Mental Health Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/188
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:37 PM on 2/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
1
New cards
what are the 6 steps of the nursing process?
assessment
diagnosis
outcomes
planning
implementation
evaluation
diagnosis
outcomes
planning
implementation
evaluation
2
New cards
who is the primary source?
the patient
3
New cards
what is the purpose of a psychiatric nursing assessment?
to assess psychosocial status
identify mutual goals for treatment
formulate a plan of care for the immediate condition and needs
\
identify mutual goals for treatment
formulate a plan of care for the immediate condition and needs
\
4
New cards
what does a mental status exam evaulate?
the current cognitive processes
* it is more objective
* it is more objective
5
New cards
what do you observe during a mental status exam?
appearance, nonverbal communication, speech patterns, mood and affect, thought processes, cognition, and insight and judgment
6
New cards
what is a psychosocial assessment?
it provides more information along the MSE to help with the plan of care
* more subjective
* more subjective
7
New cards
what does a psychosocial assessment consist of?
patient’s chief complaint (in their own words)
previous hospitalizations
educational/occupational background
social patterns
sexual patterns
interests
substance use/abuse
coping abilities
spirituality assessment
cultural assessment
previous hospitalizations
educational/occupational background
social patterns
sexual patterns
interests
substance use/abuse
coping abilities
spirituality assessment
cultural assessment
8
New cards
what technique is used for a psychosocial assessment for adolescents?
HEADSSS:
home environment
education and employment
activities
drugs, alcohol, and tobacco
sexuality
suicide risk
“savagery”
home environment
education and employment
activities
drugs, alcohol, and tobacco
sexuality
suicide risk
“savagery”
9
New cards
what does a nursing diagnosis consist of?
the problem , the etiology, and the supporting data
10
New cards
what is the purpose of a risk diagnoses?
made to help prevent a potential unwanted or dangerous future event in an effort to ensure patient safety
* high probability of a future negative event for a vulnerable individual
* EX. risk for suicide
* high probability of a future negative event for a vulnerable individual
* EX. risk for suicide
11
New cards
when are health promotion diagnoses used?
when clinical observations and/or patient (family, group, etc.) statements indicate a willingness and a wish to enhance specific health behaviors
12
New cards
what should outcomes identification reflect?
Reflect maximal patient health that can be realistically achieved through evidence-based interventions
13
New cards
how should goals be set up?
* measurable
* indicate the patients’ desired behavior
* include a set time for achievement
* short and specific
* indicate the patients’ desired behavior
* include a set time for achievement
* short and specific
14
New cards
what should occur during the implementation step?
health teaching and promotion
* such as pharmacological, biological, and integrative therapies
* such as pharmacological, biological, and integrative therapies
15
New cards
what should occur during the evaluation?
include supporting data
enables revisions to diagnoses, outcomes, \n and interventions
* it is systematic, ongoing, and criterion-based
\n
enables revisions to diagnoses, outcomes, \n and interventions
* it is systematic, ongoing, and criterion-based
\n
16
New cards
what is the 7th nursing process step?
documentation
17
New cards
what is the SOAPIE format?
**S:** Subjective data (patient statement) \n **O**: Objective data (nurse observations) \n **A:** Assessment (nurse interprets S and O and describes \n either a problem or a nursing diagnosis) \n **P:** Plan (proposed intervention) \n **I:** Interventions (nurse’s response to problem
**E:** Evaluation (patient outcome)
**E:** Evaluation (patient outcome)
18
New cards
what is evidence based practice?
* scientifically grounded methods
* research on biology and treatments
* research on biology and treatments
19
New cards
what is the recovery model’s principle?
believes that addicts can recover and lead on full lives
* social model of disability
* includes AA’s 12 steps
* social model of disability
* includes AA’s 12 steps
20
New cards
how does the recovery model help patients?
encouraging supportive relationships, engagement in community/social life, and a reduction of symptoms
21
New cards
what does trauma-informed care provide?
provides guidelines for integrating an understanding of how trauma affects patients into clinical programming
* change from “what is wrong with you?” to “what has happened to you?”
* avoid retraumatizing the patient
* change from “what is wrong with you?” to “what has happened to you?”
