MCAT- Muscle contraction and Reflexes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What determines the strength of a muscle contraction?
- The amount of overlap between actin and myosin
- increasing the actin-myosin overlap in a fiber increases the strength of contraction up to a point
What is the optimal contraction strength of a muscle?
- Occurs at mid-range fiber lengths with moderate amounts of overlap
Which type of muscle fibers have stronger contractions?
- Wider muscle fibers can have stronger contractions compared to thinner fibers because they contain more myofibrils
Which type of muscle fibers can perform more work?
- Linger muscle fibers can perform more work compared to shorter ones of the same diameter because longer fibers contract over a greater distance
What can increase contraction strength of a muscle?
- recruiting more motor units increases the number of fibers involved in a muscle contraction which increases contraction strength
What does contraction velocity increase?
- when contraction velocity increases, the power of the contraction increases
What controls muscle contractions?
- The movement of calcium ions into and out of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
- integral to the formation and breakdown of myosin- actin bridges
How is a muscle twitch propagated?
- A twitch is a result of a single contraction that comes from a sing action potential from a motor neuron
What is summation, and how does it relate to muscle contractions?
- summation occurs from repeated action potentials which leads to stronger muscle contractions
What is tetanus?
- Continuous muscle contraction without relaxation that is caused by continuous action potentials
What is a monosynaptic reflex arc?
A reflex which only involves two neurons and one synapse
- occurs when a sensory neuron transmits a message directly to a motor neuron in the spinal cord to elicit a repsonse
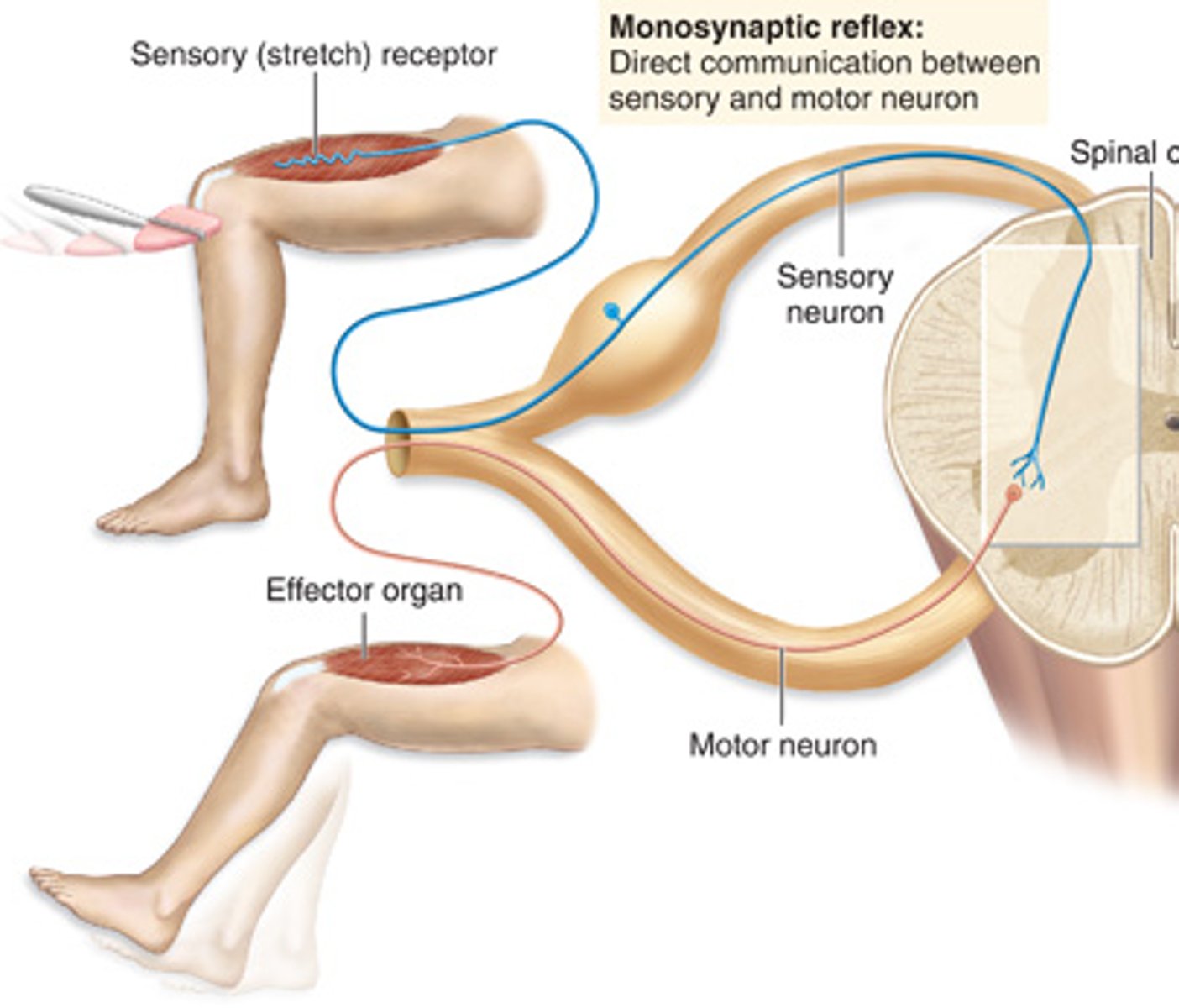
What is a knee-jerk reflex?
