MCAT Physics and Math - Thermodynamics
1/55
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Thermodynamics
the study of the flow of energy in the universe, as that flow relates to work, heat, entropy, and the different forms of energy
Classical thermodynamics
observations that can be made at the macroscopic level, such as measurements of temperature, pressure, volume, and work
zeroth law of thermodynamics
when one object is in thermal equilibrium with another object and the second object is in thermal equilibrium with a third object, then the first and third object are also in thermal equilibrium; no net heat flow
If a = b and b = c, then a = c
temperature
colloquial: how hot or cold something is
molecular: is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the particles that make up the substance
macroscopic: difference between two objects determines the direction of heat flow, from high to low
Heat
transfer of thermal energy from a hotter object with higher temperature (energy) to a colder object with lower temperature
thermal equilibrium
no net heat flows between two objects in thermal contact; temperatures are equal
Celsius (°C)
0° and 100° define the freezing and boiling temperatures of water
Fahrenheit (°F)
32° and 212° define the freezing and boiling temperatures of water
Kelvin (K)
most commonly used for scientific measurements; one of the seven SI base units; freezing point of water as 273.15 K; a change of one degree Celsius equals a change of one unit kelvin
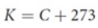
absolute zero (0K)
the theoretical temperature at which there is no thermal energy
third law of thermodynamics
the entropy of a perfectly organized crystal at absolute zero is zero
Fahrenheit-Celsius conversion
180 degrees between water’s phase changes on the Fahrenheit scale, rather than 100 degrees as on both the Celsius and the Kelvin scales
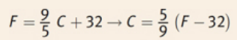
Thermal Expansion
A change in the temperature of most substances results in a change in their length/volume
coefficient of linear expansion (α)
constant that characterizes how a specific material’s length changes as the temperature changes; usually has units of K–1
linear thermal expansion
ΔL = αLΔT
where ΔL is the change in length, α is the coefficient of linear expansion, L is the original length, and ΔT is the change in temperature
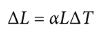
volumetric thermal expansion
ΔV = βVΔT
where ΔV is the change in volume, β is the coefficient of volumetric expansion, V is the original volume, and ΔT is the change in temperature
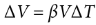
coefficient of volumetric expansion
constant that characterizes how a specific material’s volume changes as the temperature changes; three times the coefficient of linear expansion for the same material (β = 3α)
system
the portion of the universe that we are interested in observing or manipulating
surroundings
the rest of the universe, excluding the system
Isolated systems
not capable of exchanging energy or matter with their surroundings; ΔE = 0
ex. bomb calorimeter (approximate), whole universe
Closed systems
capable of exchanging energy, but not matter, with the surroundings
ex. gases in vessels with movable pistons
Open systems
can exchange both matter and energy with the environment
State functions
thermodynamic properties that are a function of only the current equilibrium state of a system; path independent
ex. include pressure (P), density (ρ), temperature (T), volume (V), enthalpy (H), internal energy (U), Gibbs free energy (G), and entropy (S)
process functions
describe the path taken to get to from one state to another
ex. work, heat
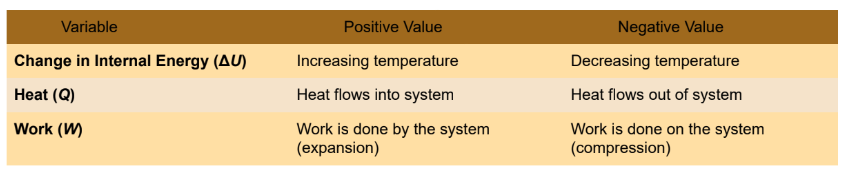
first law of thermodynamics
the change in the total internal energy of a system is equal to the amount of energy transferred in the form of heat to the system, minus the amount of energy transferred from the system in the form of work; energy conservation
ΔU = Q − W
where ΔU is the change in the system’s internal energy, Q is the energy transferred into the system as heat, and W is the work done by the system.
