CHEM 302: Detailed Study of Chapter 22 - Isomers and Enolate Chemistry
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
enolate
carbanion that forms with alpha carbon of ketone/aldehyde
nucleophile
enolates act as _____
alpha
H
when forming enolates, the _____ carbon must have at least one ____
enolate
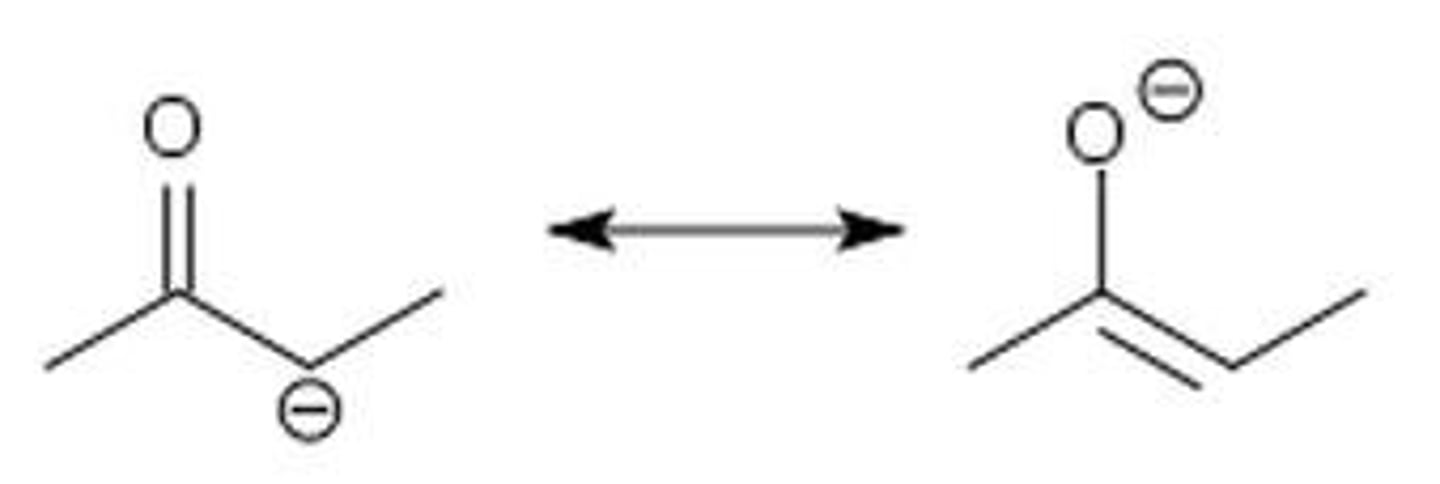
keto
the ____ form of an enolate has the double bond on the O and the lone pair on the C
enol
