AP Bio Organic Chemistry
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:54 AM on 9/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
1
New cards
Organic Chemistry
study of carbon containing compounds; carbon forms the structural basis for proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids (only few other elements make up macromolecules: H,O,P,N,Ca)
2
New cards
What is the key to carbon's versatality?
-Carbon has 4 valence electrons (valence of 4) for 4 covalent bonds; Can bond with 4 different atoms or can bond with other carbon atoms forming carbon skeleton
-Covalent bonds are stable and strong in aqueous solutions
-Can form single and double bonds
-Serves as an intersection that can branch in any direction
-Carbon skeleton can vary in 4 different ways
-Functional groups can make it nonpolar or polar like methyl vs. hydroxyl
-Covalent bonds are stable and strong in aqueous solutions
-Can form single and double bonds
-Serves as an intersection that can branch in any direction
-Carbon skeleton can vary in 4 different ways
-Functional groups can make it nonpolar or polar like methyl vs. hydroxyl
3
New cards
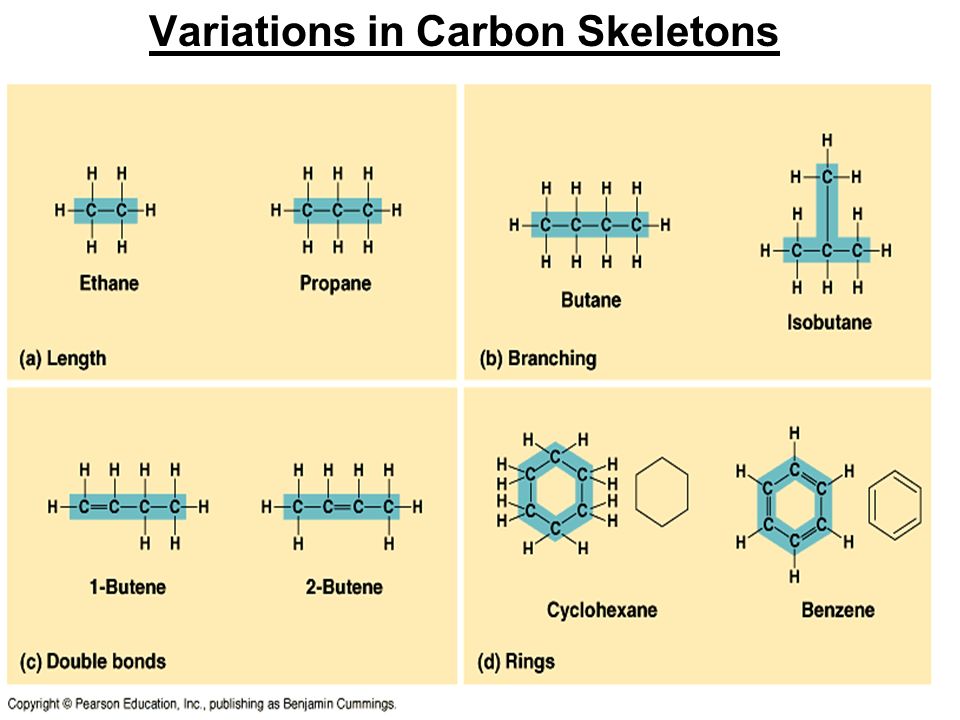
Carbon Skeleton Variations
-Length, Double bonds/single bonds (location & #), Branching, Rings
-contributes to diversity of organic molecules
-contributes to diversity of organic molecules
4
New cards
Hydrocarbons
-Simplest organic molecule; carbon skeleton surrounded by hydrogen
-Hydrophobic because of non-polar covalent bonds
-Store large amounts of energy
-Undergo reactions that release a large amount of energy
-Hydrophobic because of non-polar covalent bonds
-Store large amounts of energy
-Undergo reactions that release a large amount of energy
5
New cards
Functional groups
-Chemical attachments to the carbon skeleton other than hydrogen.
-Bring unique properties to molecules they’re attached to; this contributes to the diversity of organic molecules.
-Ex: Because of a small difference in functional groups, estradiol and testosterone are different which can have LARGE effects like the sexual characteristic of animal
-Bring unique properties to molecules they’re attached to; this contributes to the diversity of organic molecules.
-Ex: Because of a small difference in functional groups, estradiol and testosterone are different which can have LARGE effects like the sexual characteristic of animal
6
New cards
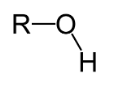
Hydroxyl
-OH; found in carbohydrates; polar/hydrophillic
7
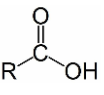
New cards
Carboxyl
-COOH; found in Amino Acids and proteins; polar/hydrophillic and acidic (releases H)
8
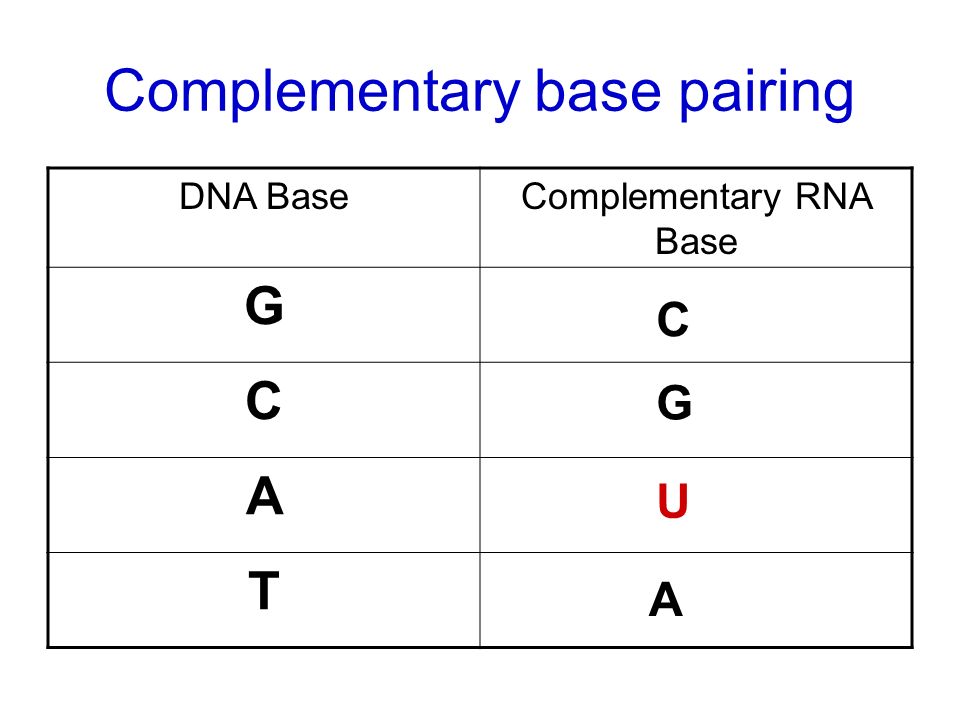
New cards
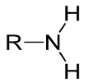
Amino
-NH2; found in amino acids and proteins; polar/hydrophillic and basic (accepts H)
