anaphy lab midterm quizz
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
special sense
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
produces aqueous humor
ciliary body
structures that are part of vascular tunic
choroid
contains photoreceptor
retina
controls the size of the pupil
iris
drains aqueous humor from the anterior chamber
scleral venous sinus
structures that are part of the fibrous tunic
sclera
most anterior part of the eyeball
cornea
anterior boundary of retina
ora serrata
attaches lens to ciliary bodu
suspensory ligaments
changes shape t focus llight on retina
lens
location of aqueous humor
anterior chamber
white though outer layer of the eye ball
sclera
auditory ossicle attached to the tympanic membrane
(middle ear)
malleus
equalizes air pressure in the middle ear with external air pressure
auditory tube
external ear structures
auricle,external,auditory canal,helix,lobule
ear drum
tympanic membrane
external feature of ear that contains the helix and lobule
auricle
stapes is attached to this membrane covered opening
oval window
middle auditory ossicle
incus
small bones of middle ear that are connected by synovial joints
mallus,incus,stapes
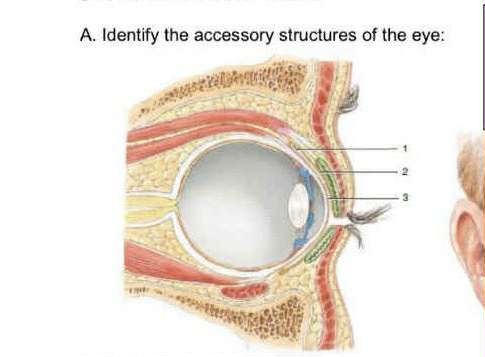
Conjunctival fold
Palpebral conjunctiva
Bulbar conjunctiva
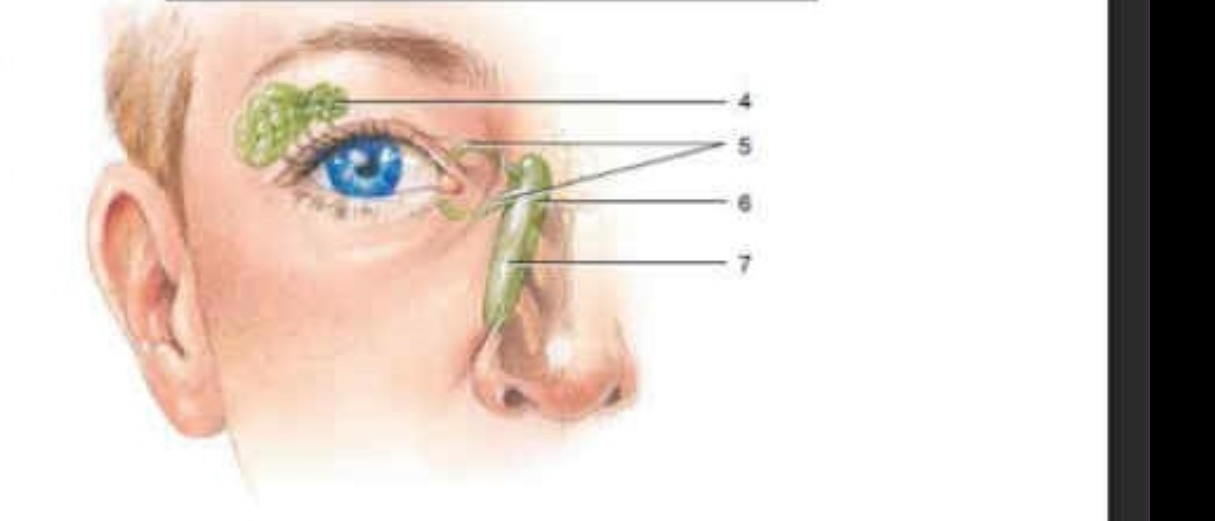
Lacrimal gland
Lacrimal canal
Lacrimal sac
Nasolacrimal duct
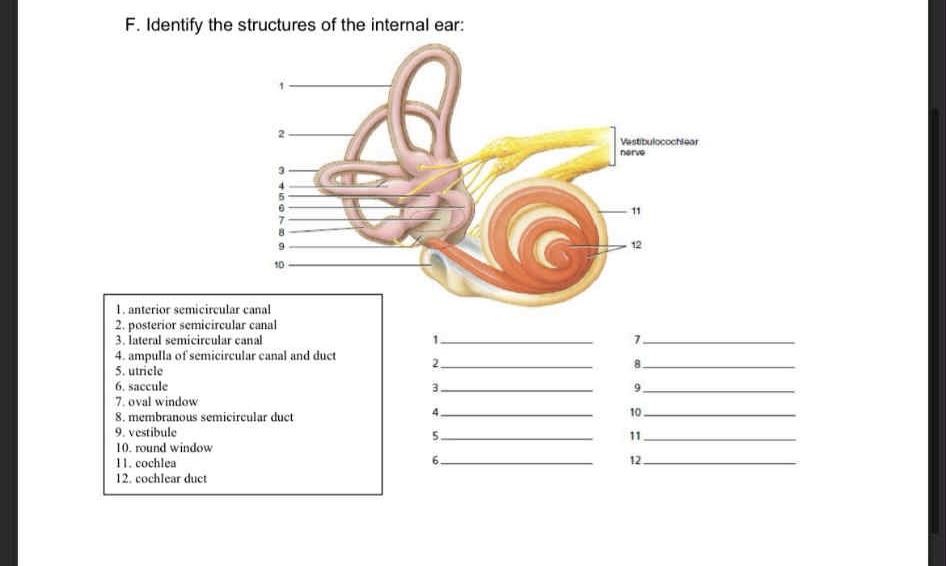
1-5
Anterior semicircular canal
Posterior semicircular canal
Lateral semicircular canal
ampulla of semicircular canal and duct
utricle
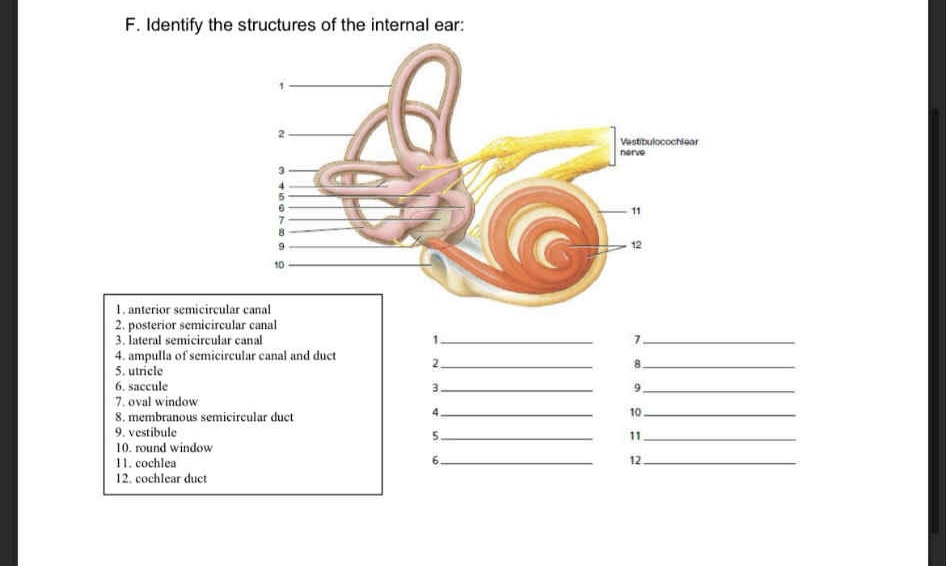
6-12
Saccule
Oval window
membranous semiciruclar duct