the _____ form of an enolate has the double bond on the C and the lone pair on the O
keto
the _____ form of the enolate is the reactive species
carbonyl
what is the electrophile that enolates attack
yes
does the addition of enolates to electrophiles require acid workup
no enolyzable H atoms
what is the requirement to be the electrophil carbonyl in enolate reactions
done
practice enolate addition to electrophiles
aldol condensation
if there is an alpha carbon what reaction will occur
aldol condensation
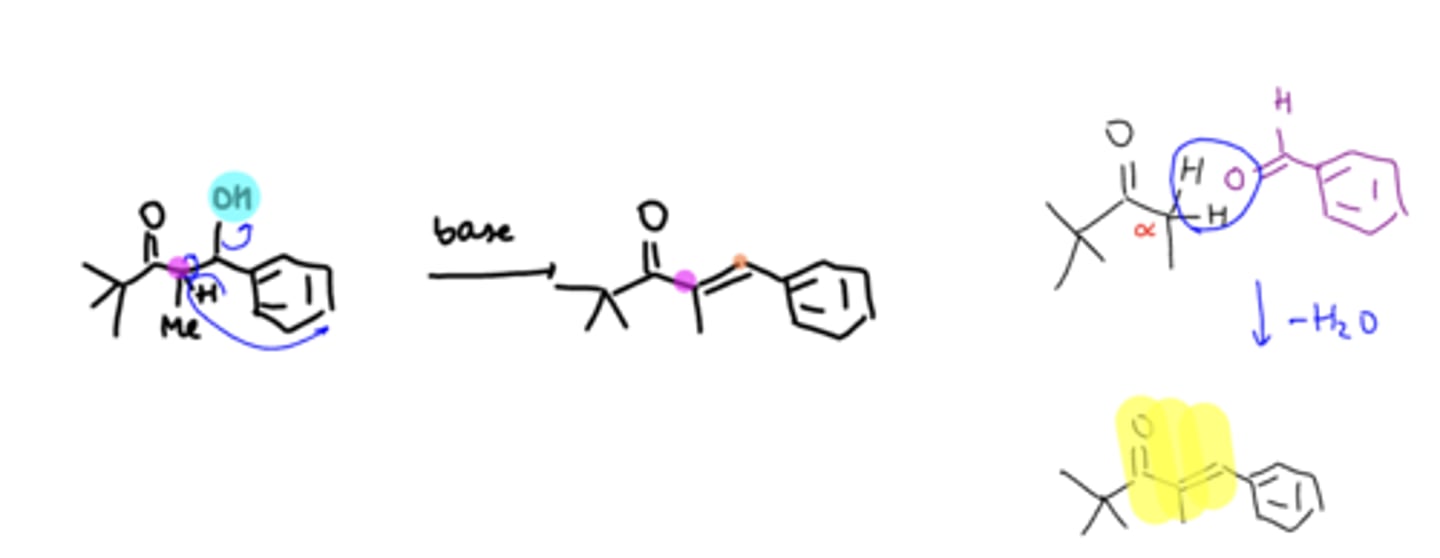
forms conjugated system
why can OH- act as a leaving group in aldol condensation
alpha-beta unsaturated carbonyl
aldol condensation forms what kind of product
aldol
what type of molecule is the reagent
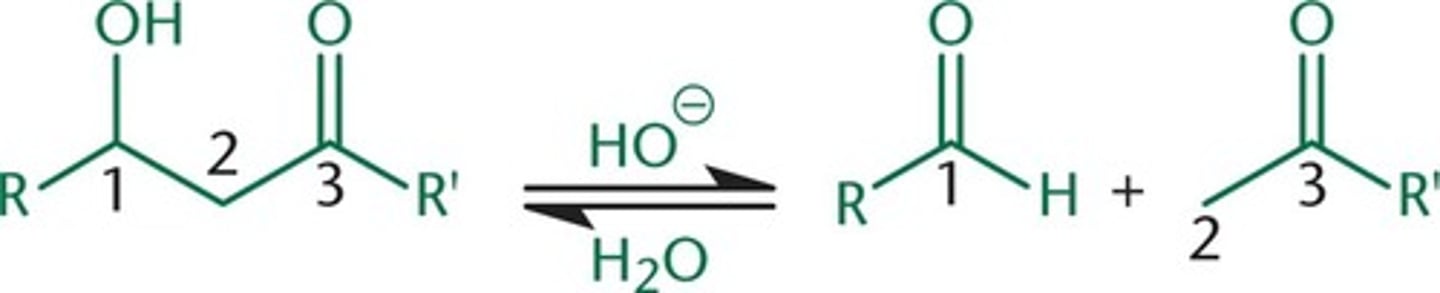
aldol + base --> alpha beta unsaturated carbonyl + water
summary of aldol condensation reaction
keto
right form
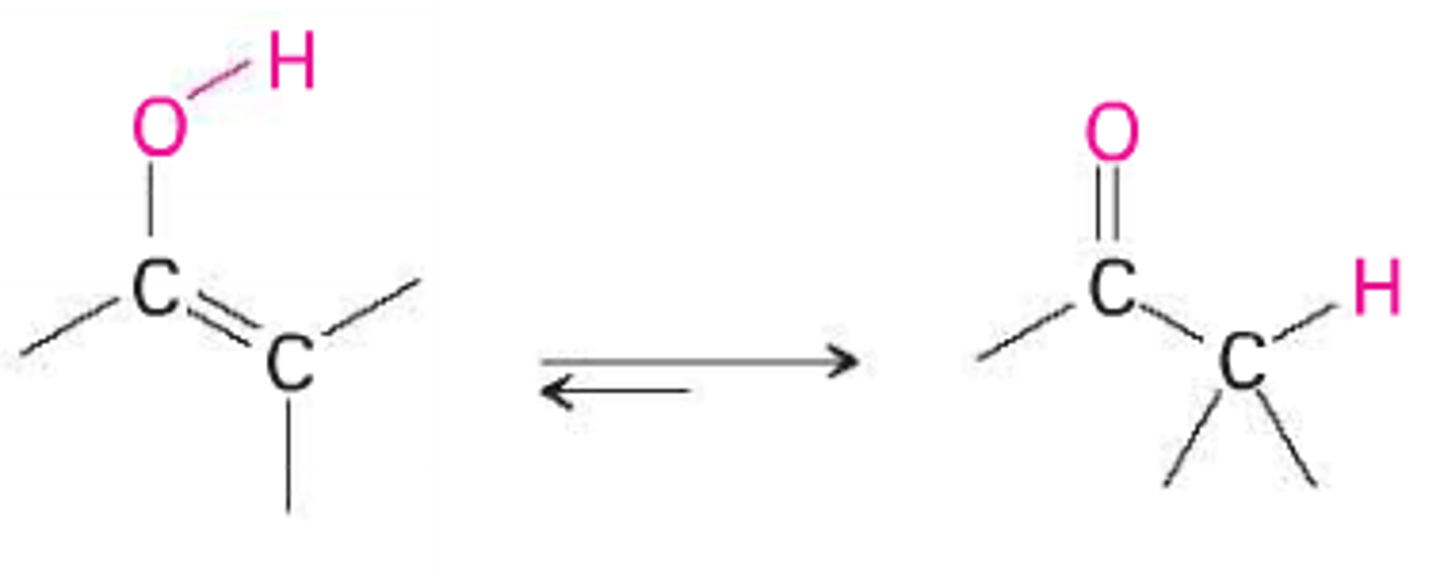
enol
left form
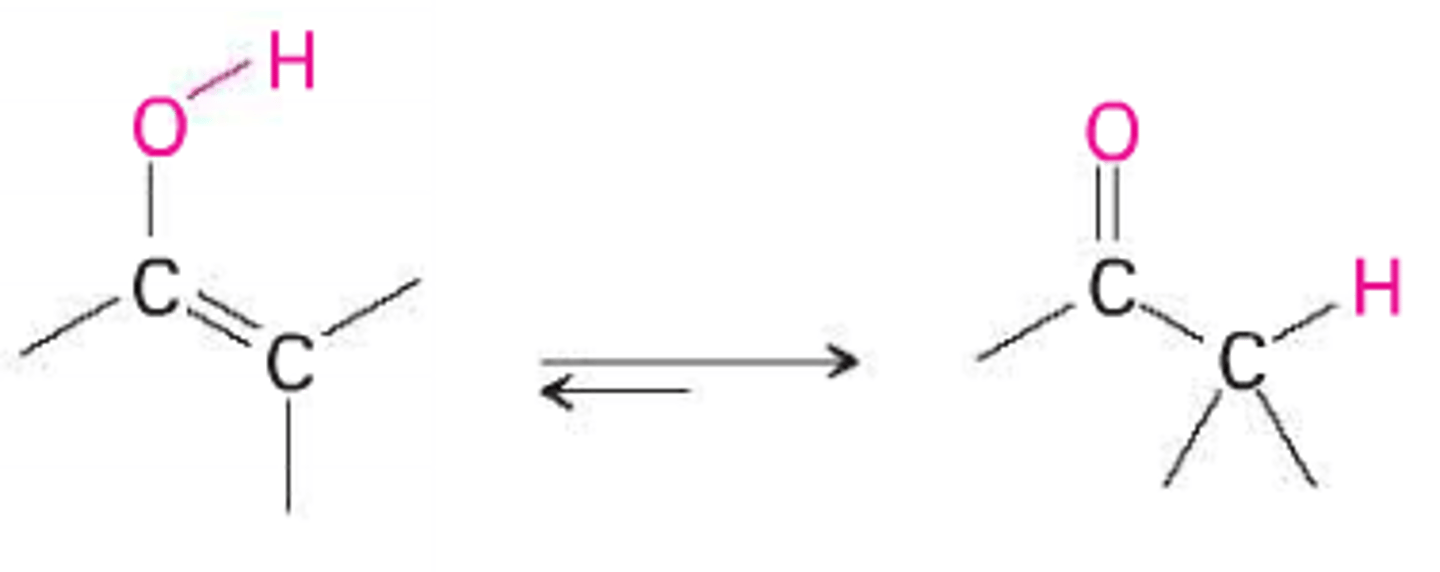
enolate
