BIO-Exam #3
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
List two of the seven criteria listed in your lab manual that are used to name muscles?
shape, location, action, etc
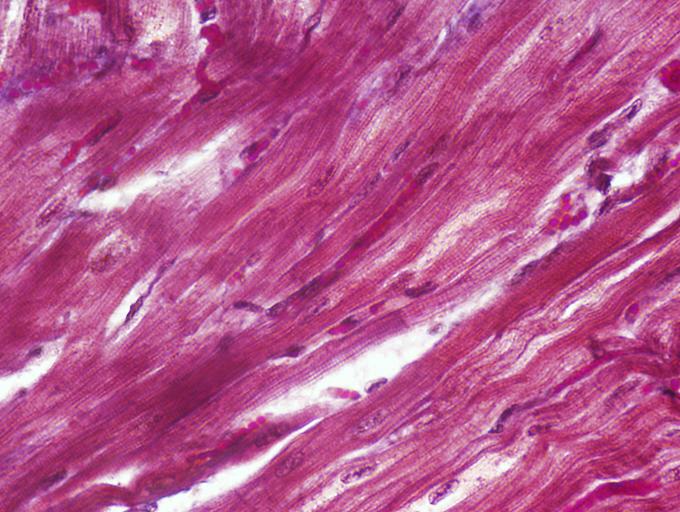
Identify the type of muscle tissue shown?
cardiac
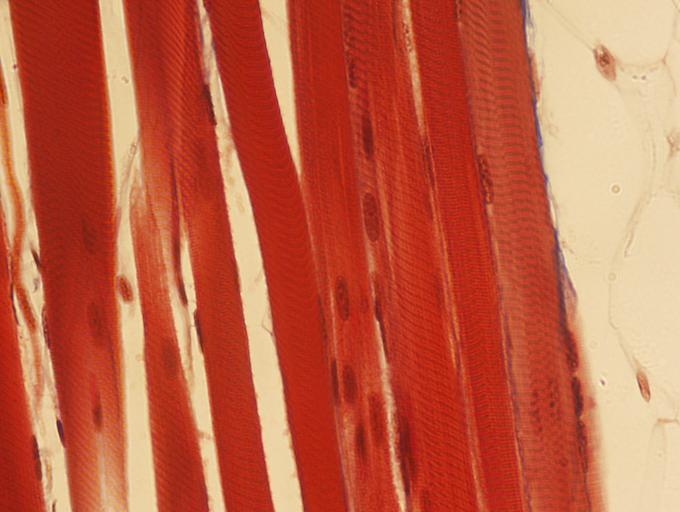

Identify the type of muscle tissue shown?
skeletal
What are the individual contractile units of a muscle cell called?
sarcomeres
What neurotransmitter do motor neurons use to stimulate muscle cells?
acetylcholine
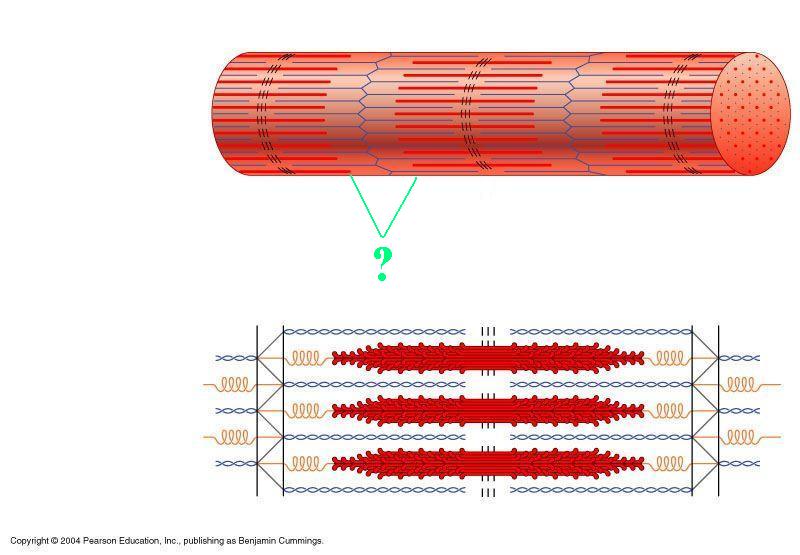
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere.
