Biology 8 - Unit 2 flashcards
1/51
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
The Cell Theory
All living things are made up of cells
Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things.
New cells are produced from existing cells.
Prokaryotes
cells that do not enclose DNA in nuclei
Smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells.
They grow, reproduce, and respond to the environment, and some can even move by gliding along surfaces or swimming through liquids.
Bacteria are prokaryotes.
Eukaryotes
cells that enclose their DNA in nuclei
Larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells.
Contain dozens of structures and internal membranes.
Many eukaryotes are highly specialized.
Many types of eukaryotes: plants, animals, fungi, and protists
organelles
cellular structures act as if they are specialized organs.
Cell Wall
Main function is to provide support and protection for the cell.
Prokaryotes, plants, algae, and fungi have cell walls.
Animal cells do not have cell walls.
Cell walls lie outside the cell membrane and most are porous enough to allow water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and certain other substances to pass through easily.
Cell Membrane
a thin, flexible barrier surrounding the cell
controls what comes into and out of a cell
Separates the cell from its surrounding environment.
Helps cell maintain homeostasis
Cytoplasm
the gel-like fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus
where many organelles are found.
Nucleus
The Main Office - the control center of the cell.
The nucleus contains nearly all the cell’s DNA and, with it, the coded instructions for making proteins and other important molecules.
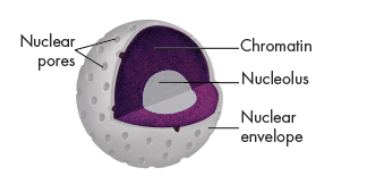
Nuclear Envelope
The nuclear envelope is dotted with thousands of nuclear pores
allows material to move into and out of the nucleus.
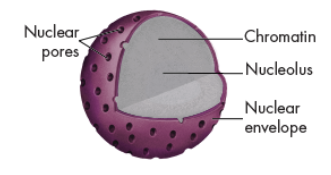
chromatin
a thread like complex of DNA bound to proteins spread throughout the nucleus.
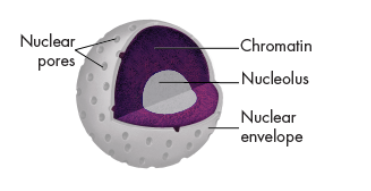
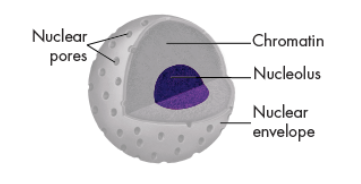
Nucleolus
small, dense region in the nucleus.
where the assembly of ribosomes begins.
Mitochondria
power plants of the cell.
They convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Network of passageways that carries materials from one part of the cell to another.
Where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are exported from the cell.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
The portion of the ER involved in the synthesis of proteins
It is given this name because of the ribosomes found on its surface.
Newly made proteins leave these ribosomes and are inserted into the rough ER, where they may be chemically modified.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
The other portion of the ER is known as smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER) because ribosomes are NOT found on its surface.
The smooth ER contains collections of enzymes that perform specialized tasks, including the synthesis of membrane lipids and the detoxification of drugs.
Ribosomes
Small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm in all cells.
Assemble proteins by following coded instructions that come from DNA.
Golgi Body
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials from the ER for storage in the cell or release outside the cell.
appears as a stack of flattened membranes.
Chloroplasts
Plants and some other organisms contain chloroplasts. Not in animal cells!
he biological equivalents of solar power plants.
They capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into food/chemical energy during photosynthesis.
Contain the green pigment chlorophyll.
Vacuoles
large, saclike, membrane-enclosed structures that store materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Vesicles
are used to store and move materials between cell organelles, as well as to and from the cell surface.
Lysosomes
Remove “junk” that might otherwise accumulate and clutter up the cell.
Breakdown lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into small molecules that can be used by the rest of the cell.
Cytoskeleton
helps the cell maintain its shape and is also involved in movement.