Vestibule
Round window
Cochlea
Cochlear duct
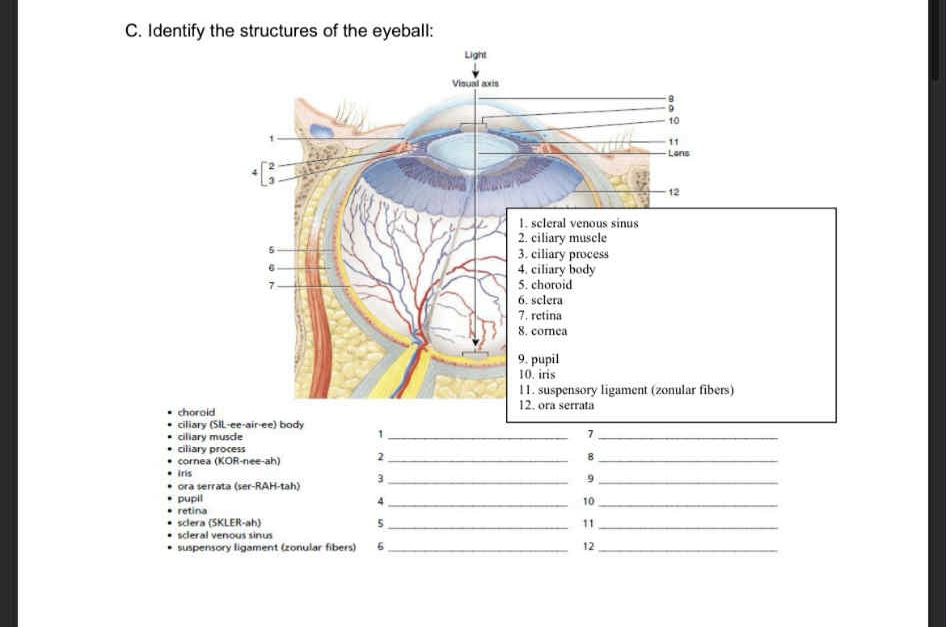
1-6
Scleral venous sinus
Ciliary muscle
Ciliary process
Ciliary body
Choroid
Sclera
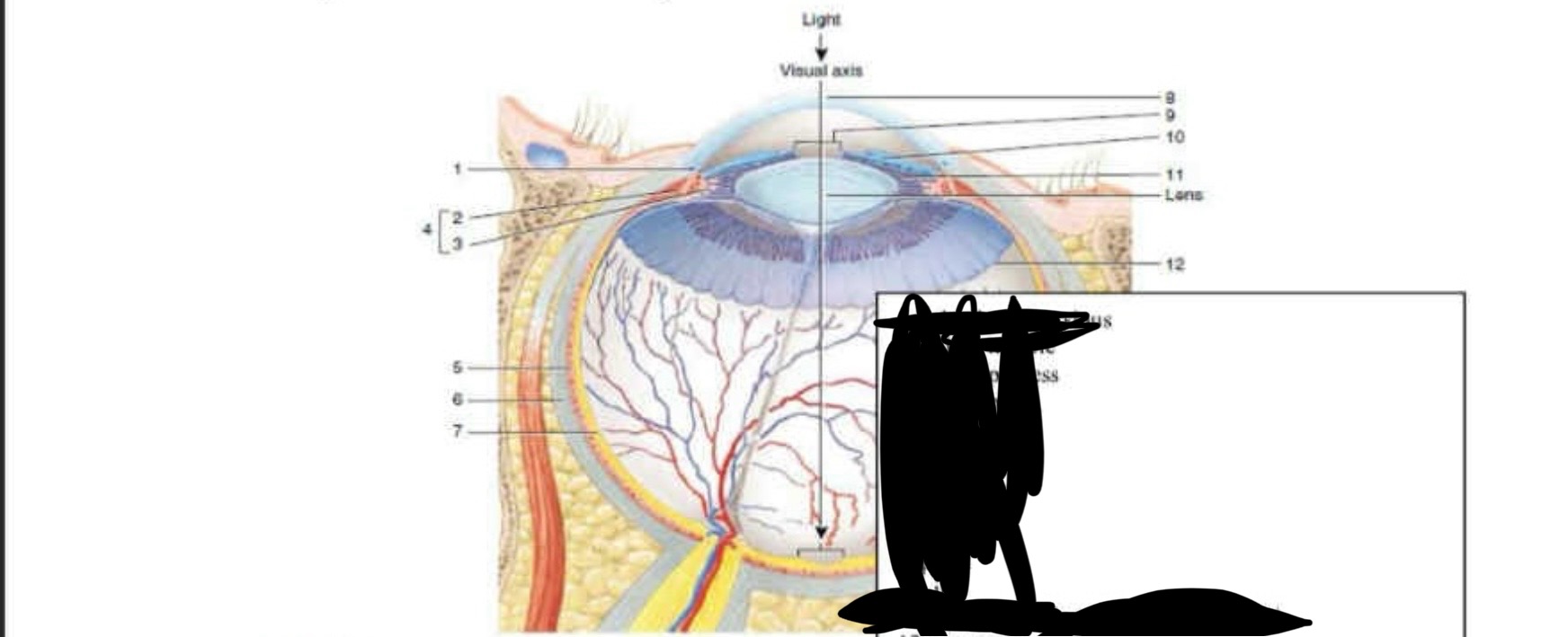
7-12
retina
cornea
pupil
iris
supensory ligament
ora serrata
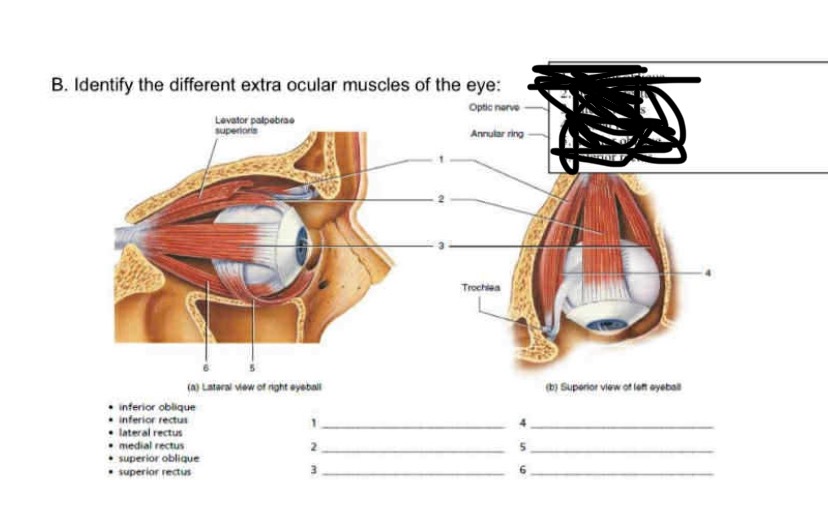
1-6
1.superior oblique
superior rectus
lateral rectus
medial rectus
inferior oblique
inferior rectus
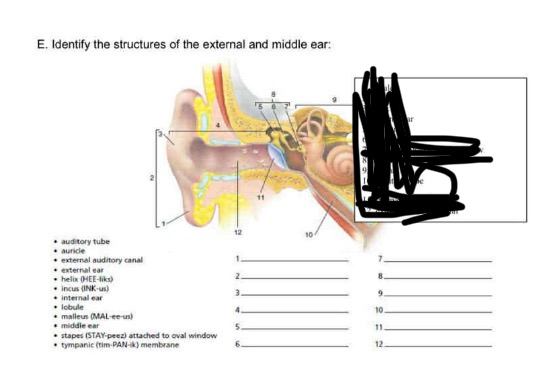
1-7
lobule
auricle
helix
external ear
malleus
incus
stape attached to the oval window
