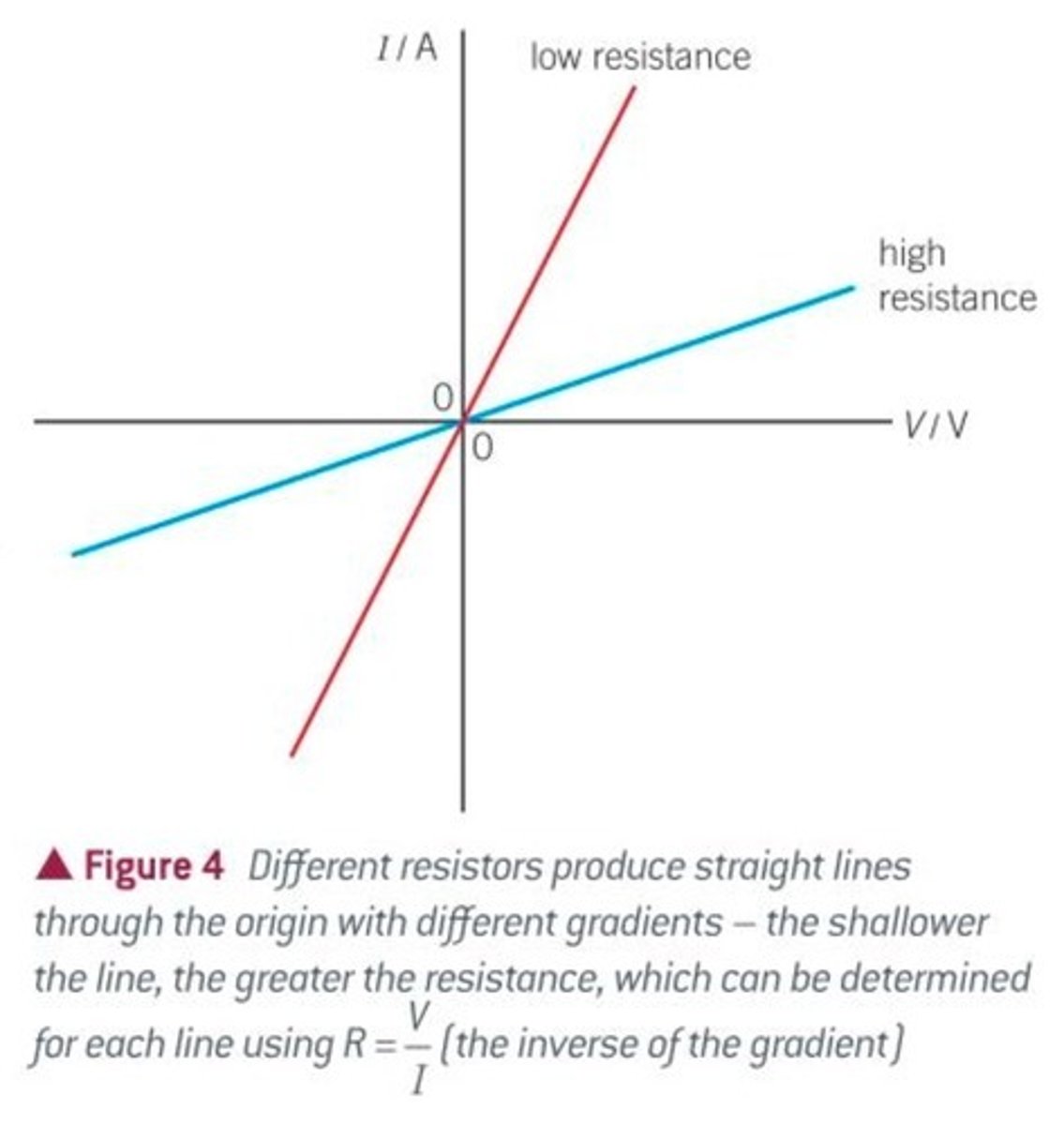
What the gradient of an IV graph represents
The resistance of a component (equal to 1/R)
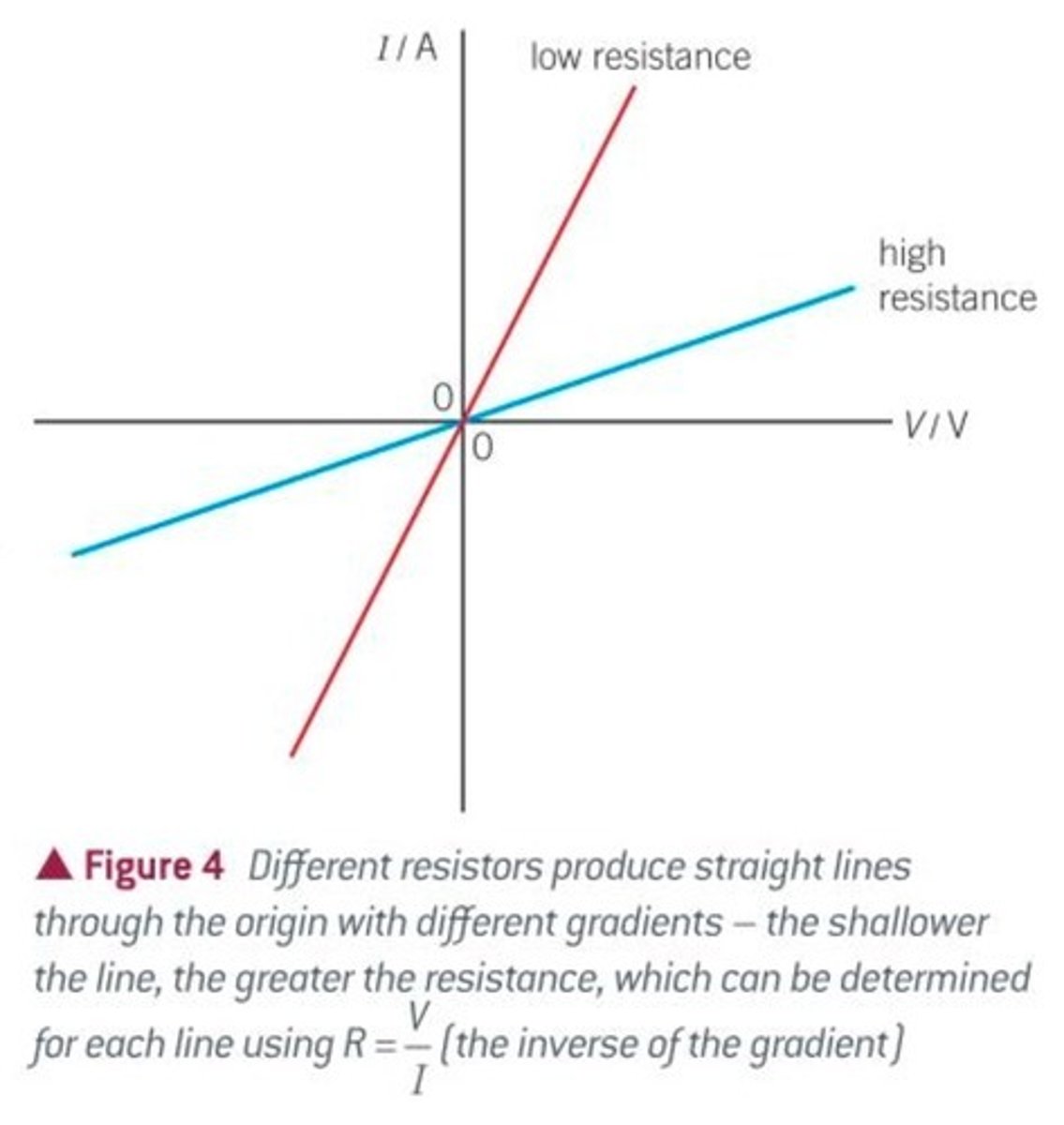
What a steep line on an IV graph represents
A device with a low resistance because increasing the potential difference by a small amount causes a large increase in current
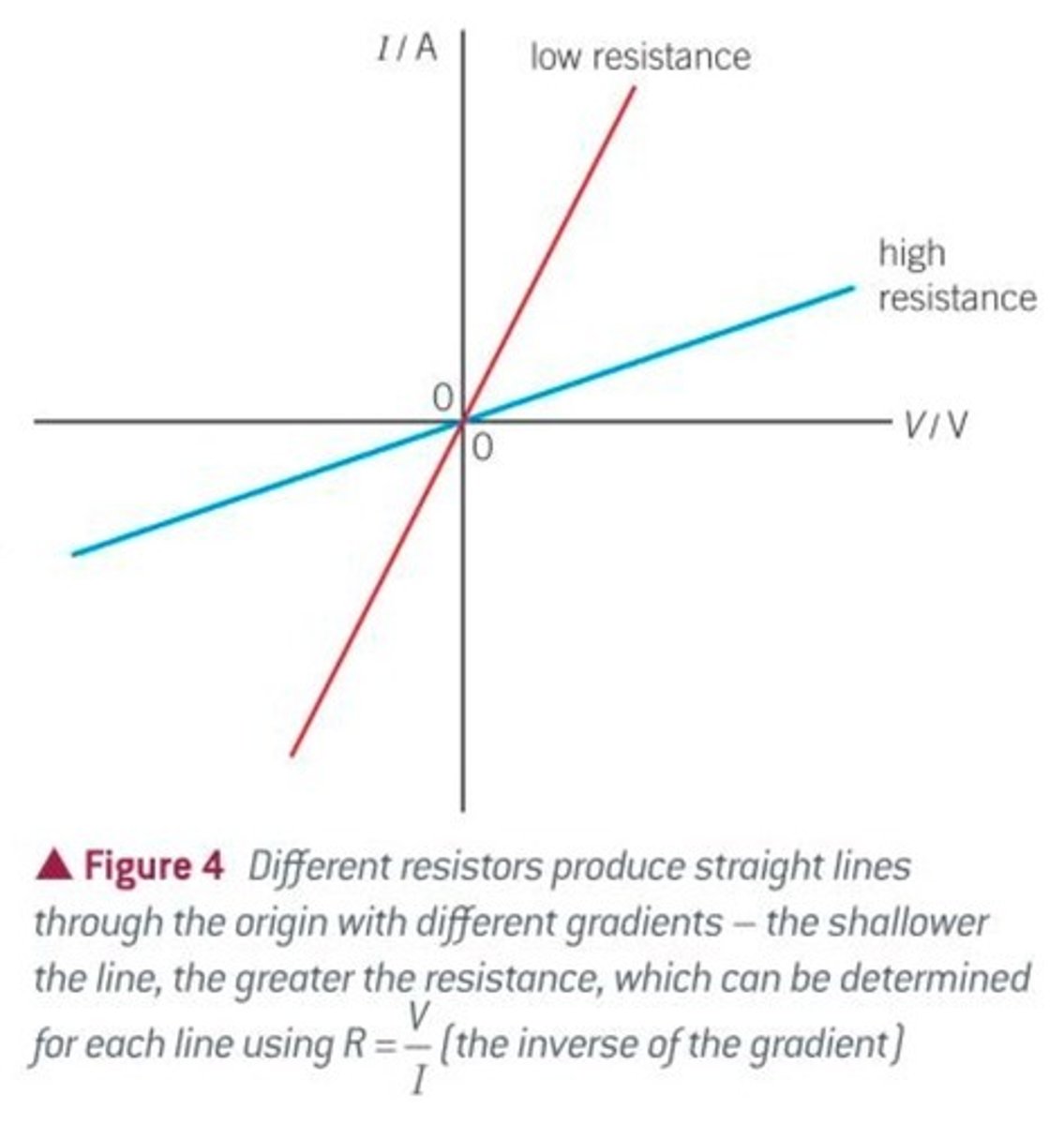
What a shallow line on an IV graph represents
