The Challenge of Resource Management
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
resources
things that people use. one are essential for surviving and others are not.
average person consumes…
between 2000 and 2500 calories (dependant on sex, age, height, activity level)
What factors does the amount of calories we need depend on?
Sex
Age
Height
Level of activity
how does not eating enough affect the workforce?
eating too few calories can cause you to feel unenergised, which may make it difficult for you to work. this negatively affects the economy/wealth of the country.
how does eating too much affect the workforce?
can lead to obesity, making it more difficult to work and move around.
how much of a person’s body is made up of water?
two thirds
why does our body need water?
to absorb nutrients and get rid of waste.
How much person should each person drink?
Between 1.6 and 2 litres of water a day
What factors does the volume of water we drink depend on?
Air temperature
Type of activity undertaken
what are other uses for water besides drinking?
irrigation
keeping ourselves clean
cleaning areas
cooling
as a raw material in production
uses of energy
heat homes and offices
to cook food
powers transport
most of these come from secondary energy sources
Most of the energy that we use is in the form of __________. This is called ____________ energy.
electricity
secondary
primary energy
energy in its raw, unchanged state, eg. oil and wind power
secondary energy
energy that has been converted into a more useful form, eg. electricity. derived from primary sources,
how does the use of electricity affect food supplies and industry?
Mining and growing biofuels takes up valuable farmland, so this reduces the amount of crops grown and therefore reduce the amount of food there is to eat. If energy is more expensive/in short supply, it costs more to produce/transport food and so customers receive an increased price in food.
inequalities in the global distribution of resources affects a country’s…
…wealth and security
food security
when people have enough nutritious and affordable food
food insecurity
when people do not have enough nutritious and affordable food to eat, often resulting in malnutrition.
malnutrition
a lack of proper food, causing illness or disease
food surplus
when there are extra crops and more than enough food to feed a population
wealthier countries are often in a food ______ because…
surplus, because they can afford to import food and subsidise farming to make food more affordable.
food deficit
when a country struggles to grow enough crops ro feed people and cannot afford subsidise farming or importing more food.
subsidise farming
To secure financial assistance by a grant ie money that does not have to be paid back.
the amount of water available in an area depends on… (3)
rainfall - more rainfall, more water
temperatures - higher temperatures, less water
population - higher population, less water
water surplus
an area which has more water than it needs. can lead to flooding.
water deficit
an area with too little water. can lead to dehydration.
Which places consume more energy and why?
…HICs and NEEs. The people living in these are usually connected to the national electricity grid and use a lot of technology in industry as well as in their day-to-day lives. They have a high standard of living.
Which places consume less energy and why?
LICs. many living there are not connected to the national electricity grid and rely on primary energy sources such as fuel-wood or animal dung.
What advantage do countries which produce a large amount of energy have?
May have fossil fuel reserves of access to other energy sources such as geothermal heat.
countries which produce a small amount of energy…
…are dependant on other countries to import energy sources in.
Why do many in LICs not have access to energy?
the price is determined by the exporting country, and as most LICs must pay high prices for the energy. This means that when it is distributed for use in the country, it will be sold at a very high price and many will not be able to afford it.
places with energy security produce…
…a high amount of the energy that they consume as they do not have to pay a high price for it.
places with energy insecurity…
…consume more than they produce as they have imported them form other countries.
Does the UK have food security?
Yes
If there is enough food on the planet to feed everyone, why do people experience food insecurity?
because the distribution of food across the world is not equal, as some places have food security and in many places, food goes to waste.
how much of the UK’s food is imported?
around 40%, and much of it has been processed
why are demands for food imports increasing?
people in wealthier nations want food that may not be in season, so they must import it from a country where it is in season.
people desire more exotic foods
people desire organic produce
UK climate may not be suitable for some foods
how can food be grown if it is not in season?
can be grown in heated greenhouses
cold storage allows food to be transported from other parts of the world
TNCs work in several countries to export food all across the globe
organic foods
grown without the use of artificial pesticides and fertilisers, or relating to/coming from living matter.
What can be used to help the crops in organic farming?
