lecture 39: brain reward pathways & drug dependence
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:25 AM on 4/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
1
New cards
what is drug dependence?
a state resulting from interaction b/w a living organism & a drug, including **compulsion** to take drug on continuous/periodic basis to experience psychic effects & sometimes avoid discomfort of its absence.
2
New cards
what is drug tolerance?
a state of reduced responsiveness to the effects of a drug caused by its previous administration OR to maintain the same response to a drug, one must administer higher doses w repeated admins
3
New cards
what is psychological dependence?
psychic drive that reqs admin of a drug to provide pleasure or to avoid discomfort
4
New cards
what is physical dependence ?
an adaptive state manifested by intense physical disturbances when drug is withdrawn
5
New cards
which 3 factors influence drug abuse?
1. drug availability
2. form of drug
* heroin vs opium
* cocaine vs cocoa leaves
* crack vs cocaine
3. route of admin
* oral vs intravenous vs inhalation
6
New cards
what is involved in the reward pathway in the brain (and which areas are affected by drugs)?
**dopaminergic mesolimbic & meso-cortical pathways**, which drugs can affect diff areas in these pathways
* nucleus accumbens (n. acc)
* ventral tegmental area (VTA)
* nucleus accumbens (n. acc)
* ventral tegmental area (VTA)
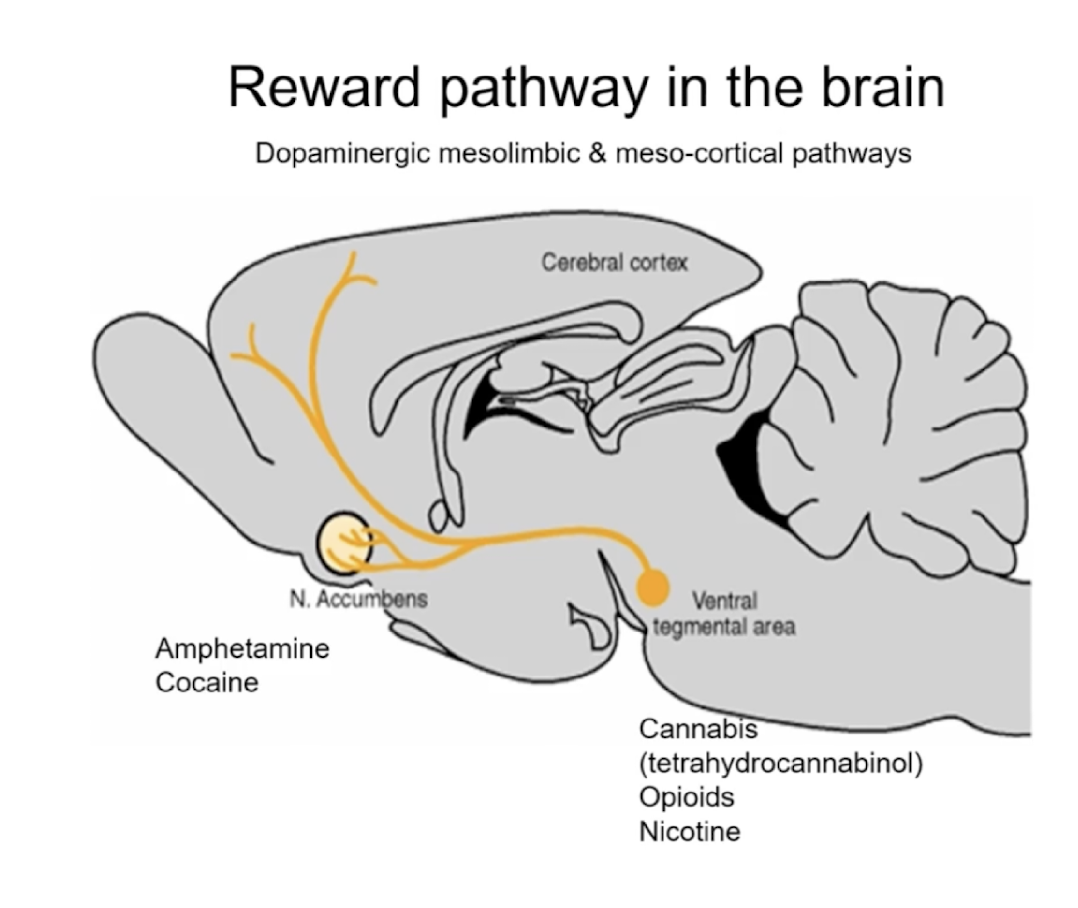
7
New cards
what are DA neurons in VTA under control of ?
tonic control of **GABA interneurons** so their activity is normally suppressed due to GABA release from these interneurons
8
New cards
what are the 4 major DA pathways in the brain?