I-band
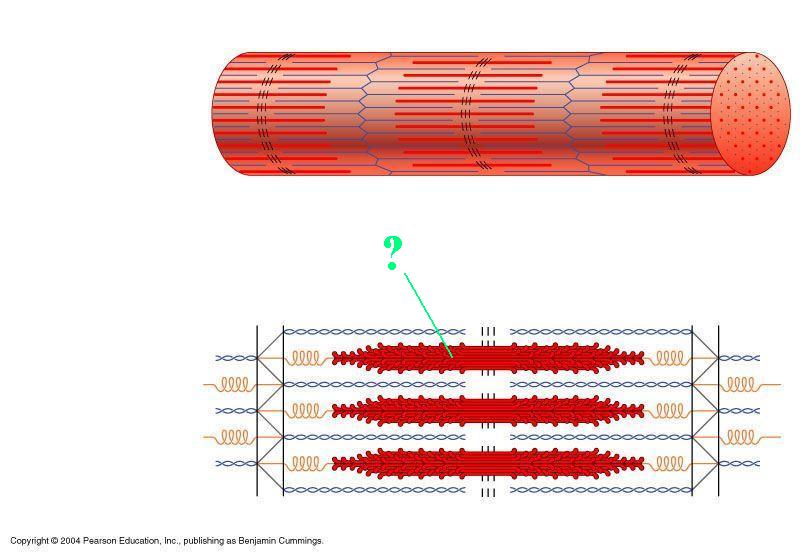
The indicated region of the sarcomere is composed of what protein?
myosin
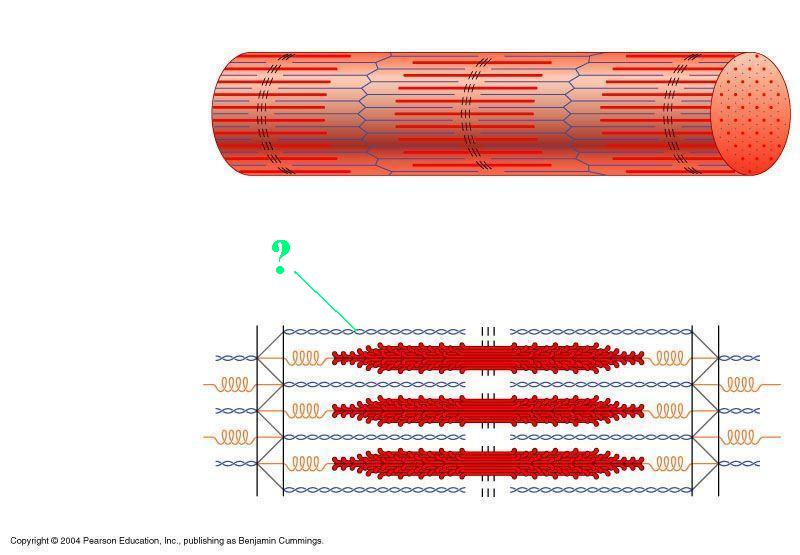
The indicated region of the sarcomere is composed of what protein?
actin
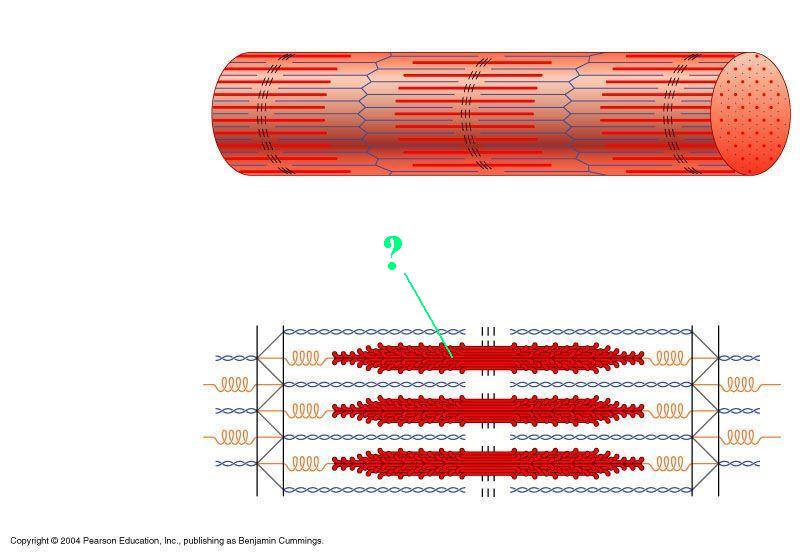
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere.