work
as the process by which energy is transferred as the result of force being applied through some distance
second law of thermodynamics
objects in thermal contact and not in thermal equilibrium will exchange heat energy such that the object with a higher temperature will give off heat energy to the object with a lower temperature until both objects have the same temperature at thermal equilibrium
that energy spontaneously disperses from being localized to becoming spread out if it is not hindered from doing so
ΔSuniverse = ΔSsystem + ΔSsurroundings > 0
Heat
the process by which a quantity of energy is transferred between two objects as a result of a difference in temperature
measured in Joules (J), calories (cal), nutritional Calorie (Cal = kcal), British Thermal Unit (BTU)
heat unit conversions
1 Cal ≡ 103 cal = 4184 J = 3.97 BTU
Conduction
direct transfer of energy from molecule to molecule through molecular collisions; direct physical contact
ex.
Metals - good (sea of electrons facilitates rapid energy transfer)
Gases - poor (space btwn individual molecules)
Convection
transfer of heat by the physical motion of a fluid over a material; flow
ex. convection oven
Radiation
transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves; can transfer through a vacuum
ex. Sun, radiant ovens
specific heat (c)
the amount of heat energy required to raise one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius or one unit kelvin; changes with phase
ex. water - 1 cal/g*K = 4.184 J/g*K
heat and temperature equation
q=mcΔT
where m is the mass, c is the specific heat of the substance, and ΔT is the change in temperature (in Celsius or kelvins).
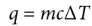
heat of transformation/latent heat
When a substance is undergoing a phase change, such as from solid to liquid or liquid to gas, the heat that is added or removed from the system does not result in a change in temperature.
q = mL
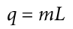
