Concept 6 Part 1: Clinical Decision Making
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
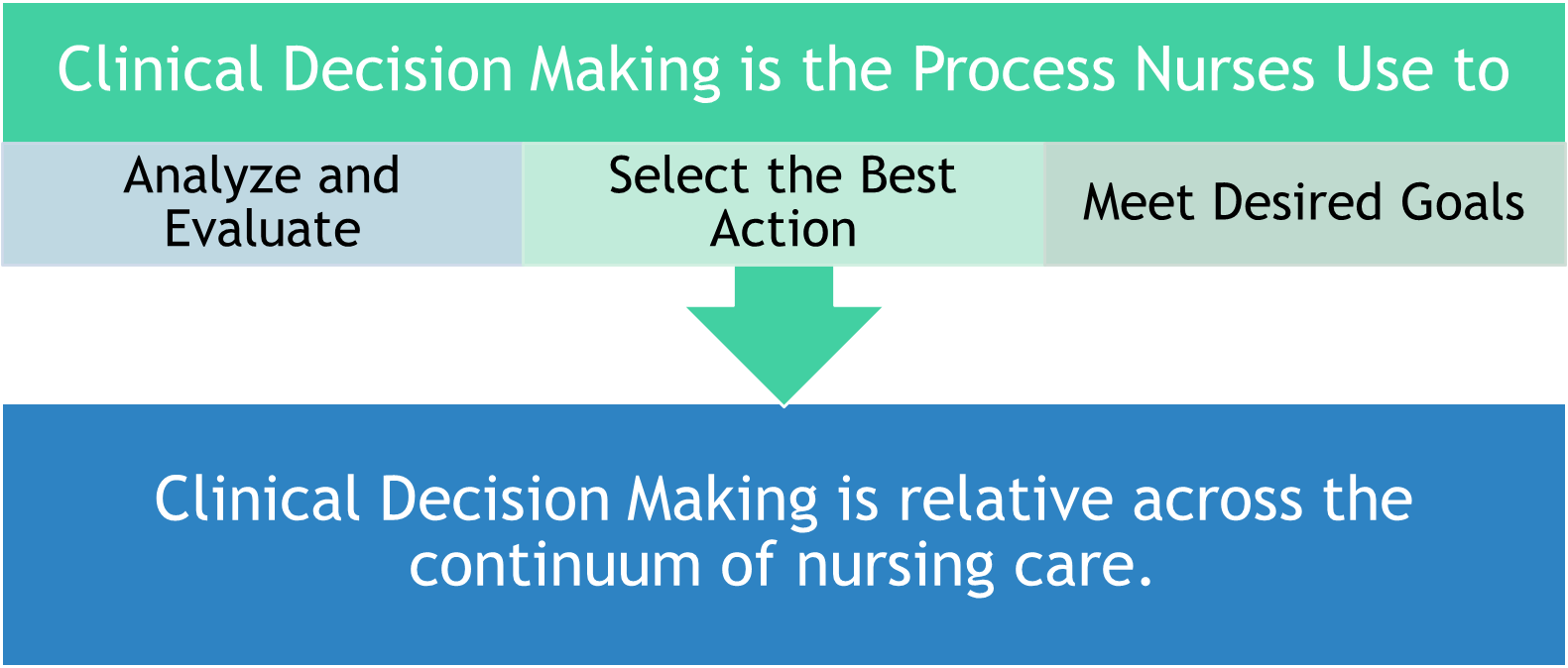
Clinical Decision Making
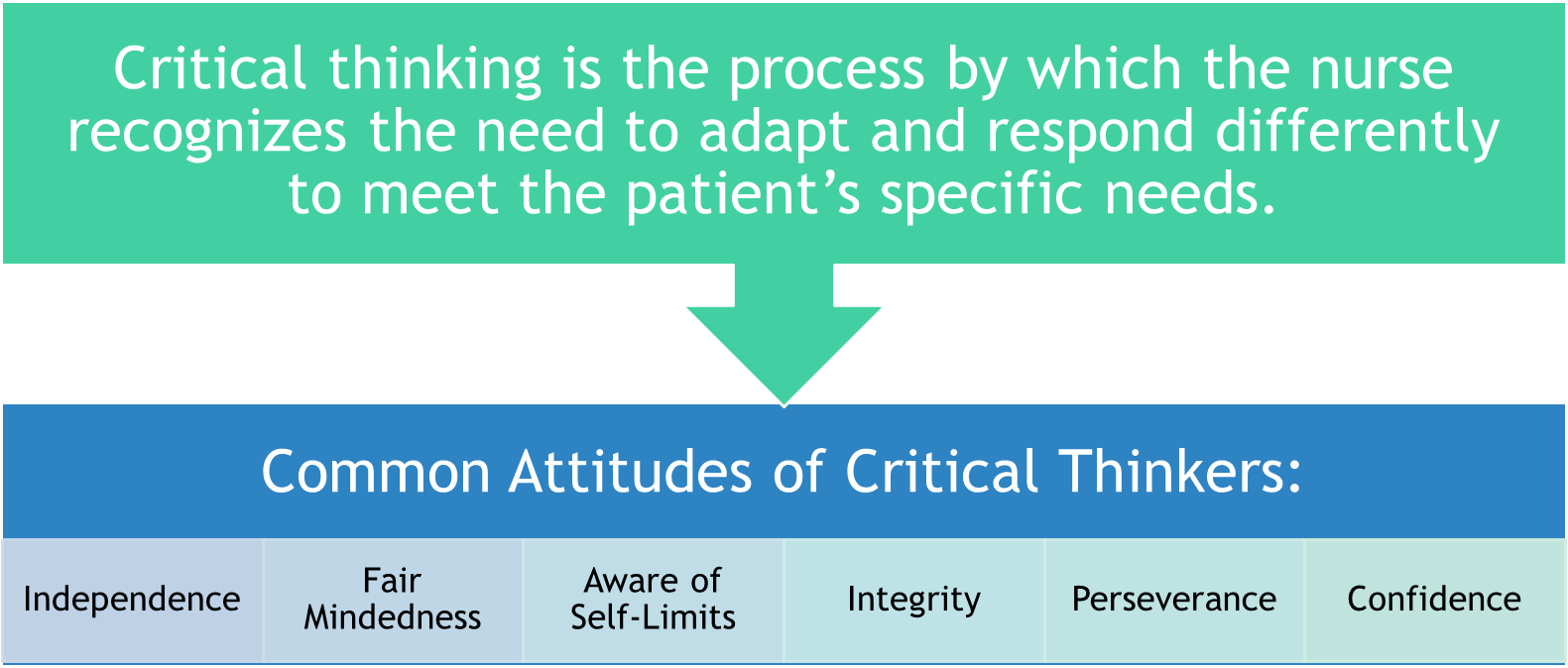
Critical Thinking
Ability to think, understand, and reason
Differentiate facts from opinions
Approach situations objectively
Clarify concepts
Salient Cues (Salient= significant; cues= data)
Vary per patient
Indicate a chance in health status (may be positive or negative)
Differs from expected findings
Suggests delayed development
Clustering data that fits together helps determine if there is a pattern
Nurses must stay up to date with best evidence to provide the best care.