A device with a high resistance because increasing the potential difference by a small amount causes a small increase in current
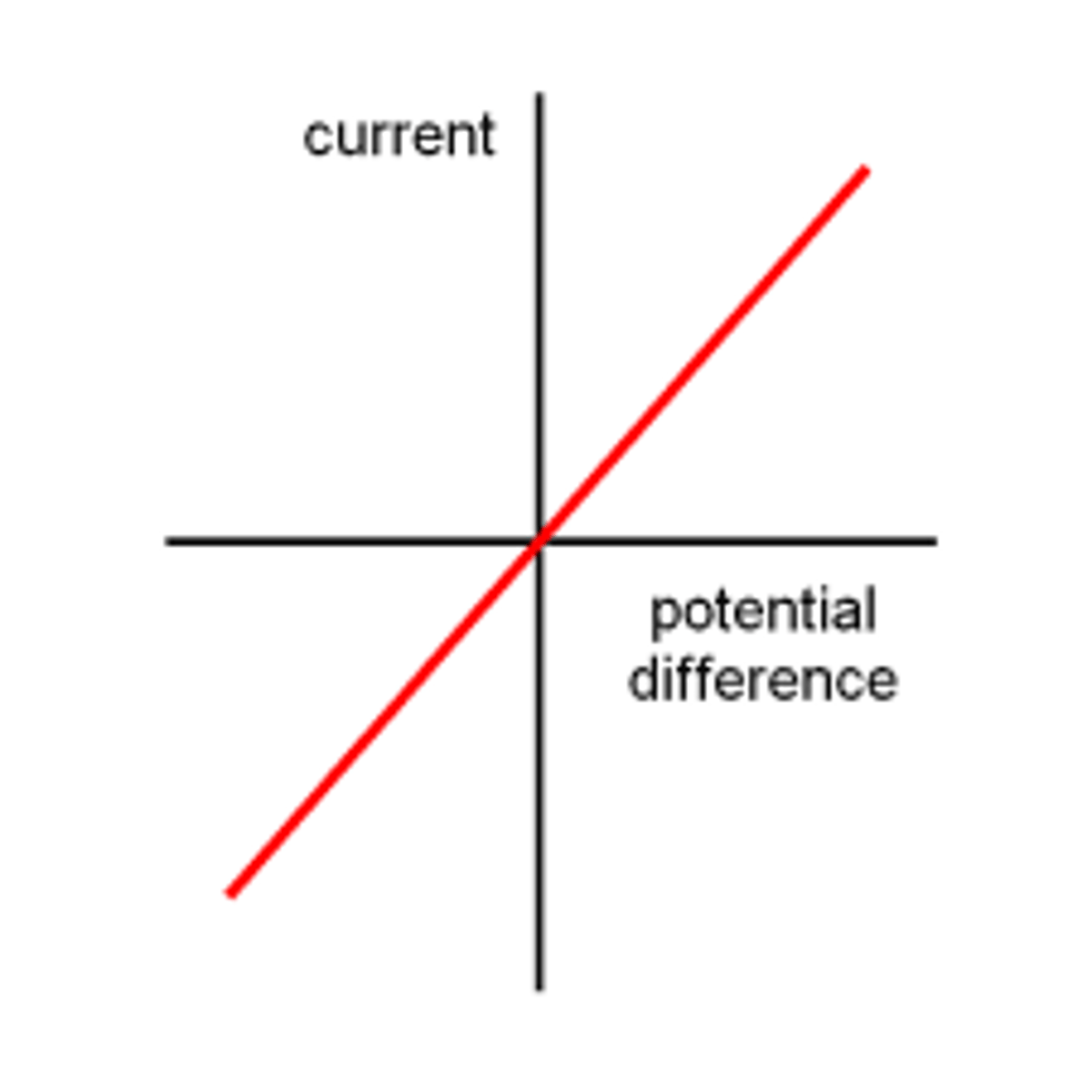
IV graph for a fixed resistor
A straight line which passes through the origin
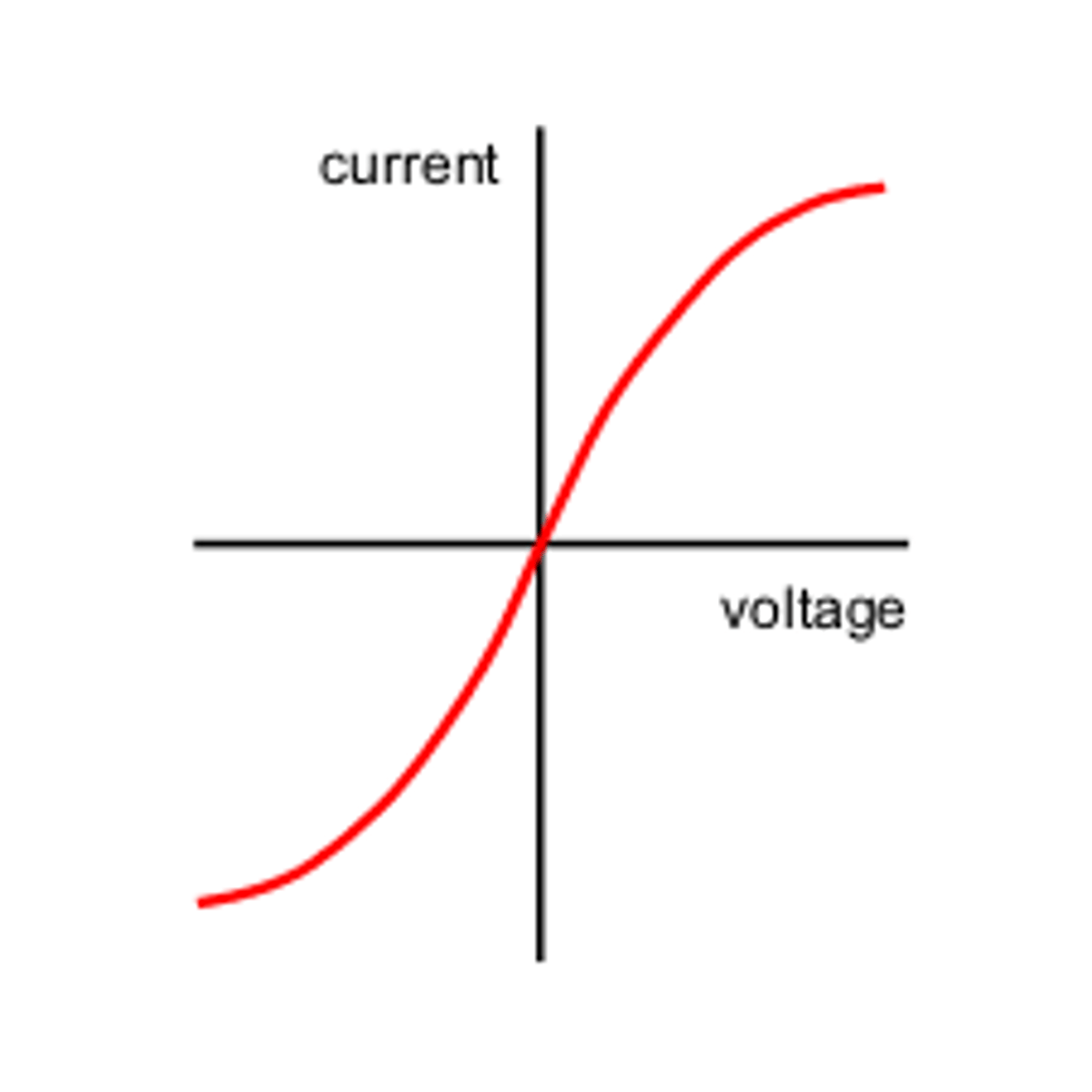
IV graph for a filament lamp
A s-shaped curve which passes through the origin
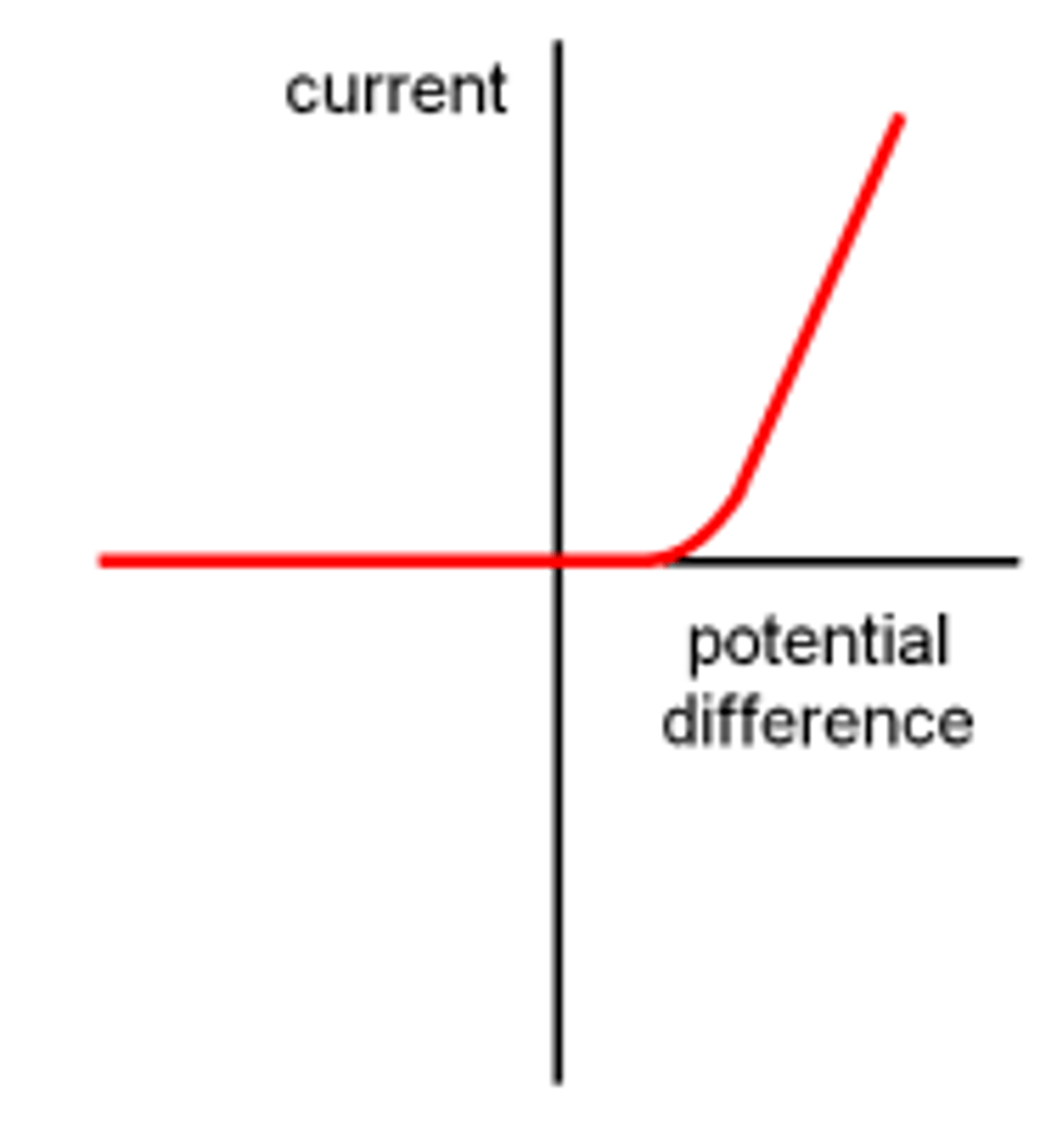
IV graph for a diode