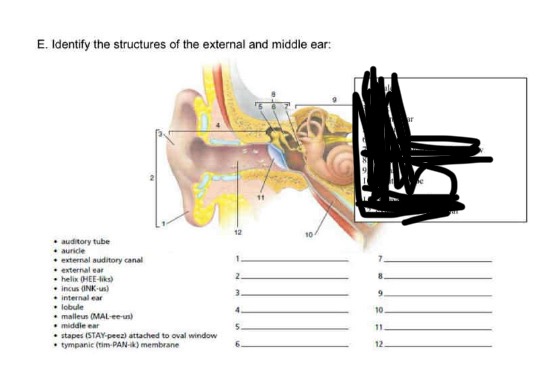
8-12
middle ear
internal ear
auditory tube
tympanic membrane
external auditory canal
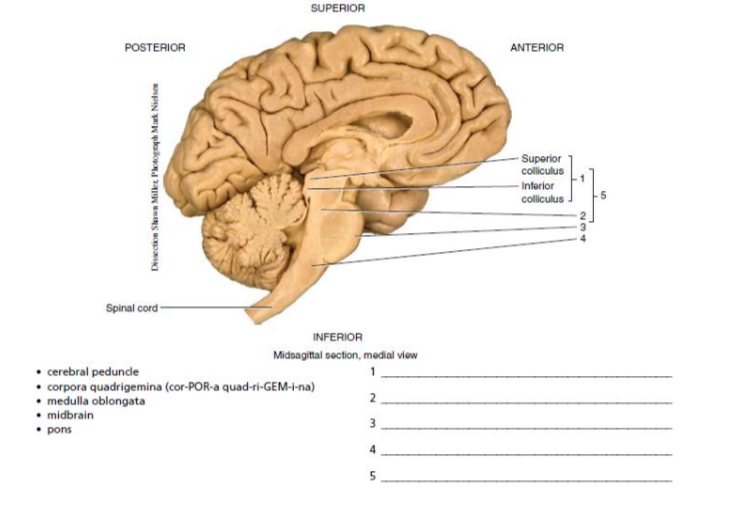
1-5
carpara quadrigemia
cerberal peduncle
pons
medulla oblongata
midbrain
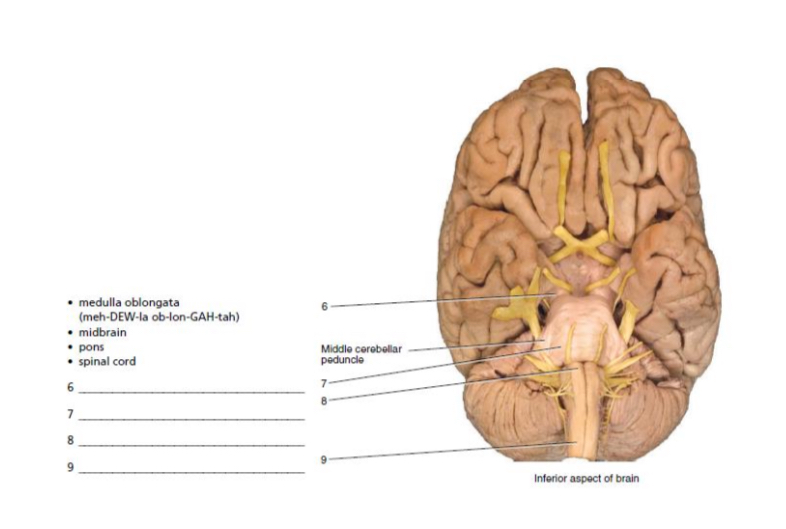
6-9
midbrain
pons
medulla oblongata
spinal cord
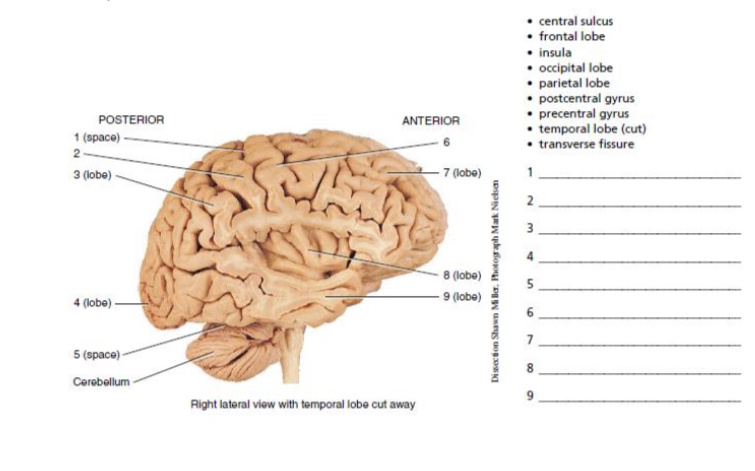
1-5
central sulcus
postcentral gyrus
parietal lobe
occipital lobe
transverse fissure
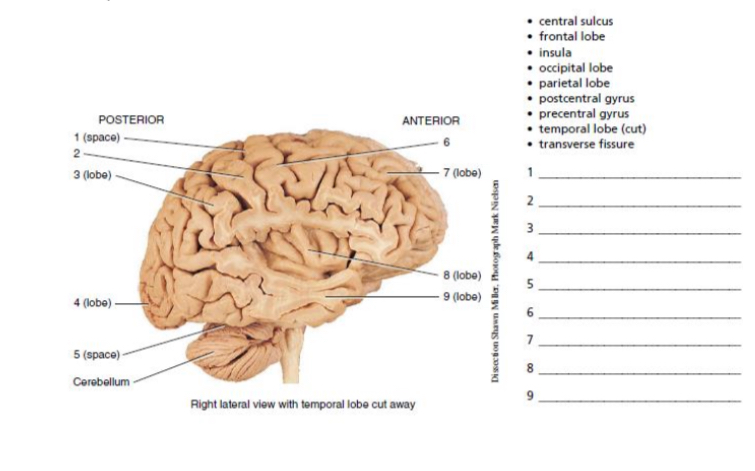
6-9
precental gyrus
frontal lobe
insula
temporal lobe
