4.1.6 Restrictions on Free Trade (copy)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are the reasons for restriction on free trade:
Infant industry argument
Job protection
Protection from potential dumping
Protection from unfair competition
Terms of trade
Danger of over specialisation
What is an infant industy
An infant industry is one that is just being established within a country

What is the infant industry argument
They need to build a reputation, establish a customer base, and cover high sunk costs, leading to higher average costs (AC) and an inability to compete internationally, so the government protects them until they can
Temporary trade barriers, like tariffs, can provide domestic industries time to grow and become competitive.
This has worked well in Japan but in general tends to be ineffective as firms grow to be inefficient and the government tend to have a poor record of ‘picking winners’. There may be other more effective methods, such as subsidies.
Why are restrictions put up to protect jobs
Governments may be concerned that allowing imports will mean domestic producers will lose out to international firms, and so there will be job losses within the country.
What is dumping and what is an example of it
Dumping is when a country or company with surplus goods sells these goods off to other areas of the world at very low prices, usually below their production cost in the domestic market, harming domestic producers in those countries.
In China, tariffs are placed on stainless steel tubes from the EU and Japan to prevent from dumping.
Why are restrictions put up to protect firms from unfair competition
Across the world, different rules apply and this means that producers in different countries can produce at different prices. Domestic producers may be unable to compete with a firm that has very low labour costs or very low health and safety costs due to regulation or with a firm that is heavily subsidised by the government
Why are restrictions put up to protect the TOT
If a country buys a large amount of imports for a certain good, this will increase demand for that good and hence increase the price. This will worsen the terms of trade and so therefore they can buy less imports with the amount of exports
Restrictions will reduce supply of the good and lead to a fall in the price received by the importer, so improve the terms of trade.
Why are restrictions put up to protect countries from over specialisation
Some people believe that no country should become totally reliant on another for important products or materials and so it is important to introduce protectionism on these goods to prevent firms and consumers becoming reliant on them.
Many of the tariffs imposed by Donald Trump in in 2018 were on the basis of national security.
What are tariffs
These are taxes placed on imported goods which make them more expensive to buy, making people more likely to buy domestic goods.
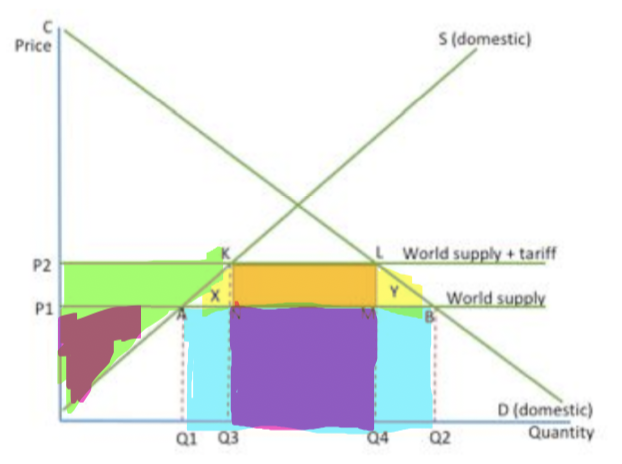
what do the different colours represent
Green - producer surplus
Brown - original producer surplus
Orange - tax revenue
Blue - spent buying imports
Yellow - deadweight loss
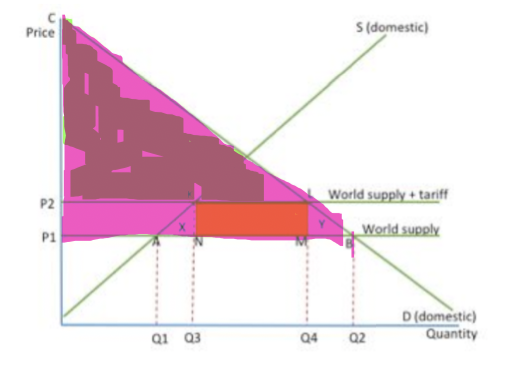
What do the colours mean
Pink - original consumer surplus
Dark pink - consumer surplus after tariffs
What are Quotas
These are limits placed on the level of imports allowed into a country , meaning people are forced to buy domestic goods if they want that good and the quota is already used up
QUOTA GRAPH NEEDED
???
What are subsidies to domestic products
These are payments to domestic producers which lower their costs and help them to be more competitive by enabling cheaper prices.
eg One example of this is China, who subsidise their car industry.
What are examples of Non-tariff barriers
Embargo, which is a total ban on imported good
Import licensing when countries/firms need a license to be able to import; by reducing the number of licenses they give out, the government can restrict the level of imports
Legal and technical standards means that some products cannot be sold in the country, for example specific specifications can be imposed for goods or intellectual property laws over patents and copyrights can be introduced. The EU has high standards, which is the main restriction on trade from outside the bloc
Voluntary export restraint agreements where they agree to limit the volume of exports to one another over an agreed period of time to allow domestic producers to grow and establish
What are the impacts of protectionist policies on consumers
There are higher prices for consumers as they are unable to buy imports at the cheaper price. It tends to raise the price of domestic producers since goods and services needed for the production of these goods may also suffer from import controls and it limits the competition for domestic producers so they have less incentive to be efficient.
They may also suffer from less choice
What are the impacts of protectionist policies on producers
Domestic producers tend to benefit from import controls since they have less competition so can sell more goods at a higher price than otherwise and they will benefit from measures to increased exports.
Foreign producers will lose out as they are limited in where they can sell their goods. Inefficient, domestic producers are kept in production, whilst efficient, foreign ones lose out.
What are the impacts of protectionist policies on Workers
Evidence suggests that there is little difference to employment figures
It can be argued that allowing inefficient firms to close would be better for workers in the long run. The market would reallocate resources and create new jobs, with greater security.
Following the steel tariffs imposed in America in 2018, it is estimated that 16 jobs will be lost elsewhere for every job gained in the steel industry. (The Economist) However, Argentina have been successful at implementing tariffs which protect jobs
What are the impacts of protectionist policies on governments
In the short run, governments benefit from protectionist policies as they can gain tariff revenues and they are politically popular.
However, it can lead to an inefficient economy which stifles growth
What are the impacts of protectionist policies on living standards
As the tariff diagram shows, the imposition of import controls results in deadweight welfare loss.
It also causes trade wars since the introduction of restrictions often leads to retaliation by other countries. A recent example of this is the US-China trade war, where each country continues to impose more tariffs on the other’s goods. This causes a reduction in trade and a reduction in growth
What are the impacts of protectionist policies on equity
it has a regressive effect on the distribution of income as the rise in price affects the poorer members of society far more than the well off as it is they are no longer able to afford the products.