Intellect
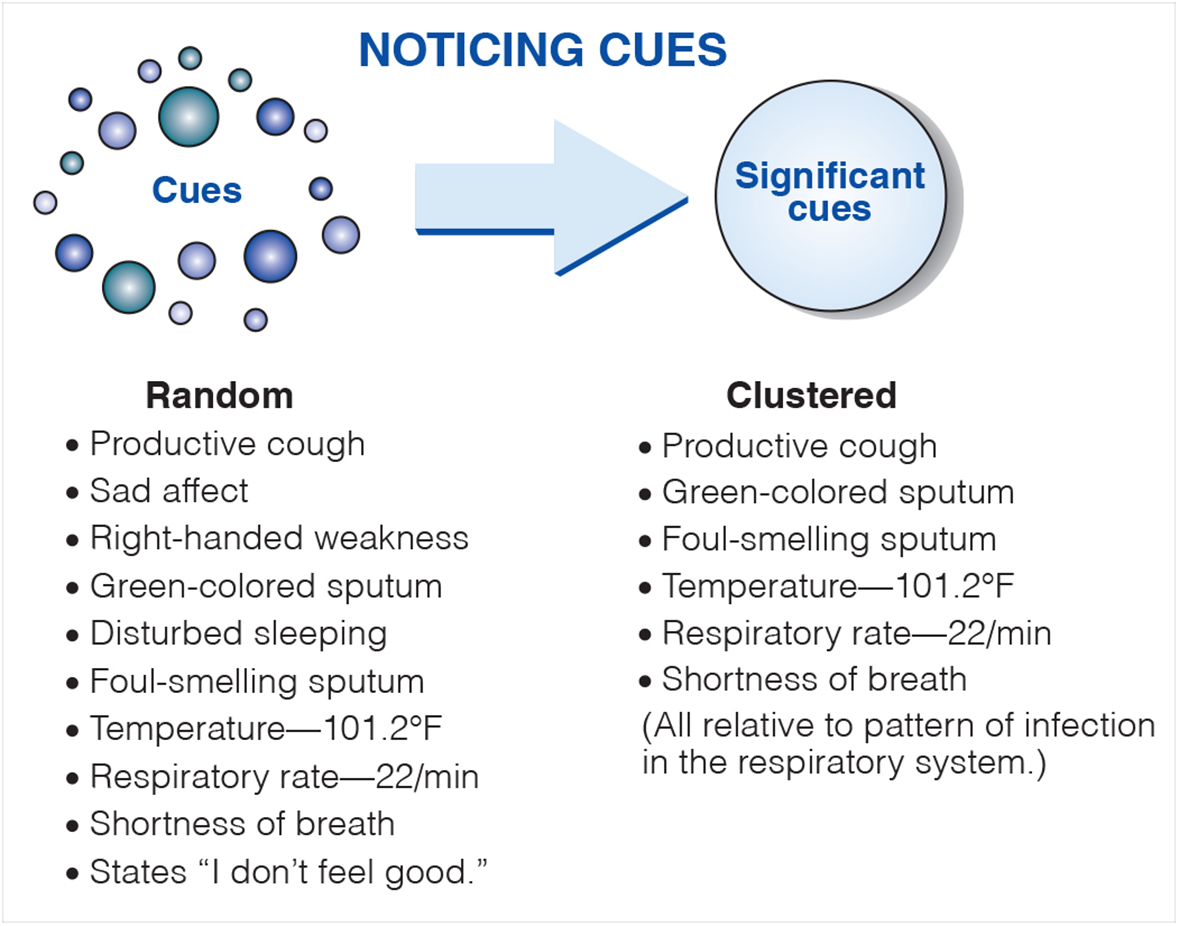
Noticing Cues
Finding unique solutions to a problem.
Individualized Patient Care
Creative thinkers must have knowledge of the situation/problem
Creativity
The search for knowledge or facts
Examine objective information for clarification
Nurses continually use inquiry in the clinical setting
Inquiry can resolve clinical problems and issues
Leads to Improved Patient Outcomes
Inquiry
General idea, observations, or principles are analyzed to develop specific predictions.
Deductive Reasoning “Top Down”
Develops general conclusion by putting together specific cues.
Inductive Reasoning “Bottom Up”
Nurse must determine whether patient information is fact, inference, judgement, or opinion
Clinical Reasoning
Use of careful reasoning in the clinical setting
A learned skill that novice nurses must practice.
