Periodic Trends
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the 4 periodic trends?
atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity
AR stands for…
atomic radius
what is atomic radius?
the distance from the centre of an atom to its outer electron orbital
describe the 2 patterns of AR
down a group, the AR will increase
addition of energy levels
right along a period, the AR decreases
Electrons are added to the same energy level, and the shielding effect stays the same along the period
the stronger positive charge pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus
as a result the AR shrinks
describe AR with cations
the same net charge is distributed among less electrons, resulting in a greater force of attraction and a smaller radius
describe AR with anions
the same net charge is distributed among more electrons, resulting in a weaker force of attraction and a larger radius
IE stands for…
ionization energy
what is ionization energy?
the amount of energy required to remove the outermost electrons
Therefore:
the 1st IE removes energy from the 1st electron (easiest to remove due to the weak force of attraction and shielding effect)
the 2nd IE removes an electron from a 1+ cation
the 3rd IE removes an electron from a 2+ cation
Describe what proximity toward the nucleus means in IE
The closer the electron is to the nucleus , the stronger the force of attraction and the higher the IE.
describe the 2 patterns of IE
down a group, the IE decreases
the addition of energy levels means the electron being removed is further from the nucleus (weaker force of attraction, can get snatched easily)
right along a period, the IE increases
the higher net charge means that there is a greater force of attraction by the valence electron to the nucleus, causing a higher IE
What is the exception to IE?
Filled and half filled sublevels have additional stability, therefore they have a higher IE and so removing them requires more energy than expected.
What must you remember about 2nd IE?
2nd IE (and so on) will always have higher values since you are now removing from a cation, however the patterns seen in the 1st IE will still be present but shifted by one position.
EA stands for…
electron affinity
what is electron affinity?
the amount of energy released when an electron is added to an atom.
Why is energy released when you add an electron to an atom?
due to the increase in stability of an atom
describe the 2 patterns of EA
down a group, EA decreases
the addition of energy levels means the electrons being added are further away from the nucleus and thus have a weaker force of attraction
right along a period, EA increases
the higher net charge means that there is a greater force of attraction by the valence electrons to the nucleus, causing a higher EA
What is the exception to EA?
Atoms that have half-filled and filled sublevels are already stable
In the case of filled sublevels, energy is actually required to generate a new sublevel for the electron to be added
This means that the amount of energy released is significantly lower or will require energy to be added to force the atom to accept the electron
EN stands for…
electronegativity
what is electronegativity?
a relative scale showing the ability of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons.
describe the 2 patterns of EN
down a group, EN decreases
the addition of energy levels means the electron pair being attracted are further from the nucleus, and so there is a weaker force of attraction
right along a period, EN increases
the sublevels become closer to being filled and “completing their set”,
closer to the nucleus as the net charge increases
What are the 2 ways we can measure electronegativity?
pauling’s scale and van arkel ketelaar triangle
What are the exception to EN?
Xe and Kr, are the only noble gasses with an EN value
pauling scale
relative scale used to measure EN (requires bonds that can be measured)
difference between EN values (ΔEN) to determine the type of bond between 2 atoms
< 0.4, non-polar
0.4-1.7, polar covalent
≥ 1.7. ionic
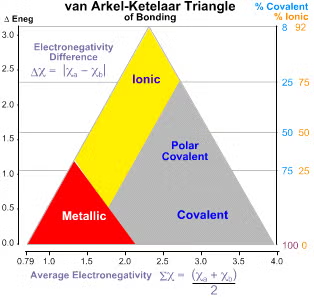
Van arkel ketelaar triangle
another scale that uses EN to determine the type of bond
average and difference EN between 2 atoms
those values are used to find the type of bond on the graph
Coulomb’s law
F = (k q1q2) / d2
F = force of attraction
k = constant
q1 and q2= charges involved (net charge and charge on e-)