Natural fertilisers: animal manure
Natural predators instead of chemical pesticides
chemical pesticides
A chemical used to kill pests, such as the potato cyst nematode which is a pest that destroys potato crops.
Why has the consumption of pesticides in the UK risen?
Fewer people are prepared to eat food that has been sprayed with harsh chemicals.
what happens to farmland which has been converted to organic?
yield initially drops
they then improve to similar levels as non-organic crops
why is organic farming sustainable / not sustainable?
it is sustainable as it does not use harsh artificial chemicals
some believe it is not sustainable as it may lead to a greater use of land area.
how much of the global population experience water insecurity?
80%, meaning water supply and consumption are not evenly distributed.
UK is in a water _______. Explain.
overall surplus, although there are variations in the nation depending on the amount of rainfall and population density.
What does the UK do to help reduce the uneven distribution of water?
Water Transfer Schemes, where water is taken from a place of surplus to a place of deficit.
Give an example of a Water Transfer Scheme in the UK.
Kielder Reservoir in Northumberland.
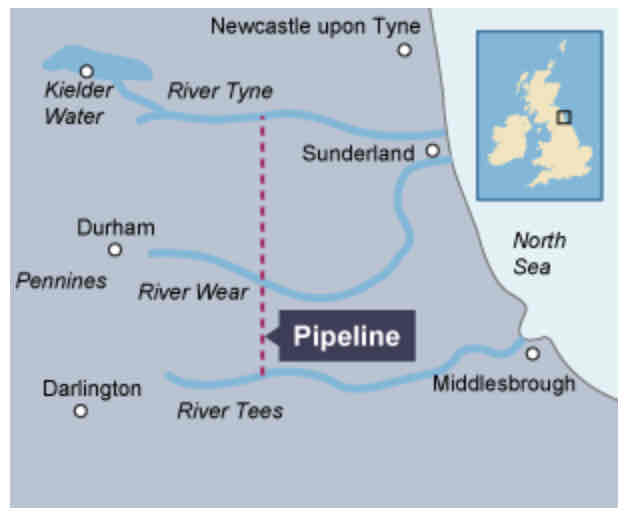
Where is the Kielder Reservoir located?
Kielder is located in an area of high land and so the rainfall there is higher than many surrounding areas.
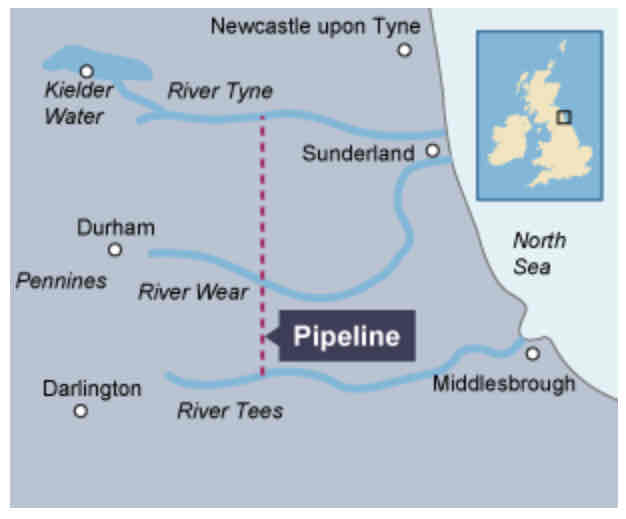
How does the Kielder Reservoir work?
The rainwater collected there travels south and is released into rivers to flow to nearby cities including Durham, Sunderland and Darlington.
The use of water in the UK has increased/decreased.
increased
Why has the demand for water in the UK increased?
more people…
wash cars
take longer showers
wash their garden
farming and industry also uses up a high quantity of water.
How much water does the average person use daily?
150 litres of clean and treated water daily.
Other than domestic uses, what else uses a lot of water in the UK?
Farming
Industry
water footprint
The amount of water used by a country, both domestically and through imports.
What has the UK Government considered creating to ensure water security?
A National Water Grid.
How would a National Water Grid work?