A reflex action that straightens the leg when the tendon below the knee cap is tapped.
- example of a monosynaptic reflex arc
What is a polysynaptic reflex arc?
- a reflex arc that has one or more interneurons in the spinal cord between the sensory neuron and the motor neuron cell body (also in spinal cord)
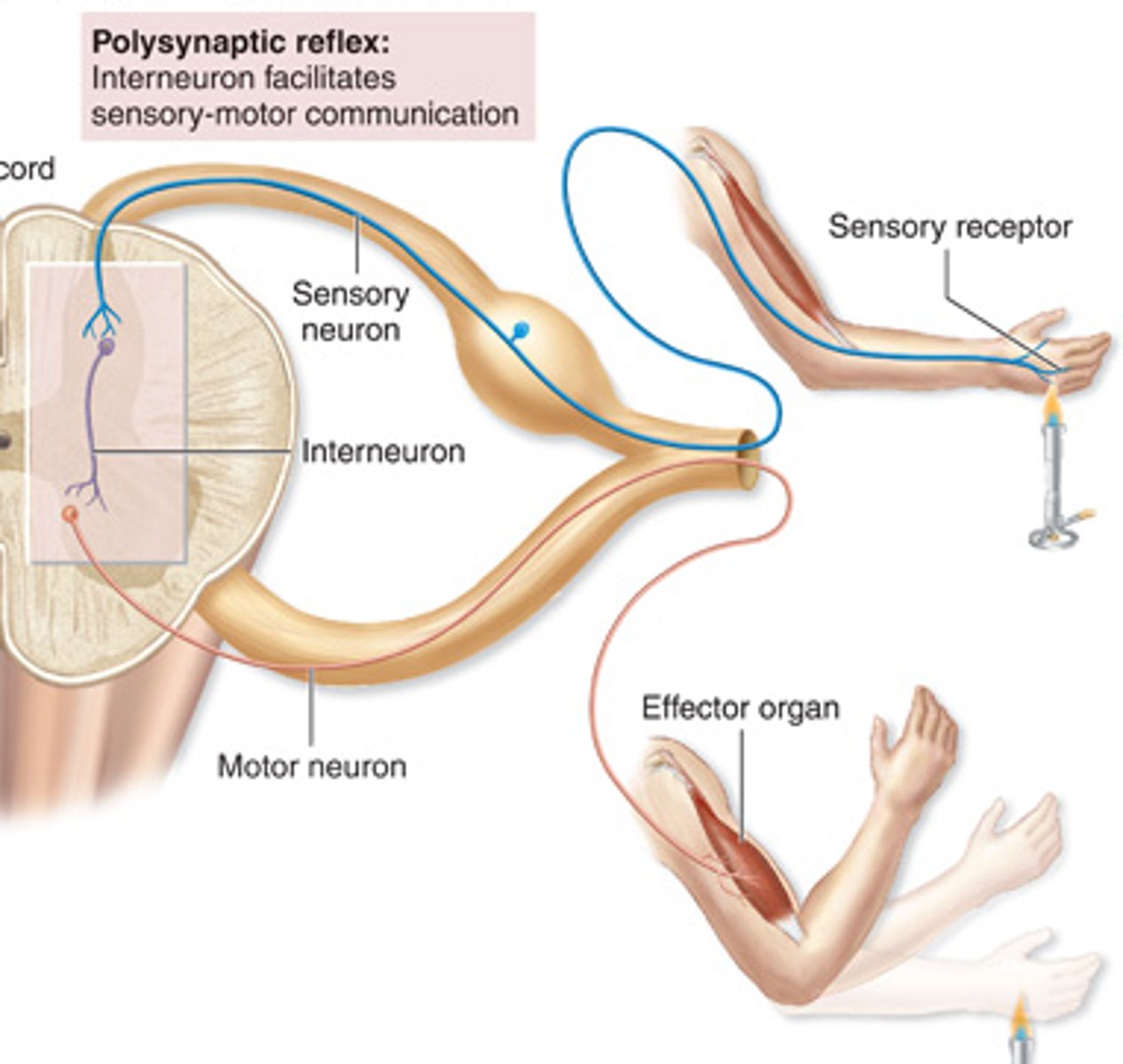
What is a withdrawal reflex?
An unconscious reaction to a painful stimulus. A sensory neuron synapses on inter neurons which synapse on motor neurons (more than one synapse occurs)
- example of a polysynaptic reflex are
- how is the brain involved in reflex responses?
- The brain is able to moderate reflex responses via connections to interneurons or motor neurons in the spinal cord