* avoid retraumatizing the patient
22
New cards
which level of evidence shows the strongest evidence?
level 1: systematic reviews or meta-analyses of randomized controlled studies and evidence-based clinical practice
\
\
23
New cards
what is the weakest level of evidence?
level 7: expert committee reports, opinions, clinical experience, and descriptive studies
24
New cards
what are resources for clinical practice?
1. internet resources
2. clinical practice guidelines
3. clinical algorithms
4. clinical/critical pathways
25
New cards
what is a clinical algorithm?
step-by-step guidelines prepared in a flowchart or decision-tree format
\
\
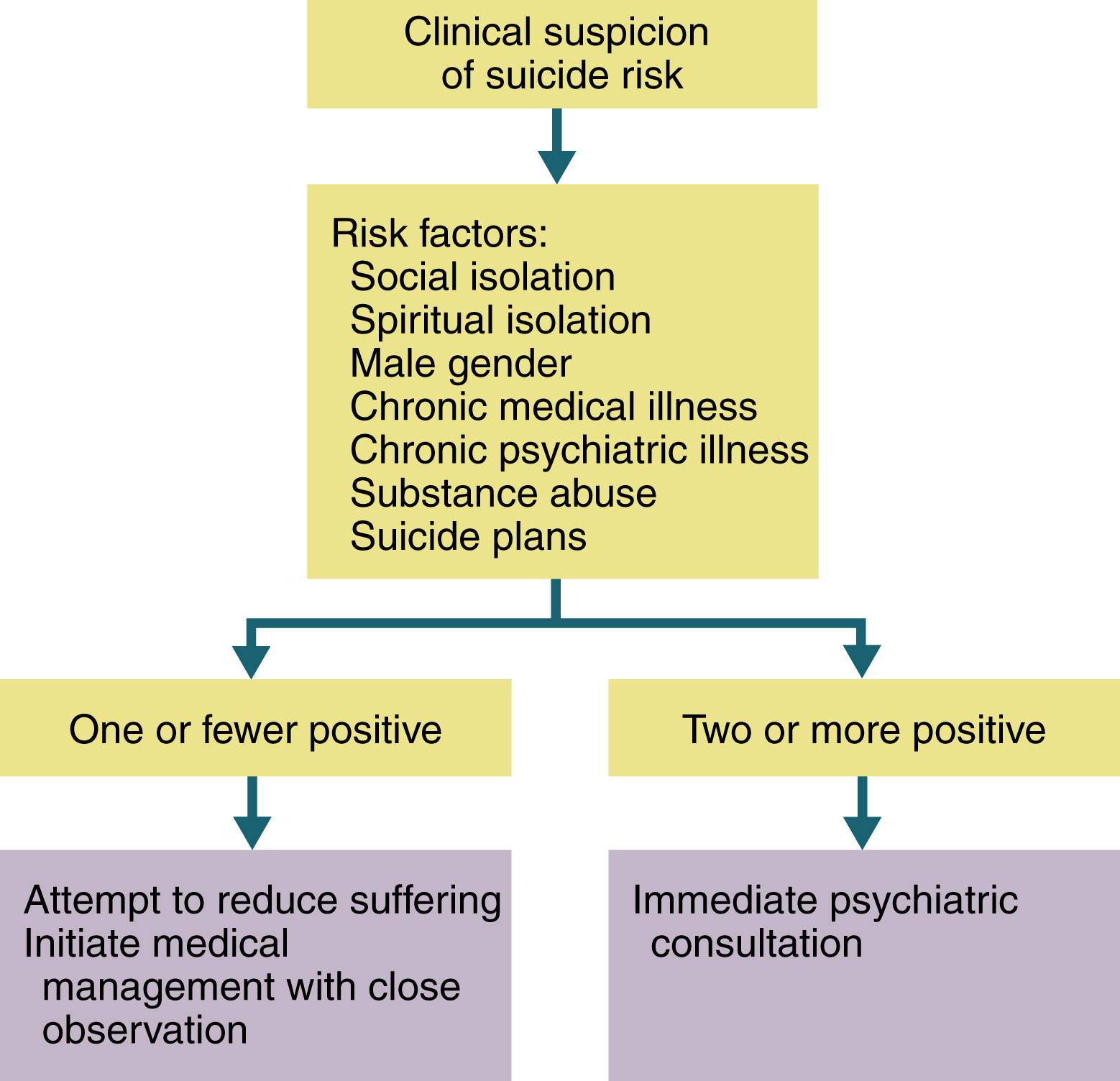
26
New cards
what are clinical/critical pathways?
serve as a “map” for specified treatments and interventions to occur within specific time frames that have been shown to improve clinical outcomes
* can include tests, health teaching, and medications
* EBP
* can include tests, health teaching, and medications
* EBP
27
New cards
what do clinical practice guidelines increase?
can increase the quality and consistency of care and facilitate outcome research
28
New cards
how do you integrate EBP into clinical practice?