9
New cards
Sulfhydryl
-SH; found in Proteins; polar/hydrophillic
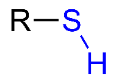
10
New cards
Phosphate
--PO4; found in Proteins, nucleotides, phospholipids; Polar/hydrophilic
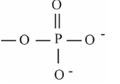
11
New cards
Carbonyl
-CO- and -COH; found in Carbohydrates; polar/hydrophillic

12
New cards
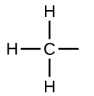
Methyl
CH3; nonpolar/hydrophillic
13
New cards
Ketone (Carboxyl)
carbonyl group that is in the MIDDLE of carbon skeleton

14
New cards
Aldehyde (Carboxyl)
carbonyl group that is on the END of carbon skeleton

15
New cards
ATP
-Adenosine Triphosphate; 3 Phosphate groups + Ribose sugar + Adenine (nitrogenous base)
-Before it is used for energy
-Before it is used for energy
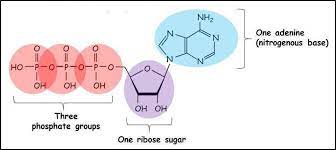
16
New cards
ADP
-Adenosine Diphosphate; 2 Phosphate groups + Ribose sugar + Adenine (nitrogenous base)
-After it is used for energy; breaking of triphosphate bonds requires Hydrolysis, investment of H2O
-After it is used for energy; breaking of triphosphate bonds requires Hydrolysis, investment of H2O
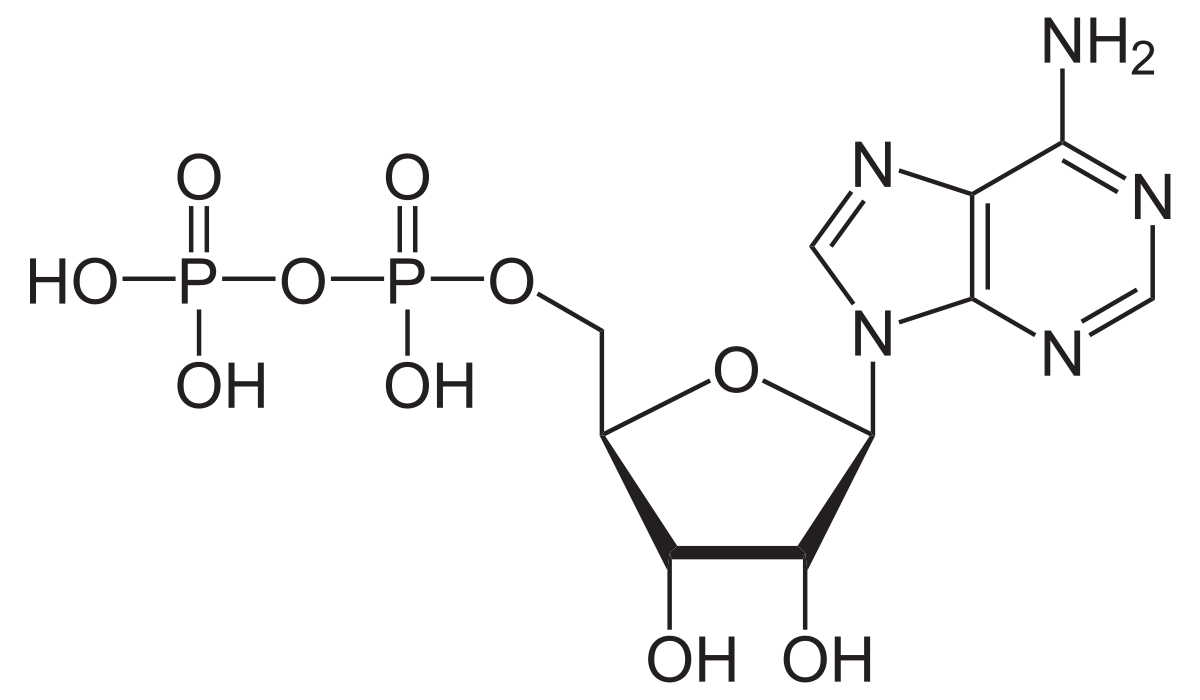
17
New cards
Polymer
Large molecules made up of repeating subunits that are similar or identical in structure (Proteins, carbs, nucleic acids)
18
New cards
Monomer
Subunits of polymer
19
New cards
enzyme
Protein that catalyzes chemical reactions
20
New cards
Dehydration reaction/synthesis
-Forming covalent bonds; one monomer provides hydroxyl (-OH), the other provides hydrogen (H+) to make a water molecule
-Releasing water; Energy invested
-Releasing water; Energy invested
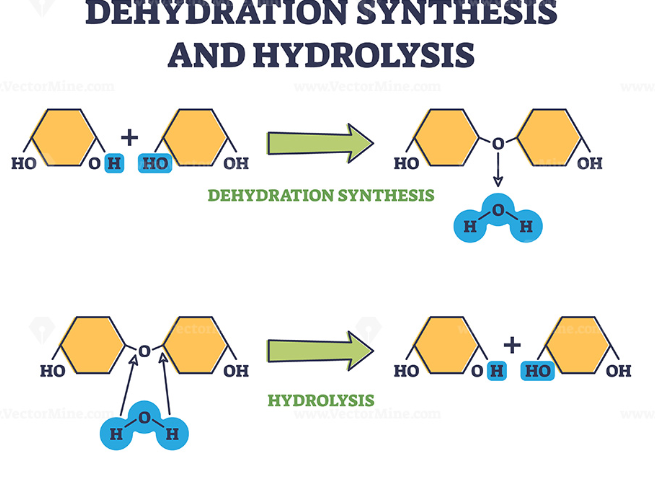
21
New cards
hydrolysis
-Reverse dehydration reaction
-Breaking covalent bonds between monomers; water molecule breaks the bond as the hydroxyl bonds to one monomer and hydrogen bonds to the other
-Investing water; releasing energy
-Breaking covalent bonds between monomers; water molecule breaks the bond as the hydroxyl bonds to one monomer and hydrogen bonds to the other
-Investing water; releasing energy
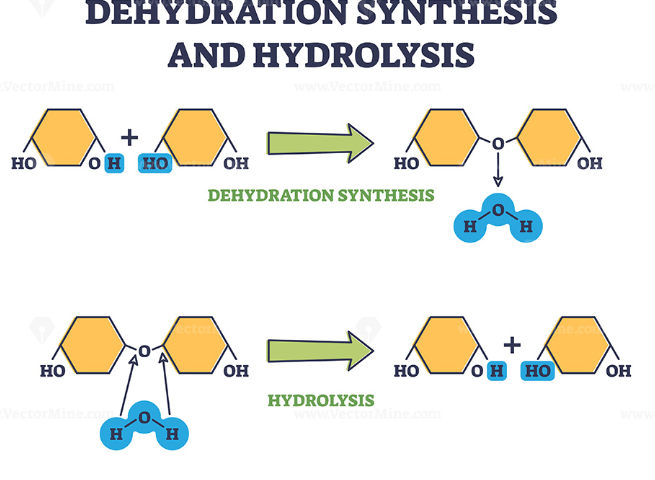
22
New cards
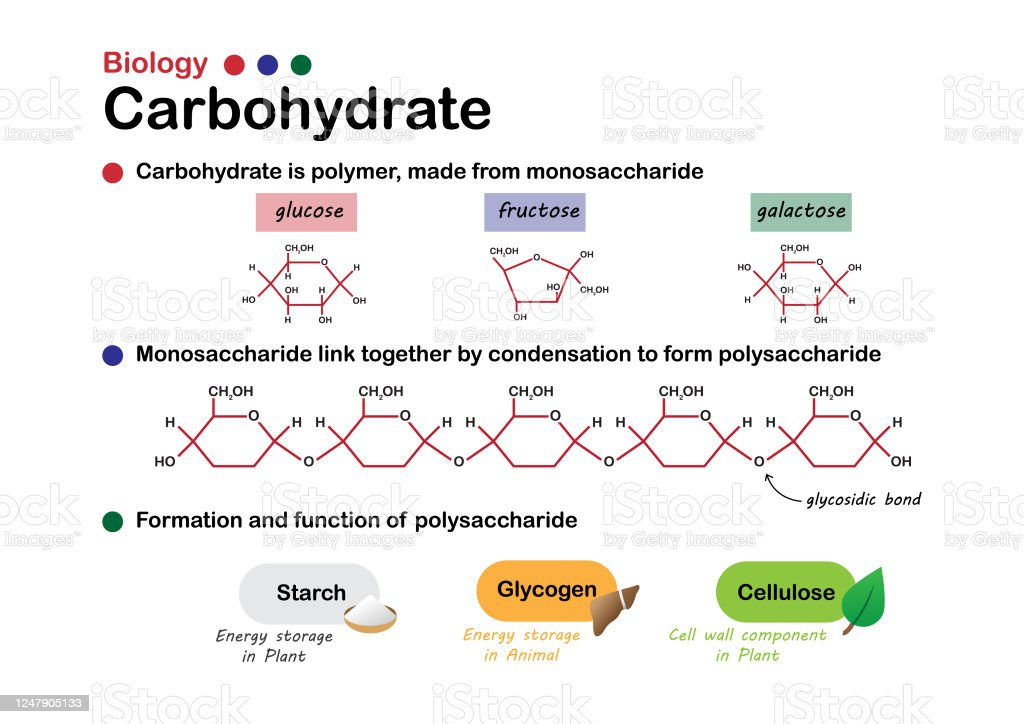
Carbohydrates
macromolecule including monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides; serve as fuel and building material
23
New cards
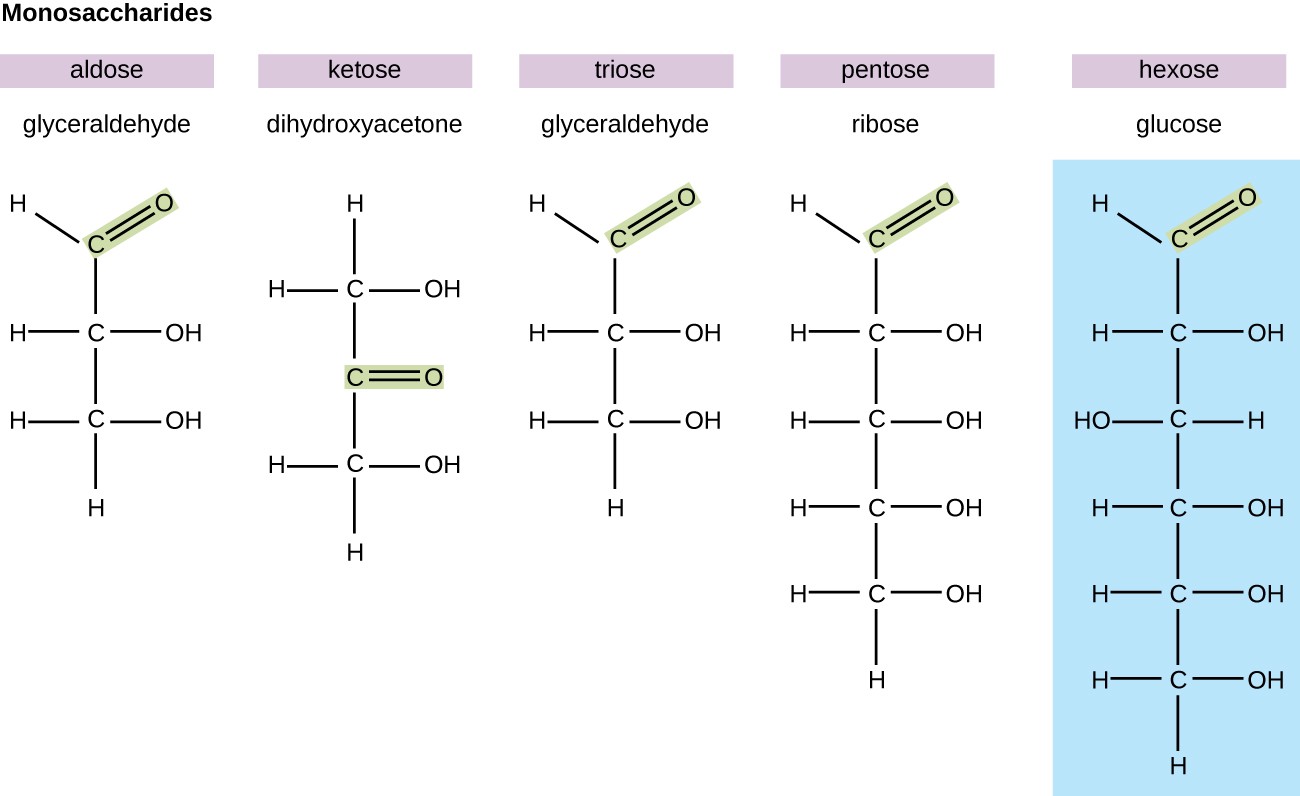
Monosaccharides
-monomers of carbohydrates (AKA simple sugars)
-contains 1 carbonyl groups and multiple hydroxyl groups
-forms rings in aqueous solutions
-Function: Energy, makes up Carbon Skeleton structure, and Make up polysaccharides
-Variation because of location of functional groups (aldose vs. ketose) and length of carbon skeleton (3-7)
-Ex. glucose and fructose
-contains 1 carbonyl groups and multiple hydroxyl groups
-forms rings in aqueous solutions