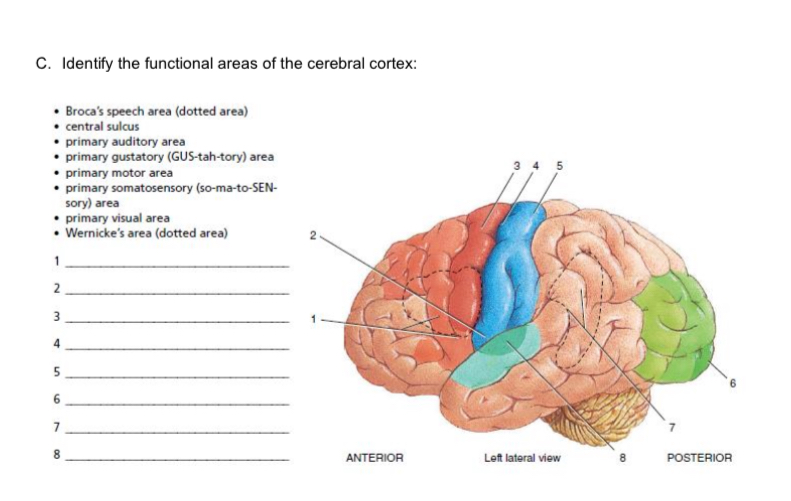
1-4
broca’s speech area
primary gustatory area
primary motor area
central sulcus
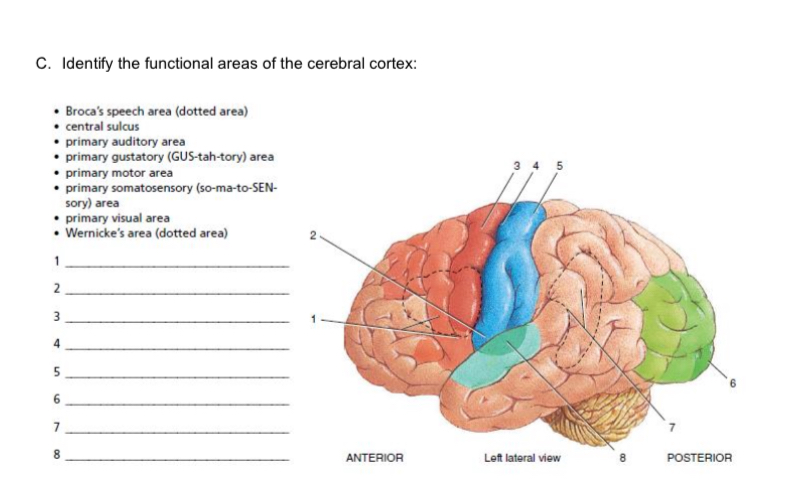
5-8
primary somatosensory area
primary visual area
wernicke’s area
primary auditory area
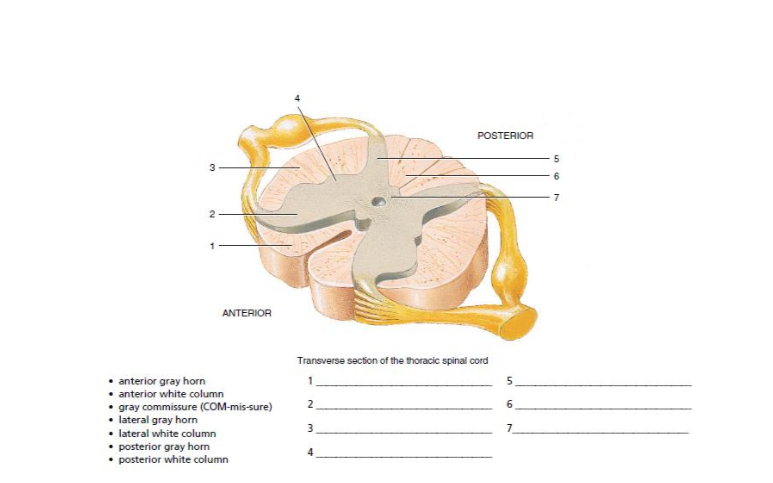
1-4
anterior white column
anterior gray horn
lateral white column
lateral gray horn
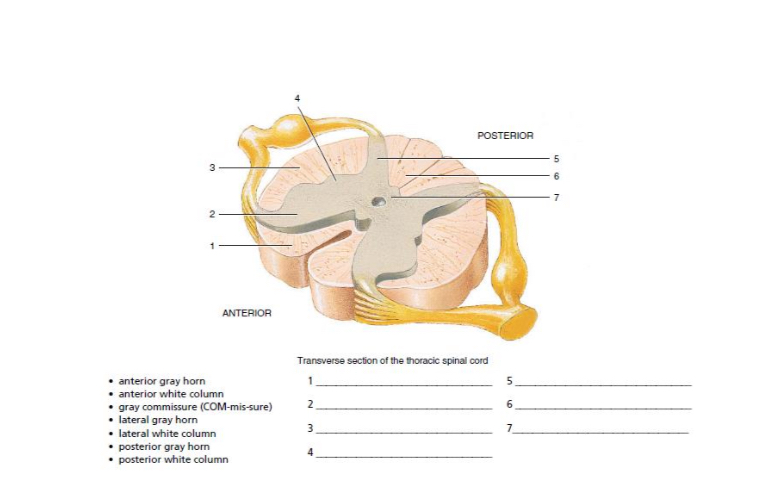
5-7
posterior gray horn
posterior white column
gray commisure
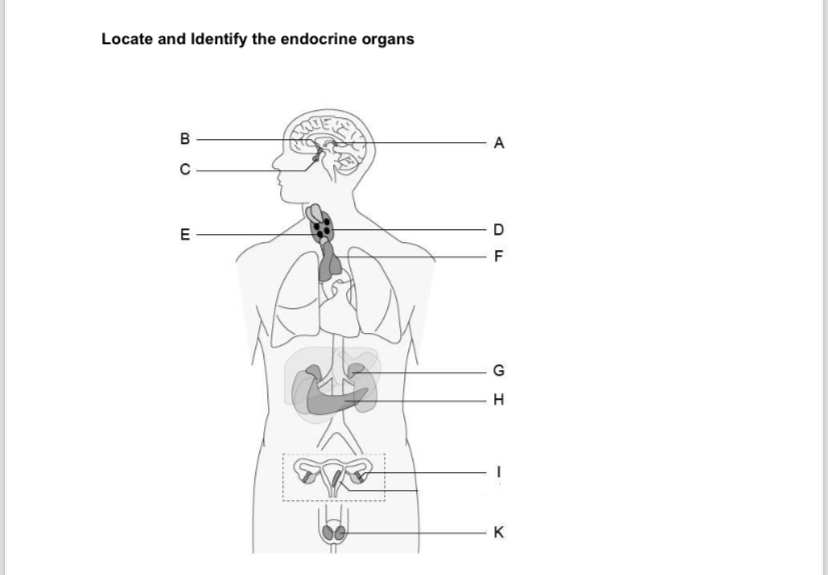
A-E
A. pineal
B. Hypothalamus