1. ask a question
2. acquire the literature
3. appraise the literature
4. apply the evidence
5. assess the performance
* the 5 A’s
29
New cards
what is the research-practice gap?
the best evidence treatments and their effective translation into practice
30
New cards
what is the need for research-practice gap?
continued research on how best to apply the findings of clinically relevant issues
31
New cards
what are the 6 QSEN competencies?
* Patient-centered care
* Teamwork and \\n collaboration
* Evidence-based practice
* Quality improvement
* Safety
* Informatics
\
* Teamwork and \\n collaboration
* Evidence-based practice
* Quality improvement
* Safety
* Informatics
\
32
New cards
what does the art of nursing consist of?
caring
attending
patient advocacy
\
attending
patient advocacy
\
33
New cards
what does a caring nurse indicate?
a competent nurse
34
New cards
what does attending indicate?
being present
using therapeutic communication -verbal and non-verbal
using therapeutic communication -verbal and non-verbal
35
New cards
what does advocating for a patient indicate?
* Providing informed consent, including refusal of treatment
* Respecting patient decisions
* Protecting against threats to well-being
* Being informed about best practices (accurate and current information)
* Respecting patient decisions
* Protecting against threats to well-being
* Being informed about best practices (accurate and current information)
36
New cards
why are mental illnesses and mental health NOT specific?
because they exist on a continuum
37
