KINS 308 - Exam 2 TA Version
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:18 AM on 11/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
1
New cards
work
force applied against gravity over distance (J)
2
New cards
What is a better measure of exercise performance? work or power
Power
3
New cards
calculating work
mass x distance x pace x time = work (kgm)
4
New cards
power
work expressed relative to time (kgm/min) or Watts.
5
New cards
calculating power
work/time = power kgm/min
6
New cards
converting power to watts
kgm/min / 6.118
7
New cards
converting power to kcal/min
kgm/min x 0.00234
8
New cards
converting kcal/min to kJmin
kcal/min x 4.186
9
New cards
calorimetry
the science that quantifies heat released from metabolism (metabolic rate)
10
New cards
vo2
oxygen consumption
11
New cards
what is resting vo2
0.25 L/min
12
New cards
vco2
carbon dioxide production
13
New cards
what is resting vco2
0.2 L/min
14
New cards
RQ
respiratory quotient (co2 / o2 for the cell)
15
New cards
RER
respiratory exchange ratio (vco2 / vo2 measured from expired air)
16
New cards
FiO2
fraction of inspired oxygen = 0.20
17
New cards
FiCO2
fraction of inspired carbon dioxide = 0.0003
18
New cards
FiN2
fraction of inspired nitrogen = 0.79
19
New cards
calculation vo2
vo2 = (Vi x FiO2) - (Ve x FeO2)
20
New cards
Haldane transformation
Vi = Ve x [1 - (FeO2 + FeCO2) / FiN2]
21
New cards
John Scott Haldane

22
New cards
Graham Lusk
23
New cards
caloric equivalent to calculate caloric expenditure
5 kcals/LO2
24
New cards
3 metabolic changes during exercise
phosphagen system
glycolysis
aerobic/mitochondrial respiration
glycolysis
aerobic/mitochondrial respiration
25
New cards
what is the rest to exercise transition?
VO2 increases rapidly until:
-steady state (w/n 3-5 min): all metabolic needs are being met
-ATP demand met aerobically: state of increased mitochondrial respiration
-steady state (w/n 3-5 min): all metabolic needs are being met
-ATP demand met aerobically: state of increased mitochondrial respiration
26
New cards
rise of vo2 in an untrained person
slower response time to steady state (can improve through aerobic training)
27
New cards
what is the relationship between exercise intensity and vo2?
higher intensity requires higher vo2
28
New cards
what is steady state exercise?
all metabolic demands are being met through mitochondrial respiration (takes 3-5 minutes)
29
New cards
Why is there a lower time to steady state when trained?
mitochondria are stimulated faster to meet demand due to increase mass and oxidative enzyme activity (safe effect during warm up)
30
New cards
effect of intensity on rest to SS transition
the larger the increment the longer the time to SS
31
New cards
oxygen deficit
O2 consumption is lower than necessary to supply appropriate ATP production required of any exercise
32
New cards
why to oxygen deficit reflect an increase in anaerobic metabolism?
-increased CrP and glycolysis to meet demands
-delay time for full mitochondrial contribution
-delay time for full mitochondrial contribution
33
New cards
would trained people have a lower o2 deficit than untrained person for given exercise intensity?
trained person has a lower deficit because they have more mitochondria and enzymes and there
34
New cards
what advise would you give to someone so that the compete at their top performance?
stimulate mitochondria before the race (30-40 min) with a dynamic warm-up
35
New cards
what is the body's response to prolonged exercise (exercise longer than 10 minutes)?
-ATP primarily from mitochondrial means
-steady state exercise can be maintained
-steady state exercise can be maintained
36
New cards
what is the body's response to intense exercise?
-vo2 increases rapidly
-CrP decreases rapidly (more intense=bigger decrease especially in FT motor units)
-increase in glycolytic rate (increases PFK and phosphorylase activity)
-increase in lactate production and release
-increase in muscle and blood acidosis
-CrP decreases rapidly (more intense=bigger decrease especially in FT motor units)
-increase in glycolytic rate (increases PFK and phosphorylase activity)
-increase in lactate production and release
-increase in muscle and blood acidosis
37
New cards
What is the body's response to incremental exercise?
vo2 increases non-linearly to vo2 max
38
New cards
vo2 max
maximum oxygen consumption
-"fitness" or "exercise performance" measure
-quantifies exercise intensity
-expresses intensity as a percent
-#1 predictor of morbidity
-"fitness" or "exercise performance" measure
-quantifies exercise intensity
-expresses intensity as a percent
-#1 predictor of morbidity
39
New cards
What are the units used to express vo2 or vo2 max?