C. Pituitary gland
D. Thyroid gland
E. Parathyroid gland
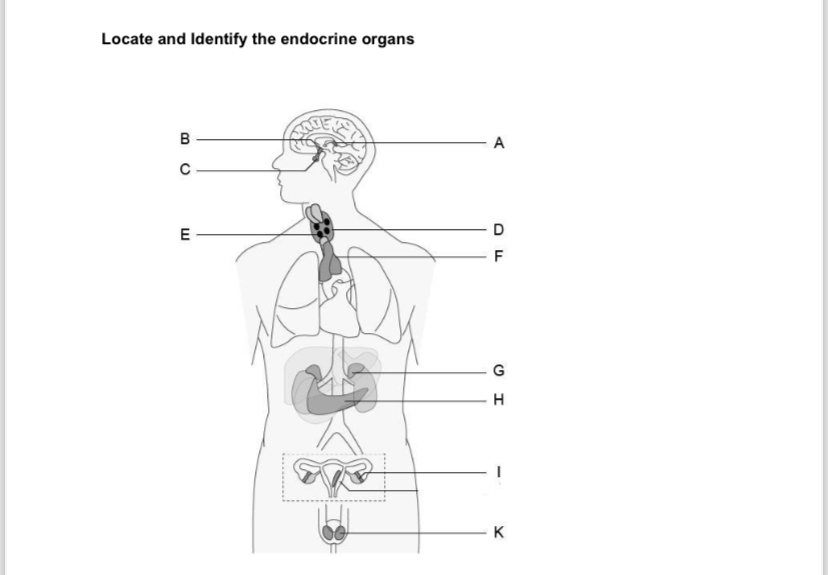
F-K
F. Thymus
G. Adrenal Gland
H. Pancreas
I. Ovary
K. Testes
Abnormal increase in the number of WBC
Leukocytosis
Abrnomal increase in the number of RBC
Polycythemia
Condition of too few RBCs or of RBCS with hemoglobin deficiencies
Anemia
Abnormal decrease in WBC
Leukopenia
Abrnomal decrease in the number of platelets
Thrombocytopenia
Abrnomal increase in the number of platelets
Thrombocytosis
what determined wether blood is bright red or a dull brick red
degree of oxygenation
describe the consistency and color of the plasma
sticky, yellowish
Fourn classes found in the plasma
Glucose
Amino acids
Lipids
Vitamins
List two gasses found in the plasma
Carbon dioxide
Oxygen
three electrolytes found in the plasma
Sodium
Potassium
Calcium
red coarse cytoplasmic granules
1-4% wbc
Eosinophils
Pale pink cytoplasm
50-70 %
neutrophils
small cell with pale blue cytoplasm
20-45% wbc
Lymphocytes
sparse dark blue cytoplasmjc granules
0-1%
Basophils
abundant gray blue cytoplasm
8% of WBC
Monocytes