thick filaments
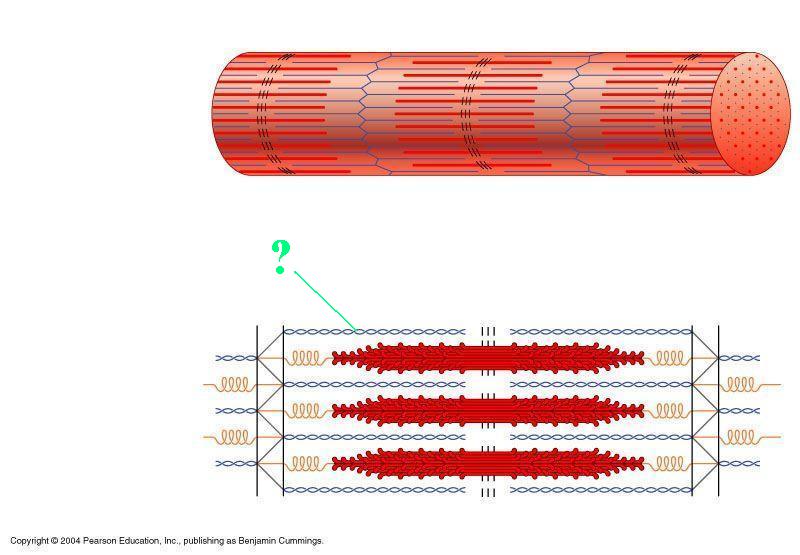
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere.
thin filaments
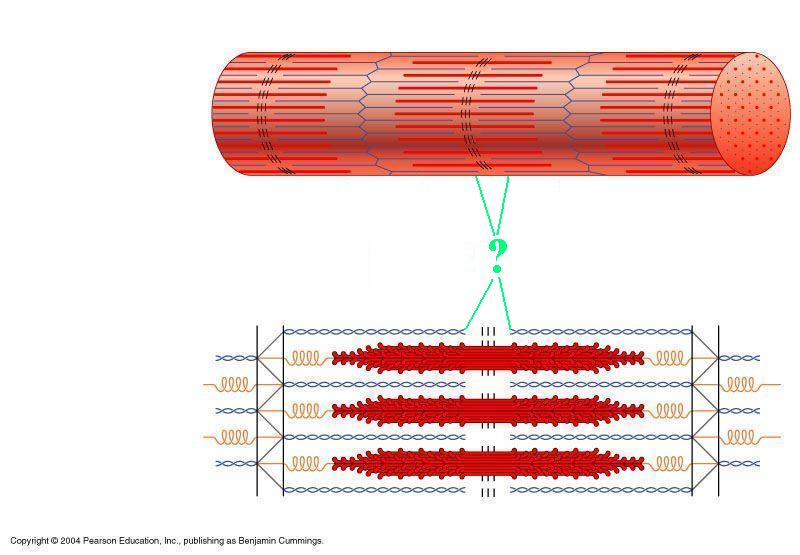
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere.
H-zone
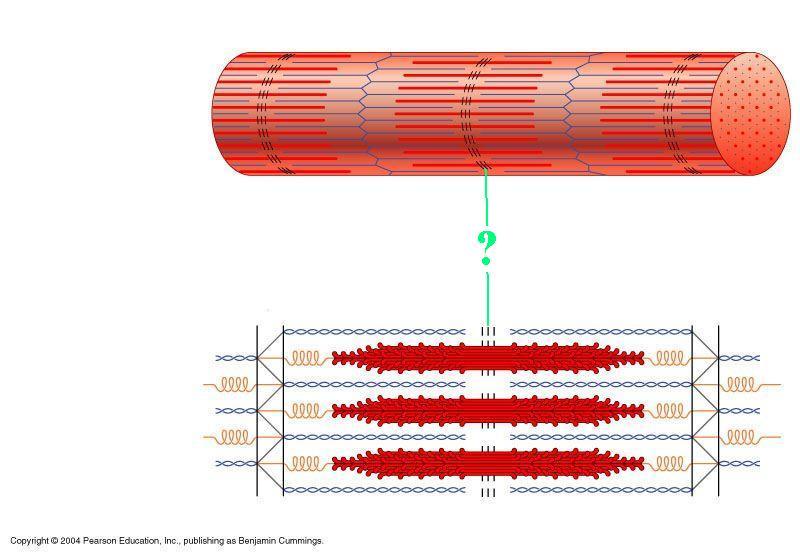
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere.