The graph a horizontal line along the x-axis until it reaches around 0.6 V, where it then becomes a straight line with a steep gradient
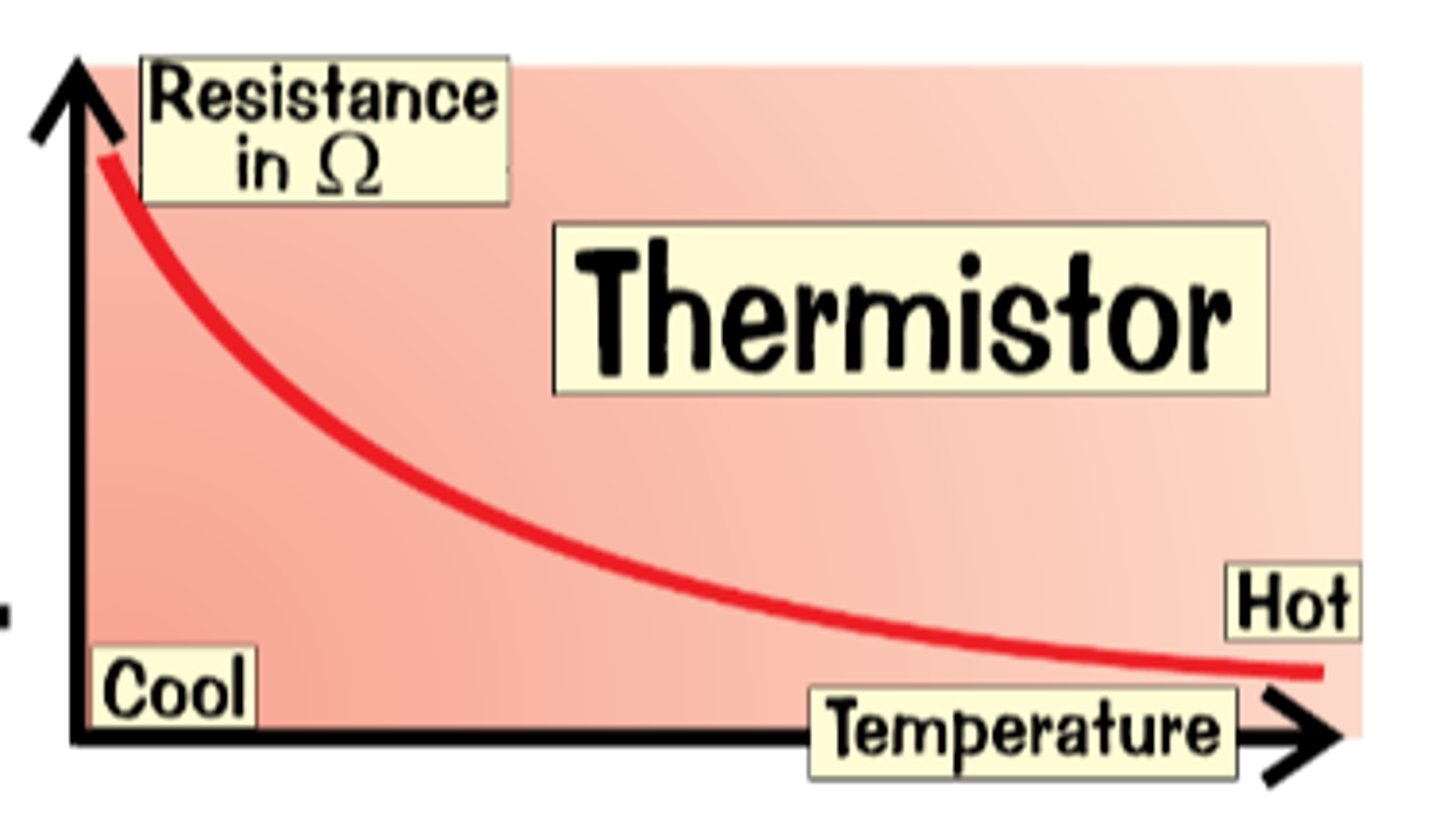
Thermistor
The resistance of a thermistor decreases as the temperature increases
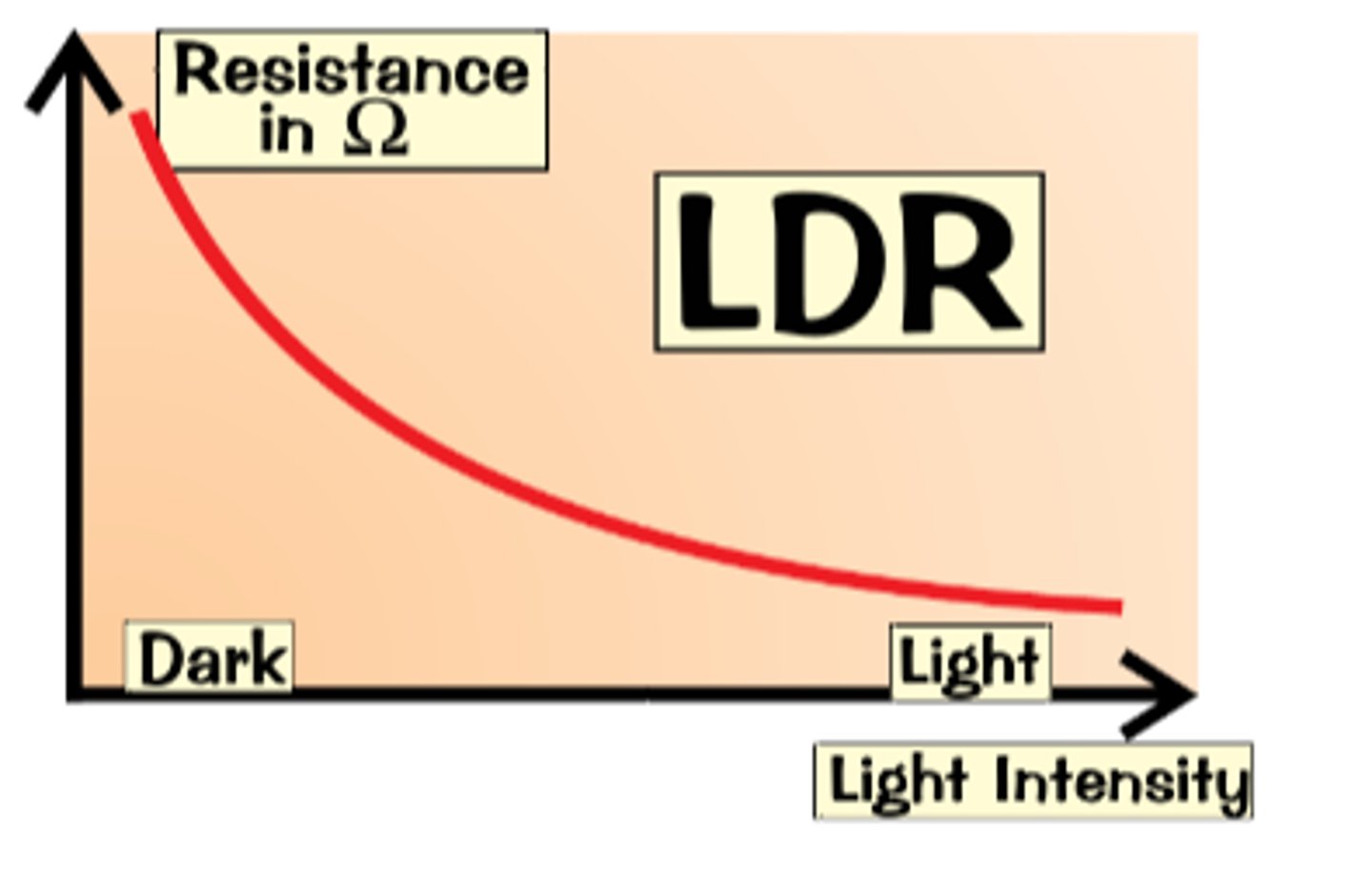
LDR (light dependent resistor)
The resistance of an LDR decreases as light intensity increases
Power
The rate at which energy is transferred or work is done
Electrical power
