Lesson 1.5: Public Goods and Externalities
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards made from a presentation segment created as a lesson on governmental public goods and economic externalities.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms

Public goods
A shared good for which it would be inefficient or impractical to make consumers pay individually and exclude those who did not pay
Schools, roads, bridges, parks, mail delivery
Externality
An economic side effect of a good or service that generates benefits or costs to someone other than the person deciding how much to produce or consume
Taxes
Funds collected by the government to spread the cost of public goods across all citizens who would benefit from it, allowing greater overall benefits
Infrastructure
Constructed systems created to aid efficiency, most seen in road construction projects for greater economic growth and better product distribution
Cost-benefit criteria
Creating a public good requires two of these:
The benefit to each individual is less than the cost to all if provided privately
The total benefits to society are greater than the total cost
Free-rider problem
When a person consumes a particular good or service that they did not contribute to, like a park offered to non-residents — illustrates the effect of a government not collecting taxes
Market failure
An inefficiency in the market to provide a good; public goods are examples of these demonstrating how free enterprise systems may require governmental intervention
Road construction may have limited profit motive in rural areas
Lack of competition may lead to price gouging
Positive externalities
Benefits given to a third party as a result of consumption of a good
Sidewalk usage reduces congestion and pollution

Negative externalities
Harms done to a third party as a result of the consumption or production of a good
Chemical production pollution can lead to a loss of fish, leading to lower income for fishermen
Governmental intervention
Used to aim for more positive than negative externalities like reducing pollution and improving education; this practice has been debated by economists

Poverty
Created as a result of uneven wealth distribution in a free market
Poverty threshold
Thresholds used for statistical purposes to estimate the number of Americans in poverty each year
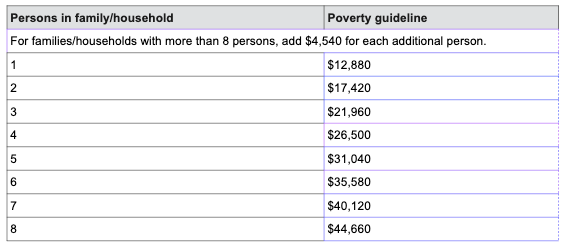
Poverty guidelines
Guidelines that simplify the poverty thresholds for administrative purposes, like determining aid eligibility
Aid programs
Governmental programs that redistribute wealth to raise the standard of living for the less fortunate, such as welfare, cash transfers, in-kind benefits, Medicaid, and grant money