M-line
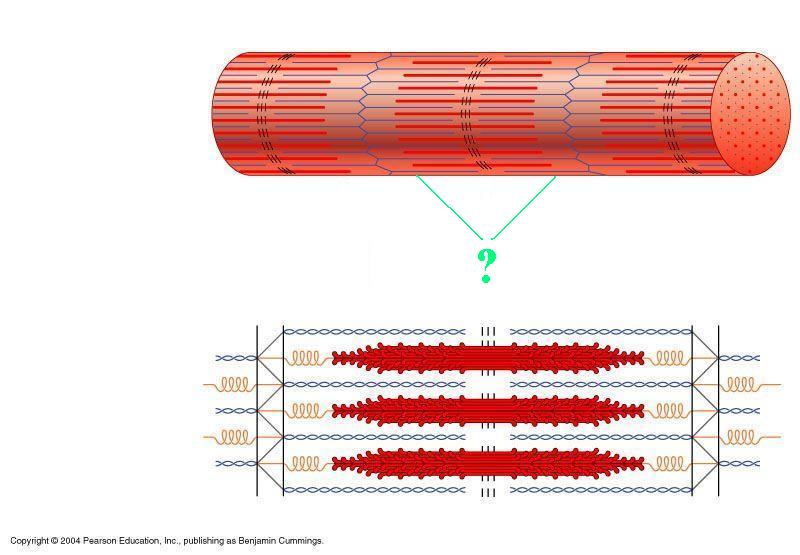
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere.
A-band
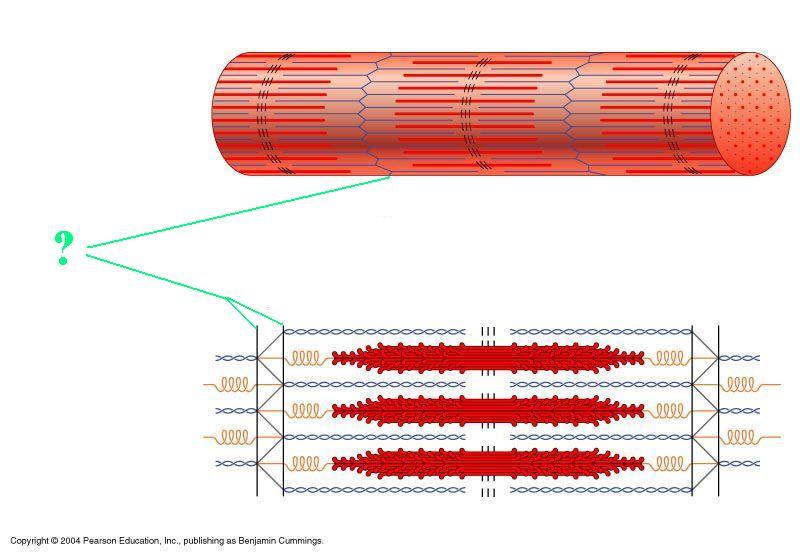
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere.
Z-disc
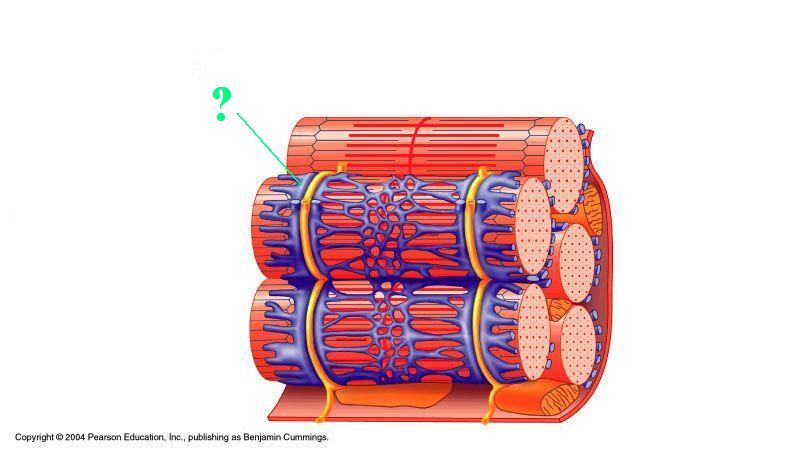
Identify the indicated structure.