Reasoning
The action of making sense of an occurrence, experience, situation, or decision and learning from it.
Common questions used for reflection:
What worked or did not work?
What could be done differently for better outcomes?
What was done well?
Must be open minded when reflecting
Reflection
“Gut reaction”
Use of nursing knowledge, experience, and expertise for understanding without the conscious use of reasoning.
Difficult for students and new nurses
Intuition
Ethical and value based
Prioritization
Time management
Scheduling
Personal/Professional
Clinical Decision Making - Types of Decision
Identify a situation or problem
Analyze the information/alternatives
Prioritize the options
Select the best option to try
Put it into action
Evaluate the success
Clinical Decision Making - Steps to Making Decisions
Nurses use decision making as part of the problem-solving process
Need to be aware of recurring problems.
Common approaches to problem solving include: The Nursing Process, Trial and Error, Intuition, The Scientific Method
Problem Solving
is a process where nurses solve problems by applying:
Clinical reasoning
Critical thinking
Decision-making skills
What actions should the nurse take to provide care?
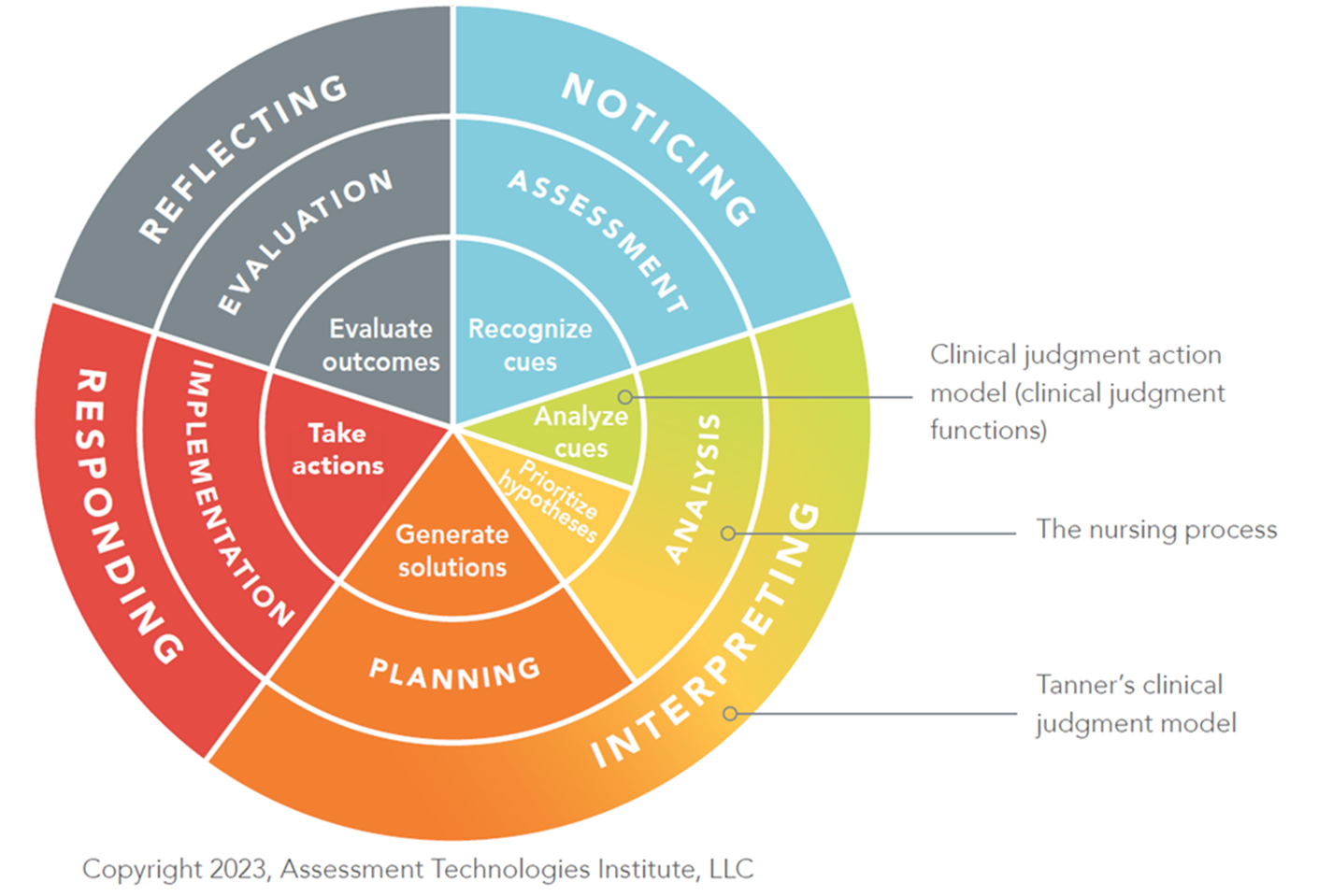
Clinical Judgement
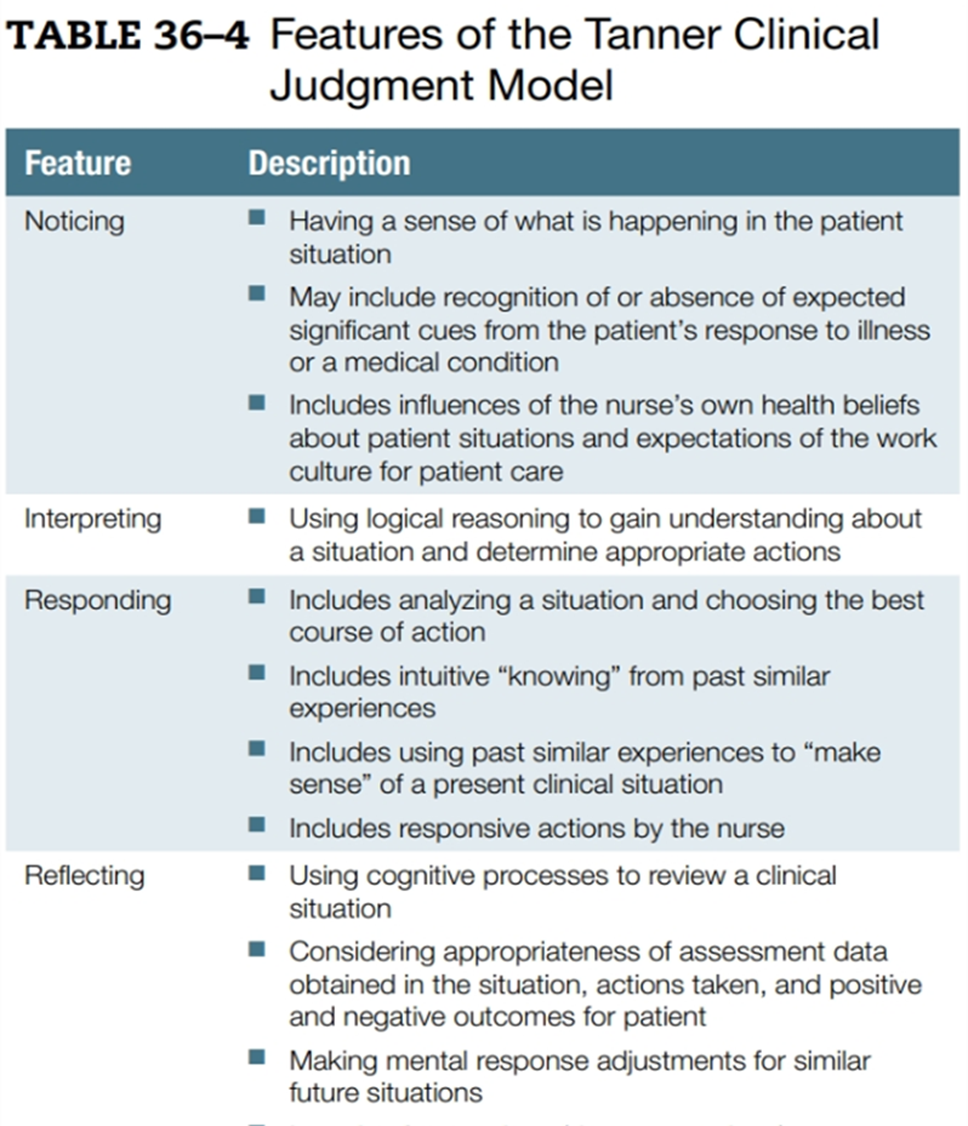
Tanner’s Clinical Judgement Model
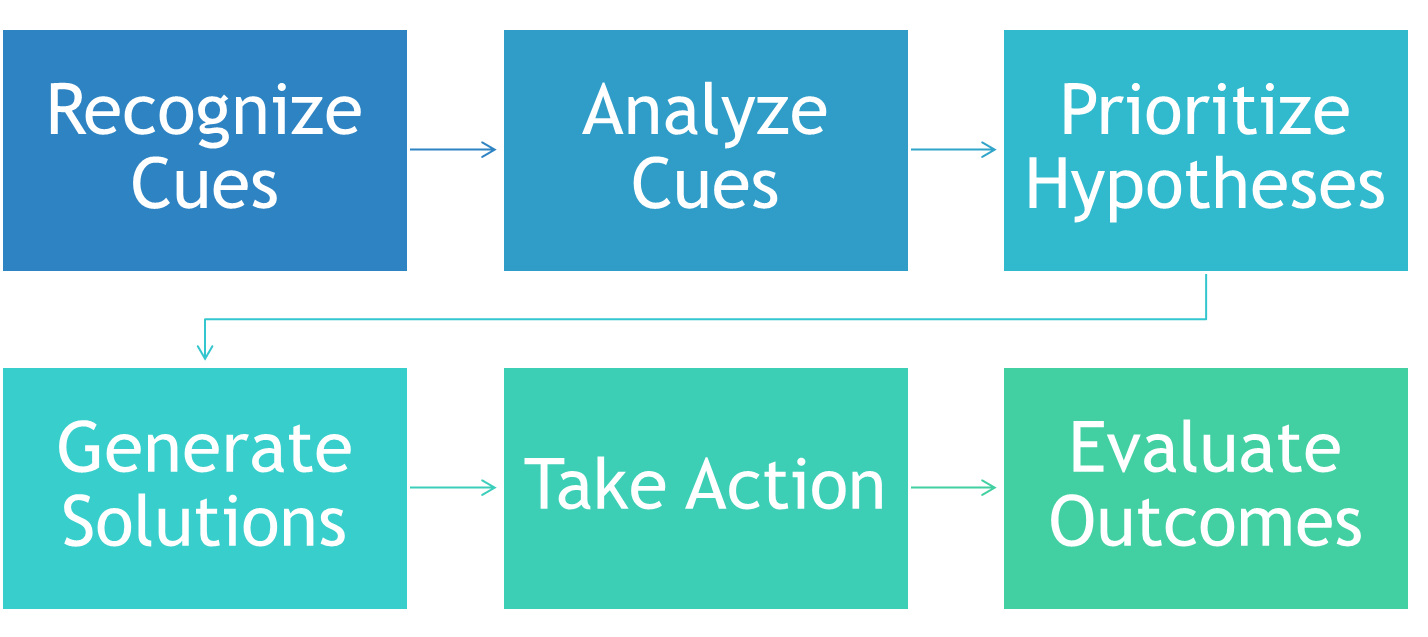
NCSBN Clinical Judgment Model Six Components
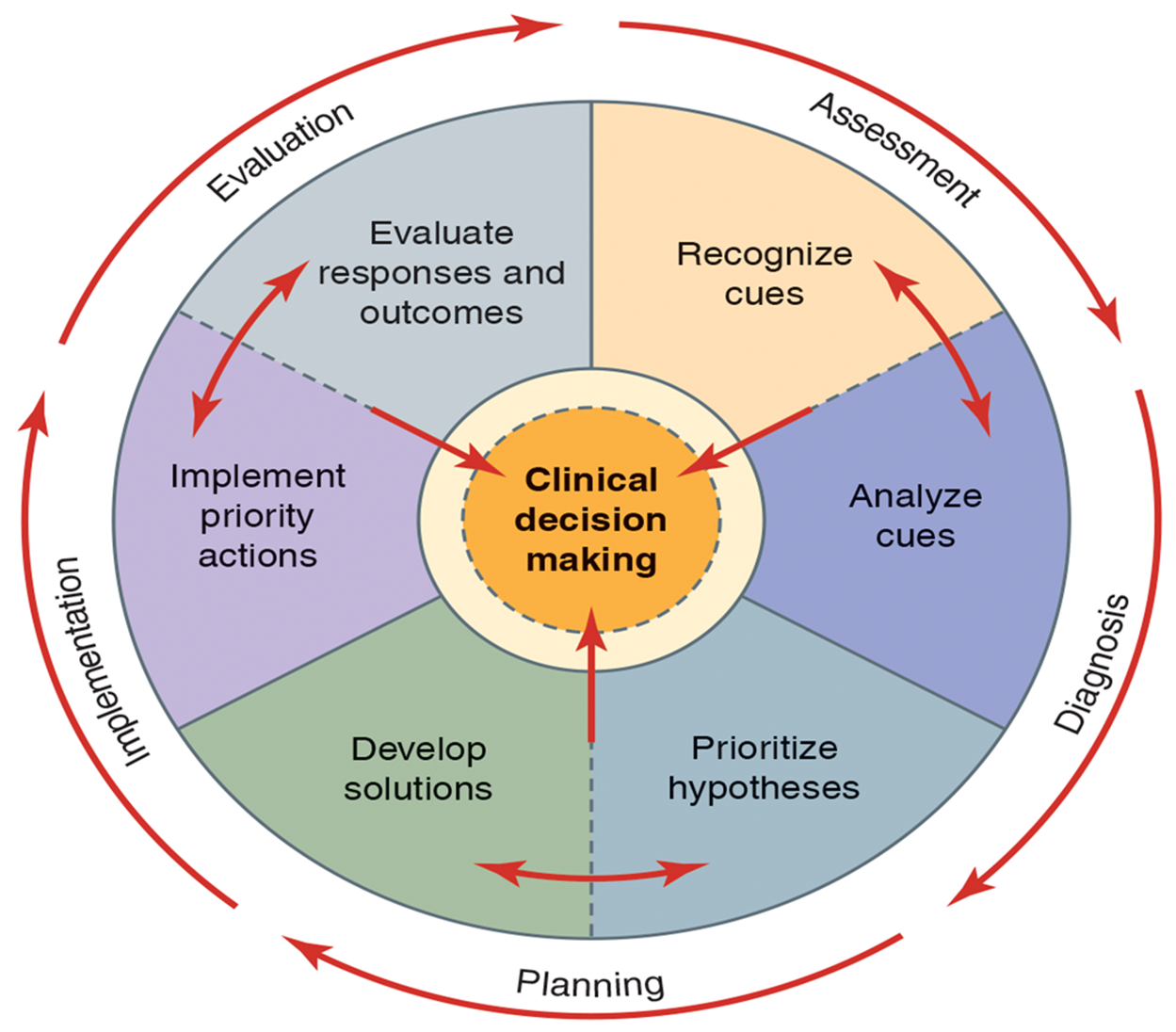
Clinical Decision Making