chemical changes
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Metals react with oxygen to produce
metal oxides. The reactions are oxidation reactions because the metals gain oxygen.
reduction reaction in terms of oxygen
losing oxygen
When metals react with other substances, what do the metal atoms form
the metal atoms form positive ions.
what is the reactivity of metal related to
The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive ions
how can metals be arranged
Metals can be arranged in order of their reactivity in a reactivity series.
The metals potassium, sodium, lithium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, iron and copper can be put in order of their reactivity from their reactions with water and dilute acids.
The non-metals hydrogen and carbon are often included in the reactivity series.
The reactions of metals with water and acids are limited to room temperature and do not include reactions with steam.
how are unreactive metals such as gold found
Unreactive metals such as gold are found in the Earth as the metal itself but most metals are found as compounds that require chemical reactions to extract the metal.
how can metals less reactive than carbon can be extracted
Metals less reactive than carbon can be extracted from their oxides by reduction with carbon.
Reduction involves the loss of oxygen.
in a compound, a more reactive element will do what
a more reactive element will displace a less reactive element from its compound
oxidation and reduction in terms of electrons
Oxidation is the loss of electrons and reduction is the gain of electrons.
write ionic equations for displacement reactions
identify in a given reaction, symbol equation or half equation
which species are oxidised and which are reduced.
4.4.2 Reactions of acids
unfinished
electrolytes.
When an ionic compound is melted or dissolved in water as solid ionic compounds cannot conduct electricity , the ions are free to move about within the liquid or solution. These liquids and solutions are able to conduct electricity and are called electrolytes.
describe process of electrolysis
Passing an electric current through electrolytes causes the ions to move to the electrodes. Positively charged ions move to the negative electrode (the cathode), and negatively charged ions move to the positive electrode (the anode). Ions are discharged at the electrodes producing elements.
-able to write half equations for the reactions occurring at the electrodes during electrolysis, and may be required to complete and balance supplied half equations.
When a simple ionic compound (eg lead bromide) is electrolysed in the molten state using inert electrodes, what happens
he metal (lead) is produced at the cathode and the non-metal (bromine) is produced at the anode.
when is metals extracted from molten compounds using electrolysis.
Electrolysis is used if the metal is too reactive to be extracted by reduction with carbon or if the metal reacts with carbon.
why is using electrolysis to extract metals not ideal
Large amounts of energy are used in the extraction process to melt the compounds and to produce the electrical current.
electrolysis of aluminium oxide
aluminium oxide is mixed with cryolite which lowers melting point -reduces amount of energy needed and saves money
the aluminium ions will be attracted to cathode, where each ion gains 3 electrons and forms aluminium atom Al3+ +3e- =Al
oxide ions attracted to anode where each oxide ion loses 2 electrons to form oxygen atom
why must the anode be replaced regularly
the oxygen molecules produced at the anode react with graphite(carbon) to form carbon dioxide gas
during electrolysis of aqueous solution, what is the rule
-in the cathode
-at the anode
-hydrogen will be produced if the metal is more reactive than hydrogen
-if the aqueous solution contains halide ions, then the halogen will be produced at the anode or else oxygen and water will be produced
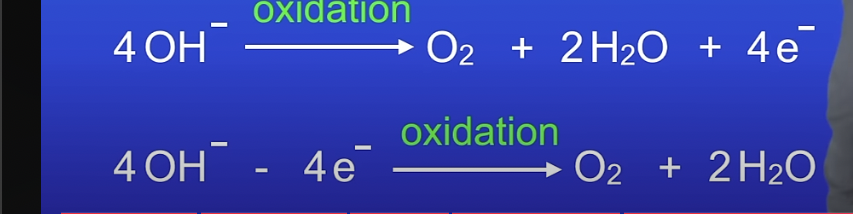
oxidation of OH at the anode -ionic equation
Required Practical 3: Electrolysis of copper(II) chloride
first pour approximately 50cm3 of copper(II) chloride solution into beaker
then place a plastic Petri dish over the beaker-the Petri dish should have two holes
insert a carbon graphite rod into each hole (electrodes) and carbon graphite is unreactive so these electrodes are inert
the 2 electrodes must not touch each other because cause a short-circuit
attach crocodile leads to the rods and then connect the rods to the terminals of a low-voltage power supply and switch it on
observe the cathode which you will see that it is being coated with copper
see bubbles of gas in the anode and notice smell of chloride in the air and holding a damp blue litmus paper near the anode will become bleached - gas is chlorine
Required Practical 3: Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution
first pour approximately 50cm3 of sodium chloride solution into beaker and turn on power supply
at the anode, bubbles of gas being produced which will bleach damp blue litmus paper and that tells us gas is chlorine
at the cathode, bubbles of gas which will be hydrogen gas and prove that it is hydrogen by collecting it and testing it with a lit splint and produce a squeaky pop
a key fact about acids
in aqueous solutions, acid molecules ionise produce hydrogen ions (H+)
bases
are chemicals which can neutralise acids producing salt and water
what are bases usually
metal oxides or metal hydroxides
alkalis
bases which are soluble in water
a key fact about alkalis
in aqueous solutions, alkalis produce hydroxide ions (OH- ions)
how to determine the ph
using a ph probe, which will detect ph electronically or universal indicator which will change colour
Acids react with some metals to produce
Acids react with some metals to produce salts and hydrogen.