terminal cistern of sarcoplasmic reticulum
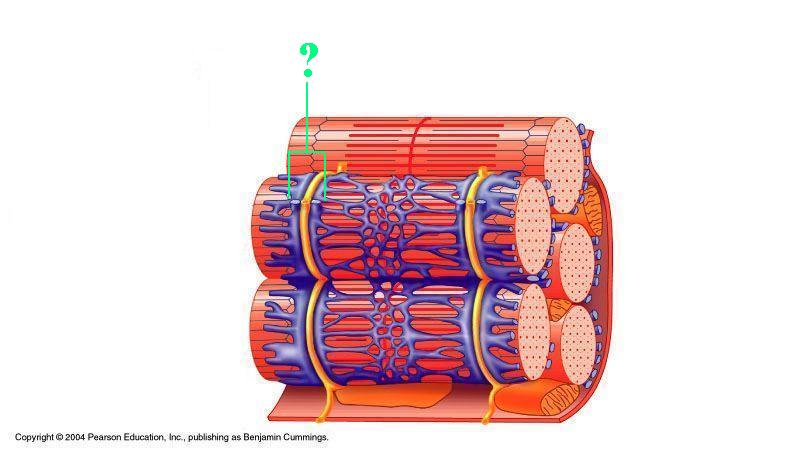
Identify the indicated structure.
triad
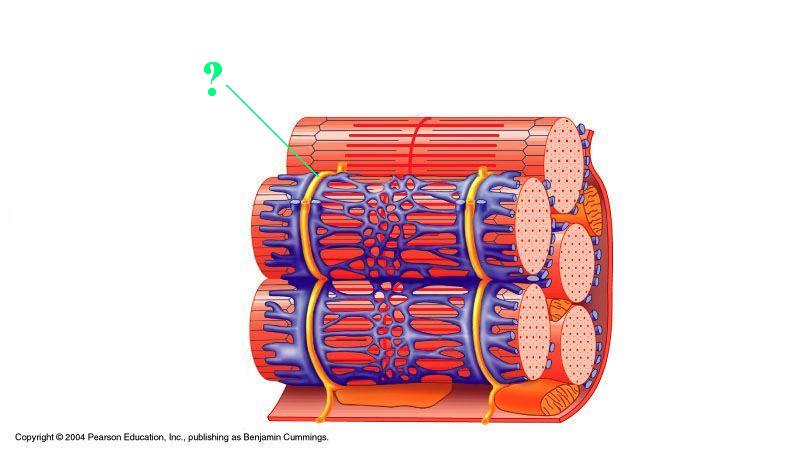
Identify the indicated structure.
t-tubule
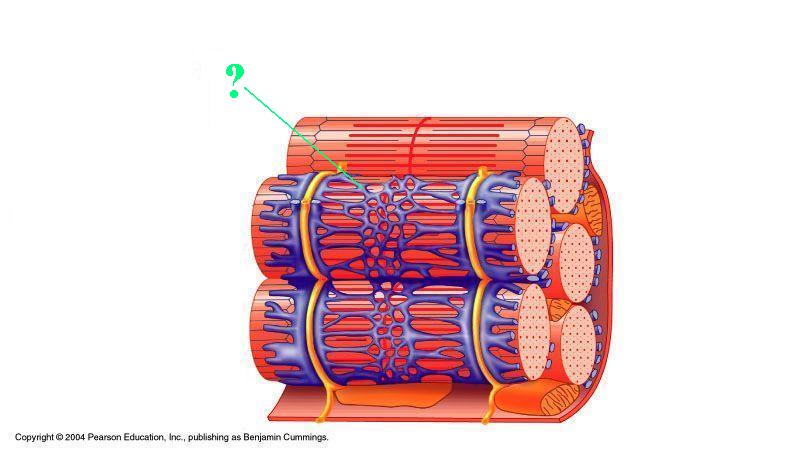
Identify the indicated structure.
