Chem: VSEPR & Polarity Test
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bond types, electronegativity, molecular Geometry, VSEPR, and Naming compounds
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
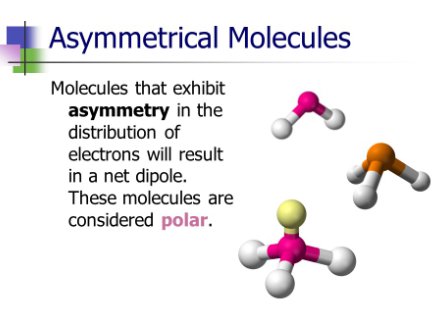
asymmetrial
lack of symmetry in a molecule
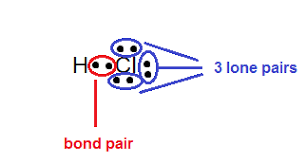
bond location
independent of the number of bonds at that location- whether single, double, or triple, its seen as one
bonding pair
electron pair being shared between two atoms
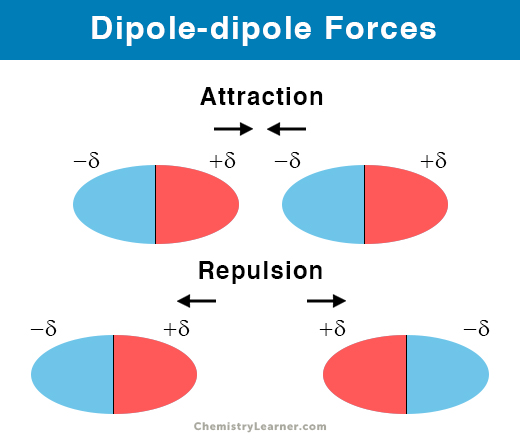
dipole-dipole
force between 2 oppositely-charged ends of 2 polar molecules