Made up of Microfilaments and Microtubules
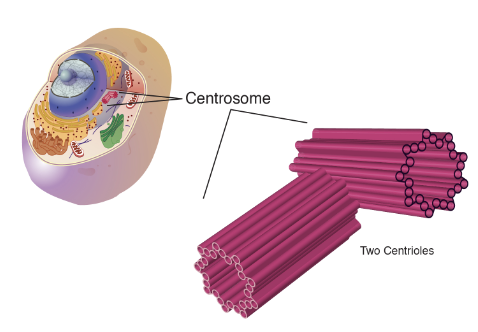
Centrioles
are located near the nucleus and help to organize cell division. Centrioles are not found in plant cells!
Organic Compounds
compounds that contain carbon
macromolecules
“giant molecules,” made from thousands or even hundreds of thousands of smaller molecules.
Elements in Carbohydrates
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (CHO)
Examples of carbohydrates
sugars, starches (potatoes), bread, rice…
Functions of carbohydrates
main source of energy for living things, and some organisms also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. (ex. Cell Wall = Cellulose)
Elements in lipids
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (CHO)
Examples of Lipids
fats, oils, and waxes
Functions of lipids
long-term energy, stores more energy than carbohydrates, some are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings, and some hormones are derived from lipids
Elements in proteins
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms (CHON)
Examples of proteins
The complement system, enzymes, and meat
enzymes
proteins that speed up chemical reactions
Functions of proteins
controlling the rate of reactions and regulating cell processes (enzymes)
forming cellular structures (cytoskeleton)
transporting substances in or out of cells (protein channels)
and helping to fight disease (antibodies and complement system)
growth and repair of cells
Elements in nucleic acids
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus atoms (CHONP)
Examples of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
Functions of nucleic acids
Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information.
RNA helps to make proteins
Selectively Permeable
some substances can pass through while others cannot.
Diffusion
Moving from area of HIGH conc. to area of LOW conc.
Main method on how small molecules (O2 and CO2) move across the cell membrane.
Particles constantly move and collide randomly. Spread out evenly. (Random kinetic motion of particles)
Requires no energy.
Equilibrium
When the conc. of a system is the same throughout
(same conc. on both sides)
Osmosis
the diffusion of WATER through a selectively- permeable membrane.
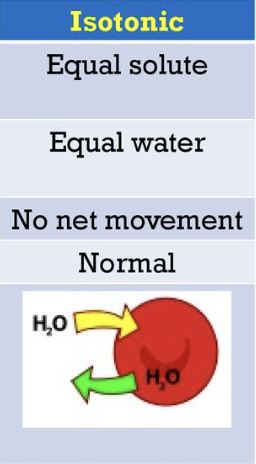
Isotonic
Concentration of water inside the cell is the same as outside
no net movement of water
cell stays the same
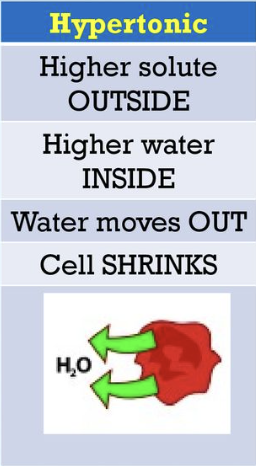
Hypertonic
Low water concentration and high solute conc. outside the cell,
water moves out of the cell
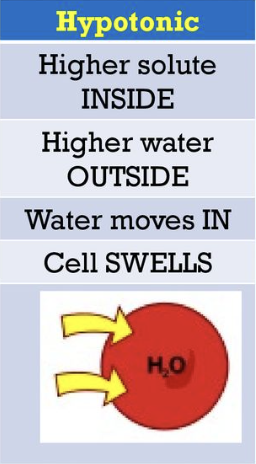
Hypotonic
High water concentration and low solute conc. outside the cell
water moves into the cell
Facilitated Diffusion
Molecules that cannot directly diffuse across membrane get help from special proteins.
called these protein channels
Allow specific things thru
NO energy needed!
Aquaporins
Water channel proteins that allow water to pass right through them.
Without aquaporins, water would diffuse in and out of cells very slowly.
Type of facilitated diffusion
Passive Transport
The movement of dissolved materials through a cell membrane without the use of energy
Active Transport
the movement of materials through a cell membrane using cellular energy (from low conc. to high conc.)
Transport Protein Pumps
form of active transport
When small ions and molecules are carried across membrane by protein pumps
Eg. Ca, K, Na
Endocytosis
The process of taking material INTO the cell
a form of active transport.
Exocytosis
The process of releasing large amounts of material OUT of the cell.
a form of active transport.