sarcoplasmic reticulum
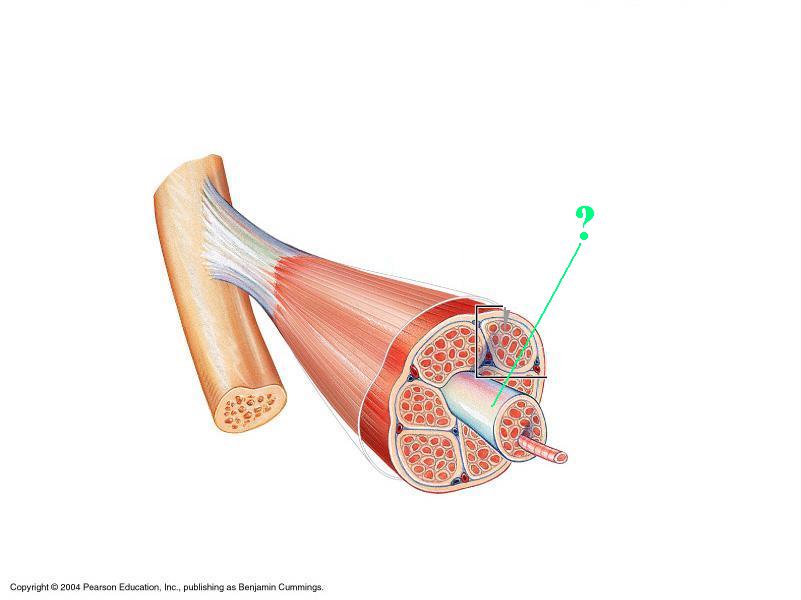
Identify the indicated layer of connective tissue.
perimysium
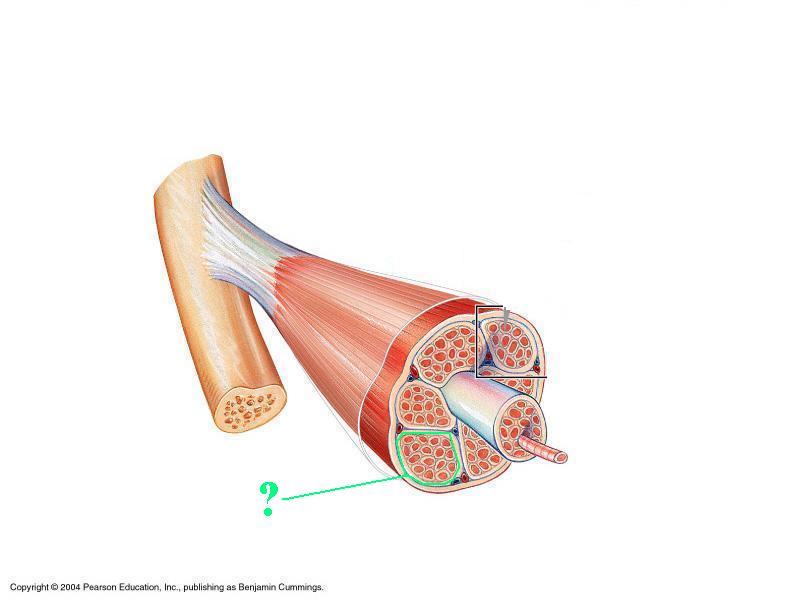
Identify the indicated structure.
fascicle
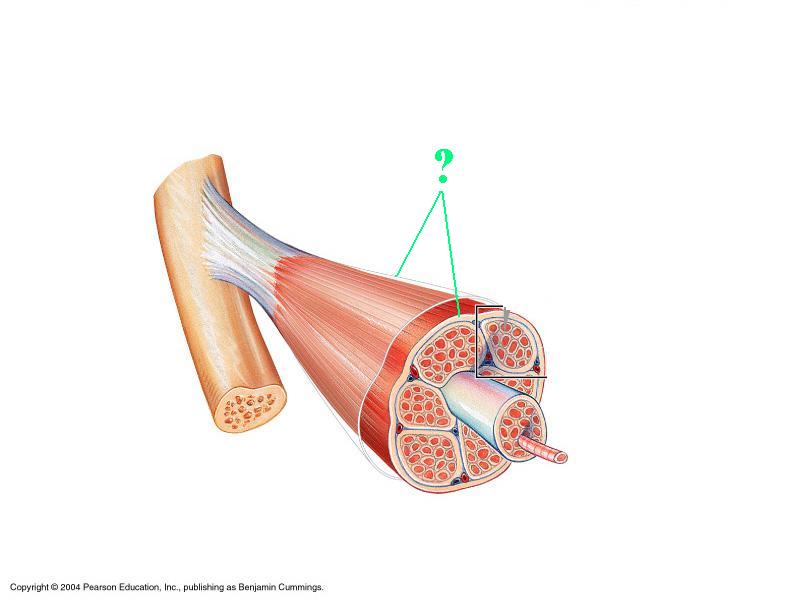
Identify the indicated layer of connective tissue.