-Knowledge of reactions limited to those of magnesium, zinc and iron with hydrochloric and sulfuric acids.
reacting acid with alkali
the hydrogen ions react with hydroxide ions to produce water
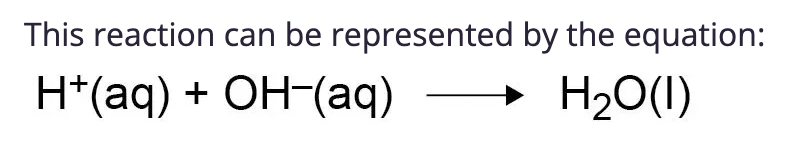
hydrochloric acid+ iron
-what does it produce
-what is getting reduced and what is getting oxidised
-iron chloride+hydrogen
-iron=oxidation
hydrogen=reduction
how can acids be neutralised
by alkalis and bases
examples of alkalis
soluble metal hydroxides
examples of bases
insoluble metal hydroxides and metal oxides
what happens when we react an acid with an alkali or base
o produce salts and water,
The particular salt produced in any reaction between an acid and a base or alkali depends on:
the acid used (hydrochloric acid produces chlorides, nitric acid produces nitrates, sulfuric acid produces sulfates)
the positive ions in the base, alkali or carbonate
acids reacting with metal carbonates
to produce salts, water and carbon dioxide.
how can soluble salts be made
Soluble salts can be made from acids by reacting them with solid insoluble substances, such as metals, metal oxides, hydroxides or carbonates. The solid is added to the acid until no more reacts and the excess solid is filtered off to produce a solution of the salt.
how to form solid salts
Salt solutions can be crystallised to produce solid salts.
required practical 1 : making soluble salts
reaction between solid copper oxide and dilute sulfuric acid
start with a fixed amount of dilute sulfuric acid. this is our limiting reactant (because do not want any acid at the end as will contaminate the salt)
gently heat the acid until almost boiling but do not want it to boil because could bubble over when we add our other reactants
using a spatula to add small amounts of copper oxide to the acid and stir the solution with a glass rod
-the copper oxide will react and seem to disappear and the solution will turn blue
continue adding copper oxide and if solution continues to be clear blue
sttop adding copper oxide if some powder remains after stirring
at this point the reaction has stopped. all of the acid has reacted
use filtration to remove unreacted copper oxide
get copper sulfate solution and place this in an evaporating basin. heat gently over a beaker of boiling water. heat until around half of the solution remains
leave the solution for 24 hours in a cool place for crystals to form
scrape crystals onto paper towel and gently pat them dry
what is the pH scale
The pH scale, from 0 to 14, is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, and can be measured using universal indicator or a pH probe.
A solution with pH 7 is neutral. Aqueous solutions of acids have pH values of less than 7 and aqueous solutions of alkalis have pH values greater than 7
difference between strong and weak acids
strong acids fully ionise in aqueous solutions whereas weak acids partially ionise in aqueous solutions
3 examples of strong acids
-hydrochloric acid
-sulfuric acid
-nitric acid
3 examples of weak acids
-carbonic acid
-ethanoic acid
-citric acid
ph of strong acids
the pH scale gives us an idea of the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+)
As the pH decreases by one unit…..
the hydrogen ion concentration of the solution increases by a factor of 10.(one order of magnitude)
concentration of acids
tells us amount of acid molecules in a given volume of solution
a dilute acid
will have a fewer acid molecules in a given volume than a concentrated acid even if the strength of the acid is the same
The volumes of acid and alkali solutions that react with each other can be measured by
titration using a suitable indicator.
frate of reaction with dilute acids
magnesium-very rapid reaction
zinc-quite rapid reaction
iron-slow reaction
titration
The volumes of acid and alkali solutions that react with each other can be measured by titration using a suitable indicator.
describe the steps for titrations to work out concentration of sulfuric acid needed to neutralise sodium hydroxide
use a pipette to transfer 25cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution into a conical flask (reduces risk of splashing)
you add drops of indicator such methyl orange to the alkali in the conical flask
place conical flask on a white tile so we can see a colour change more clearly
fill a burette with sulfuric acid
add acid to the alkali until the solution is neutral. we need to add just enough acid for this to happen.
once we start to see a colour change, we now add the acid drop by drop until solution is neutral
it is important to swirl the solution to make sure the acid and alkali mix (yellow to red)
read the volume of acid added from the burette
when reading the burette you need to make sure your eye level is with the surface of the liquid. the surface of the liquid naturally curves (meniscus) -always read the bottom of the meniscus
important fact about using pipette filler to draw liquid into pipette
important to allow the liquid to drain out of the pipette rather than blowing it out using the pipet filler. blowing the liquid out will give you an incorrect volume