This would work in a similar way to the national electricity grid, but would be used to link up the country’s water supplies.
energy mix
the balance of the different types if energy which a country uses.
What does the energy mix of the UK mostly consist of?
mostly…
gas
coal
nuclear fuel
The last oil-fired power station in the UK closed in ____.
2015
Are fossil fuels running out?
As the world was once heavily reliant on fossil fuels, they were believed be running out.
However, as technology becomes more developed, new supplies can be discovered/accessed.
What are the estimations for how much longer gas and coal will last?
gas - 50 years
coal - 112 years
Where does the UK’s gas supply come from?
Around 40% comes from domestic supplies (the North Sea). However, the Uk could run out within just 5 years.
How much of the UK’s energy mic do renewable fuels make up?
Under 10%
What are the government’s aims for renewable energy?
Government aimed to increase RE use to 15% by 2020 to meet its European Union target.
Where does the UK’s renewable energy sources come from? (4)
50%+ from wind farms, mostly from onshore turbines.
hydroelectric power remained the same since 2012, will not increase until new dams are built.
less than 0.01% generated through tidal power b/c UK = island. This could increase to 20% using waves and tides.
solar panels are more common on people’s homes, government planed to increase the electricity from solar panels to 4% by 2020.
What is exploitation?
When the natural environment is destroyed for its natural resources, eg deforestation as a result of cutting timber.
Economic Issues with energy exploitation:
Generating electricity costs a lot of money, and so the Government must balance these costs with other costs the country must buy.
Why does generating electricity cost a lot of money? (which factors)
Initial costs, eg. Building…
power stations
dams
wind farms
Maintenance and running costs…
Buying fuel
Repairing damage to structures
Disposing of waste products
Environmental issues with energy exploitation:
fossil fuel powered stations create emissions, noise pollution (from production and transportation) and waste products (ash). Also been linked to high levels of radiation.
Uranium used in nuclear power stations is highly radioactive
Renewable energies (wind, solar etc.) are visual pollution as they are not aesthetically pleasant.
Tidal power and HEP dams may affect marine ecosystems
What does ‘emissions’ mean?
substances that are given off, especially in the form of gas.
Which foods are primarily produced in Asia?
Rice
Sugar
Meat
Milk
Fish
Which foods are primarily produced in South America?
Oil crops
Which foods are primarily produced by North America?
Coarse grain (for animal feed and brewing)
Which foods are primarily produced by Europe?
Barley
Meat
Milk
Fish
Which foods are primarily produced by Africa, Central America and Oceania?
Do not produce more of any type of food than other nations.
What is food energy intake measured in?
Calories (kcal)
Global Calorie Intake map
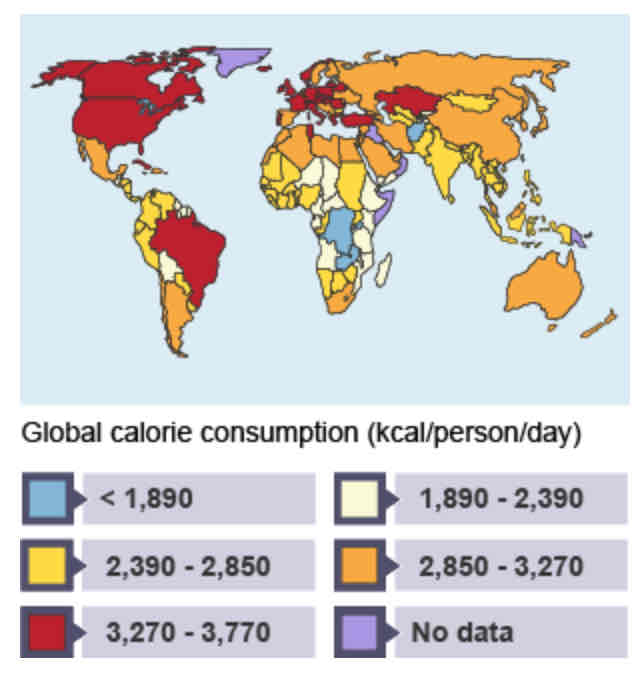
Food consumption has been rising globally for over __ years.