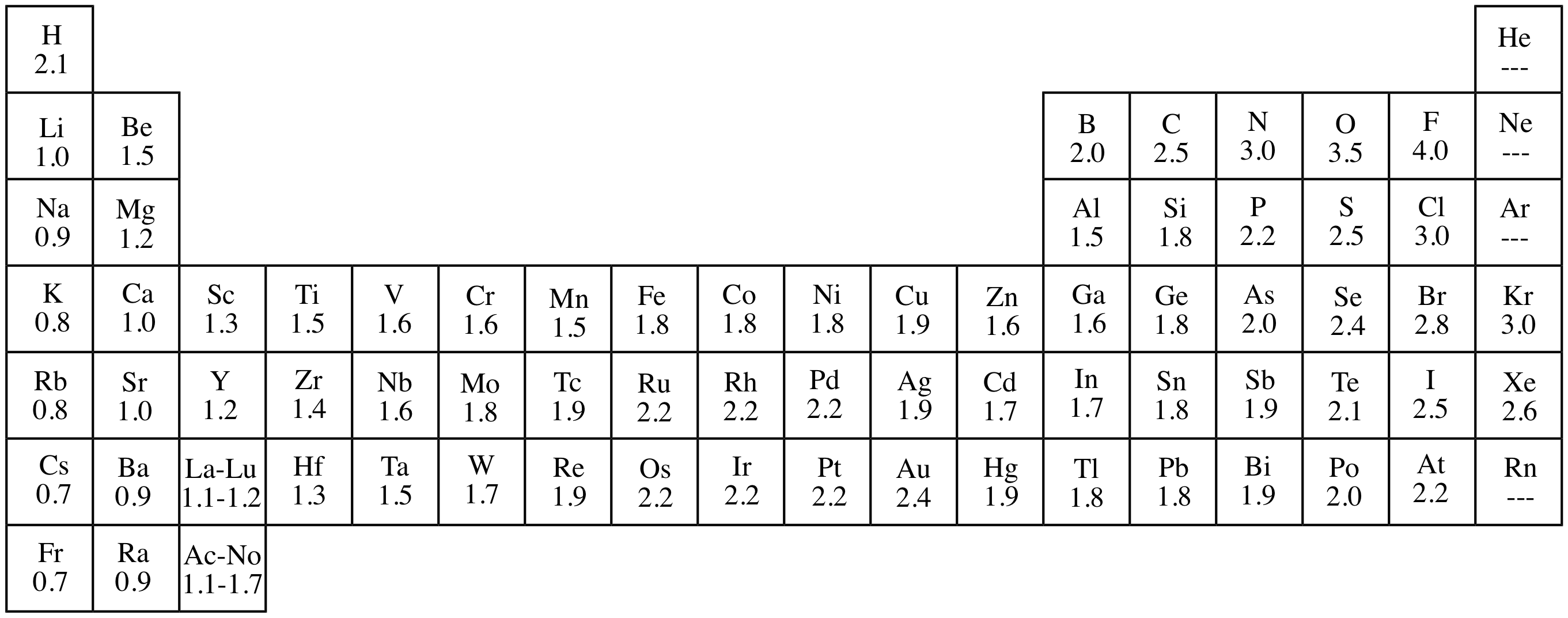
electronegativity
relative ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond
electron affinity
measures the tendency of an atom to acceptan electron
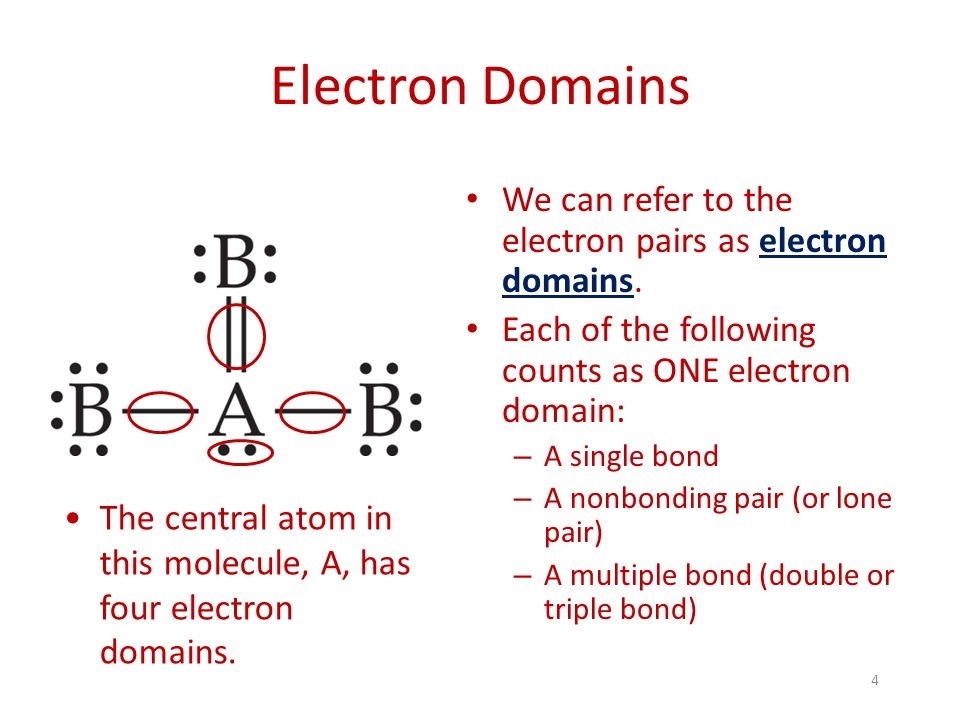
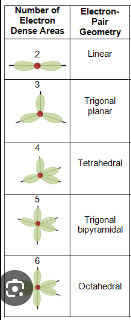
electron domain
the number of lone pairs or bond locations around a particular atom
molecular shape
linear, trigonal planar, bent, tetrahedral, trigonal pyramid, trigonal bipyramid, see saw, T shape, octahedral, square pyramid, square planar
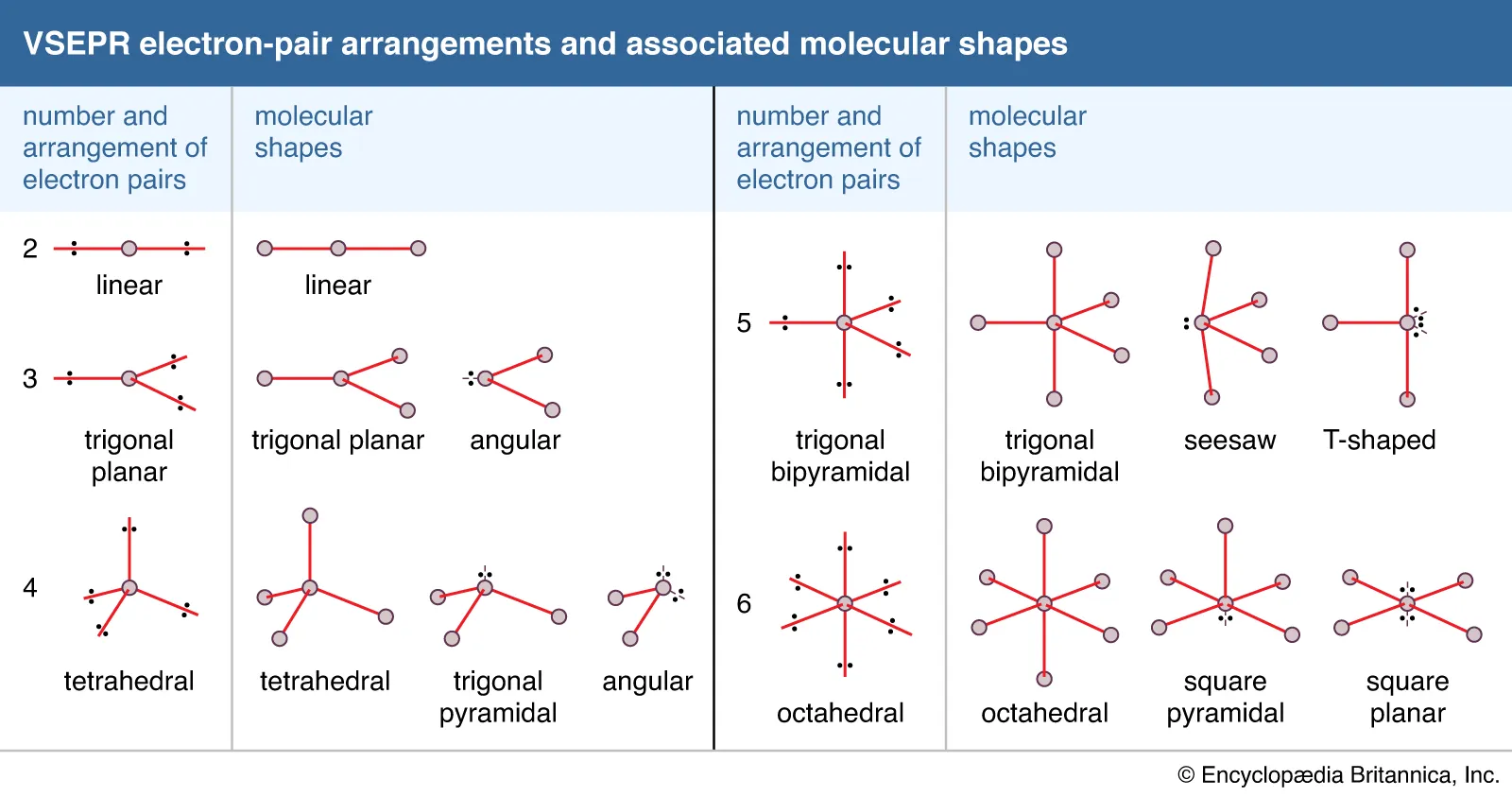
electron geometry
linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramid, and octahedral