The amount of work energy transferred or work done by an electrical current each second
P = VI
The equation linking power, potential difference and current
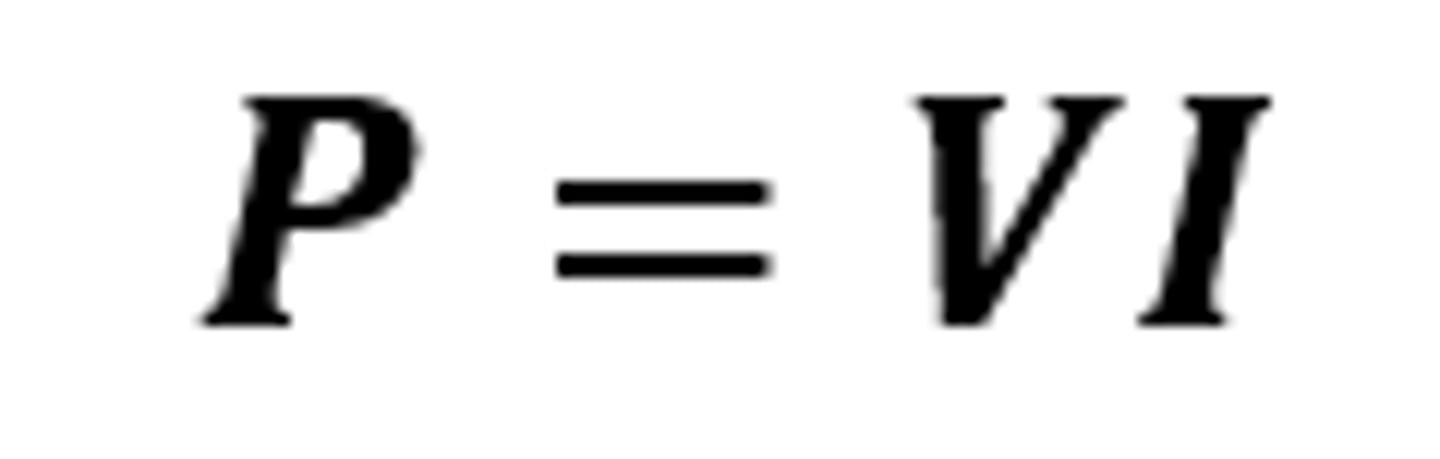
P
The symbol for power
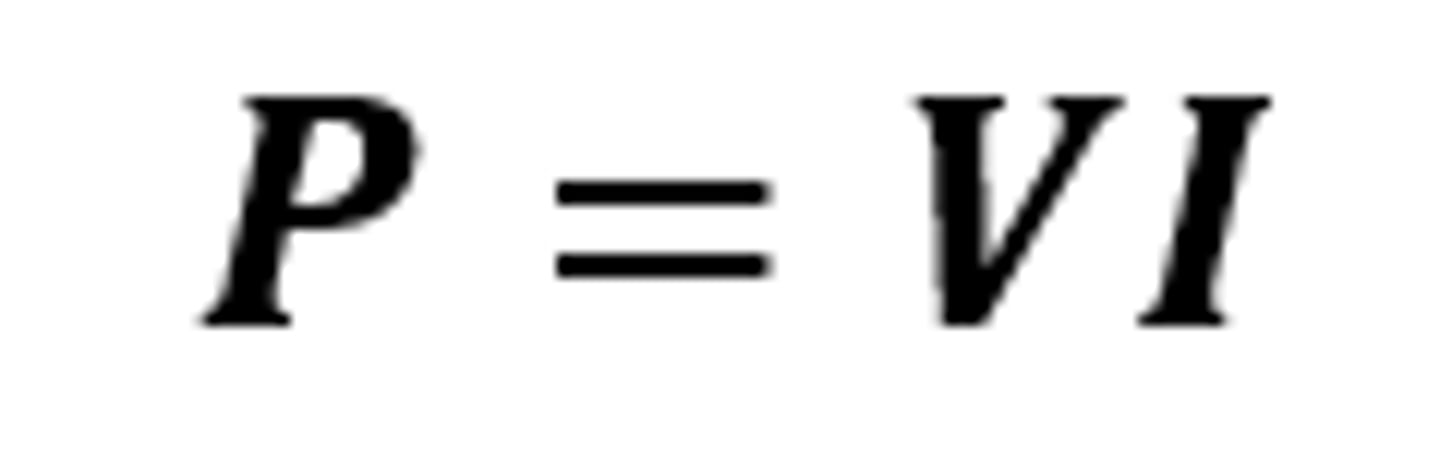
V
The symbol for potential difference (voltage)
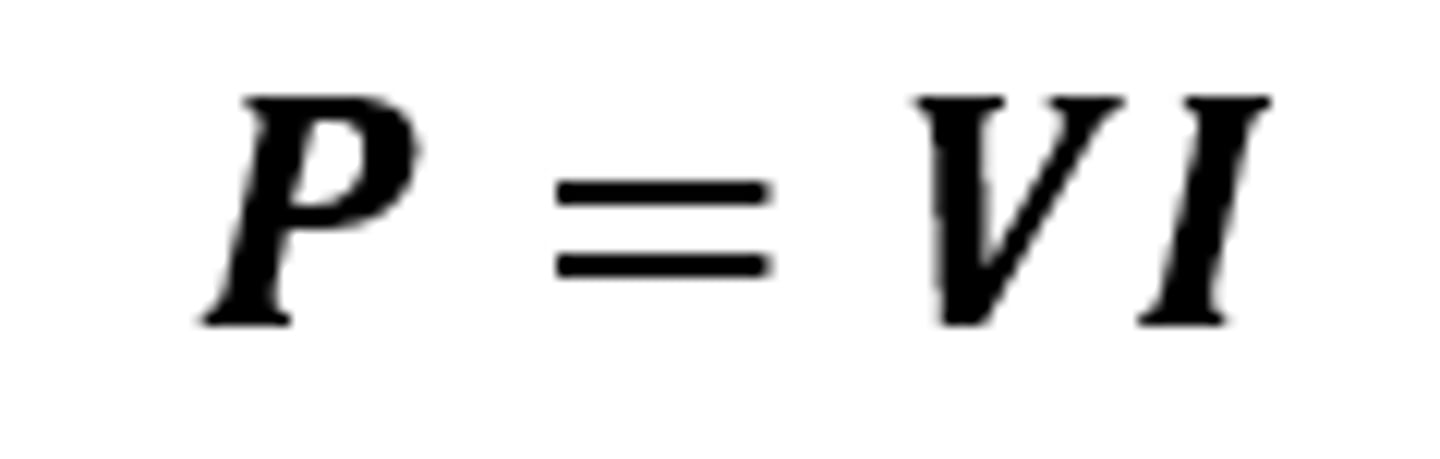
I
The symbol for current
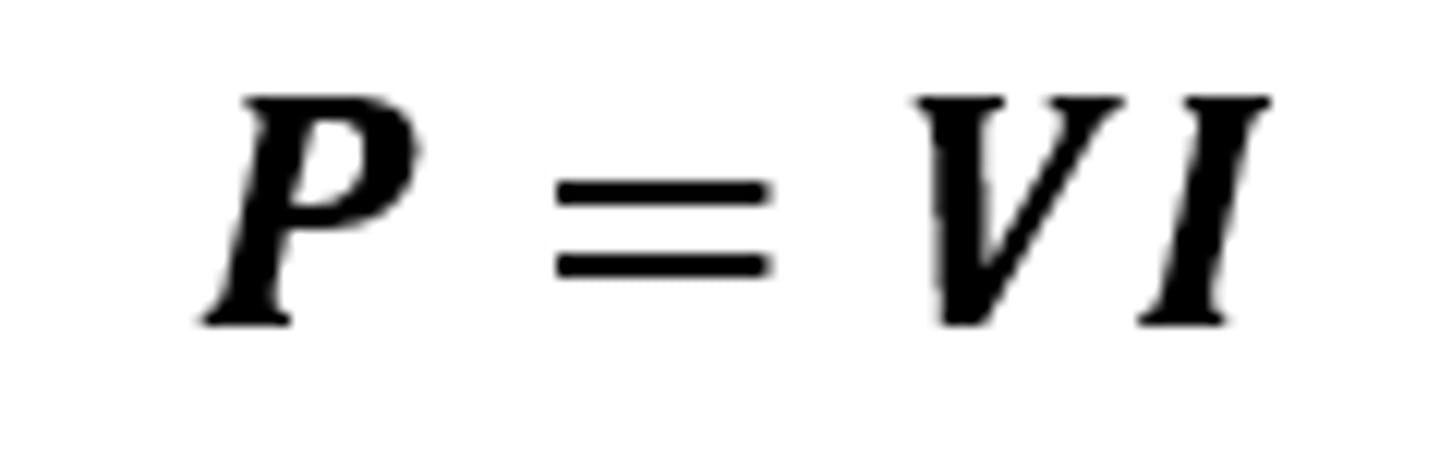
Watts (W)
The SI unit for power

One watt is equal to