1. **nigrostriatal** (sub. nigra → caudate nucleus)
2. **mesolimbic** (VTA → n.acc)
3. **mesocortical** (VTA → cortex of hippocampus)
4. **tubero**-**infundibular** (median eminence → ant.pit)
9
New cards
what are DA1 & DA2 receptors, and how they act?
important DARs involved in the reward pathway of the brain
* D1 = E
* D2 = I
* D1 = E
* D2 = I
10
New cards
what DA neuron subtype is important in the mesolimbic system (and assoc. DARs?)
A10, WITH DA1 & DA2 RECEPTORS
11
New cards
how do A10 neurons and DA1/2 receptors mediate action of reward in the mesolimbic pathway?
1. A10 DA neruons project → n.acc
2. as majority of neurons in **n.acc** are **GABAergic**, they loop back onto VTA to __inhibit activity of DA neurons__
3. reward = increased activation of DA neurons which act….
* on VTA to *inhibit GABA release*
* directly on DA neurons to increase firing rate
* on n.acc to stim release of DA from terminals
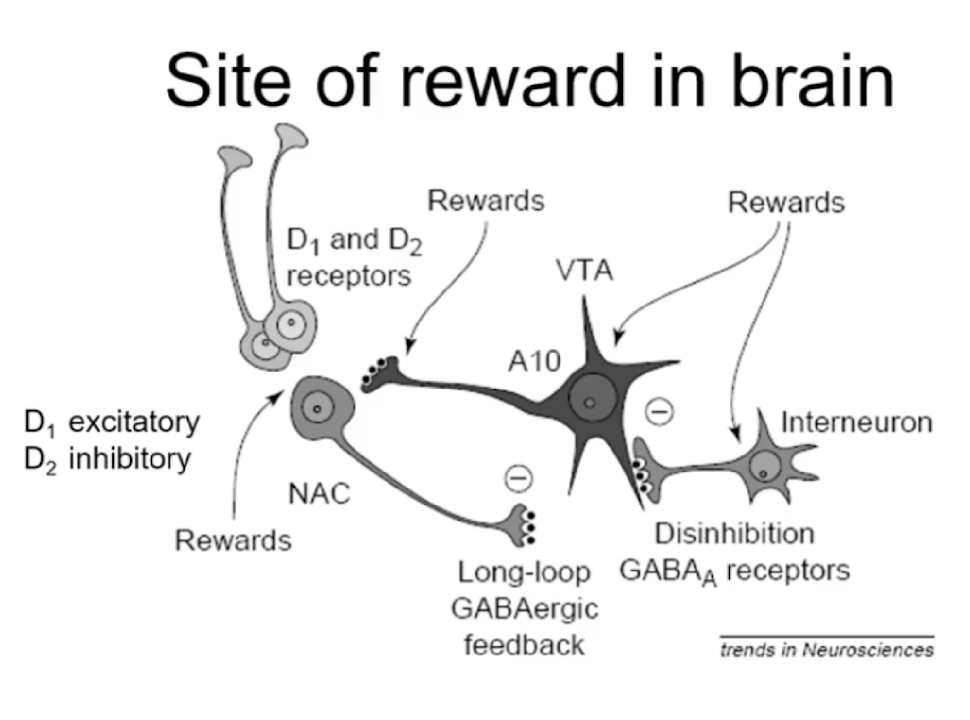
12
New cards
how is morphine involved in the mesolimbic reward pathway (where does it act, what does it do, and when we remove what happens)?
* acts on µ-opioid GPCRs
* inhibits adenylate cyclase, decreasing \[cAMP\]
* opens K+ channels, hyperpolarise neuron
* cause __decreased GABA release__ in VTA
* leads to __increased DA release__ in n.acc by **disinhibition of DA neurons in VTA**
* when morphine is __removed__, there is a *spike in [cAMP]* linked to withdrawal signs in tolerance
* inhibits adenylate cyclase, decreasing \[cAMP\]
* opens K+ channels, hyperpolarise neuron
* cause __decreased GABA release__ in VTA
* leads to __increased DA release__ in n.acc by **disinhibition of DA neurons in VTA**
* when morphine is __removed__, there is a *spike in [cAMP]* linked to withdrawal signs in tolerance
13
New cards
how is nicotine involved in the mesolimbic reward pathway (where does it act, what does it do, and how does it act on GABA/glutamate neruons)?
* acts on cationic LGICs; nAChRs
* mainly on nerve terminals
* increased transmitter release by depolarising membrane
* nicotine acts on specific receptors on **GABAergic neurons** for GABA release in __rapid desensitisation__
* nicotine also acts on diff receptors on **Glutamate neurons** for Glu release in __slower desensitisation__
* mainly on nerve terminals
* increased transmitter release by depolarising membrane
* nicotine acts on specific receptors on **GABAergic neurons** for GABA release in __rapid desensitisation__
* nicotine also acts on diff receptors on **Glutamate neurons** for Glu release in __slower desensitisation__
14
New cards
what treatments are available to help addicts in opioid overdose?
naloxone (remember the def of an opioid! any drug whose action **reverses** naloxone, thus it is used to treat OD)