-meters/min
-mL/min
-ml/kg/min
-mL/min
-ml/kg/min
40
New cards
why is it important to express vo2 max in ml/kg/min when making comparisons?
difference between male and female and body mass
41
New cards
what is greatest above lactate threshold?
-lactate production and release
-glycolytic rate and acidosis
-glycolytic rate and acidosis
42
New cards
what is the lactate threshold?
point where lactate production exceeds it's removal
-curvilinear response with increase exercise intensity
-curvilinear response with increase exercise intensity
43
New cards
LT in untrained people
40-60% of vo2 max
44
New cards
LT in trained people
greater than 70% of vo2 max
45
New cards
what is the point of maximal ss exercise?
when max intensity ss is maintained
46
New cards
factors of LT physiology
-represents increase in anaerobic metabolism
-can't maintain prolonged exercise above LT
-large increase in glycogenolysis above LT
-recruitment of fast-twitch motor units
-can't maintain prolonged exercise above LT
-large increase in glycogenolysis above LT
-recruitment of fast-twitch motor units
47
New cards
what is the best measurement for predicting performance?
exercise intensity at LT (middle to long distance events)
-higher LT = faster one can sustain pace
-higher LT = faster one can sustain pace
48
New cards
cells that produce glucose?
liver and kidney
49
New cards
glycogen synthesis
glucose to glycogen
50
New cards
glycogenolysis
glycogen to glucose
51
New cards
gluconeogenesis
making glucose from other sources than CHO (glycerol, amino acids, and lactate)
52
New cards
why is gluconeogenesis needed?
-Energy for brain
-When blood glucose levels are low
-Glycogen stores are low
-When blood glucose levels are low
-Glycogen stores are low
53
New cards
what is the source of fat during lower intensity exercise?
Plasma FFA (adipose tissue)
54
New cards
what is the source of fat during moderate to high intensity exercise (usage affected by training status)?
Intramuscular TGL
55
New cards
what are amino acids used for during exercise?
an emergency source via gluconeogenesis
-can increase up to 10-15% in prolonged exercise but little used during rest
-can increase up to 10-15% in prolonged exercise but little used during rest
56
New cards
what is the purpose to metabolism?
maintain blood glucose homeostasis
57
New cards
fuel selection during low-intensity exercise (less than 30% vo2 max)
fats are primary fuel
58
New cards
fuel selection during high-intensity exercise (greater than 70% vo2 max)
CHO are primary fuel
59
New cards
"crossover" concept
shift from fat to CHO as exercise intensity increases
60
New cards
what causes the shift in fuel during "crossover"?
recruitment of FT MUs increasing blood levels of Epi (increasing rate of glycolysis overtakes beta-oxidation for ATP)
61
New cards
fuel selection during prolonged exercise
shift from CHO toward fat metabolism
62
New cards
what causes increased rates of lipolysis?
the increase of lipase activity (activated by catecholamines)
63
New cards
what does increased rates of lipolysis cause?
decreased muscle glycogen stores (greater than 2 hours with moderate to high intensity)
64
New cards
The lower the ________ and the better the _________________, the longer the time to muscle glycogen depletion
exercise intensity
training status
training status
65
New cards
fuel mix during prolonged exercise
glycogen early (30-45 min) ---> glucose and FFA usage increases ---> glucose usage decreases and FFA usages increases (greater than 60 minutes) ---> protein usage slowly increases as glucose decreases
66
New cards
components of the cardiovascular system
-heart and blood
-systemic circulation
-pulmonary circulation
-systemic circulation
-pulmonary circulation
67
New cards
purposes of the cardiovascular system
-deliver o2 to tissues and transport co2 to lungs
-transport nutrients and hormones to tissues
-maintain thermoregulation and blood pH
-maintain blood pressure
-transport nutrients and hormones to tissues
-maintain thermoregulation and blood pH
-maintain blood pressure
68
New cards
how many liters of blood are in the system?