The power when one joule of energy is transferred in one second (1 W = 1 J/s)
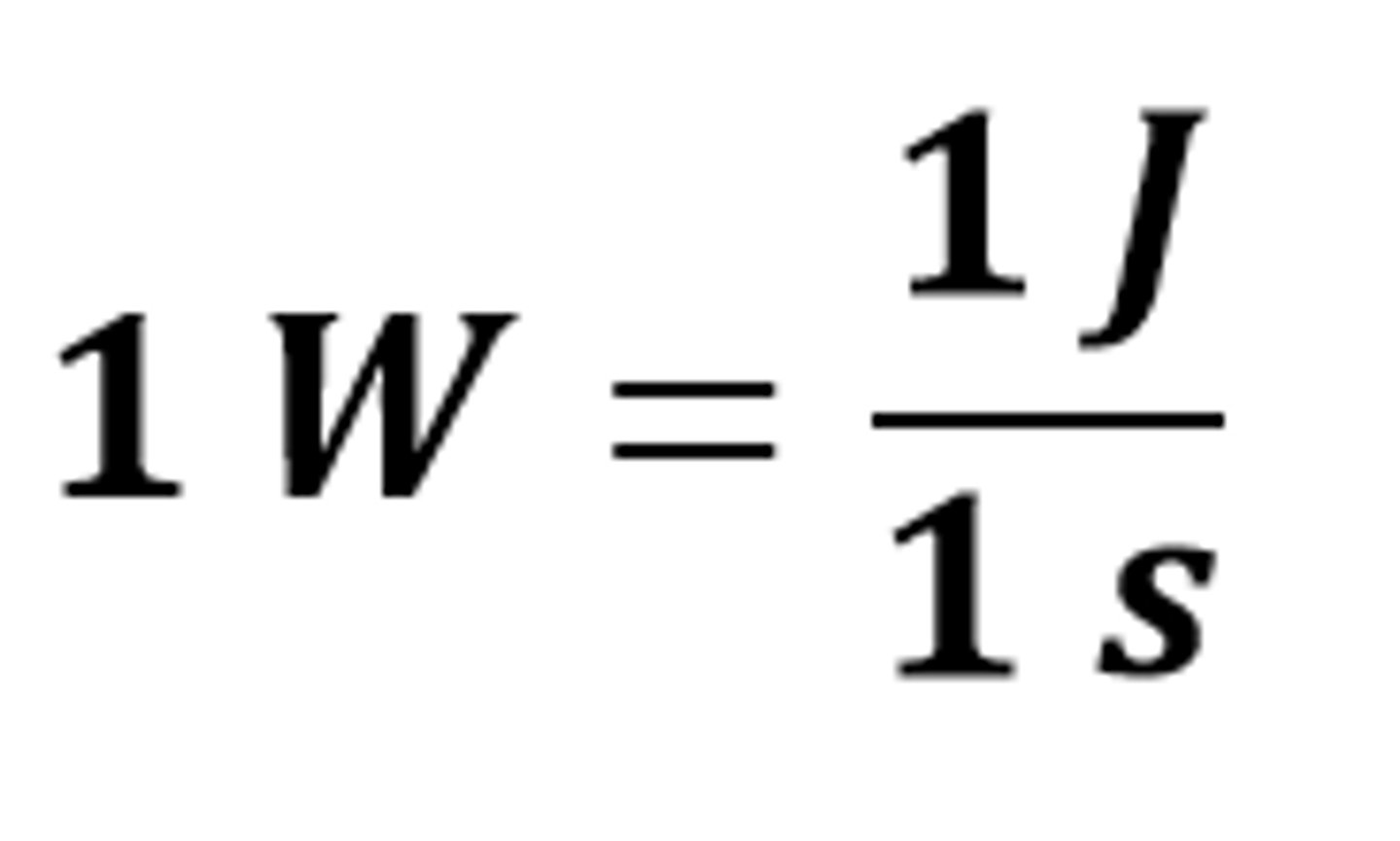
One kilowatt (kW) is equal to _____ watts (W)
1000 watts (W)
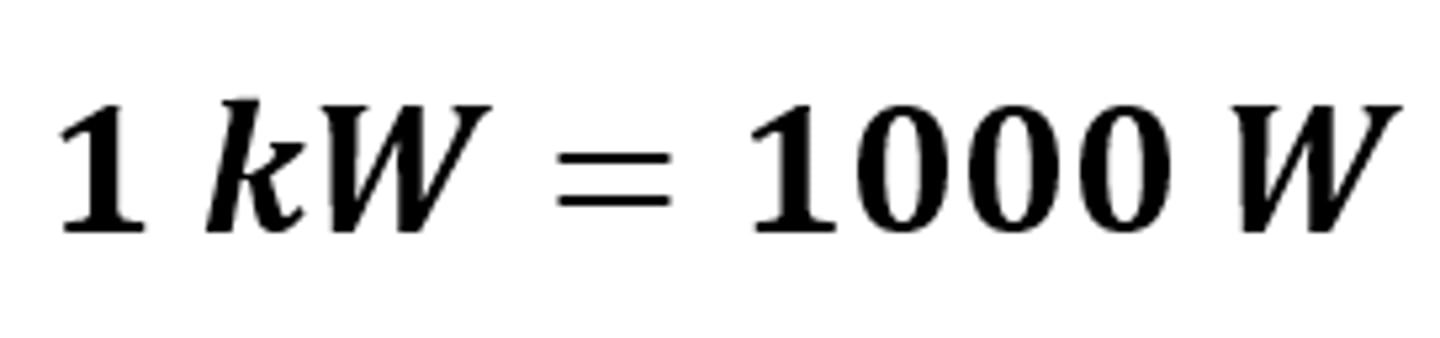
Volts (V)
The SI unit for potential difference (voltage)

Amps (A)
The SI unit for current

P = I²R
The equation linking power (dissipated), current and resistance
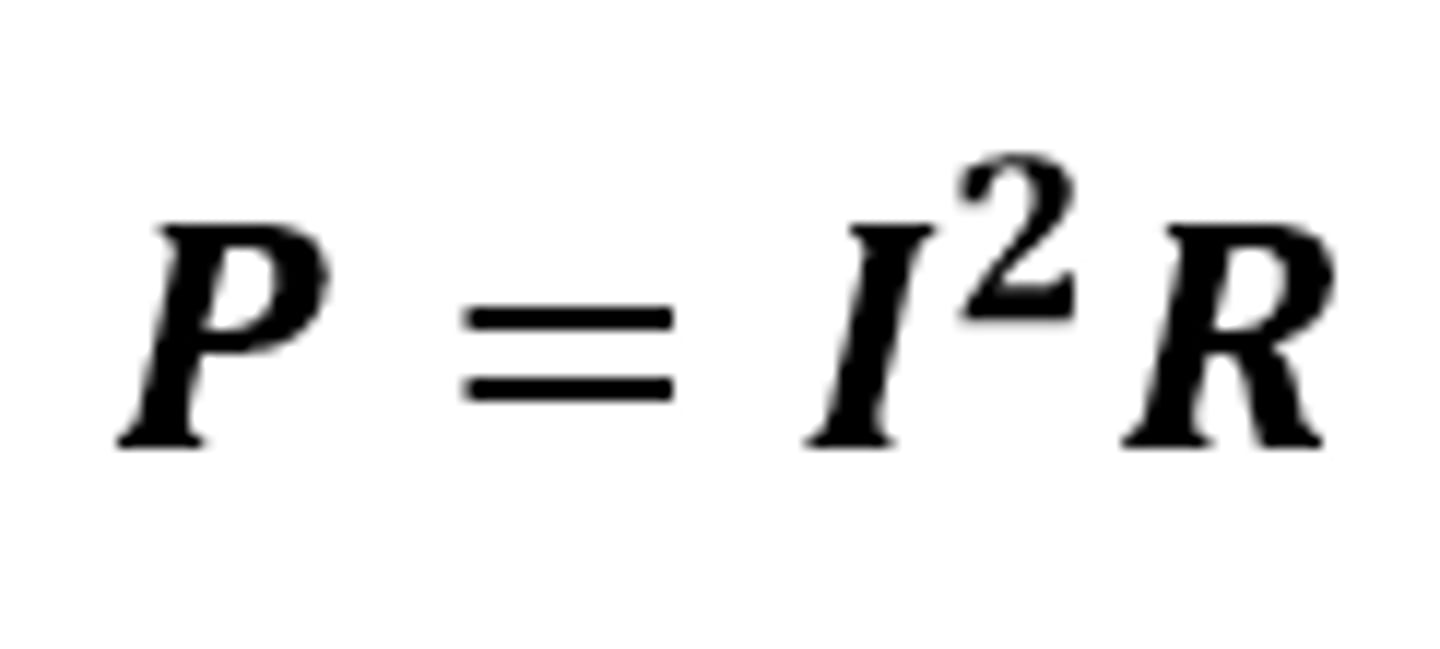
R
The symbol for resistance
