ELECTRICITY
5.0(3)
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:59 AM on 2/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
Electrostatics
The study of stationary electric charges.
2
New cards
Electrodynamics
The study of electric charges in motion.
3
New cards
Electrification
can be created by contact, friction, or induction.
4
New cards
negative electric charge
Electrification is due to the movement of
5
New cards
electron
The smallest unit of electric charge is the
6
New cards
coulomb (C)
The fundamental unit of electric charge is
7
New cards
6\.3x10^18
1 C =
8
New cards
1\.6x10^-19 C/electron charge
What is the electrostatic charge of one electron?
9
New cards
Unlike charges attract; like charges repel.
Electrostatic Laws
10
New cards
Coulomb’s Law
The electrostatic force is directly proportional to the product of the electrostatic charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
11
New cards
Coulomb’s Law Formula
\
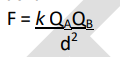
12
New cards
Electric potential
is sometimes called voltage.
13
New cards
volt (V)
The unit of electric potential is the
14
New cards
Electric Current
• Flow of electrons in a conductor.
• Measured in amperes (A)
• Measured in amperes (A)
15
New cards
ampere
is proportional to the number of electrons flowing in the electric circuit.
16
New cards
One ampere
is equal to an electric charge of 1 C flowing through a conductor each second.
17
New cards
DC and AC
2 Types of Current
18
New cards
DC
- Electrons flowing only in one direction
19
New cards
AC
Electrons flowing alternately in opposite directions.
20
New cards
Electric Resistance
is measured in ohms (Ω)
21
New cards
Resistor
is a passive two terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.
22
New cards
electronics circuits
, resistors often used to limit current flow, to adjust signal levels, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines among other uses.
23
New cards
Conductors
is any substance through which electrons flows easily.
24
New cards
Copper (Cu),
Aluminum (Al),
water
Aluminum (Al),
water
Conductors (3 examples)
25
New cards
Insulators
is any material that does not allow electron flow
26
New cards
Glass,
clay other earthlike material,
rubber
clay other earthlike material,
rubber
Insulators (3 examples)
27
New cards
semiconductor
is a material that under some conditions behave as an insulator and in other conditions behaves as a conductor.
28
New cards
William Shockley
demonstrated semiconduction
29
New cards
1946
William Shockley demonstrated semiconduction
30
New cards
Silicon (Si), germanium (Ge)
Semiconductors (2 examples)
31
New cards
Superconductivity
is the property of some materials to exhibit no resistance below a critical temperature (Tc).
32
New cards
1911
When were superconductors discovered?
33
New cards
1960s
When were superconductors commercially available in
34
New cards
Electric Circuits
When the resistance is controlled and the conductor is made into a closed path, the result is an electric current.
35
New cards
Ohm’s Law
The voltage across the total circuit or any portion of the circuit is equal to the current times the resistance.
36
New cards
series circuit
All circuit elements are connected in a line along the same conductor.
37
New cards
parallel circuit
Contains elements that are connected at their ends rather than lie in a line along a conductor.
38
New cards
1. The total resistance is equal to the sum of the individual resistances.
2. The current through each circuit elements is the same and is equal to the total circuit current.
3. The sum of the voltages across each circuit element is equal to the total circuit voltage.
Rules for Series Circuits
39
New cards
1. The sum of the currents through each circuit element is equal to the total circuit current.
2. The voltage across each circuit element is the same and is equal to the total circuit voltage.
3. The total resistance is the inverse of the sum of the reciprocals of each individual resistance.
Rules for Parallel Circuits
40
New cards
Electric Power
is measured in watts (W)
41
New cards
Electrical Fault
Is an electric power system, a fault or fault current is any abnormal electric current
42
New cards
ground fault (earth fault)
is any failure that allows unintended connection of power circuit conductors with the earth.
43
New cards
Electrical grounding
provides an alternate path for electricity to follow, rather than going through a person.
44
New cards
Electric Shock
happens when current passes through the body.
45
New cards
Electrocution
Refers to the injury or lethal dose of electrical energy
46
New cards
Electrical fires
may be caused by excessive resistance that generates heat
47
New cards
• Too much current running through wiring where overcurrent protection fails or does not exist • Faulty electrical outlets resulting in poor contact or arcing • Poor wiring connections and old wiring that is damaged and cannot support the load
Causes of Electrical fires
48
New cards
explosion
can occur when electricity ignites a flammable gas or combustible dust mixture in the air.
49
New cards
circuit breaker
is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current from an overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to interrupt current flow after a fault is detected.