-Function: Energy, makes up Carbon Skeleton structure, and Make up polysaccharides
-Variation because of location of functional groups (aldose vs. ketose) and length of carbon skeleton (3-7)
-Ex. glucose and fructose
24
New cards
Monosaccharides formula

25
New cards
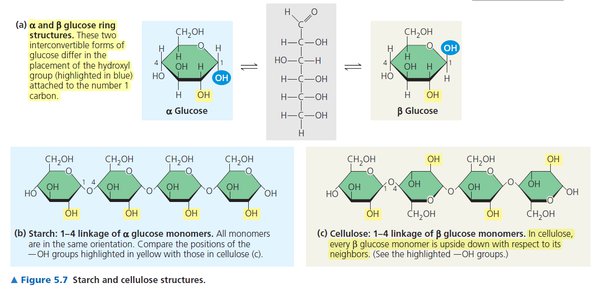
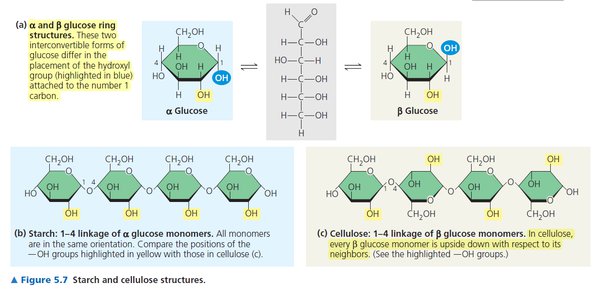
alpha glucose
glucose going in the same configuration
26
New cards
beta glucose
glucose switching directions because of a difference in the location of the hydroxyl group on Carbon 1
27
New cards
Disaccharides
-two monosaccharides bonded together through glycosidic linkages
-Ex: Lactose (Milk), Maltose (Beer), Sucrose (table sugar)
-Ex: Lactose (Milk), Maltose (Beer), Sucrose (table sugar)
28
New cards
glycosidic linkages
a covalent bond between 2 monosaccharides by dehydration reaction (# in name represents carbons being bonded)
29
New cards
Polysaccharides
-polymers of carbohydrates
-Storage Polysaccarides include starch and glycogen
-Structural Polysaccarides include cellulose and chitin
-Storage Polysaccarides include starch and glycogen
-Structural Polysaccarides include cellulose and chitin
30
New cards
Starch
-Storage polysaccharide for storing sugars in plants
-made up of Alpha glucose (same direction every time)
-Carbons 1-4 forming glycosidic linkages
-Helical structure
-made up of Alpha glucose (same direction every time)
-Carbons 1-4 forming glycosidic linkages
-Helical structure
31
New cards
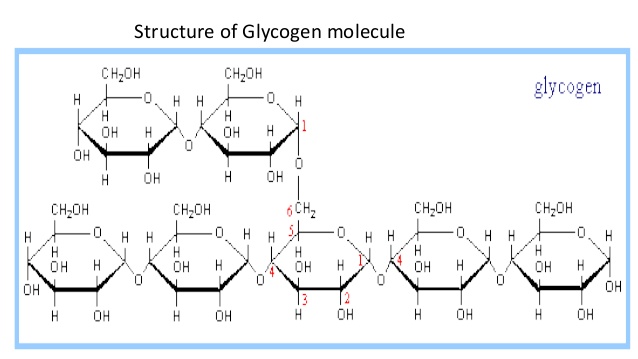
Glycogen
-Storage polysaccharide in animals; Can only last about a day; Stored in liver and muscles
-made up of Alpha glucose (same direction every time)
-Carbons 1-4 & 1-6 (when branching) forming glycosidic linkages
-Helical Branched structure
-made up of Alpha glucose (same direction every time)
-Carbons 1-4 & 1-6 (when branching) forming glycosidic linkages
-Helical Branched structure
32
New cards
cellulose
-Structural polysaccharide in plants
- makes up Cell wall of plant cells; Most abundant organic molecule on earth
-Carbons 1-4 form glycosidic linkages
-made up of Beta glucose (switching directions) because of a difference in the location of the hydroxyl group on Carbon 1
-Straight, allowing parallel molecules to bond with each other creating microfibrils
-Can’t be digested by humans (bc they can't break beta linkages) but it stimulates our digestive system through the stimulation of stomach lining which releases mucus (“fiber”)
-Symbioses in cow and termites: Both have microorganisms in their guts that can break down cellulose for them
- makes up Cell wall of plant cells; Most abundant organic molecule on earth
-Carbons 1-4 form glycosidic linkages
-made up of Beta glucose (switching directions) because of a difference in the location of the hydroxyl group on Carbon 1