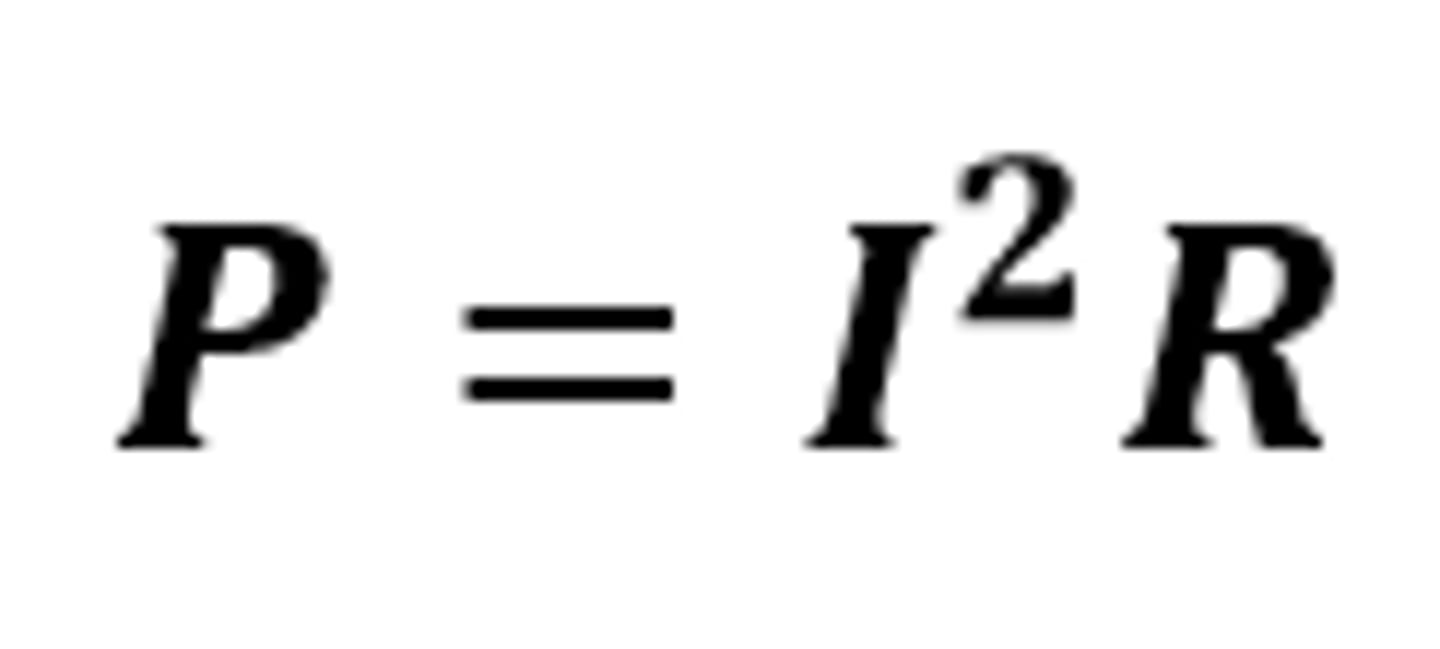
Ohms (Ω)
The SI unit for resistance

Charge (not about fields)
A property of matter that causes a non-contact force to be exerted when two charged objects are brought together
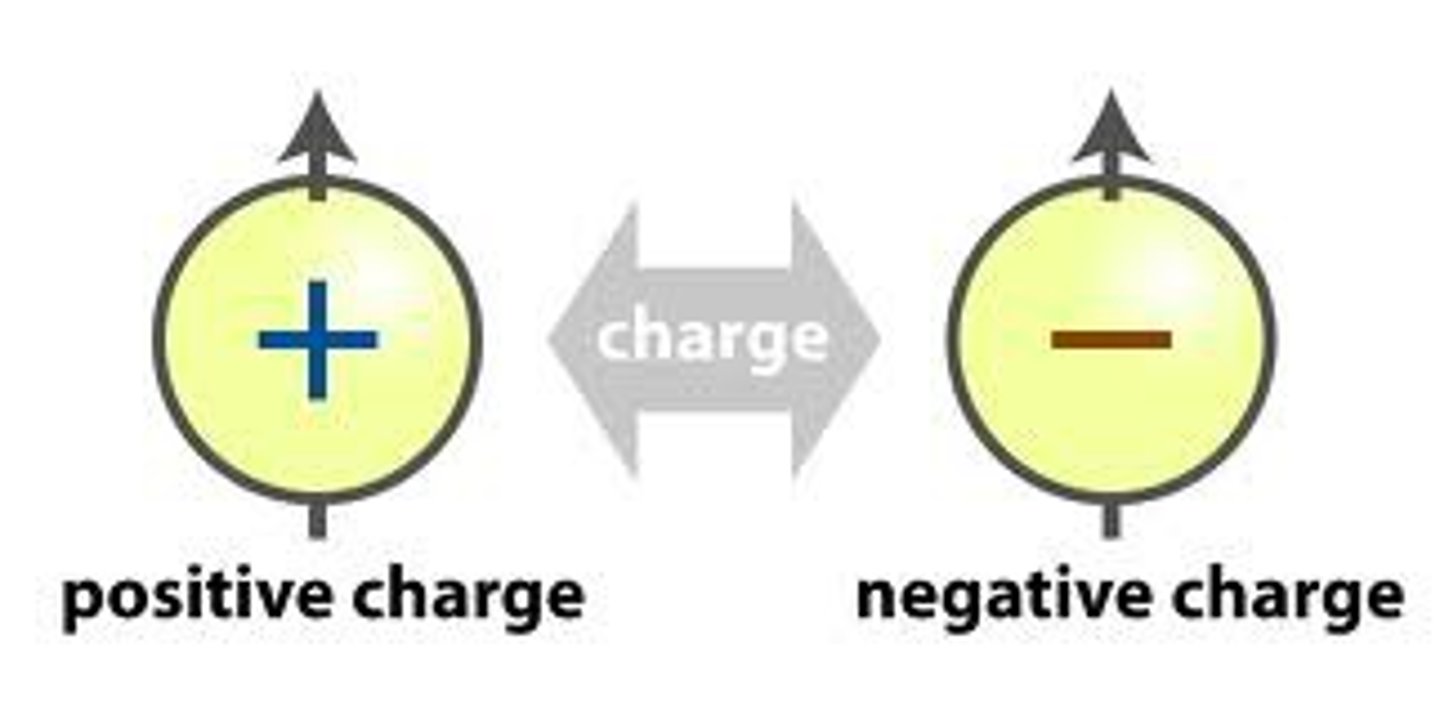
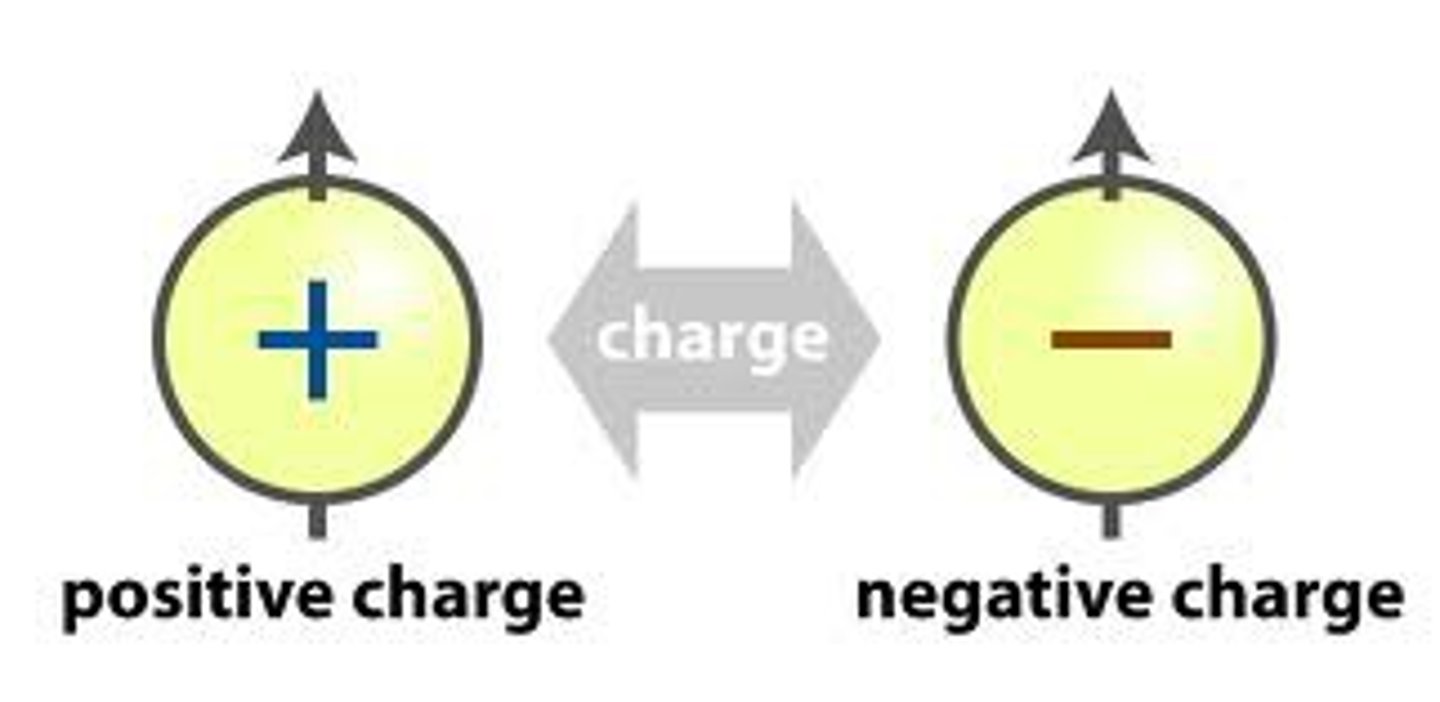
Two types of charge
Positive and negative
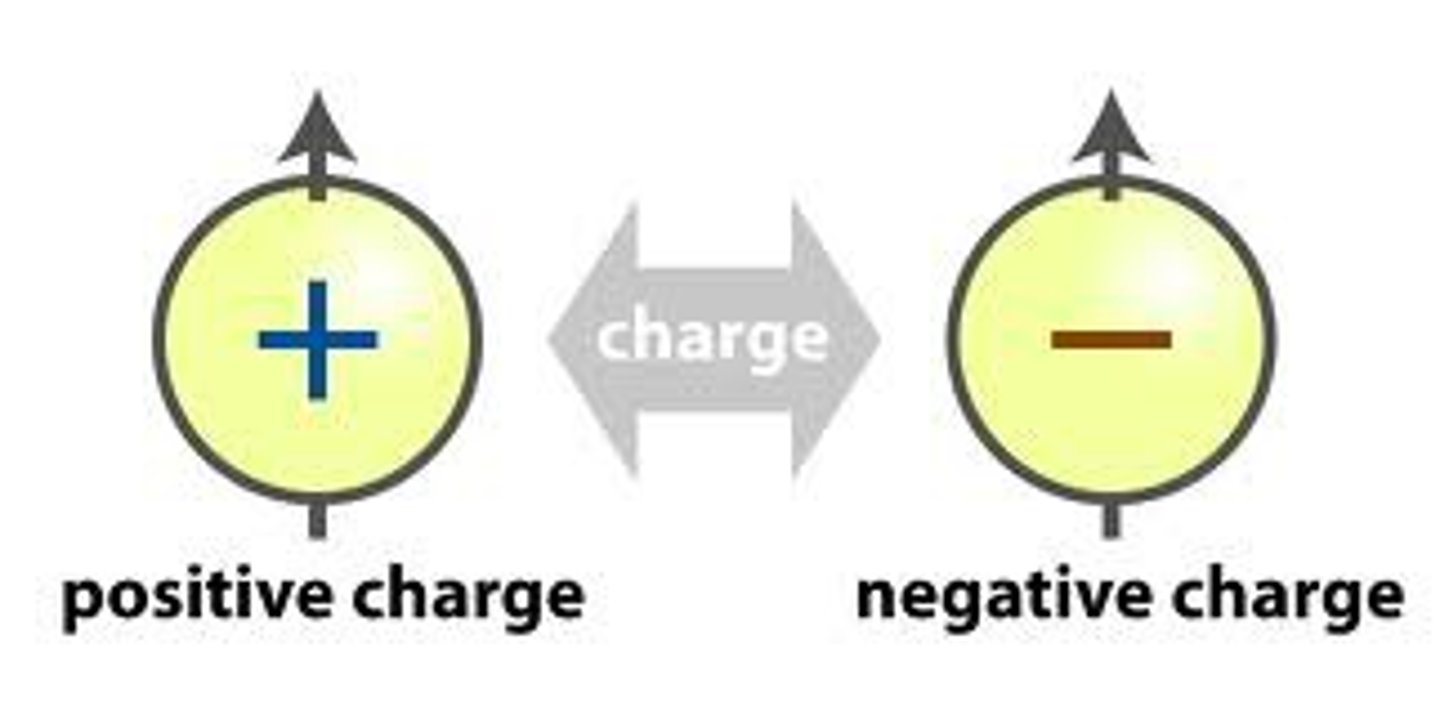
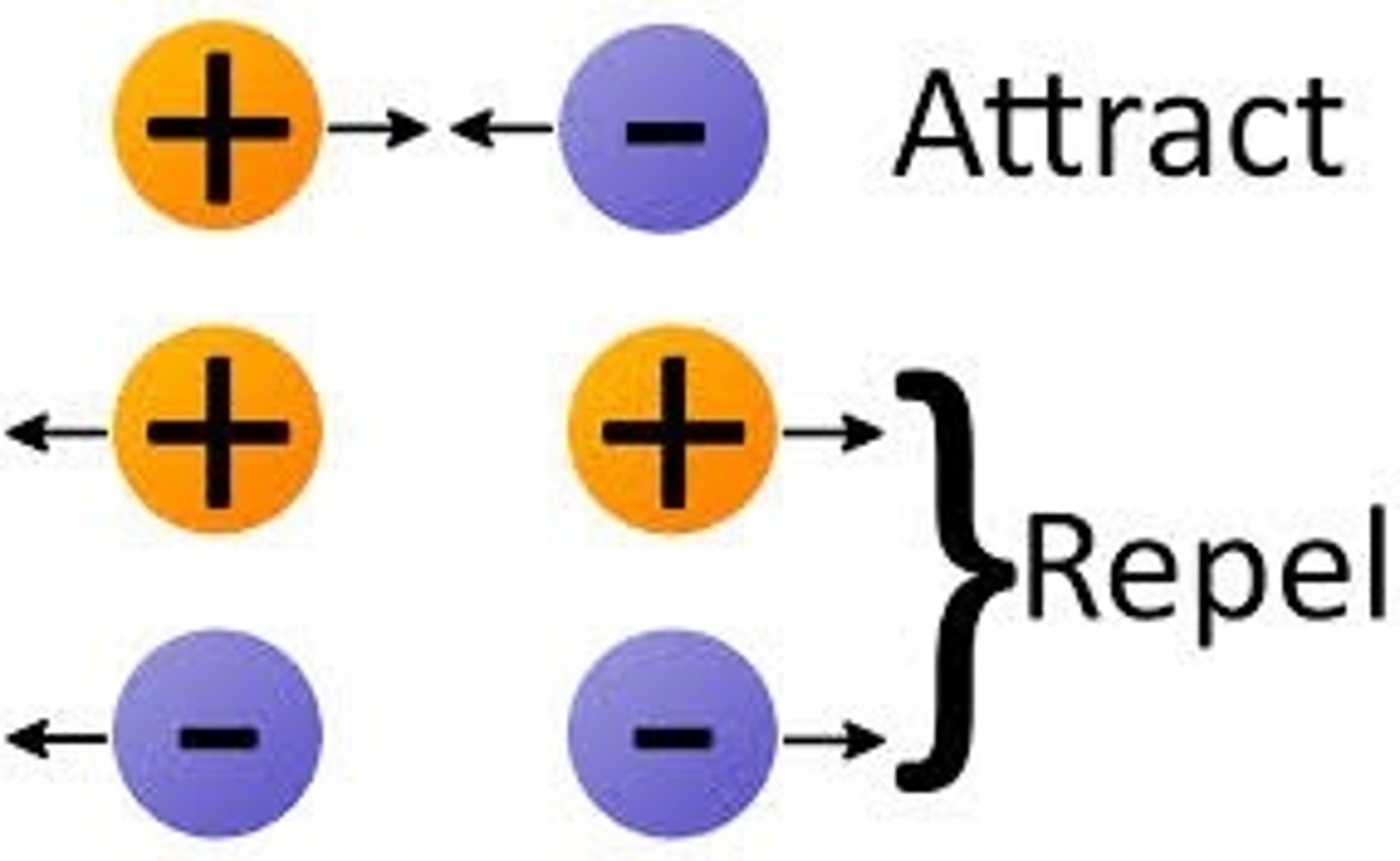
Like charges
Repel each other