fusion/melting
solid to liquid
freezing/solidification
liquid to solid
boiling/evaporation/vaporisation
liquid to gas
condensation
gas to liquid
sublimation
solid to gas
deposition
gas to solid
heat of fusion
corresponding heat of transformation to fusion/melting
heat of vaporisation
corresponding heat of transformation to
boiling/evaporation/vaporisation
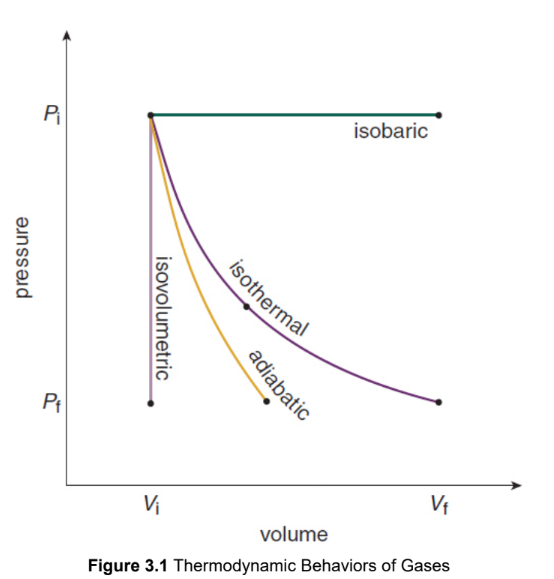
isothermal
constant temperature, and therefore no change in internal energy
ΔU = 0
Q = W
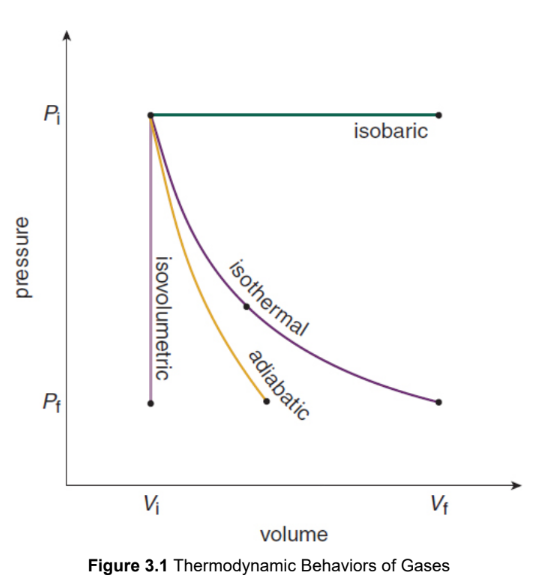
adiabatic
no heat exchange
Q = 0
ΔU = −W
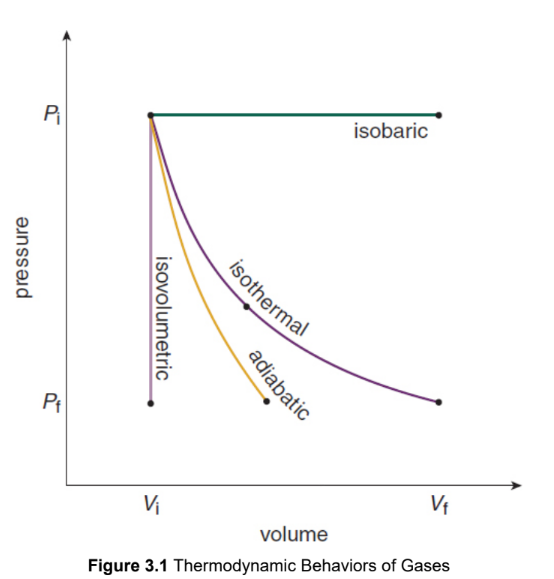
isovolumetric/isochoric
no change in volume, and therefore no work accomplished
W = 0
ΔU = Q
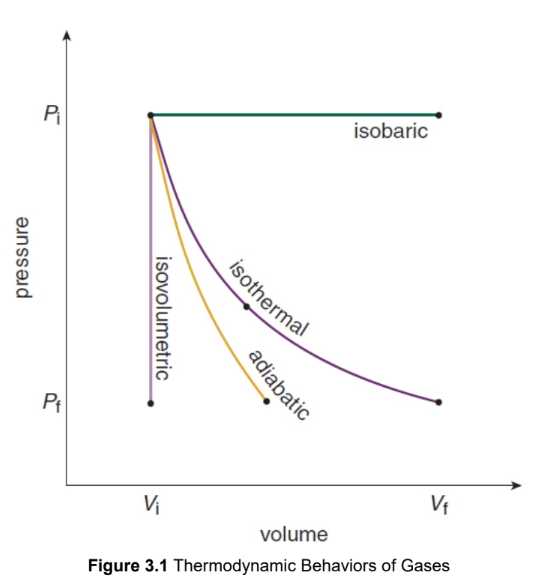
Isobaric
occur at a constant pressure
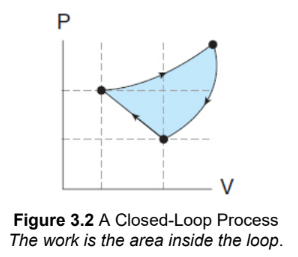
closed-loop thermodynamic process
Because the work on a P–V graph is simply the area under the curve, the work done in this closed-loop process is the area inside the loop
Entropy
measure of the spontaneous dispersal of energy at a specific temperature: how much energy is spread out, or how widely spread out energy becomes in a process; number of microstates; more freedom of movement
units usually J/mol*K
Change in entropy
ΔS = Qrev/T
where ΔS is the change in entropy, Qrev is the heat that is gained or lost in a reversible process, and T is the temperature in kelvin
time’s arrow
second law; because there is a unidirectional limitation on the movement of energy by which we recognize before and after or new and old
natural process
a process existing in or produced by nature (rather than by deliberate intent)
irreversible
a process that is not reversible
reversible
a process, involving a system and its surroundings, whose direction can be reversed by infinitesimal changes in some properties of the surroundings, such as pressure or temperature; thermodynamic equilibrium
unnatural process
process that woukd not be observed in nature spontaneously