5 liters
69
New cards
what is hematocrit?
percent of RBCs in blood
-40-45% in males
-35-40% in females
-40-45% in males
-35-40% in females
70
New cards
how do you blood dope?
-remove one unit of blood every 4-8 weeks up to 3 times
-reinfuse one week prior to competition
-reinfuse one week prior to competition
71
New cards
superior vena cava
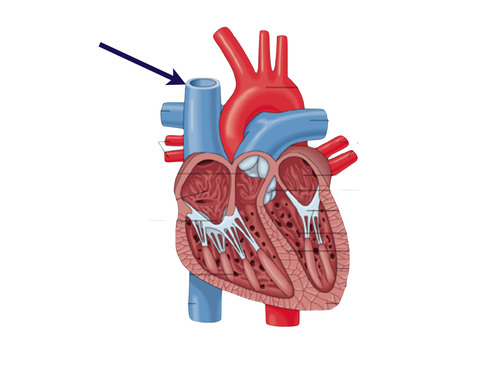
72
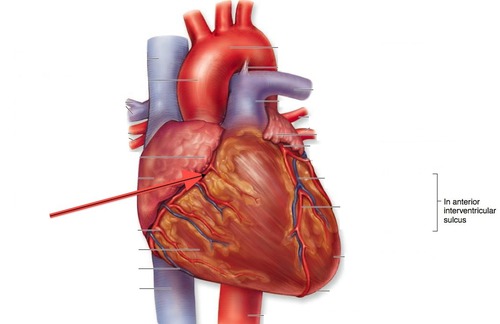
New cards
right coronary artery
73
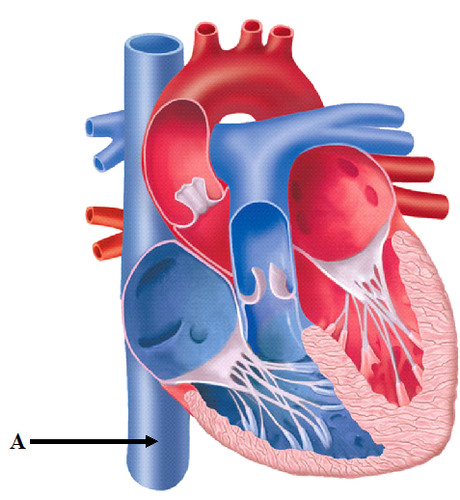
New cards
inferior vena cava
74
New cards
aorta
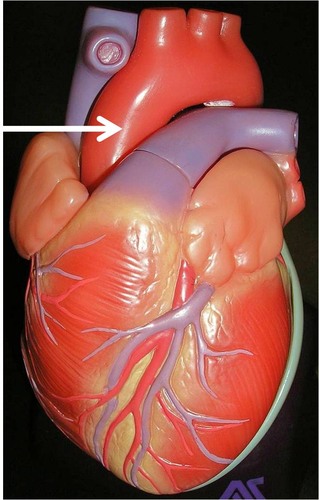
75
New cards
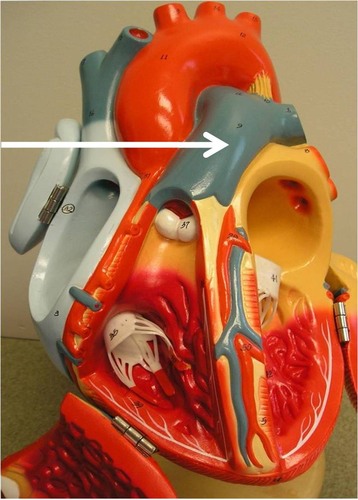
pulmonary trunk
76
New cards
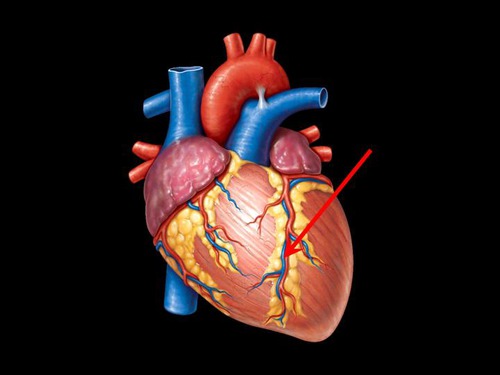
great cardiac vein
77
New cards
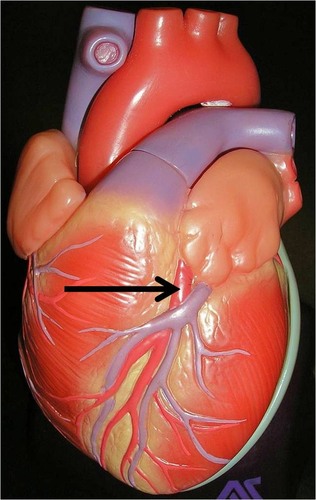
left anterior descending artery
78
New cards
right pulmonary artery
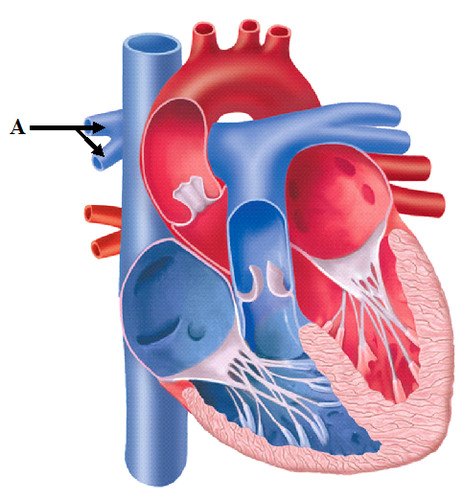
79
New cards
tricuspid valve (right AV valve)
80
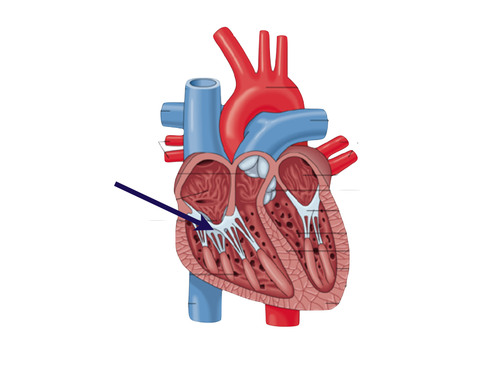
New cards
chordae tendinae
81
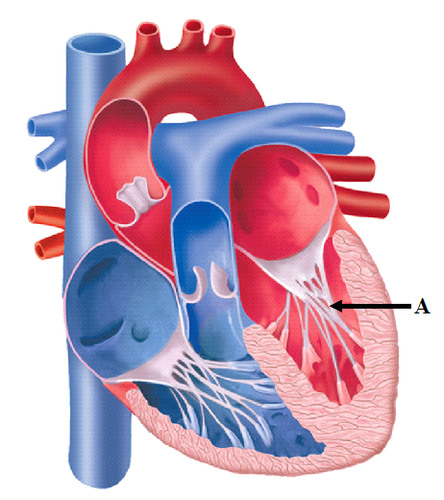
New cards
papillary muscle
