S1L3_ PART 1_Typical Signs & Symptoms of Psychiatric Illness
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Observations and objective clinical findings
Signs
Manifestation of disease that the physician perceives
Signs
Subjective experiences expressed by the patient
Symptoms
Manifestation of disease apparent to patient himself
Symptoms
Chief complaint
Symptoms
A group of signs and symptoms that, together, make a recognizable condition
Syndrome
Characterized by a set of associated symptoms
Syndrome
Mental illness where symptoms that are understandable (reality-based) and can be empathized with
Neurosis
Exaggerated forms of normal reactions to stressful events
Neurosis
No loss of contact with reality
Neurosis
Insight is usually maintained
Neurosis
May still significantly impair function
Neurosis
“Nerves,” anxiety
Neurosis
Abnormal psychogenic reactions, maladaptive reactions to stress that reflect excessive and inappropriate use of defense mechanisms
Neurosis
2 components of neurosis
Vulnerable personality
Stress factors triggering the reaction
Mental illness where there is loss of contact with reality, and the symptoms, such as delusions or hallucinations, are not understandable and cannot be empathized with
Psychosis
Impairment of mental functions
Psychosis
“Madness”
Psychosis
This is madness- baliw= psychosis
Neurotic & stress-related disorders based on ICD 10
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Mixed Anxiety and Depression
Panic Disorder
Phobic Disorder
Agoraphobia
Social Phobias
OCD
PTSD
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Generalized and persistent anxiety symptoms with the following elements:
Apprehension
Motor tension
Autonomic overactivity
Symptoms of both anxiety and depression are both present but neither predominates
Mixed Anxiety and Depression
Recurrent attacks of severe anxiety not restricted to any particular situation or set of circumstances
Panic disorder
Comparative freedom from anxiety between attacks
Panic Disorder
Anxiety is evoked only or predominantly by well-defined situations or objects external to the subject, which are not currently dangerous, and these are characteristically avoided or endure with dread
Phobic Disorder
Fear of open spaces, crowds, and difficulty of immediate easy escape
Agoraphobia
Fear of scrutiny by other people in comparatively small groups, leading to avoidance of social situations
Social Phobias
Recurrent obsessional thoughts or compulsive acts
OCD
Delayed or prolonged response to stressful event or situation of threatening or catastrophic nature, likely to cause distress in anyone
PTSD
2 Components of Consciousness
Arousal
Awareness
2 Types of Consciousness
Primary consciousness
Secondary consciousness
Sensory awareness, attention, perception, memory (learning), emotion and action
Primary Consciousness
Self-conscious or aware
Secondary Consciousness
Conscious recognition that we are conscious beings
Secondary Consciousness
Ability to experience oneself as autonomous with subjective feelings
Secondary Consciousness
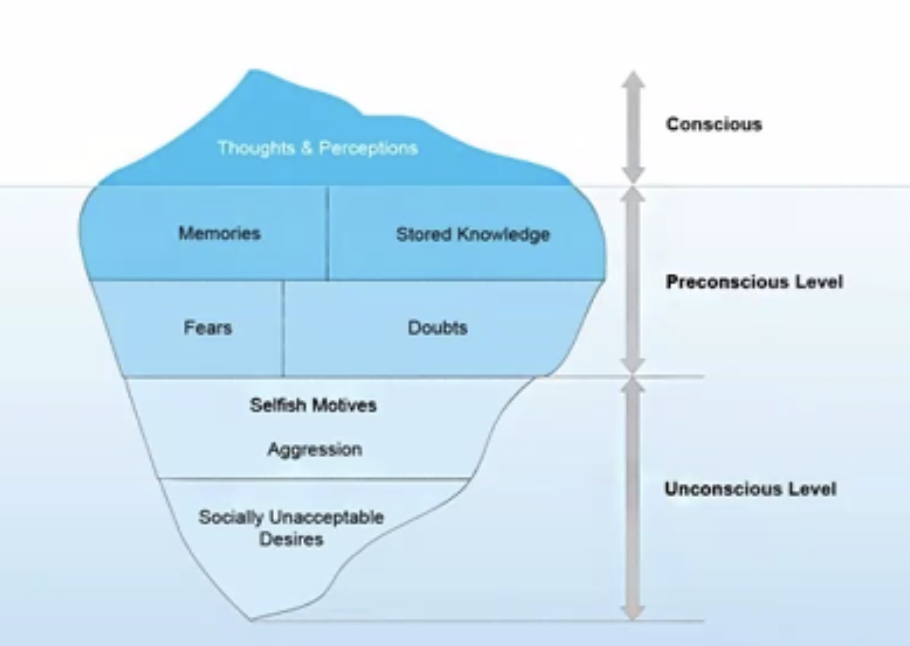
What we are fully aware of at any one time
Conscious
What we could become aware of quite easily if we switched our attention to it
Preconscious
Serves to maintain repressive barrier and to censor unacceptable wishes and desires
Preconscious
What have pushed out of our conscious minds, through repression, making it inaccessible, although it continues to influence our throughs, feelings, and behaviors
Unconscious
Closely related to instinctual drives
Unconscious
Can become conscious by passing through __
Unconscious
Iceberg diagram: What fall under these categories (from top to bottom)
Conscious:
Preconscious:
Unconscious:
Disorders of Consciousness
COLDDD CoCo CoSST (Consciousness)
Clouding of consciousness
Obtundation
Lethargy
Disorientation
Delirium
Drowsiness
Coma
Coma Vigil
Concentration/Focus
Stupor
Somnolence
Twilight State
Confusion
Disorientation
Impaired awareness of time, place and person
Disorientation
Very mild form of altered mental status in which a patient has inattention and reduced wakefulness
Clouding of consciousness
Not fully awake, alert and oriented
Clouding of consciousness
Severe drowsiness in which patient can be aroused by moderate stimuli and then drift back to sleep
Lethargy
Similar to lethargy in which a patient has lessened interest in the environment, slowed response to stimulation and tends to sleep more than normal with drowsiness in between sleep states physical but non painful stimuli
Obtundation
Only vigorous and repeated (painful) stimuli will arouse the patient and when undisturbed, will immediately lapse back to unresponsiveness
Stupor
Unarousable unresponsiveness
Coma
Acute reversible mental disorder characterized by some confusion and some impairment of consciousness, generally associated with emotional lability, hallucinations or illusions, and inappropriate, impulsive, irrational or violent behavior
Delirium
Persistent vegetative state
Coma vigil
Coma in which a patient appears to be awake with eyes open but cannot be aroused
Coma vigil
Disturbed consciousness with hallucinations
Twilight State
Pathological sleepiness or drowsiness from which one can be aroused to a normal state of consciousness
Somnolence
State of impaired awareness with a desire or inclination to sleep
Drowsiness
Aspect of consciousness that relates to the amount of effort exerted in focusing on certain aspects of an experience, activity, or task
Concentration / Focus
Type of Attention: Suppose you arrive at a lecture hall, open your notebook, and rather than scanning the room indiscriminately, turn your attention to the instructor, who is just beginning to speak
Selective attention
Type of Attention: The lecture is mildly interesting, and you are able to pay attention for the full 20-minute presentation
Sustained attention or vigilance
Type of Attention: At the same time that you are listening to the instructor, you are taking handwritten notes incorporating headings and subheadings. It appears that you are able simultaneously to listen, write, and organize rather effortlessly, although you are probably shifting your attention among these competing tasks
Divided Attention
Type of Attention: A fire engine goes by the lecture hall and you look up (__) but are then able to ignore the dimming noise of the siren (__) and continue to listen to the lecture (__)
Distraction
Inhibition
Sustained attention