Chapter 4 - Fold Mountains
1/12
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Formation of fold mountains
Found on convergent plate boundaries. Two plates push against each other. Heavier oceanic plate forced under lighter continental into mantle below. Oceanic plate melts and puts pressure on continental plate. Pressure forces land to buckle upwards in folds

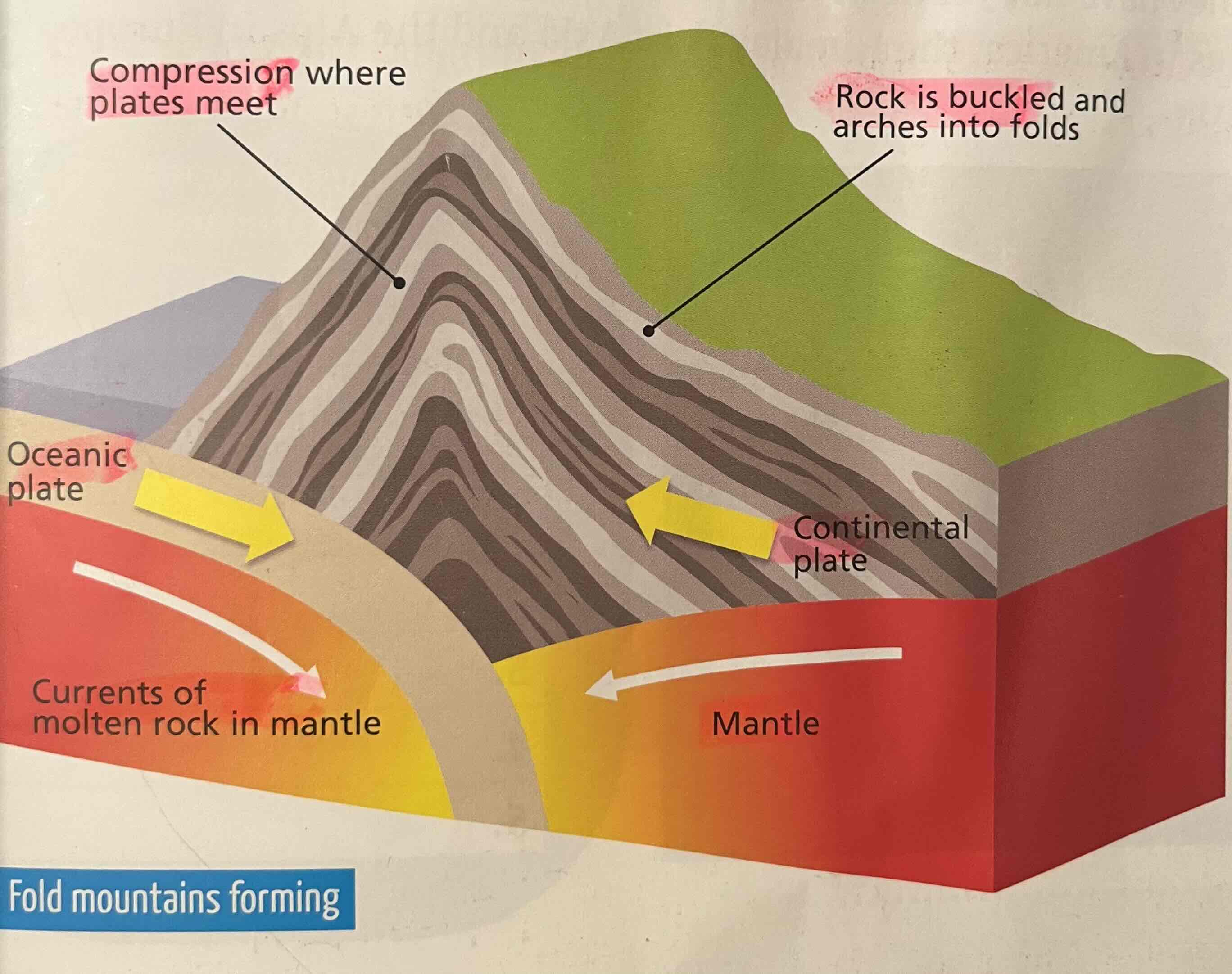
Anticline - meaning
Upfold of fold mountain
Syncline - definition
Downfold of fold mountain
Three periods of fold mountain formation
Caledonian, armorican, alpine
Caledonian - time period and example
400 million years ago, Dublin-Wicklow mountains
Armorican - time period and example
250 million years ago and Galtee mountains, Tipperary
Alpine - time period and example
35 million years ago, Alps, Europe
When were Alps formed
35 million years ago, alpine folding period
What plates were involved in the formation
Collision of Eurasian and African plates
Highest peak of alps
Mont Blanc (4810m) on France-Italy border
Economic impacts of Alps
Farming: sheep, goats and cattle. Moved further up slope in summer to graze
Hydro-electric power: melting snow generates
Tourism: skiing, snowboarding, hiking. Income improves standard of living for locals
Social impacts of Alps
Accessibility: many parts difficult to access, very steep
Soil: thin, poor quality. Only suitable for rough grazing, makes farming unprofitable or difficult
Avalanches: snow and ice come loose and crash down mountains