New cards
what percentage of people in the US will experience mental illnesses in their lifetime?
50%
38
New cards
what are some attributes to mental health?
\
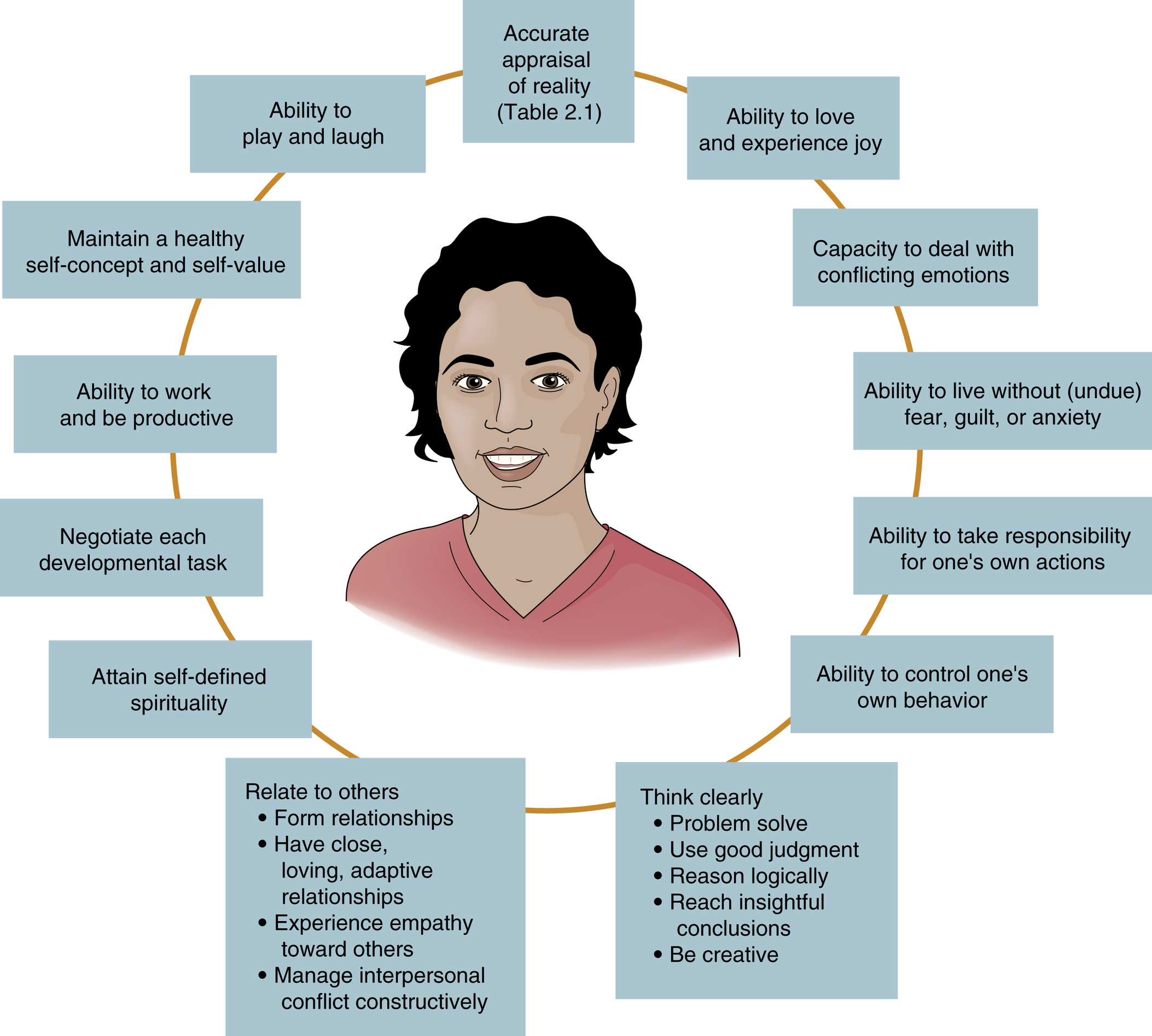
39
New cards
what is the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5)?
the current official guidebook for categorizing and diagnosing psychiatric mental health disorders in the United States
40
New cards
does the DSM-5 identify the patient?
NO; classifies a disorder a patient has
41
New cards
what is resiliency?
the ability to recover from or adjust successfully to trauma or change
42
New cards
what is the mental health parity act(1996)?
requires insurers to offer mental health benefits at the same level provided for medical coverage
43
New cards
what are some factors that affect mental health?
\
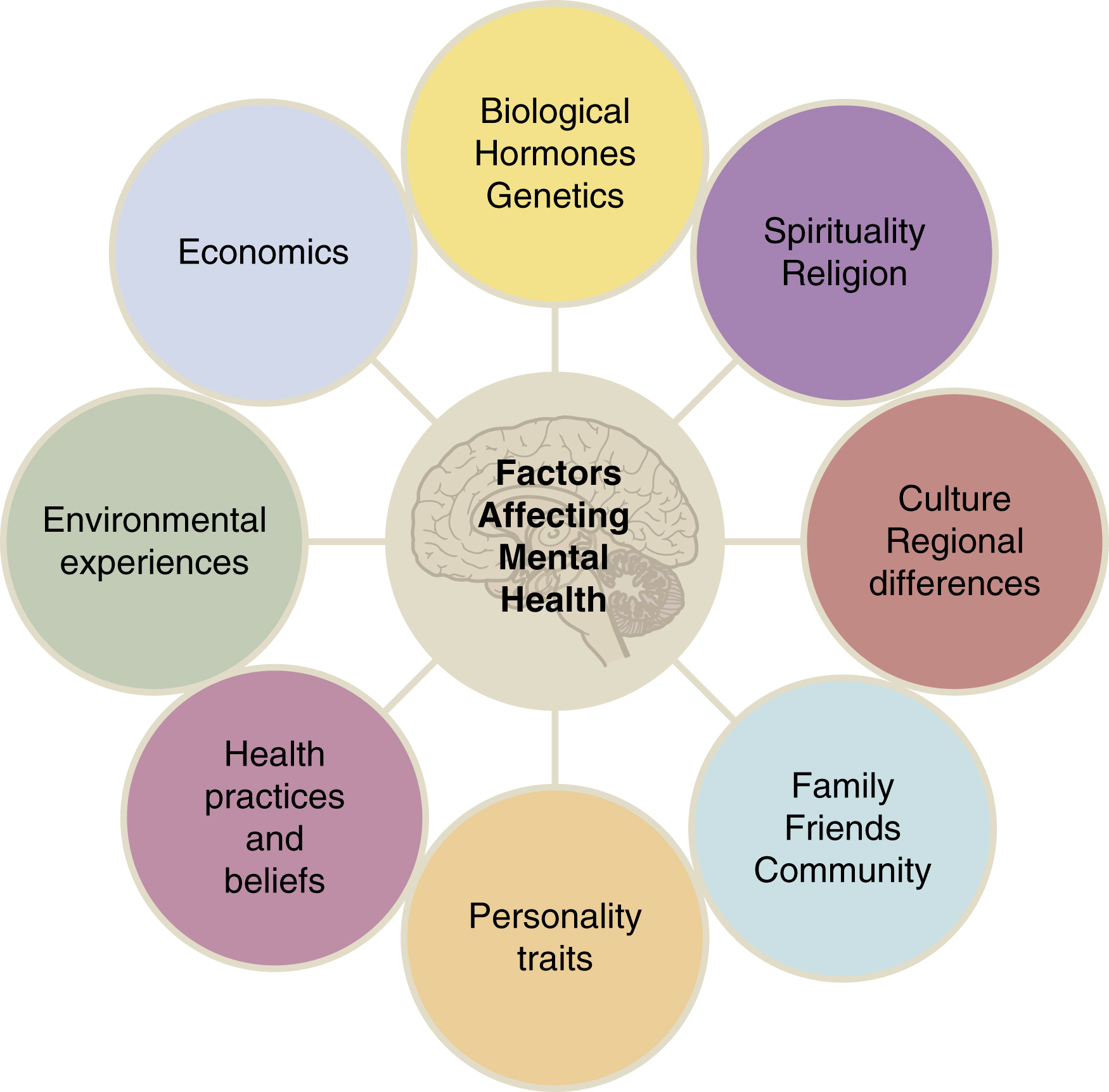
44
New cards
how does the “stigma” affect mentally ill patients?
stigma of mental illness affects how an individual is viewed
* affects housing, employment, and health services
* has harmful effects on the patient and family
\
* affects housing, employment, and health services
* has harmful effects on the patient and family
\
45
New cards
what is freud’s psychoanalytic theory?
most psychological disturbances are the result of early trauma or incidents that are often not remembered or recognized
\
leads to the personality structure which includes: the id, ego, and superego
\
leads to the personality structure which includes: the id, ego, and superego
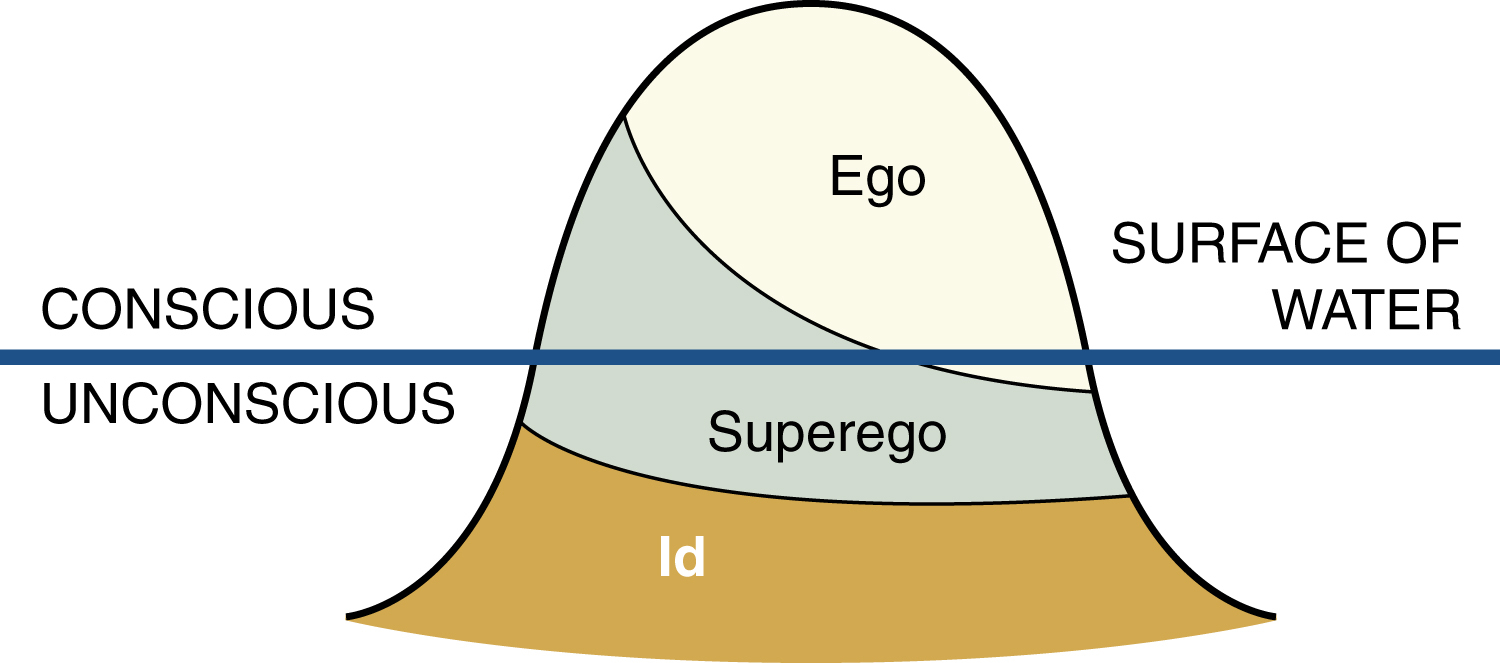
46
