Rock Transformations
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
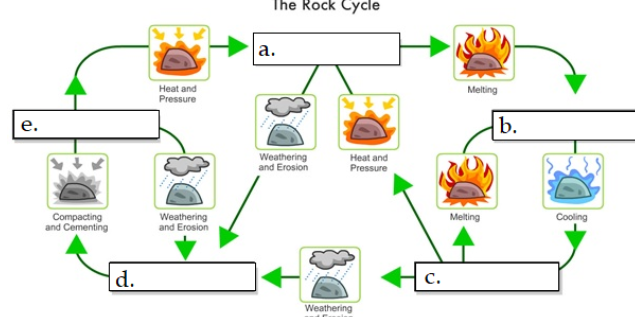
what is A
metamorphic
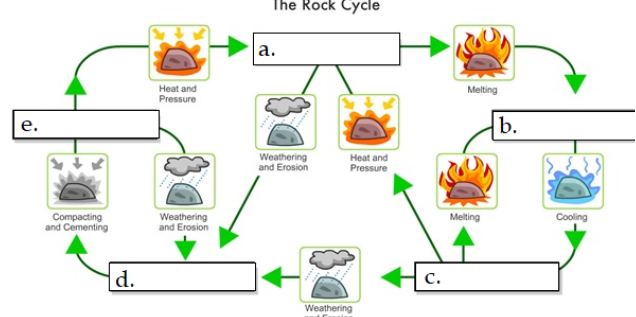
what is B
Magma
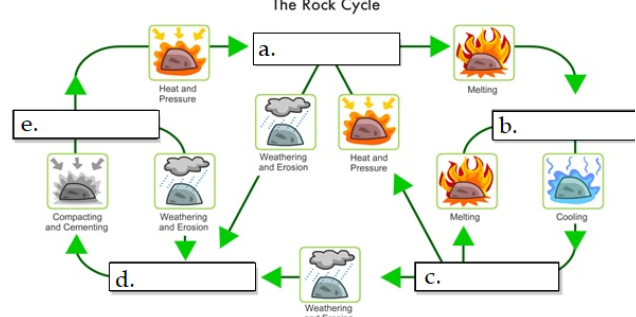
what is C
igneous rock
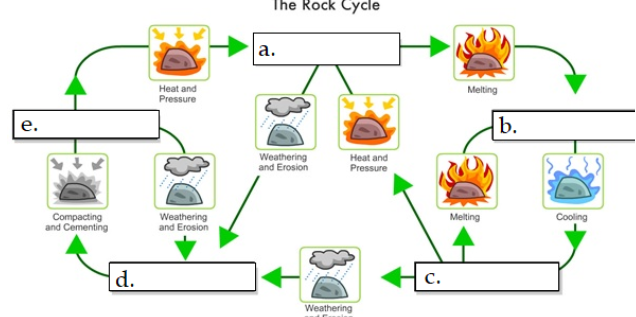
what is D
sediment
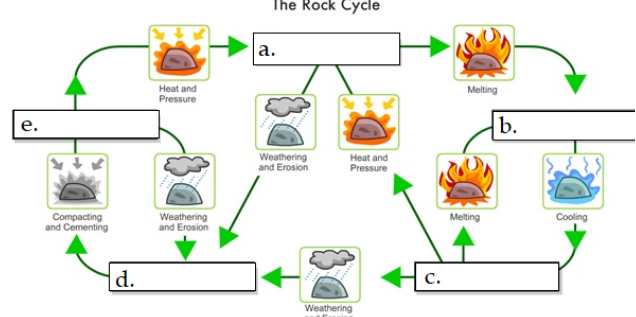
what is E
sedimentary rock
What do we call rocks that form from cooling magma?
igneous rock
Which process leads to the formation of sedimentary rocks?
compaction and cementation
What is required for a rock to become metamorphic?
heat and pressure
Which type of rock might contain fossils?
sedimentary rock
if you find a rock with layers of sand and tiny pebbles, it is most likely
sedimentary rock
what is it called when magma cools underground
intrusive
what is it called when magma cools outside
extrusive
the way sedimentary rock forms
compaction and cementation
what does metamorphic rock cause
recrystallization or banding
what is the crystal size of extrusive igneous rock
small/none
what is the crystal size of intrusive igneous rock
big
Rocks break into smaller pieces
weathering
Sediments are moved by water, wind, or ice
erosion
Sediments settle in new locations
deposition
Sediments turn into sedimentary rock
compaction and cementation
Existing rock becomes metamorphic
metamorphism
Rock turns into magma
melting
Magma/lava solidifies into igneous rock
cooling
what powers weathering, erosion, deposition
the sun
what powers melting, pressure, and metamorphism
the earth’s interior
what powers sediment layering
gravity
Volcanic eruptions → extrusive rock
fast process
Landslides → quick movement and redeposition of sediment
fast process
Earthquakes → rapid changes in landscape
fast process
Weathering and erosion over long periods
slow process
Mountain building through plate collisions
slow process
intrusive rock forming underground
slow process
Formation of sedimentary layers
slow process
Which type of rock forms from heat and pressure?
metamorphic
Large crystals in an igneous rock indicate
slow cooling
Fossils are MOST likely found in
sedimentary rock