hybridization
concept of mixing 2 atomic orbitals to give rise to a new type of hybridized orbitals
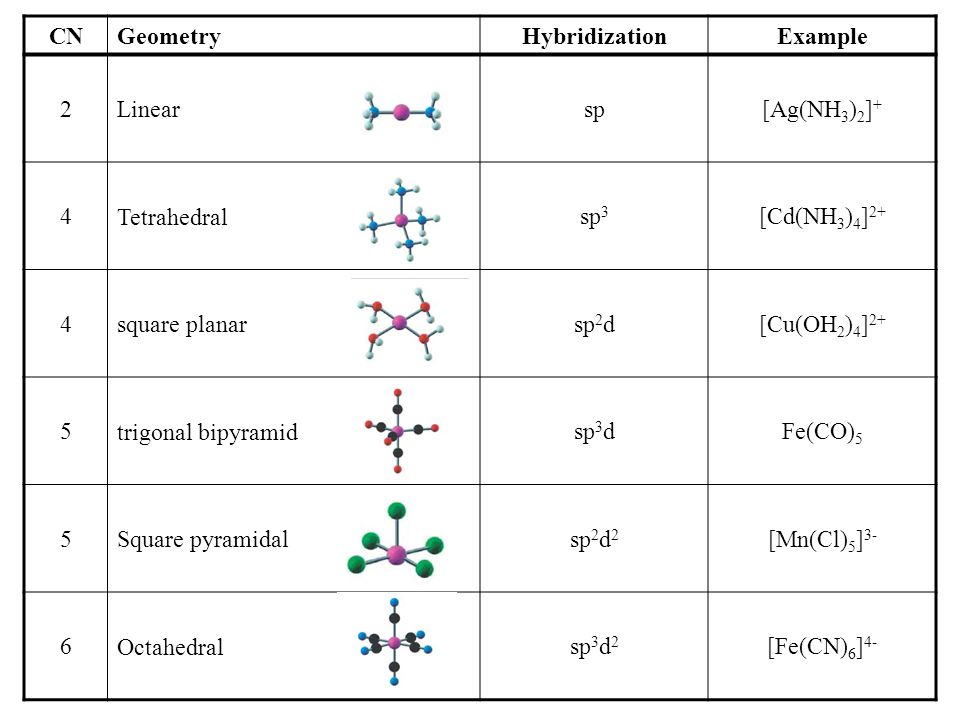
intermolecular forces
london dispersion forces, dipole-dipole, and hydrogen bonding; forces that mediate interactions between molecules
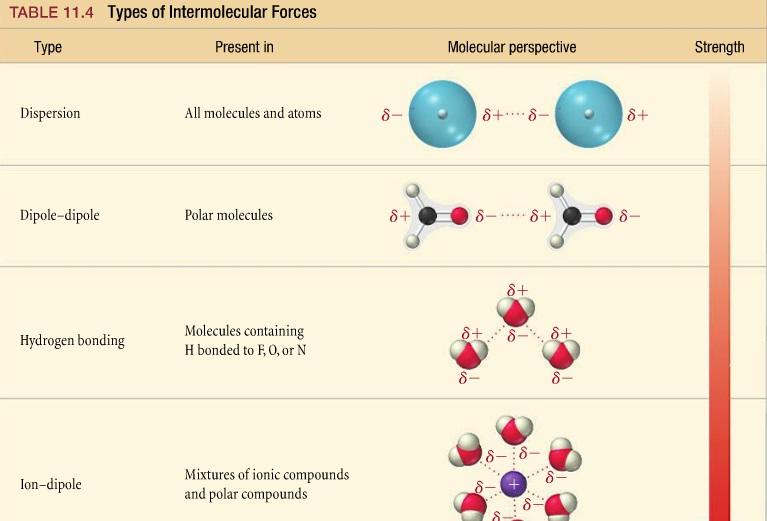
intramolecular forces
force that holds atoms together to form a molecule; covalent, ionic, and metallic
lone pair
pair of valence electrons that aren’t shared with another atom in a covalent bond
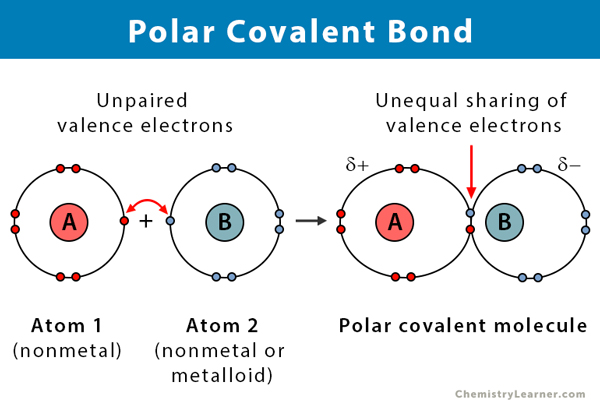
polar covalent
0.5-1.7
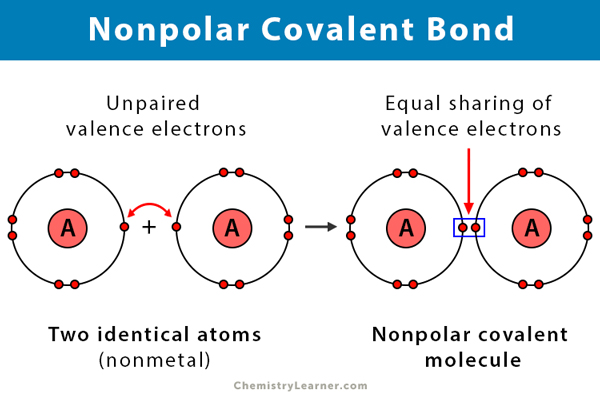
