Membranes- Chapter 3.1
Chapter 3.1:
membranes- surround and help protect the body’s surfaces
Epithelial:
epithelial membranes- provide a %%lining for the internal and external%% surfaces of the body
epithelial membrane structure- a sheet of epithelial cells with an underlying layer of connective tissue
Mucous:
mucous membranes- line the %%body cavities that are open%% to the outside world, also line hollow organs of the respiratory system, all moist
mucous membranes structure- a layer of epithelium over a layer of loose connective tissue called %%lamina propria%%
Serous:
serous membranes- line %%body cavities that are closed%% to the outside world
pleura- encloses the lungs (serous)
peri%%cardi%%um- surrounds the %%heart%% (serous)
peritoneum- lines the abdominal cavity (serous)
serous membrane structure- outer layer of simple squamous epithelium on a thin layer of loose connective tissue
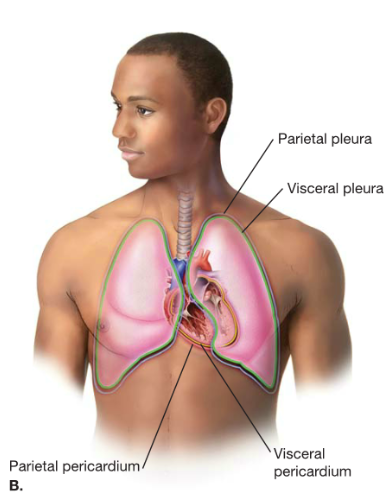
serous fluid- serves as a %%lubricant%% between parietal and visceral membranes to %%minimize friction%%
Cutaneous:
cutaneous membrane- another name for %%skin%%
structure of cutaneous membrane- keratinizing, stratified squamous epithelium over dense, fibrous connective tissue
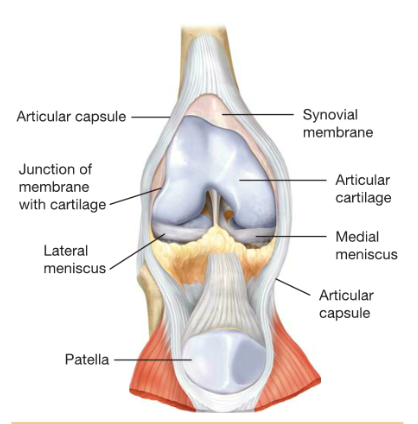
Synovial:
synovial membrane- composed %%solely of connective tissue, no epithelial cells%%
synovial membrane location- line capsules that surround synovial joints, also line tendon sheaths
synovial fluid- provides cushioning and %%reduces friction%%
bursae- small, connective tissue sacs that serve as %%cushions%% for tendons and ligaments surrounding the joints