New cards
what is the id?
the primitive, pleasure-seeking, and impulsive part of our personalities that lurks in the unconscious mind
47
New cards
what is the ego?
problem solver and reality tester that navigates in the outside world
48
New cards
what is the superego?
represents the moral component of the personality that Freud referred to as our conscience (our sense of what is right or wrong)
* greatly influenced by parents or caregivers
* greatly influenced by parents or caregivers
49
New cards
what are the levels of awareness?
conscious, preconscious, and unconscious
50
New cards
what is the conscious level of awareness?
thoughts, beliefs, and feelings
51
New cards
what is the preconscious level of awareness?
information that is not currently the subject of our attention, but accessible
52
New cards
what is the unconscious level of awareness?
biggest chunk; seat of primitive feelings, drives, and memories, especially those that are unbearable and traumatic
53
New cards
what are the erogenous body zones?
parts of the body that excite sexual feelings when stimulated
\
personality formation is associated with this
\
personality formation is associated with this
54
New cards
what erogenous zones does the id focus on?
the oral, anal, and phallic zones
55
New cards
what is transference?
occurs as the patient projects intense feelings onto the therapist related to unfinished work from previous relationships
ex. patient treats therapist differently because they remind them of their sister
ex. patient treats therapist differently because they remind them of their sister