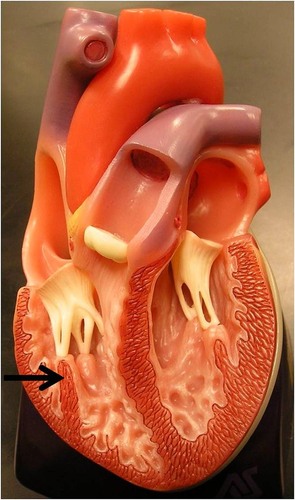
82
New cards
aortic valve
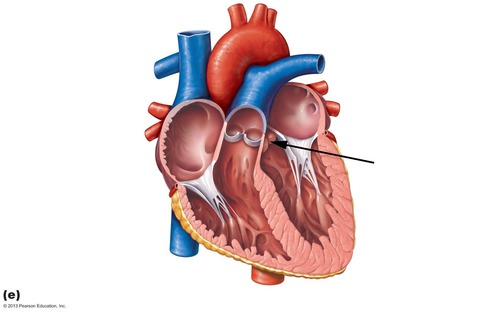
83
New cards
left pulmonary artery
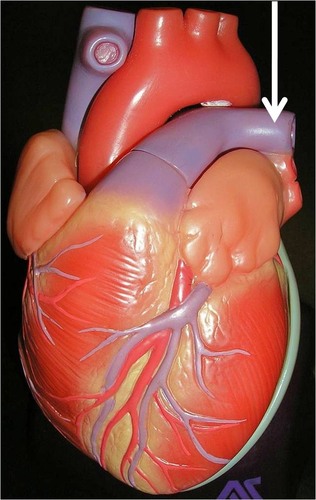
84
New cards
pulmonary valve
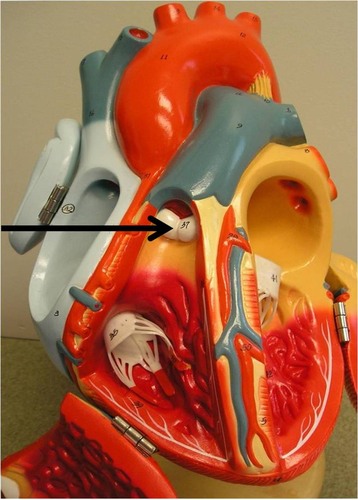
85
New cards
bicuspid valve (mitral valve)
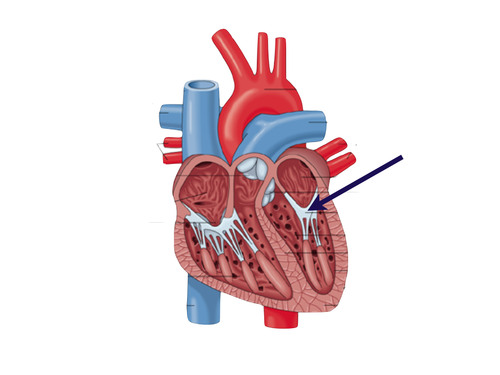
86
New cards
how does the myocardium work?
-myocardial cells are interconnected
-action potential spreads from cell to cell to promote synchronicity
-high amount of ST muscle fibers (no motor units)
-action potential spreads from cell to cell to promote synchronicity
-high amount of ST muscle fibers (no motor units)
87
New cards
is the myocardium highly aerobic or anaerobic?
aerobic (lots of mitochondria and capillaries)
88
New cards
why are veins considered high compliance vessels (capacitance vessels)?
can hold increased blood volumes and contain valves to direct flow one-way
89
New cards
why are arteries considered windkessel vessels?
property provides constant blood flow
90
New cards
arterioles
-primary function = blood flow regulation
-contain smooth muscle (SNS controlled)
-resistance vessels = decreased blood velocity
-contain smooth muscle (SNS controlled)
-resistance vessels = decreased blood velocity
91
New cards
capillaries
-exchange of gases and nutrients
-thin walled, one layer of cells (porous)
-thin walled, one layer of cells (porous)
92
New cards
venules
-fluid and molecule exchange
-on venous side of capillaries
-on venous side of capillaries
93
New cards
what vessel has the lowest velocity?
capillaries (allows for gas exchange)
94
New cards
what vessels have the highest cross sectional area?
capillaries and veins
95
New cards
what vessel has the greatest drop in pressure?
arterioles
96
New cards
Is cross sectional area higher in pulmonary capillaries or systemic capillaries?
pulmonary capillaries
97
New cards
what are the catecholamines in the blood?
epinephrin and norepinephrine
98
New cards
cardiac output (Q)
volume of blood pumped per minute
Q = HR x SV
Avg = 5 L/min
Q = HR x SV
Avg = 5 L/min
99
New cards
stroke volume (SV)
volume of blood ejected per beat (ml/beat)
SV = EDV - ESV
SV = EDV - ESV
100
New cards
EDV
end diastolic volume