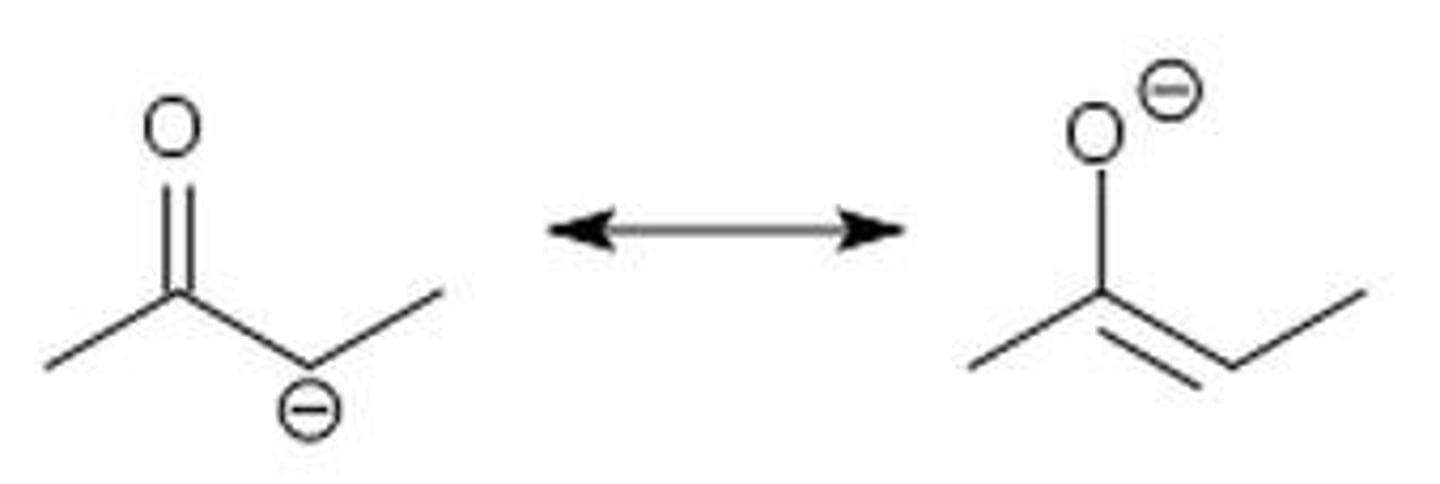
constitutional isomers
the keto and enol forms are ________ in equilibrium
base
acid
keto enol tautomerization can either be ____ or ____ catalyzed
abstract H from alpha C
resonance
deprotonate water to enol
summary of base catalyzed keto enol tautomerization
protonate O
resonance
abstract H from alpha C to enol
summary of acid catalyzed keto enol tautomerization
20
pKa of the alpha C hydrogen of ketones
NaOH
LDA