nonpolar covalent
<0.5
symmetrical
certain parts of a molecule can be interchanged with others without altering it
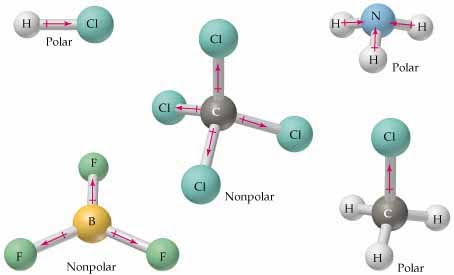
VSEPR
valence, shell, electron, pair, repulsion; used to find out what the molecule would look like in 3-D
<0.5
nonpolar covalent
0.5-1.7
polar covalent
>1.7
ionic
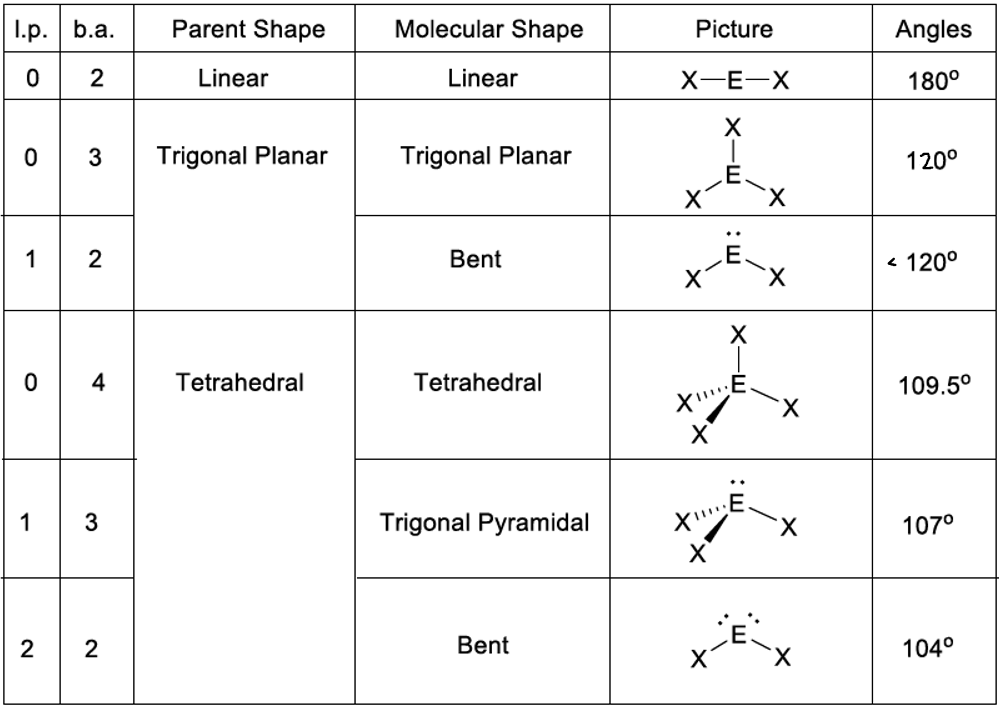
VSEPR/molecular shapes
1 domain: AX, 1 BP 0 LP, MS: linear, EG: linear, Hybridization: s, angle: 180
2 domains: AX2, 2 BP 0 LP, MS: linear, EG: linear, Hybridization: sp, angle: 180
2 Domains: AXE, 1 BP 1 LP, MS: linear, EG: linear, Hybridization: sp, angle: 180