56
New cards
what is countertransference?
redirection of a pscyhotherapist’s feelings onto a client
57
New cards
what is pavlov’s behavior theory?
classical conditioning-- pavlov’s dogs became accustomed to receiving food after a bell was rung
\
associated being fed when the bell rung
\
associated being fed when the bell rung
58
New cards
what is watson’s behavior theory?
believed behavior is learned-- conditioned a 9 month old child to be terrified at the sight of white fur
\
concluded that anyone can be trained to be anything
\
concluded that anyone can be trained to be anything
59
New cards
what is skinner’s behavior theory?
operant conditioning-- conditioned behaviors through positive and negative reinforcement
60
New cards
what is behavioral modification?
a technique used to correct or eliminate maladaptive behaviors by rewarding and reinforcing adaptive behavior
61
New cards
what is the systematic desensitization?
based on classical conditioning-- this theory attempts to reverse a learned response by promoting relaxation and then gradually facing an anxiety-provoking stimulus
62
New cards
what is the systematic desensitization usually used to treat?
extreme fears and phobias
63
New cards
what is aversion therapy?
therapy based on both operant and classical conditioning that is used to eradicate unwanted habits by associating unpleasant consequences with them
64
New cards
what is biofeedback?
a technique in which individuals learn to control physiological responses (breathing, HR, etc.)