two bases used to deprotonate ketones to enolates
LDA
base that deprotonates to enolates quantitatively
33
pKa of LDA
lithium diisopropyl amine
what does LDA stand for
LDA
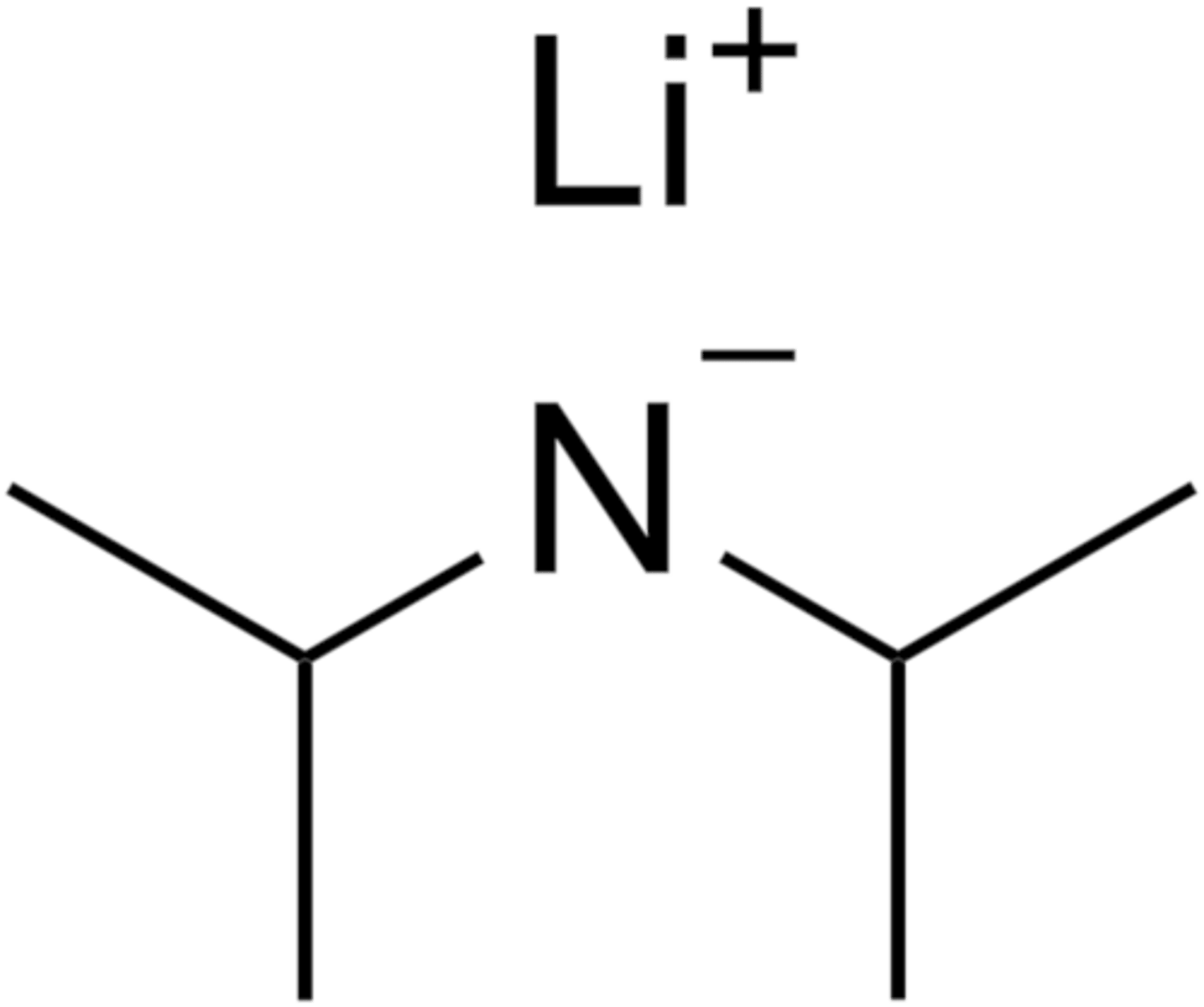
sterically hindered
quality of LDA
NaOH
base that deprotonates a few % at a time as equilibrium is shifted as products react
reagents
helpers
enolates can either be ____ or _____ in SN2 reactions
cyclohexanone
what is a good symmetrical reagent used in many enolate reactions