-Straight, allowing parallel molecules to bond with each other creating microfibrils
-Can’t be digested by humans (bc they can't break beta linkages) but it stimulates our digestive system through the stimulation of stomach lining which releases mucus (“fiber”)
-Symbioses in cow and termites: Both have microorganisms in their guts that can break down cellulose for them
33
New cards
Chitin
-Structural polysaccaride in anthropods and fungi
-make up exoskeleton of anthropods and cell walls of fungi
-Contains nitrogen group which makes it a unique carbohydrate
-make up exoskeleton of anthropods and cell walls of fungi
-Contains nitrogen group which makes it a unique carbohydrate
34
New cards
Lipids
General characteristic all lipids have in common: Hydrophobic, because of nonpolar covalent bonds; Consist mostly of hydrocarbons
35
New cards
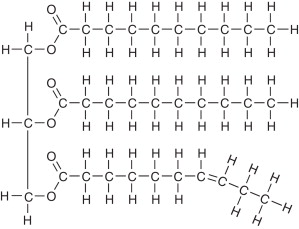
Triglyceride (fats)
-Made up of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
-held together by nonpolar covalent bonds
-An Ester bond formed through dehydration synthesis holds fatty acids to glycerol
-Function: Energy storage, also Cushions, Protects, Insulates
-held together by nonpolar covalent bonds
-An Ester bond formed through dehydration synthesis holds fatty acids to glycerol
-Function: Energy storage, also Cushions, Protects, Insulates
36
New cards
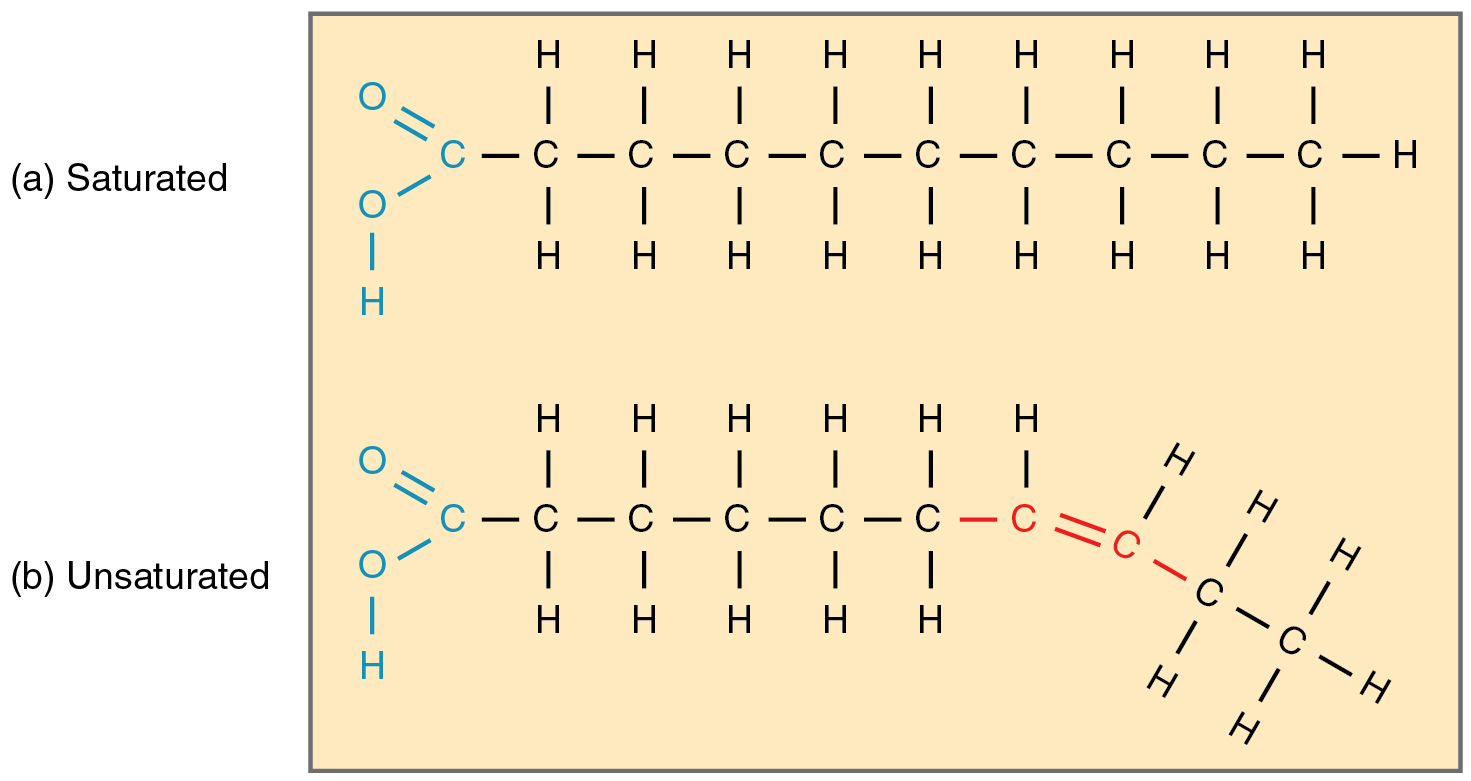
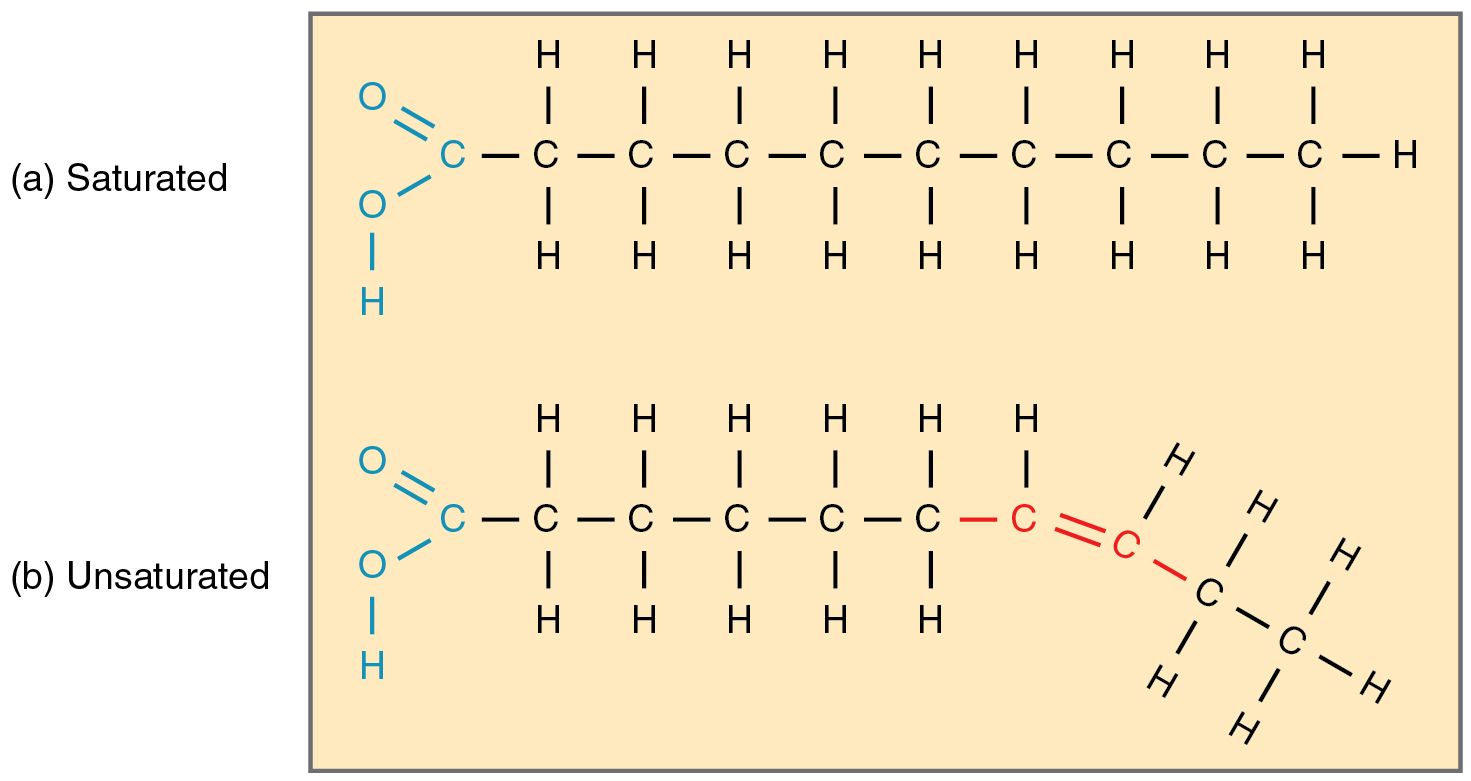
Saturated fats
-contains NO carbon double bonds in the fatty acids
-Straight; no kinks (double bonds)
-Solid at room temp
-Usually from an animal source
-Examples: butter, lard, coconut oil
-Straight; no kinks (double bonds)
-Solid at room temp
-Usually from an animal source
-Examples: butter, lard, coconut oil
37
New cards
Unsaturated fats
-1 or more double bonds between carbon
-Kinks/bends
-Liquid at room temp because of kinks (can't fit closely together)
-Usually a plant source
-Examples: Olive and canola oil
-Kinks/bends
-Liquid at room temp because of kinks (can't fit closely together)
-Usually a plant source
-Examples: Olive and canola oil
38
New cards
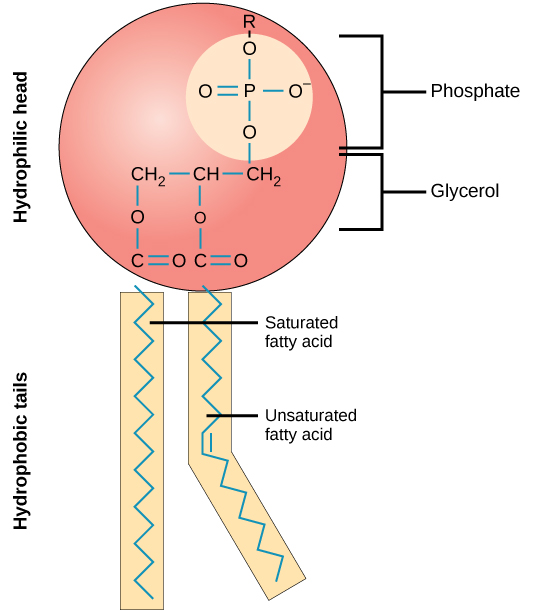
Phospholipids
-Amphipathic
- make up the Cell membrane/phospholipid bilayer
-made up of 2 Fatty Acids, 1 Glycerol, 1 Phosphate head
-Phosphate group: hydrophilic because it has a charge
-Fatty acid tails: hydrophobic because it has no charge
- make up the Cell membrane/phospholipid bilayer
-made up of 2 Fatty Acids, 1 Glycerol, 1 Phosphate head
-Phosphate group: hydrophilic because it has a charge
-Fatty acid tails: hydrophobic because it has no charge
39
New cards
Amphipathic
molecule that has hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
40
New cards
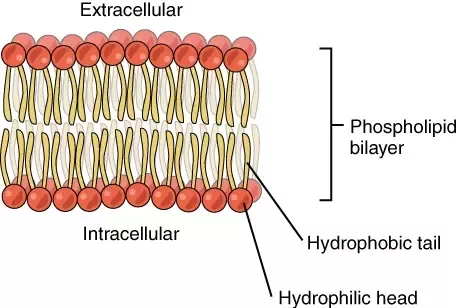
Explain how phospholipids form a bilayer in aqueous solutions.