* achieved by providing visual or auditory biofeedback of the physiological response and then using relaxation techniques such as slow, deep breathing or meditation
* achieved by providing visual or auditory biofeedback of the physiological response and then using relaxation techniques such as slow, deep breathing or meditation
65
New cards
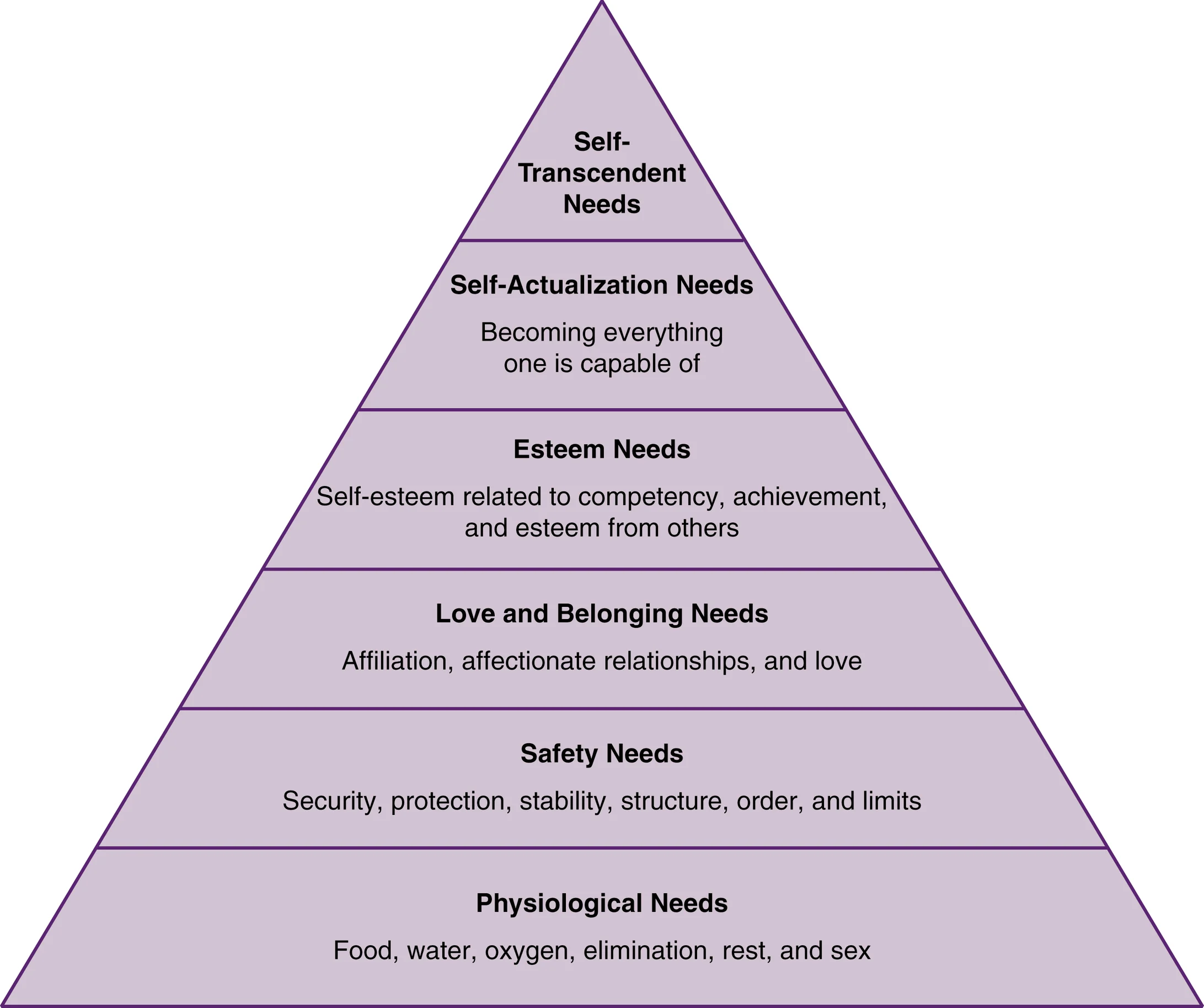
what are maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
classification of needs ascending from basic biological needs to more complex psychological motivations
\
from most complex to basic:
self-actualization
self-esteem
love and belonging
safety and security
physiological needs
\
from most complex to basic:
self-actualization
self-esteem
love and belonging
safety and security
physiological needs
66
New cards
what is cognitive-behavioral therapy?
a therapeutic tool based on both cognitive and behavioral theories that seek to modify negative thoughts that lead to dysfunctional emotions and actions
67
New cards
what do biological theories suggest?
mental disorders are from physical causes
68
New cards
what are some examples of biological therapy?
medications, electroconvulsive therapy(ECT), and other brain stimulation therapies
\
usually used in conjunction to talk therapies
\
usually used in conjunction to talk therapies
69
New cards
what is piaget’s theory of cognitive development?
suggests that cognitive development is a progression from primitive awareness to complex thought and responses
70
New cards
what are the stages of cognitive development?