ketone + base --> enolate + 1 alkyl halide --> ketone + alkyl group on alpha C
summary of enolates in SN2 reactions
enamine
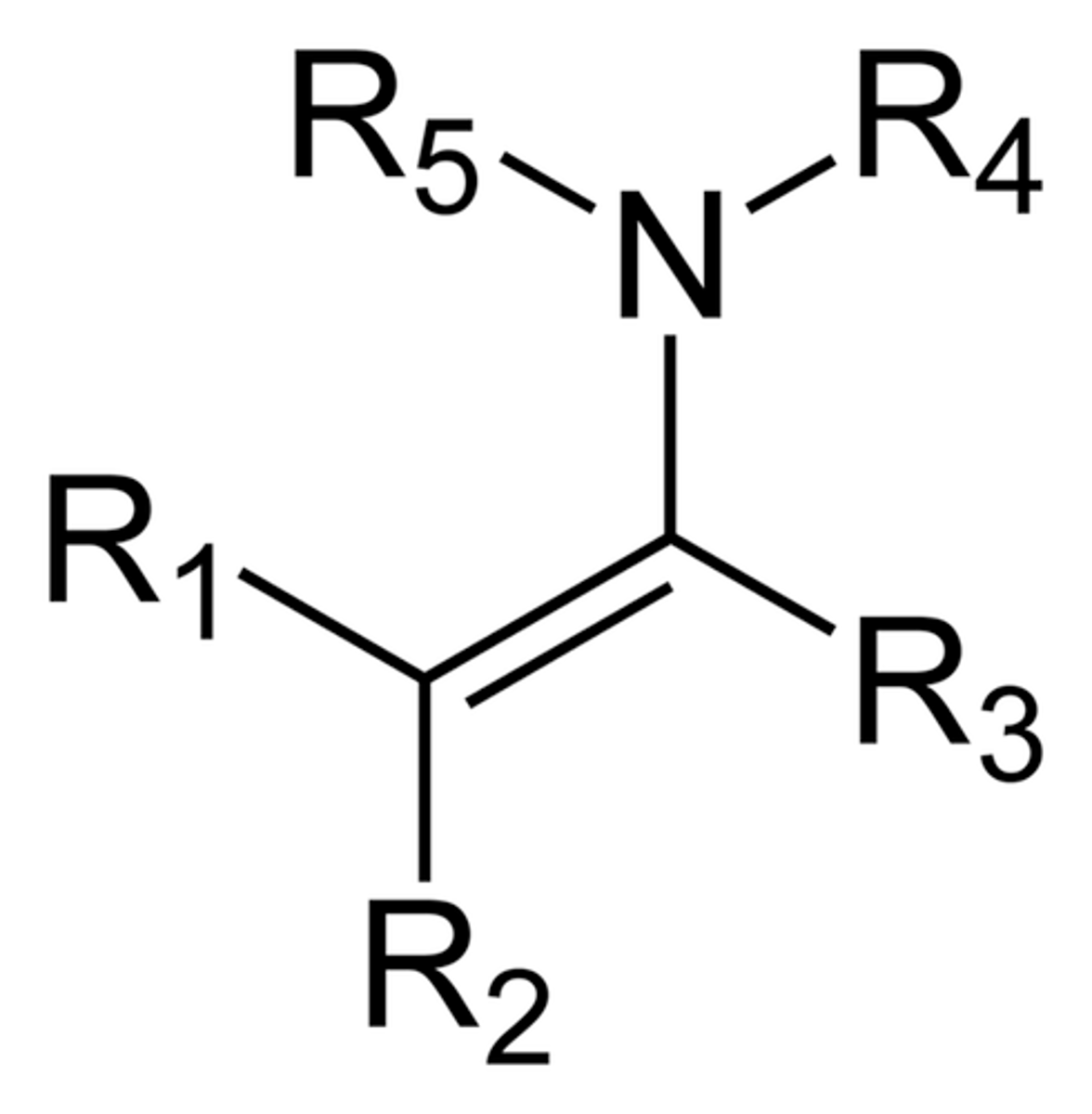
ketone + 2 amine --> enamine
summary of enamine formation
enamine
nitrogen equivalent of keto/enols
H3O+ heat
how to hydrolyze enamine back to amine and ketone
enamine + base --> deprotonated enamine + alkyl bromide --> + H3O+ --> alkylated ketone
summary of enamine as helper in SN2 with alkyl bromide
alkylation
final result of enamine/enolate reactions