The phosphate group will interact with the water because it is polar and so is water, and the nonpolar fatty acid tails will flip inwards. This creates a sandwich of phosphate groups on the outside and fatty acid tails on the inside.
41
New cards
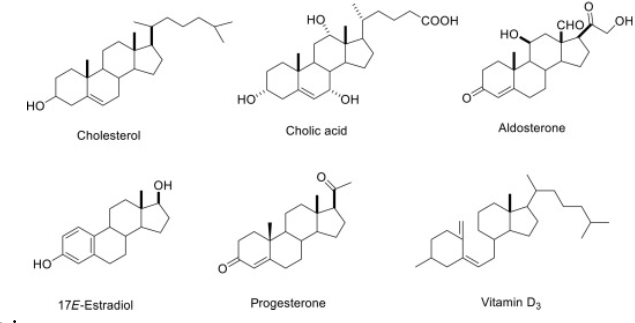
Steroids
-Carbon skeleton consisting of 4 fused rings
-Functional groups attached to rings create variation between steroids
-Ex: Cholesterol, Testerone and Estrogen (steroid hormones)
-Functional groups attached to rings create variation between steroids
-Ex: Cholesterol, Testerone and Estrogen (steroid hormones)
42
New cards
Cholesterol
-Crucial steroid to animals
-In vertebrates, synthesized in liver and obtained from diet
-Maintain integrity of cell membrane, precursor from which other steroids are synthesized
-In vertebrates, synthesized in liver and obtained from diet
-Maintain integrity of cell membrane, precursor from which other steroids are synthesized
43
New cards
Protein
biologically functional molecule that consists of one or more polypeptides folded and coiled in a 3D structure
44
New cards
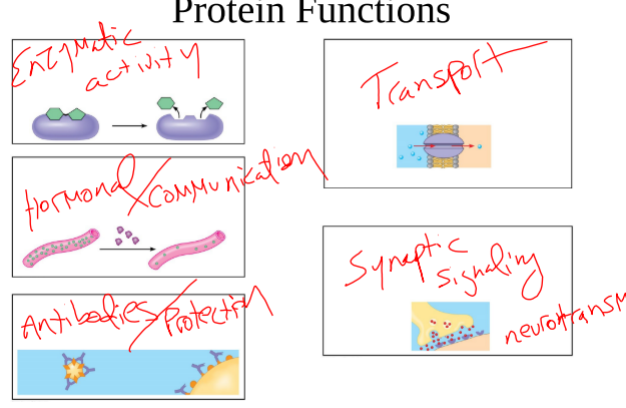
Functions of Proteins
-Enzymatic Activity
-Communication of organisms activity (hormones)
-Antibodies/Protection
-Transport proteins (Transporting chemicals across the cell membrane)
-Synaptic Signaling (Neurotransmitters)
-Communication of organisms activity (hormones)
-Antibodies/Protection
-Transport proteins (Transporting chemicals across the cell membrane)
-Synaptic Signaling (Neurotransmitters)
45
New cards
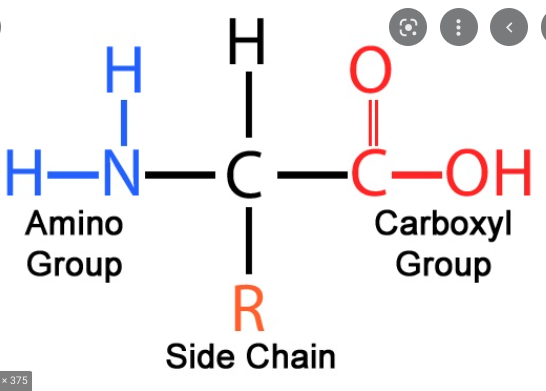
Amino Acids
-Monomers of Proteins
-Has a carboxyl group, amino group, R-group, and hydrogen bonded to a central carbon
-20 different amino acids
-Has a carboxyl group, amino group, R-group, and hydrogen bonded to a central carbon
-20 different amino acids
46
New cards
R-groups
give amino acids their unique properties that influence shape of protein
47
New cards
Peptide Bond
an Amino acid bond between a carboxyl and amino group via dehydration reaction; forms polypeptides
48
New cards
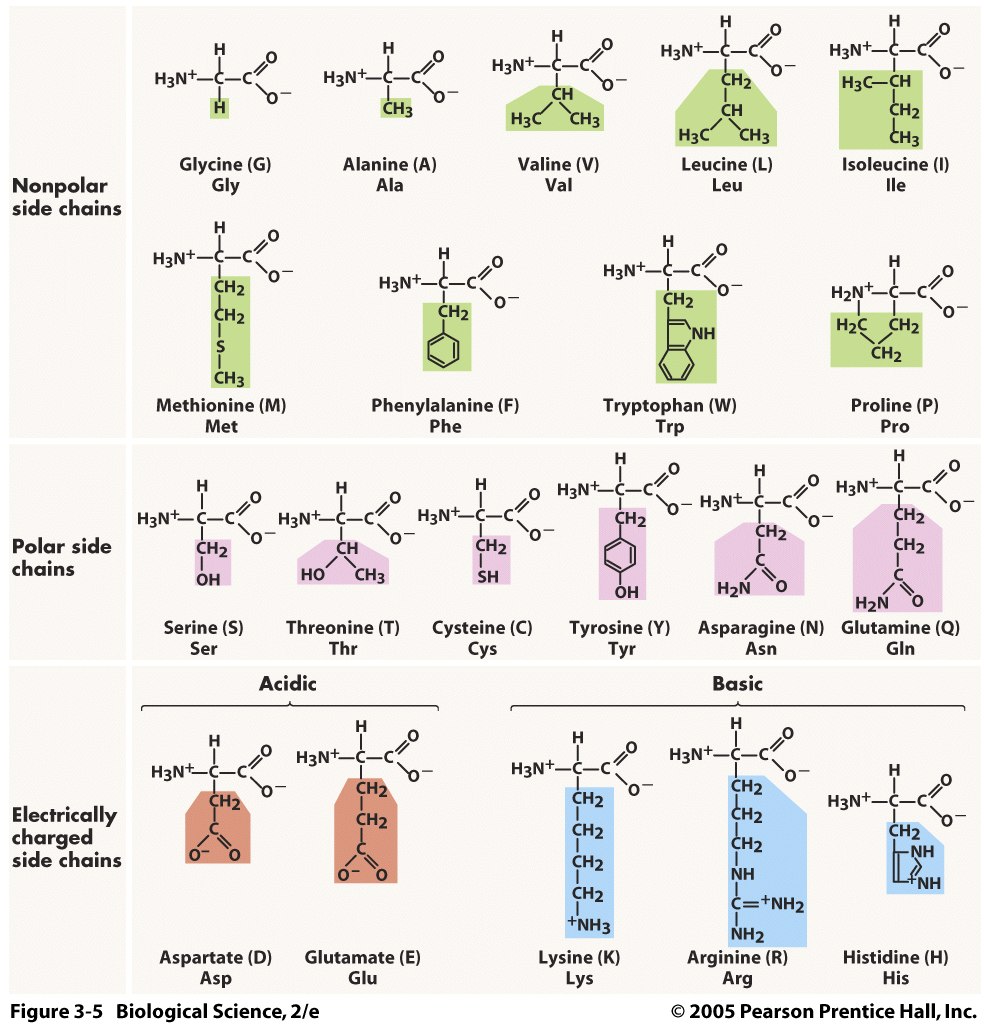
Groups of amino acids and defining elements/characteristics
1. Nonpolar R-groups (hydrophobic): contain hydrogen and carbon
2. Polar R-groups (hydrophilic): contain nitrogen and oxygen
3. Electrically Charged R-groups (hydrophilic): have a charge
- contains acidic (negatively charged) and basic (positively charged)
2. Polar R-groups (hydrophilic): contain nitrogen and oxygen
3. Electrically Charged R-groups (hydrophilic): have a charge
- contains acidic (negatively charged) and basic (positively charged)
49
New cards
Make a connection between the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide and
the resulting function of the protein.