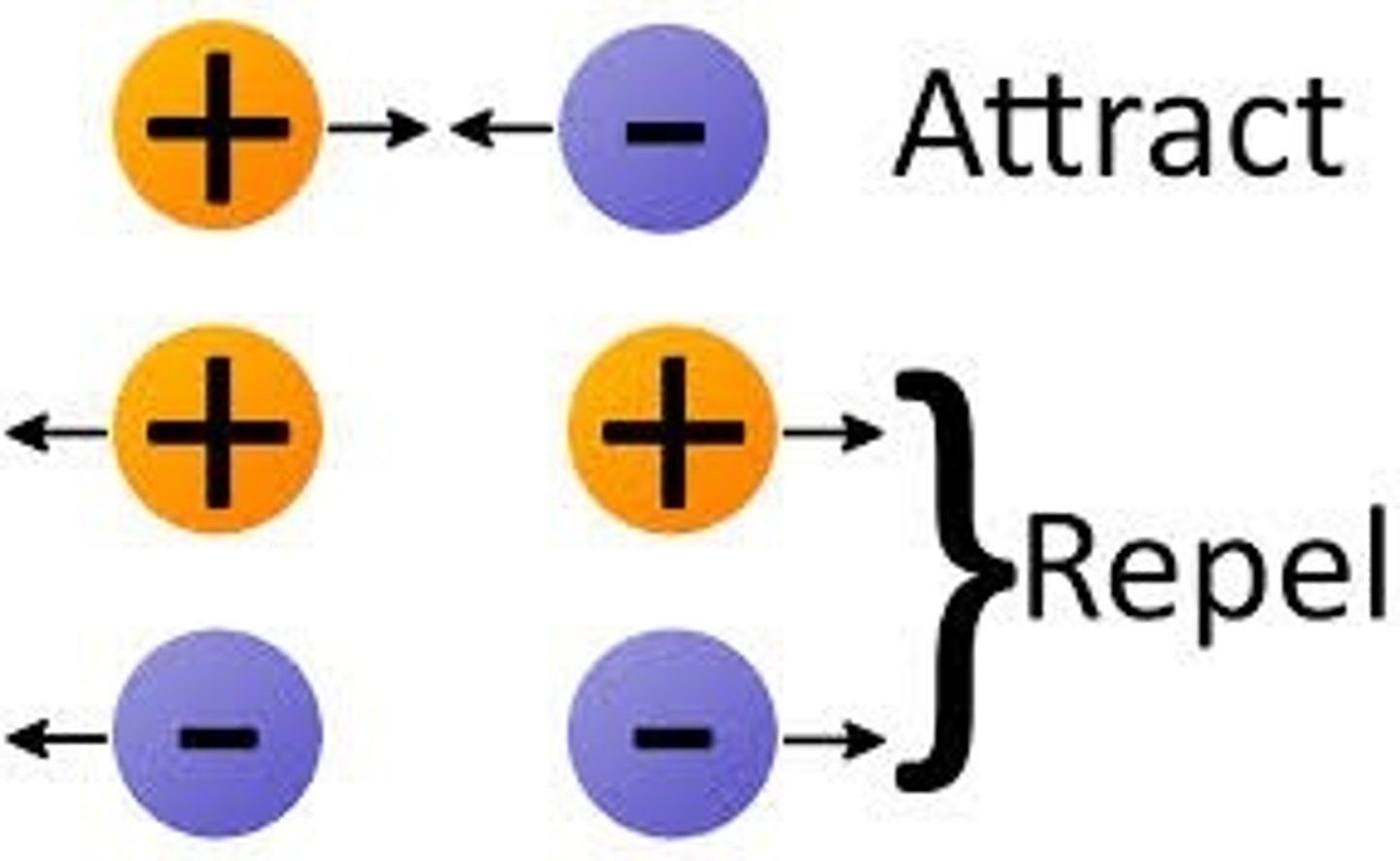
Opposite charges
Attract each other
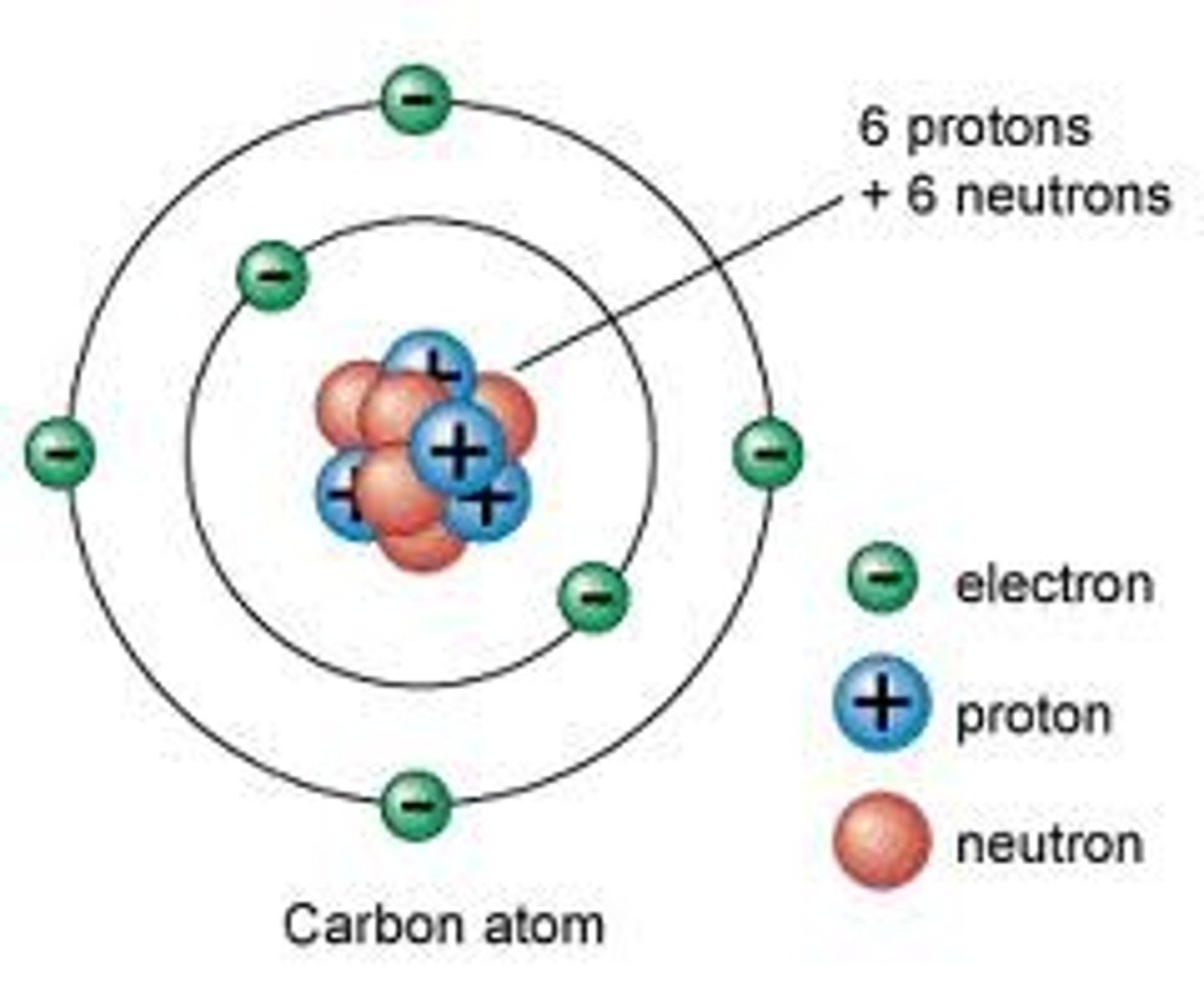
Charge on an atom
Atoms are neutral because they contain equal numbers of positively and negatively charged particles
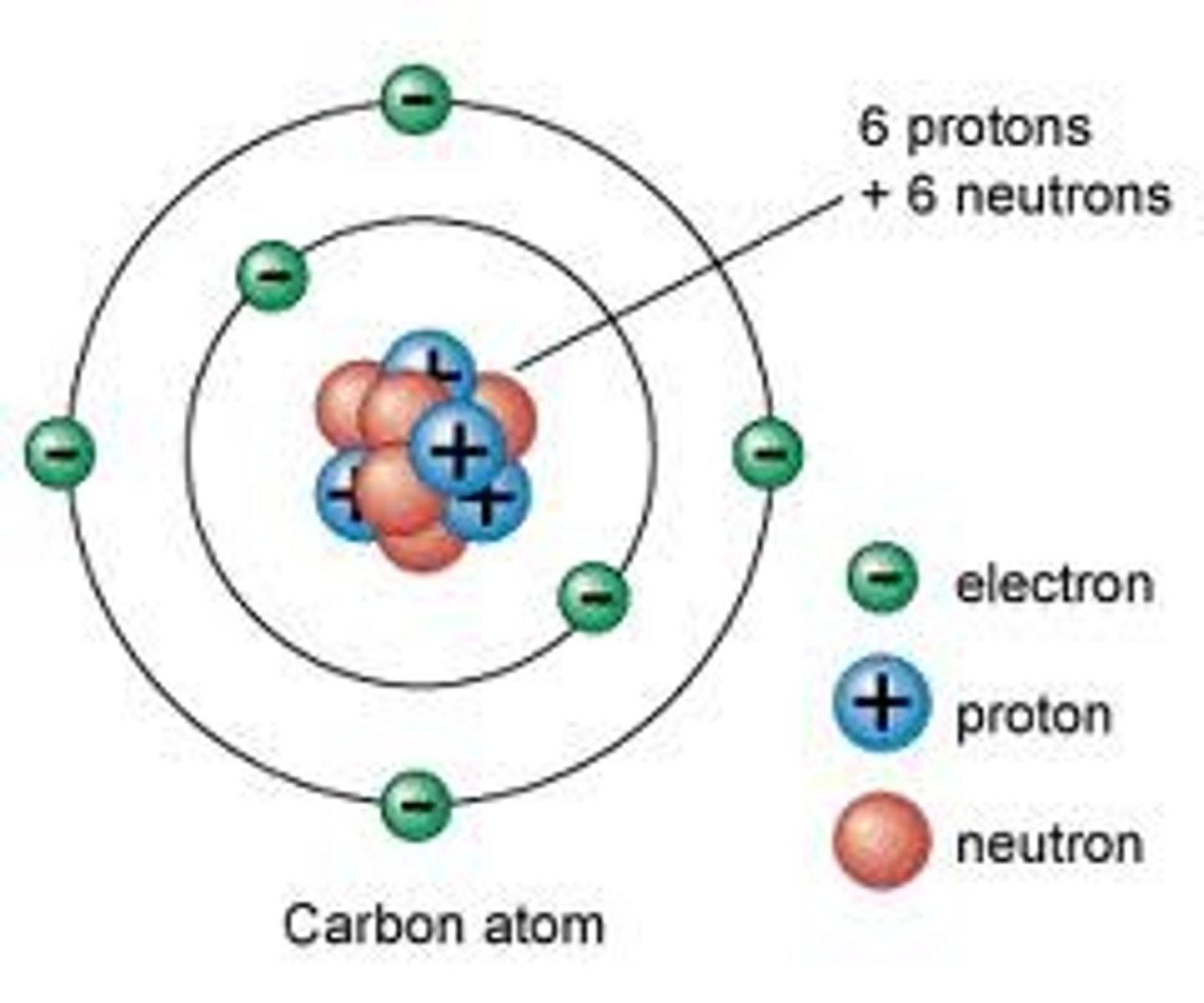
Charge on a proton
A proton carries a positive charge (+1)
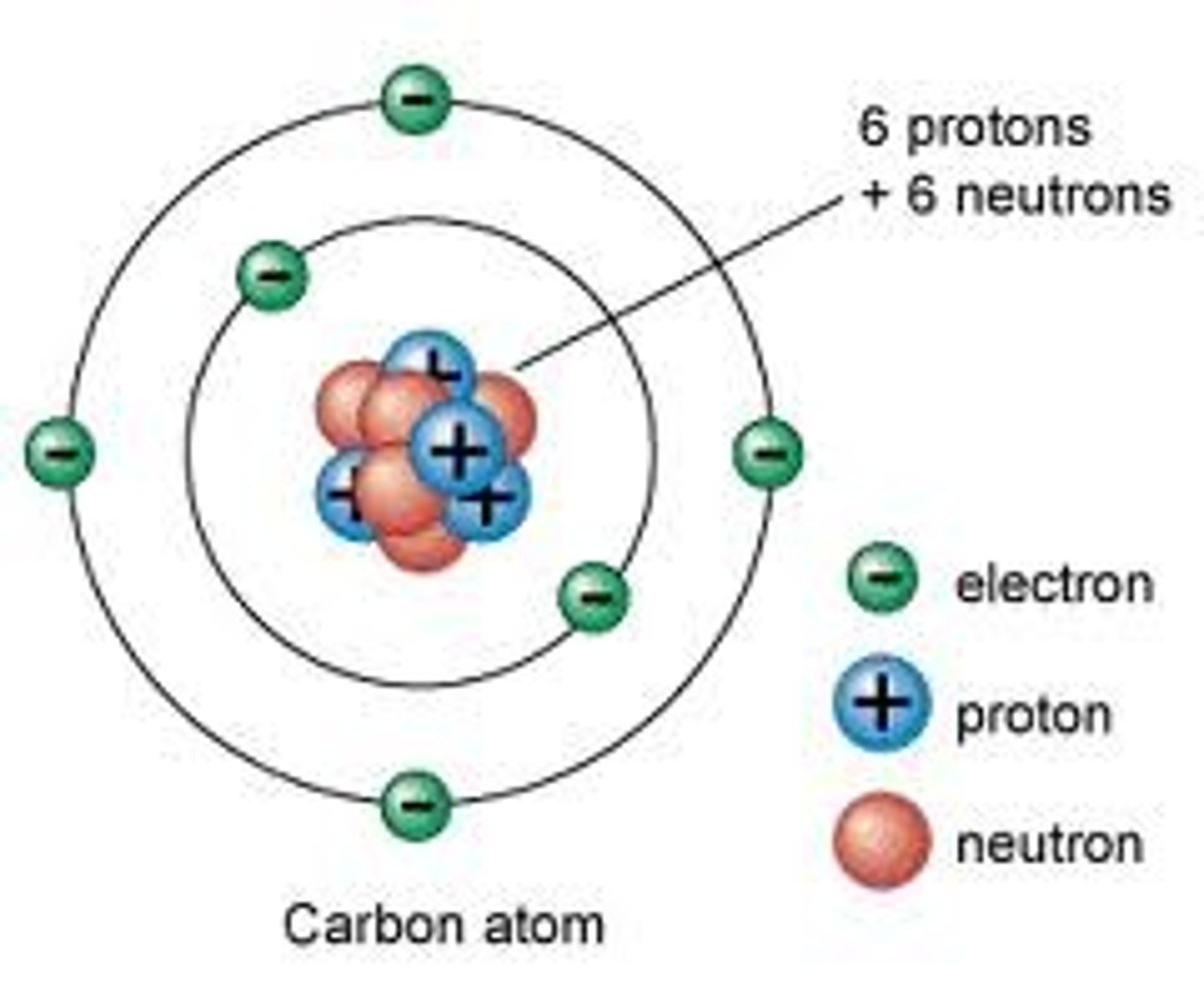
Charge on a neutron
A neutron carries no charge
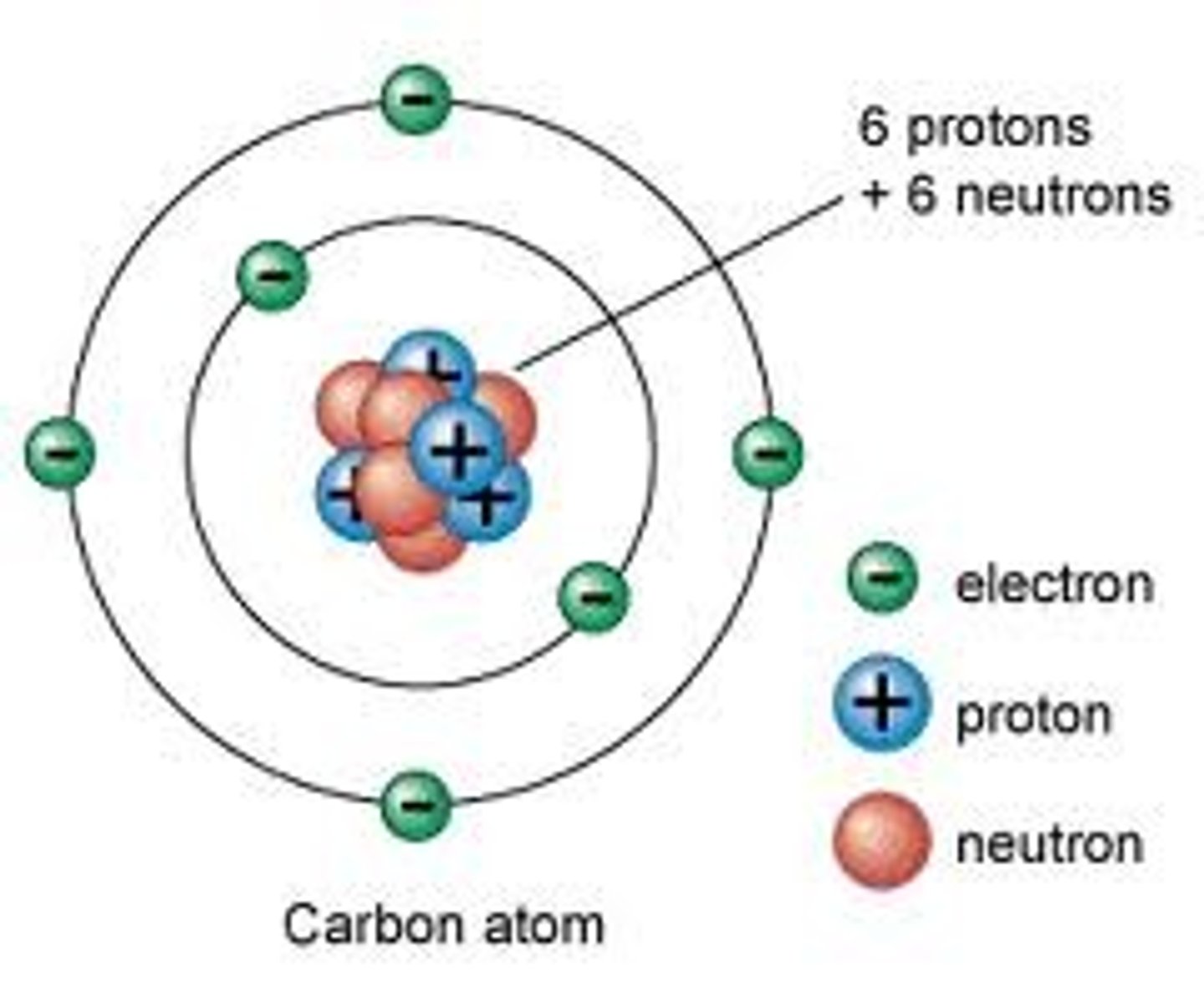