epimysium
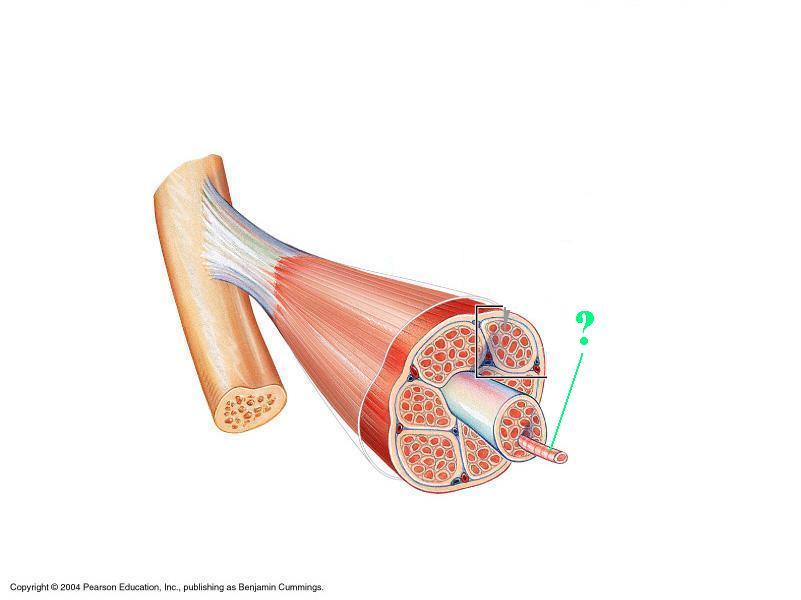
Identify the indicated structure.
muscle fiber
A single motor neuron, along with all of the muscle fibers that it innervates, is called:
motor unit
A strong, cord-like bundle of connective tissue that connects a muscle to another muscle or to a bone is called:
tendon
The connective tissue sheath that forms around an individual skeletal muscle cell is called:
endomysium
The connective tissue sheath that forms around a bundle of skeletal muscle cells is called:
perimysium
The connective tissue sheath that forms around an entire skeletal muscle is called:
epimysium
The endoplasmic reticulum of a skeletal muscle cell is called:
sarcoplasmic reticulum
The light segments of the striations of a skeletal muscle cell are called:
I-bands
A portion of the plasma membrane of a skeletal muscle indents into the cytoplasm and surrounds the bundles of muscle filaments. This structure is called:
t-tubule
The space between a neuron axon terminal and the target cell is called:
sypnatic cleft
A flat, sheet-like bundle of connective tissue that connects a muscle to another muscle or to a bone is called:
aponeurosis
The structure formed by two terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and a transverse tubule is called:
triad
The dark segments of the striations of a skeletal muscle cell are called:
A-bands
Skeletal muscles cells are called:
muscle fibers
Bundles of protein filaments within a muscle cell are arranged into structures called:
myofibrils
What do we call muscles that immobilize the origin of another muscle so that all of the tension is exerted at the insertion?
fixators
What do we call muscles that aid the action of other muscles by reducing undesirable or unnecessary movement?
synergists
Define "insertion" as it applies to skeletal muscles.
moveable site of attachment
What do we call muscles that are primarily responsible for producing a specific movement?
agonists
What do we call muscles that oppose or reverse a particular movement?
antagonists
Which of the seven criteria used for naming a muscle applies to the adductor magnus muscle?
action and relative size
Which of the seven criteria used for naming a muscle applies to the deltoid muscle?
shape
Which of the seven criteria used for naming a muscle applies to the extensor digitorum muscle?
action and location
Which of the seven criteria used for naming a muscle applies to the transversus abdominis muscle?
direction of fibers and location
Which of the seven criteria used for naming a muscle applies to the brachioradialis muscle?
location of origin and insertion
Which of the seven criteria used for naming a muscle applies to the sternocleidomastoid muscle?
location of origin and insertion
Which of the seven criteria used for naming a muscle applies to the rectus femoris muscle?