the resulting function of the protein.
Each specific polypeptide has a unique linear sequence of amino acids, which means they also have unique side chains. The chemical nature depends on the kind and sequence of side chains, which in turn would impact the resulting function/shape of the protein.
50
New cards
Briefly describe two examples illustrating the importance of a protein's shape
in its ability to perform its function.
in its ability to perform its function.
1. The exact shape between an antibody and a particular foreign substance on a flu virus that the antibody binds to and marks for destruction
2. Endorphin molecules or morphine molecules that fit into receptor molecules on the surface of brain cell in humans
-Producing euphoria and relieving pain
2. Endorphin molecules or morphine molecules that fit into receptor molecules on the surface of brain cell in humans
-Producing euphoria and relieving pain
51
New cards
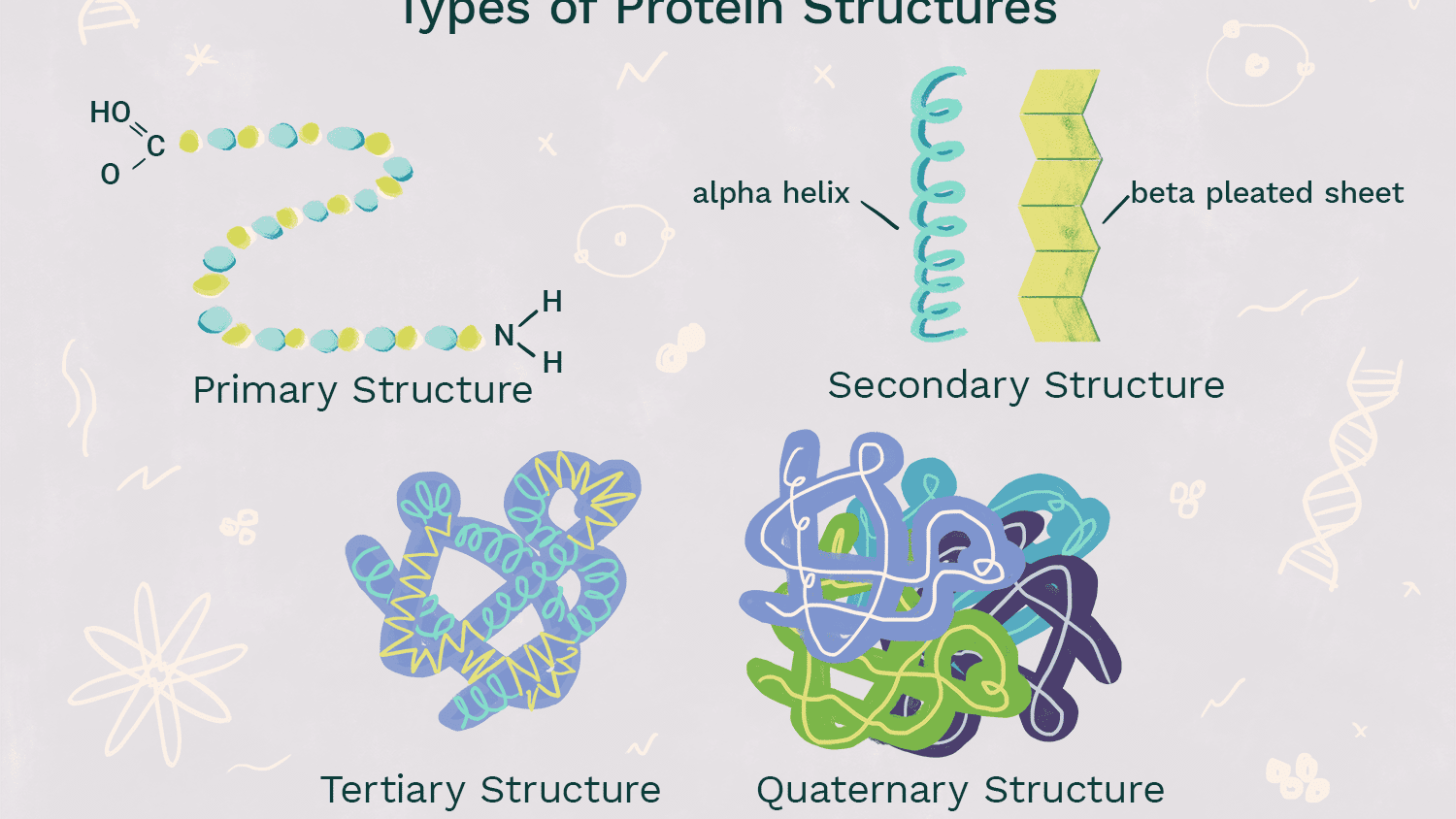
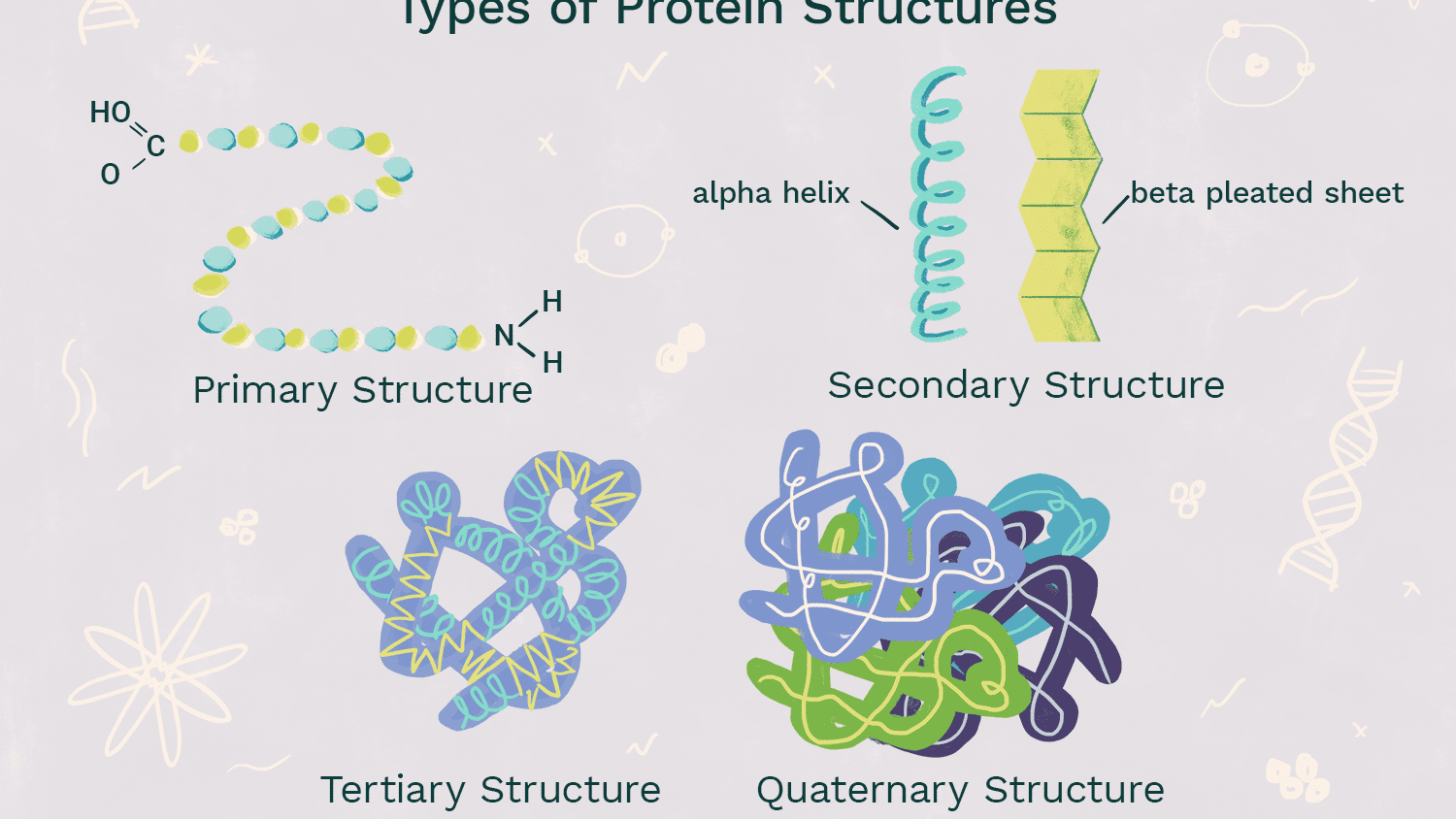
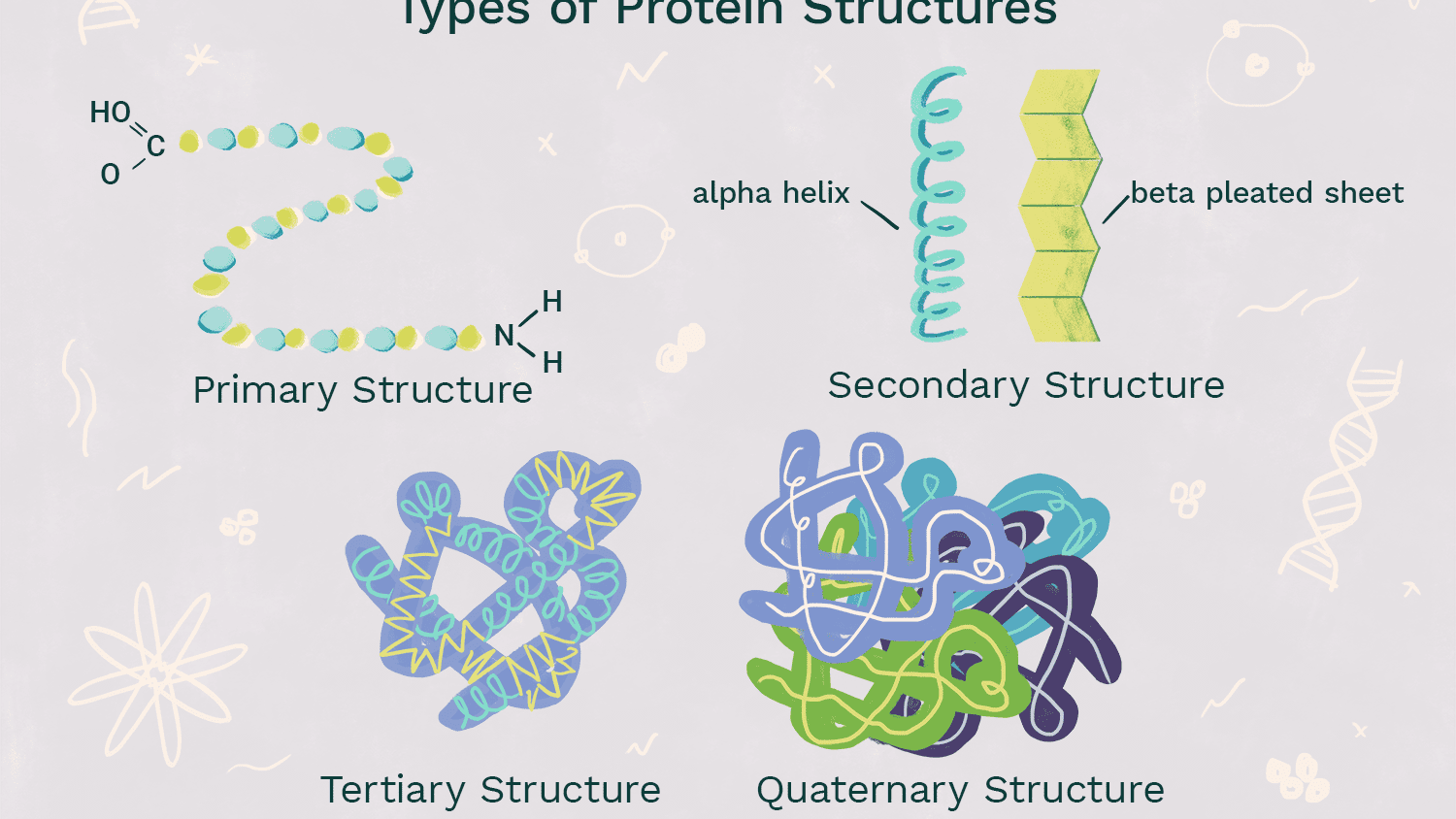
Primary level of Protein structure (structure and bonds)
-Sequence of amino acids
-Determined by genetic information (DNA)
-amino acids are held together by peptide bonds between the amino group of one amino acid and carboxyl group of another
-Determined by genetic information (DNA)
-amino acids are held together by peptide bonds between the amino group of one amino acid and carboxyl group of another
52
New cards
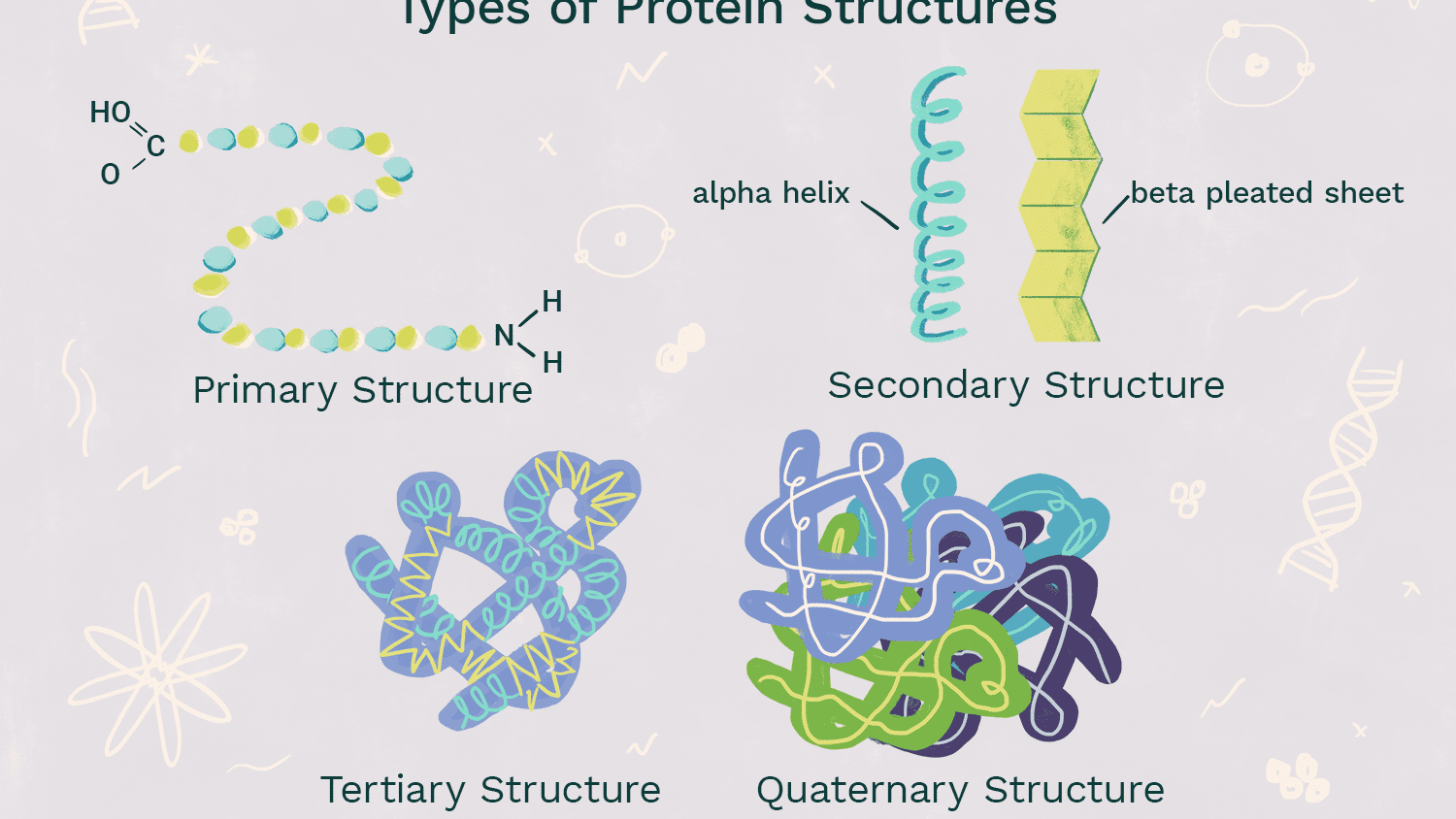
Secondary Level of Protein Structure (structure and bonds)
-coils and folds that are patterned in protein
-result from Hydrogen bonding of the peptide backbone causing the amino acids to bend into repeating patterns (oxygen has partial negative, and hydrogen attached to nitrogen have a partial positive, so weak hydrogen bonds from that strengthen and shape protein)
-Alpha Helix: Polypeptide coils into a helix shape because of hydrogen bonding between every 4th amino acid
-Beta Pleated Sheet: 2 or more segments of the polypeptide bend sharply and lie parallel to each other, hydrogen bonds form between parts of these segments
-result from Hydrogen bonding of the peptide backbone causing the amino acids to bend into repeating patterns (oxygen has partial negative, and hydrogen attached to nitrogen have a partial positive, so weak hydrogen bonds from that strengthen and shape protein)
-Alpha Helix: Polypeptide coils into a helix shape because of hydrogen bonding between every 4th amino acid