* sensorimotor: object permanence--birth to 2 years
* preoperational: language; egocentric thinking-- 2 to 7 years
* concrete operational: conservation, logic, abstract problem solving, patterns, and reversibility-- 7 to 11 years
* formal operational: conceptual reasoning-- 11 to adult
* preoperational: language; egocentric thinking-- 2 to 7 years
* concrete operational: conservation, logic, abstract problem solving, patterns, and reversibility-- 7 to 11 years
* formal operational: conceptual reasoning-- 11 to adult
71
New cards
what is erikson’s stages of psychosocial development?
a theory that supports the continuation of our personality as we age
72
New cards
what stage of development would an infant be in?
trust v. mistrust-- birth to 1.5 years
73
New cards
what stage of development would an toddler be in?
autonomy v. shame/doubt-- 1.5 to 3 years
74
New cards
what stage of development would an preschooler be in?
initiative v. guilt-- 3 to 6 years
75
New cards
what stage of development would an school-age child be in?
industry v. inferiority-- 6 to 12
76
New cards
what stage of development would an adolescent be in?
identity v. role confusion -- 12 to 20
77
New cards
what stage of development would an young adult be in?
intimacy v. isolation --20 to 30 years
78
New cards
what stage of development would an middle-aged adult be in?
generativity v. self-absorption --30 to 65
79
New cards
what stage of development would an older adult be in?
integrity v. despair -- 65 to death
80
New cards
what does a therapeutic milieu refer to?
a healthy environment--people, setting, structure, and emotional climate are all important to healing
81
New cards
what did the affordable care act of 2010 do?
* allowed young adults to stay on parent’s health insurance up to age 26
* banned dollar limits
* mental health is no longer a pre-existing condition
* banned dollar limits
* mental health is no longer a pre-existing condition
82
New cards
what are some communication factors?
emotional and social factors
cultural and language factors
lifestyle differences
cognitive differences
\
cultural and language factors
lifestyle differences
cognitive differences
\
83
New cards
what are some cultural considerations for communication?
1. communication styles
2. use of eye contact
3. perception of touch
4. cultural filters
84
New cards
what is the function of acetylcholine?
enables muscle contraction for motor movement, learning, and memory
85
New cards
what is the function dopamine?
influences movement and attention; alertness
86
New cards
what is the function of endorphins?
controls pain, reduces stress, and promotes feelings’ of pleasure-- natural opiate
87
New cards
what is the function of GABA?
this is the brain’s major inhibitory neurotransmitter
88
New cards
what is the function of glutamate?
this is the brain’s major excitatory neurotransmitter; it creates a links between neurons that form basis of learning and long-term memory
89
New cards
what is the function of norepinephrine?
activates “fight or flight” -- alertness, elevates mood, and increases heart rate and circulation
90
New cards
what is the function of serotonin?
regulates mood, hunger, and sleep
91
New cards
what can a deficit in acetylcholine result in?
alzheimer’s disease, parkinson’s disease, and huntington chorea
92
New cards
what might an excess of acetylcholine result in?
depression
93
New cards
what might an excess of dopamine result in?
schizophrenia
94
New cards
what neurotransmitter deficits may result in parkinson’s disease?
acetylcholine and dopamine
95
New cards
what neurotransmitter deficit might potenitally be involved in addiction?
endorphins
96
New cards
what might a deficit in GABA result in?
seizures or insomnia
97
New cards
what might an excess of glutamate result in?
overstimulation of the brain--seizures
\
avoid foods with glutamate (MSG)
\
avoid foods with glutamate (MSG)
98
New cards
which neurotransmitter deficits can result in a depressed mood?
norepinephrine and serotonin
99
New cards
what are the functions of the occipital lobe?
vision and color
100
New cards
what are the functions of the frontal lobe?
reasoning, thinking, planning, expressive language, emotions, judgment, motor function, movement, and short term memory