enamine + base --> deprotonated enamine + acid chloride --> + H3O+ --> beta keto ketone
summary of enamine as helper in SN2 with acid chloride
alkyl bromide
using _____ with enamine forms alkylated ketone
acid chloride
using ____ with enamine forms beta ketoketone
beta keto ketone
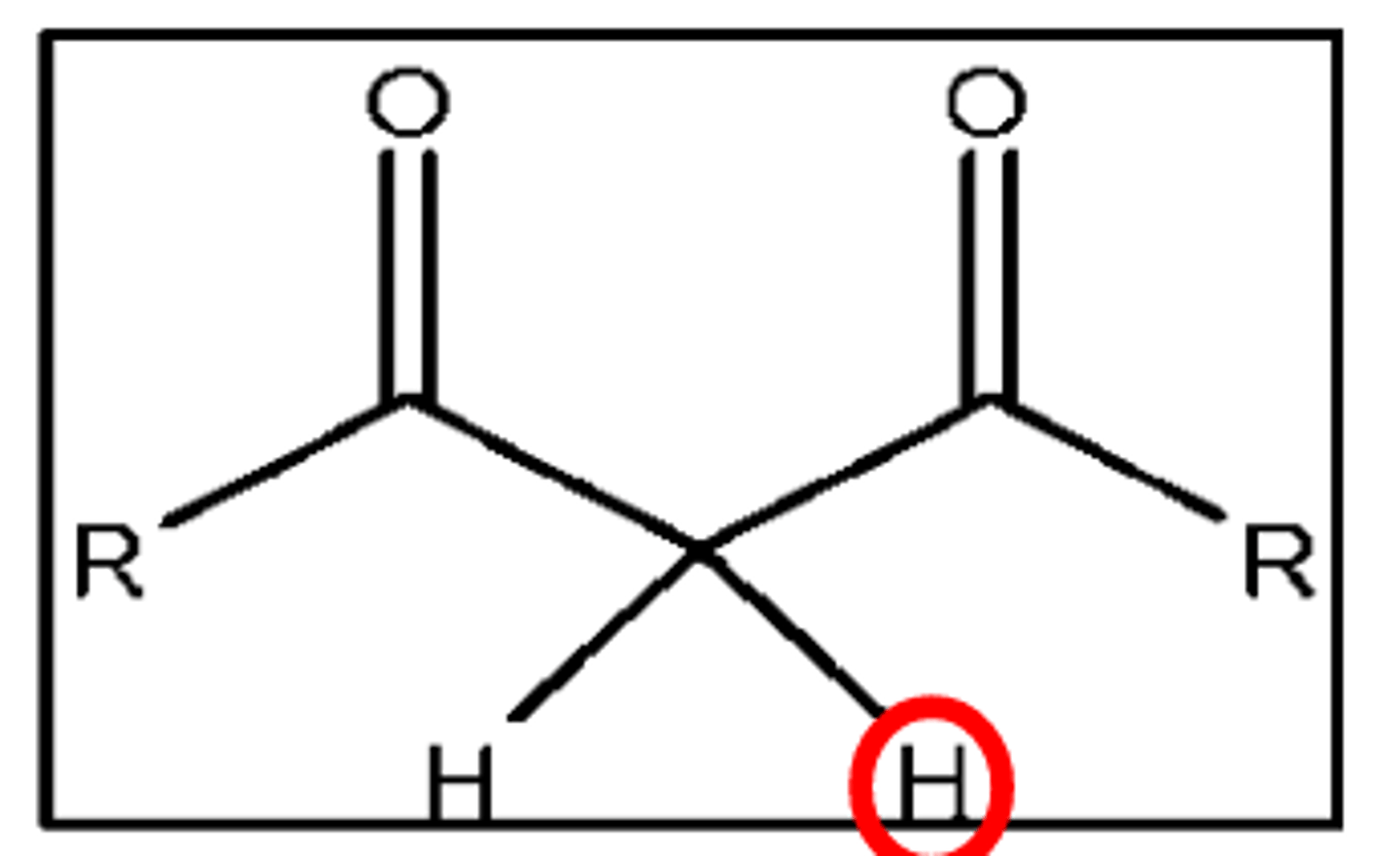
9
pKa of the H on the alpha carbon of a beta keto ketone
H3O+ heat
what reagents are needed to remove the enamine group and reform the ketone