-Beta Pleated Sheet: 2 or more segments of the polypeptide bend sharply and lie parallel to each other, hydrogen bonds form between parts of these segments
53
New cards
Tertiary level of Protein structure (structure and bonds)
-Overall shape of a polypeptide resulting from the interactions between the R-groups of multiple amino acids
-Hydrogen bonds: between 2 polar R-groups
-Ionic Bonds: positively charged + negatively charged R-groups
-Hydrophobic interactions/Van der Waals bonds: nonpolar amino acids concentrate at the center of the protein due to hydrophobic tendencies and form very weak Van der Waals bonds
-Disulfide bridge: covalent bonds between the sulfhydryls of 2 cysteine AAs
-Hydrogen bonds: between 2 polar R-groups
-Ionic Bonds: positively charged + negatively charged R-groups
-Hydrophobic interactions/Van der Waals bonds: nonpolar amino acids concentrate at the center of the protein due to hydrophobic tendencies and form very weak Van der Waals bonds
-Disulfide bridge: covalent bonds between the sulfhydryls of 2 cysteine AAs
54
New cards
Quaternary Level of Protein Structure (structure and bonds)
-Overall protein structure that results from the aggregation of 2 or more polypeptide chains
-same types of interactions that hold together tertiary structure contribute to quatenary
-globular proteins: roughly spherical shaped; usually hormone or enzyme; ex. hemoglobin
-fibrous proteins: straight, structural, woven; ex. collagen
-same types of interactions that hold together tertiary structure contribute to quatenary
-globular proteins: roughly spherical shaped; usually hormone or enzyme; ex. hemoglobin
-fibrous proteins: straight, structural, woven; ex. collagen
55
New cards
Sickle Cell Disease
-Inherited blood disorder caused by the sub of one amino acid for the normal once at a particular position in the primary structure of hemoglobin (valine for glutamic acid)
-The abnormal hemoglobin tends to crystallize, deforming some cells into sickle shapes; normal RBC are disk shaped
-Clog tiny blood vessels, impeding blood flow and not carrying oxygen
-The abnormal hemoglobin tends to crystallize, deforming some cells into sickle shapes; normal RBC are disk shaped
-Clog tiny blood vessels, impeding blood flow and not carrying oxygen
56
New cards
Denaturation
-when protein loses its shape
-pH, salt concentration, temperature, or other environmental factors are altered, weak chemical bonds in protein may be destroyed (on every level but primary level)
-can go back because it still has primary structure