50
Which countries are experiencing the highest increase in calorie intake?
LICs
What are the 2 main reasons for increasing food consumption?
Economic development
Rising population
What patterns can we see with wealthier countries?
Higher calorie intake → USA and Italy 3,440+
High levels of food wastage
Fast food + advertising → higher consumption
The higher the population…
…the more mouths there are to feed.
How do we measure hunger?
The Global Hunger Index (GHI)
Who calculates the GHI?
The International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI)
How is GHI scored?
Each country is given a score…
0 → no hunger
100 → everyone is hungry
What is used to calculate GHI?
undernourishment
number of underweight children
child mortality
Undernourishment meaning
Not having enough food to be able to grow and stay healthy.
Undernourishment World Map
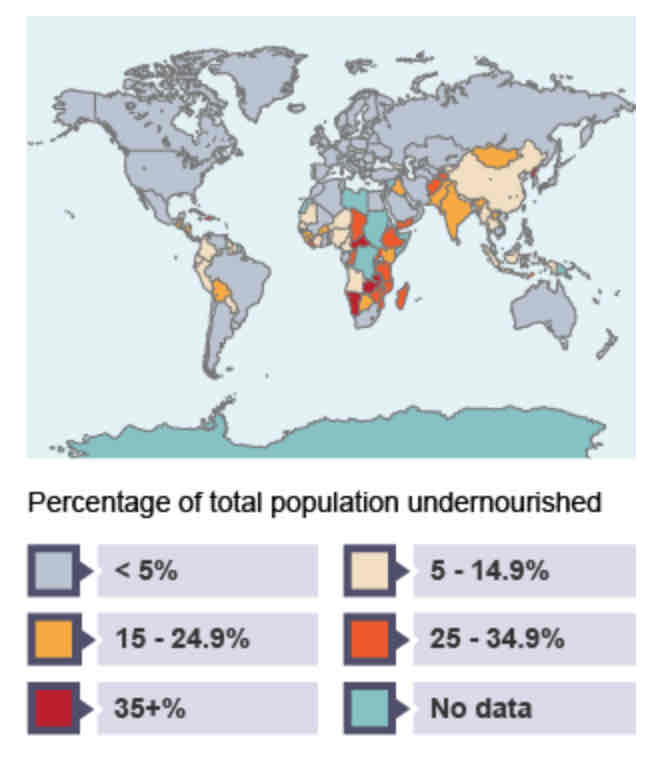
Which factors affect food supply? (6)
Climate
Technology
Pests and Disease
Water Stress
Conflict
Poverty
How is climate affecting food supply? (3)
Global warming increases temp by 0.2°C every 10 years
Rainfall increasing in some areas and decreasing in others
High temp and unreliable rainfall → difficult farming, especially for those at marginal lands
How is technology affecting food supply? (3)
Developments → increased amount of food available
Technology can overcome temp, water and nutrient deficiencies → greenhouses, irrigation, fertilisers
Growth of biofuel market is taking up valuable farmland.
How are pests and diseases affecting food supply? (2)
pesticides → increased crop yields
Farmers in poor countries cannot afford them
How is water stress affecting food supply? (4)
Irrigation systems → Provide water for countries with unreliable/low rainfall
Irrigation can double crop yields
Irrigation is expensive
Taking water from underground aquifers or directly from rivers has environmental consequences
How is conflict affecting food supply? (3)
Food can be used as a weapon → enemies cut off food to gain ground
Crops destroyed during fighting
Food shortages can cause riots and conflict
When have food supplies caused conflict before?
The Dafur region has faced conflict for many years because of disagreement over grazing rights.
What is grazing?
When animals feed on grass.
How is poverty affecting food supply?
Some have less money → cannot afford food → unable to work
Families in NEEs/LICs spend much income on food
What are the impacts of food insecurity? (4)
Hunger
Soil erosion
Rising prices
Social unrest
How does food insecurity cause hunger? (3)
Lack of food
Can cause undernutrition, or in severe cases, famine
UN: 828 million people affected by hunger globally