direction of fibers and location
Which of the seven criteria used for naming a muscle applies to the trapezius muscle?
shape
What phenomenon is considered an extreme form of wave summation in which a steady, sustained contraction is acheived?
tetany
A neuron and all of the muscle cells that it stimulates are together called a _________________?
motor unit
What type of force is produced by the physiological contraction of a muscle rather than by elastic recoil?
active
By steadily increasing the number of motor units that are activated, we produce a steady increase in the force produced by a muscle. This process is called __________________?
recruitment
If we increase the frequence of stimulation of a muscle untill we acheive a steady sustained contraction, we will have caused what phenomenon?
tetany
If we place a muscle under more load than it can lift and stimulate it, what type of contraction will we produce?
isometric
If a muscle contracts against a load that is too heavy for the muscle to lift, what type of contraction is the muscle demonstrating?
isometric
The absence of what molecule is involved in the phenomenon of rigor mortis?
ATP
If we require a muscle to contract until it starts to run out of ATP, what do we call the state of the muscle at that point?
fatigue
From what cellular organelle is calcium released during the latent period of a muscle twitch?
sarcoplasmic reticulum
What type of force is produced by the elastic recoil of a stretched muscle?
passive
What do we call the period of time between the application of a stimulus to a muscle and the first observable response or movement of the muscle?
latent period
If we place a muscle under a load that it can lift and stimulate it, what type of contraction will we produce?
isotonic
The three phases of a muscle twitch are the contraction period, the latent period, and the:
relaxation period
If a muscle contracts against a load that it is able to lift, what type of contraction is the muscle demonstrating?
isotonic
Although no force is generated by a muscle fiber during the latent period, chemical changes, such as the release of ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum do occur. Which ion is released
calcium
compresses the cheeks
compresses the cheeks
Name one action of the rectus abdominis muscle.
Flexion and rotation of the vertebral column
Name one action of the trapezius muscle.
elevation of the scapula
Name one action of the pectoralis major muscle.
flexion of arm
Name one action of the tibialis anterior muscle.
dorsiflexion of the foot at the tarsal joints
Name one action of the platysma muscle.
tenses the skin of the neck
Name one action of the external oblique muscle.
flexion and rotation of vertebral column
Name one action of the triceps brachii muscle.
extension of the forearm at the elbow
Name one action of the extensor digitorum muscle.
extension of the fingers at the metacarpal and phalangeal joints
Name one action of the gastrocnemius muscle.
plantar flexion of foot at the tarsal joints
Name one action of the vastus medialis muscle.
extension of the lower leg at the knee
Name one action of the semimembanosus muscle.
extension of the thigh at the hip
Name one action of the zygomaticus major muscle.
elevation of the lateral corners of the mouth
Name one action of the gracilis muscle.
adduction of thigh at the hip
Name one action of the supraspinatus muscle.
abduction of the arm at the shoulder
Name one action of the flexor carpi radialis muscle.
flexion of the hand at the carpal joints
Name one action of the deltoid muscle.
abduction of the arm at the shoulder
Name one action of the masseter muscle.
elevation of the mandible
Name one action of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
rotation of the head
Name one insertion of the platysma muscle
lower margin of the mandible
Name one insertion of the external oblique muscle.
linea alba
Name one insertion of the masseter muscle.
angle and ramus of the mandible
Name one insertion of the rectus abdominis muscle.
xiphoid process of the sternum
Name one insertion of the infraspinatus muscle.
greater tubercle of the humerus
Name one insertion of the supraspinatus muscle.
greater tubercle of the humerus
Name one insertion of the vastus medialis muscle.
tibial tuberosity
Name one insertion of the zygomaticus minor muscle.
skin and muscle at the corner of the mouth
Name one insertion of the pectoralis major muscle.
intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
Name one insertion of the tibialis anterior muscle.
medial cuneiform bone
Name one insertion of the buccinator muscle.
orbicularis oris muscle
Name one insertion of the brachialis muscle.
coronoid process of the ulna
Name one insertion of the triceps brachii muscle.
olecranon of ulna
Name one insertion of the semimembranosus muscle.
medial condyle of the tibia
Name one insertion of the flexor carpi radialis muscle.
base of metacarpals 2 and 3
Name one insertion of the semitendinosus muscle.
medial aspect of upper tibial shaft