3 domains: AX3, 3 BP 0LP, MS: trigonal planar, EG: trigonal planar, Hybridization: sp2, angle: 120
AX2E, 2 BP 1 LP, MS: bent, EG: trigonal planar, Hybridization: sp2, angle: 120
AXE2, 1 BP 2 LP, MS: linear, EG: trigonal planar, Hybridization: sp2, angle: 120
4 domains: AX4, 4 BP 0 LP, MS: tetrahedral, EG: tetrahedral, Hybridization: sp3, angle 109.5
AX3E, 3 BP 1 LP, MS: trigonal pyramid, EG: tetrahedral, Hybridization: sp3, angle: 109.5
AX2E2, 2 BP 2 LP, MS: bent, EG: tetrahedral, Hybridization: sp3, angle: 109.5
AXE3, 1 BP 3 LP, MS: linear, EG: tetrahedral, Hybridization: sp3, angle 109.5
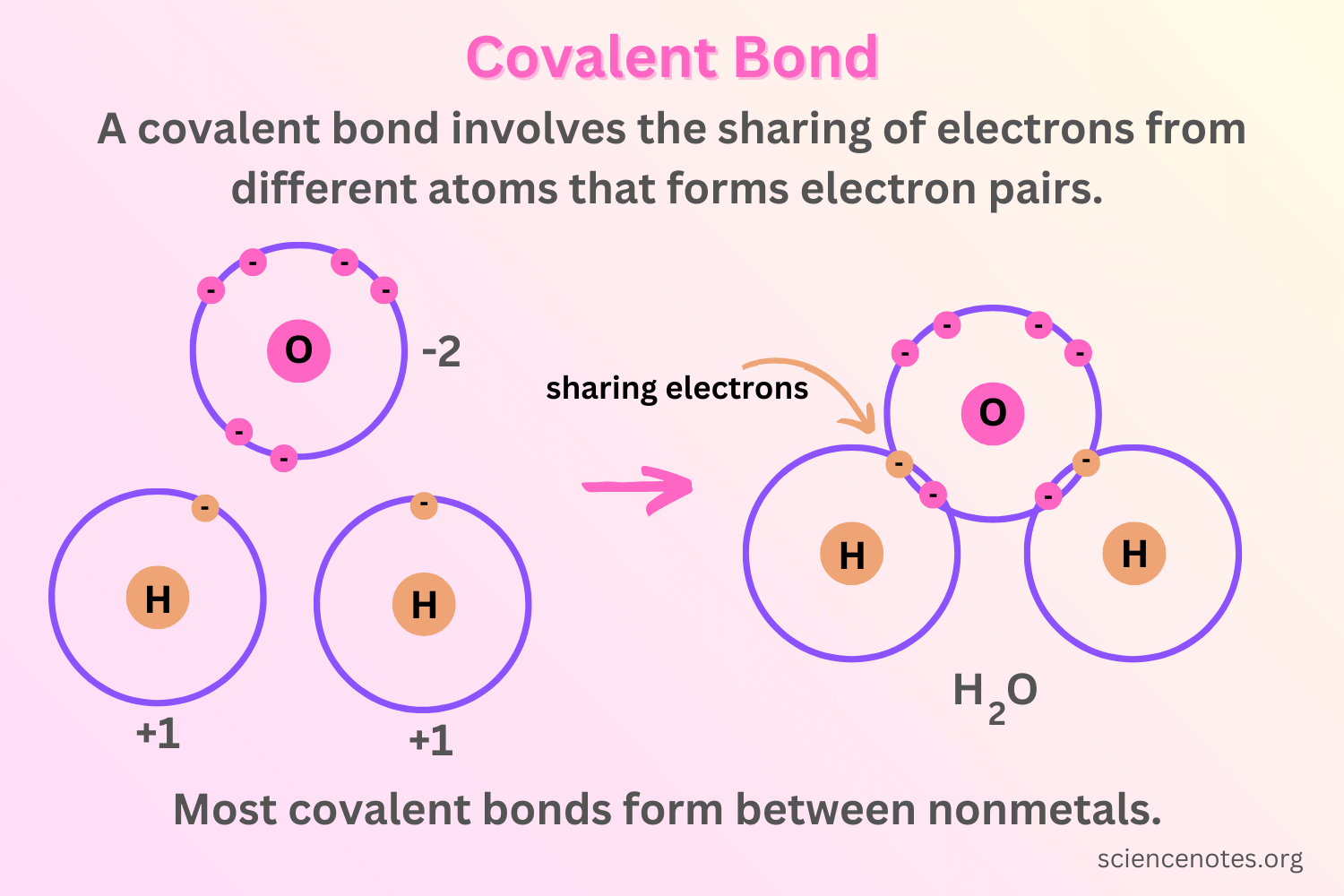
characteristics of a covalent bond
state at room temp: gases, liquids, or low-melting solids
solubility: soluble in organic liquids
formation: formed between two nonmetals
conductivity: doesn’t conduct electricity
boiling point: low
determine a symmetrical or asymmetrical molecule
Non polar molecules are symmetric with no unshared electrons. Polar molecules are asymmetric, either containing lone pairs of electrons on a central atom or having atoms with different electronegativities
weakest to strongest intermolecular forces
van der waals, dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonds, ion-dipole and then ion-ion
Percy Julian: compounds discovered & synthesized
physostigmine, drug that treats glaucoma
stigmasterol, bean oil extract used to make steroid
progesterone, sex hormone
hydrocortisone, synthesized and treats arthritis
Percy Julian: key events + places in his life
high school diploma: montgomery, alabama, 1916
college education: depauw Uni, 1920
M.A. degree: Harvard, 1923
Ph.D. in chem: university of Vienna, 1931
Chemistry instructor: Fisk Uni, 1932
Chemistry department head: West Virginia state cell, 1923
Research fellow: DePauw Uni, 1933
Director of research: Chicago, 1936
Julian Lab established: Chicago, 1953
Julian Research Institute: Chicago, 1961