-pH, salt concentration, temperature, or other environmental factors are altered, weak chemical bonds in protein may be destroyed (on every level but primary level)
-can go back because it still has primary structure
57
New cards
Chaparonins
Multi-protein complex that protects the polypeptide from environmental influences that may affect its folding
58
New cards
Nucleic Acid
polymers made up of monomers called nucleotides
59
New cards
2 types of Nucleic Acids
RNA and DNA
60
New cards
What two functions make DNA unique among molecules?
Provides directions for its own replication and directs RNA synthesis and through RNA, controls protein synthesis
61
New cards
What is the flow of genetic information in a cell?
-Synthesis of mRNA in the nucleus (transcription)
-Movement of mRNA into cytoplasm via nuclea pore which is part of nuclear envelope
-Synthesis of protein using information carried on mRNA (translation)
-Movement of mRNA into cytoplasm via nuclea pore which is part of nuclear envelope
-Synthesis of protein using information carried on mRNA (translation)
62
New cards
three components of a nucleotide
Nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and 1 or more phosphate groups
63
New cards
Two families of nitrogenous bases
-Pyrimidines: 1 ring; Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and Uracil (U)
-Purines: 2 rings; Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
-Purines: 2 rings; Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
64
New cards
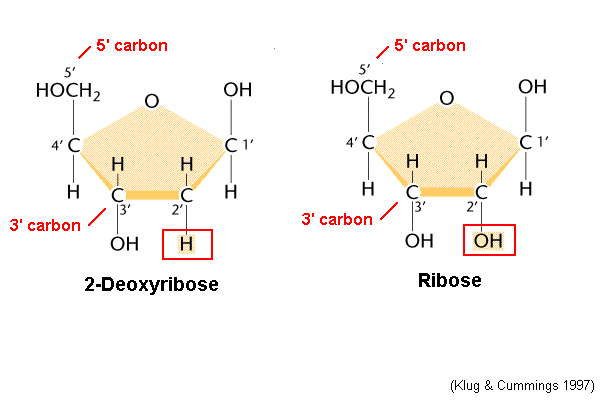
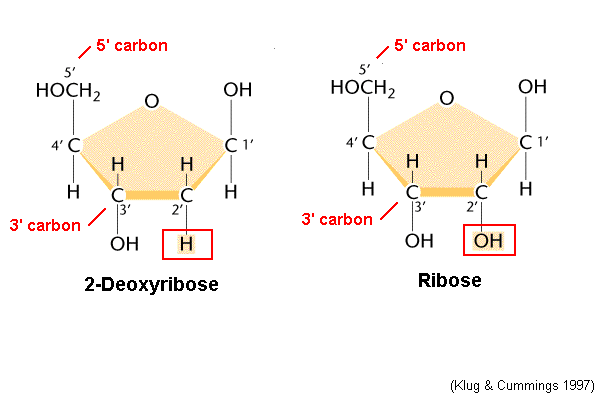
DNA (bases, sugars, strandedness, genes)
ATGC; Deoxyribose sugar; 2 strands; 100s of thousands of genes
65
New cards
RNA (bases, sugars, strandedness, genes)
AUGC; Ribose Sugar; 1 strand; 1 gene
66
New cards
What is the specific name for the bonds holding the nucleotides in a single strand together?
Phosphodiester Bonds
67
New cards
What makes up the backbone of a polynucleotide?
Pentose Sugar and Phosphate group
68
New cards
Which end of a strand is the 5’ end and which is the 3’ end?
-5’ is the end that is connected to the 5th carbon on the sugar
-3’ is the end that is the 3rd carbon on the sugar that is not connected to anything
-3’ is the end that is the 3rd carbon on the sugar that is not connected to anything
69
New cards
What is the overall shape of a DNA molecule?
Double Helix
70
New cards
When describing the two strands of DNA, what does the term antiparallel mean?
The two strands of DNA run in different directions
71
New cards
What bases are complementary between DNA & RNA?