Charge on an electron
An electron carries a negative charge (-1)
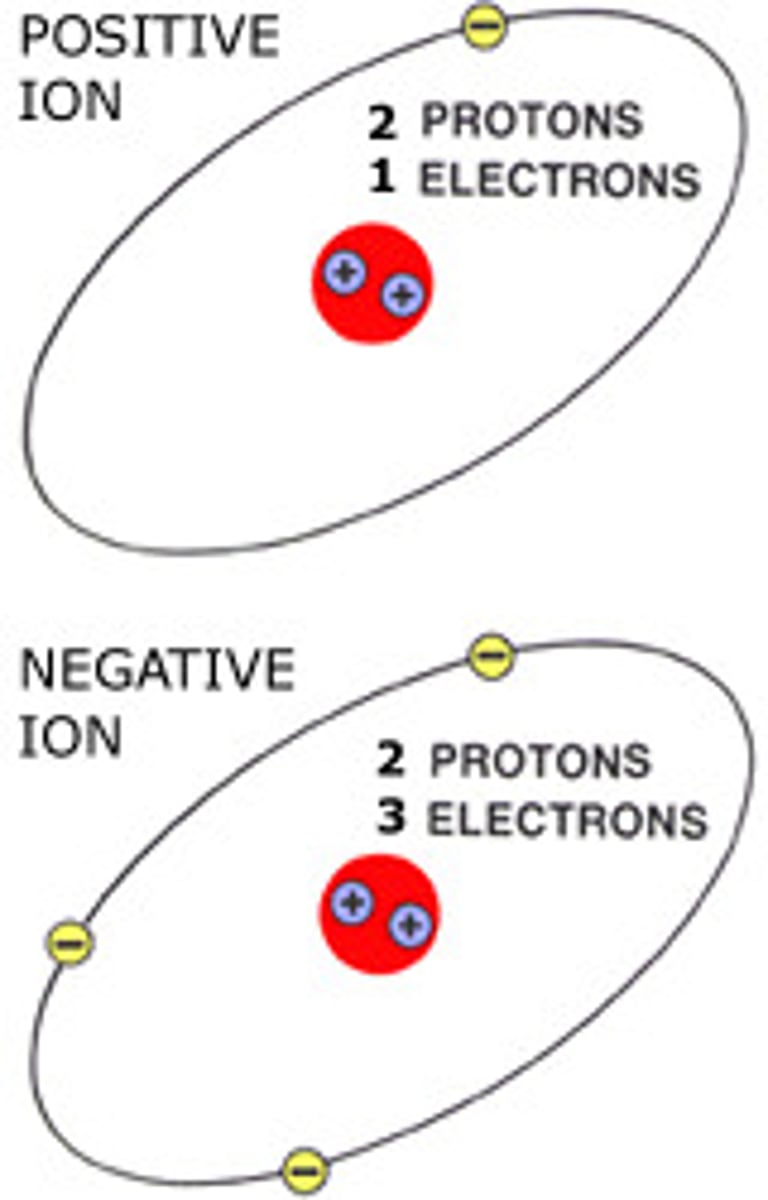
Ion
An atom (or molecule) with an overall electric charge due to losing or gaining one or more electrons
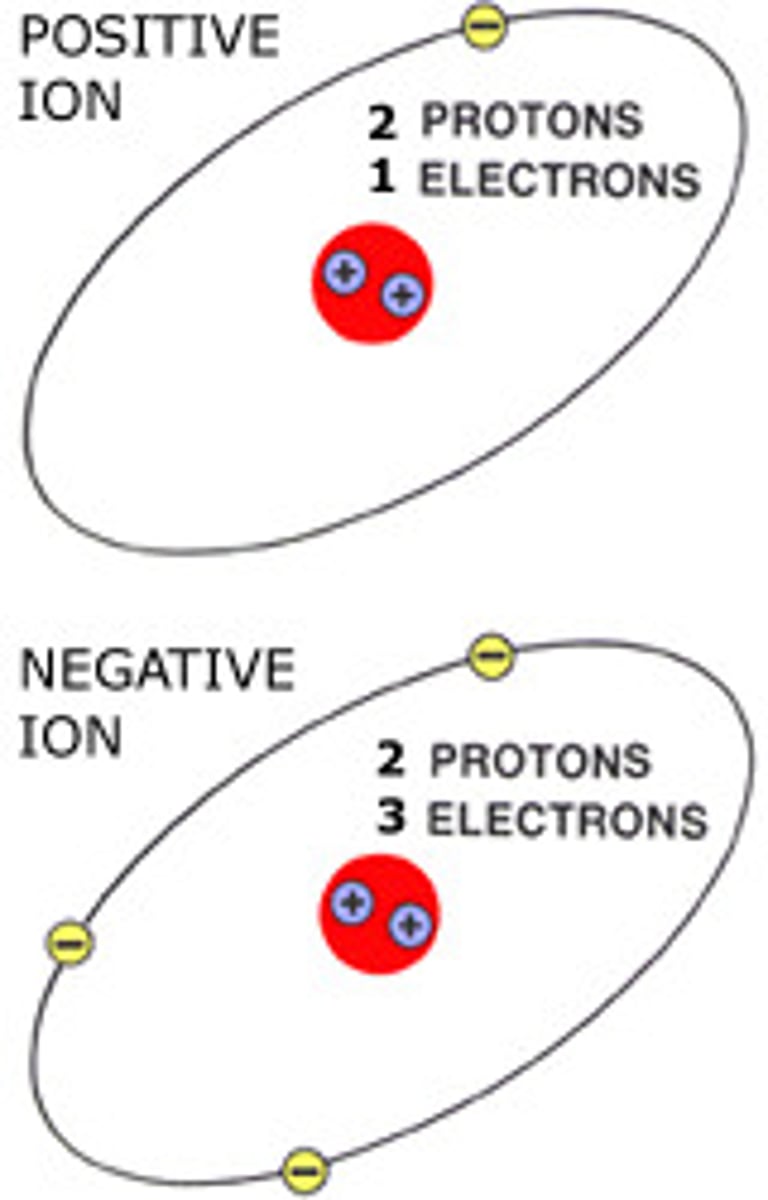
Positively charged ion
An atom or molecule that has lost one or more electrons
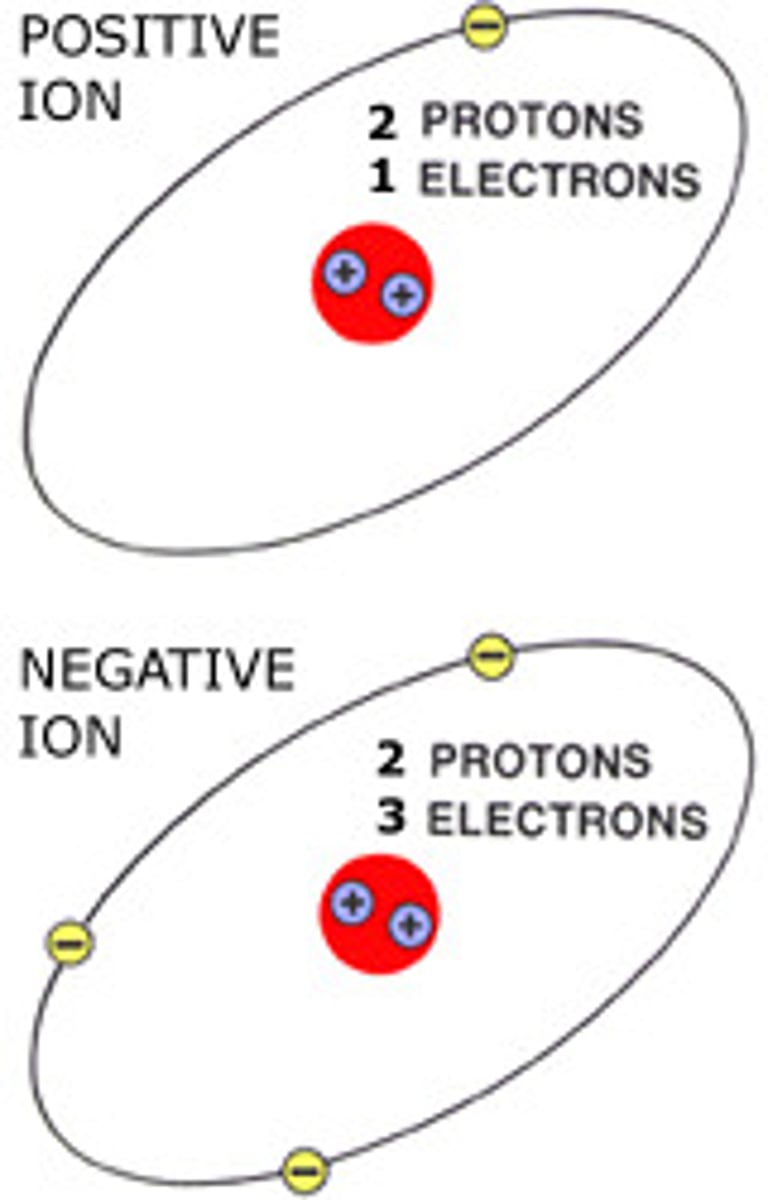
Negatively charged ion
An atom (or molecule) that has gained one or more electron