MMET 206 - Exam 1 - TAMU - Asadi
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
What are the 4 environmental stressors taken into account when analyzing a product's life cycle?
-Resource and water consumption
-energy consumption over life
-emission of CO2, NOx, SOx, particulates, etc
-toxic residues, acidification, ozone depletion
How much embodied energy in steel?
29 (MJ/Kg)
How much embodied energy in Polyethylene?
80 (MJ/Kg)
6 types of physical material properties
Mechanical
Thermal
Electrical
Magnetic
Optical
Corrosion
Definition of Normal Strain
volume change
Definition of stiffness
measures how well a material can resist the change in length under a normal stress
Definition of Rigidity
Measures how well a material can resist the change in shape under a shear stress
what machine is used to measure stresses in a structure?
Strain Gages
What does an impact test measure?
the energy absorbed by the high strain rate fracture
in an Impact Test, the impact energy absorbed by the sample = ___
change in potential energy
how is a materials resistance to crack propagation determined?
notched bar impact method
viscoelastic materials can transition from ___ state to ___ state
glass sate to rubber state
what does fatigue testing do?
identifies the endurance limit, a stress below which fatigue will not occur
definition of hardness
a mineral's resistance to being scratched/ localized plastic deformation
What are the 4 methods of measuring hardness?
1. Rockwell - depth of penetration
2. Brinell - curved surface area
3. Vickers - projected area
4. Shore durometer -A for rubber/D for hard plastic
definition of bond energy
the amount of energy required to break apart a mole of crystals/ molecules into its component atoms, a measure of bond strength
definition of crystalline materials
made up of a single or multiple crystals
definition of crystal lattice
imaginary skeleton of a crystal structure
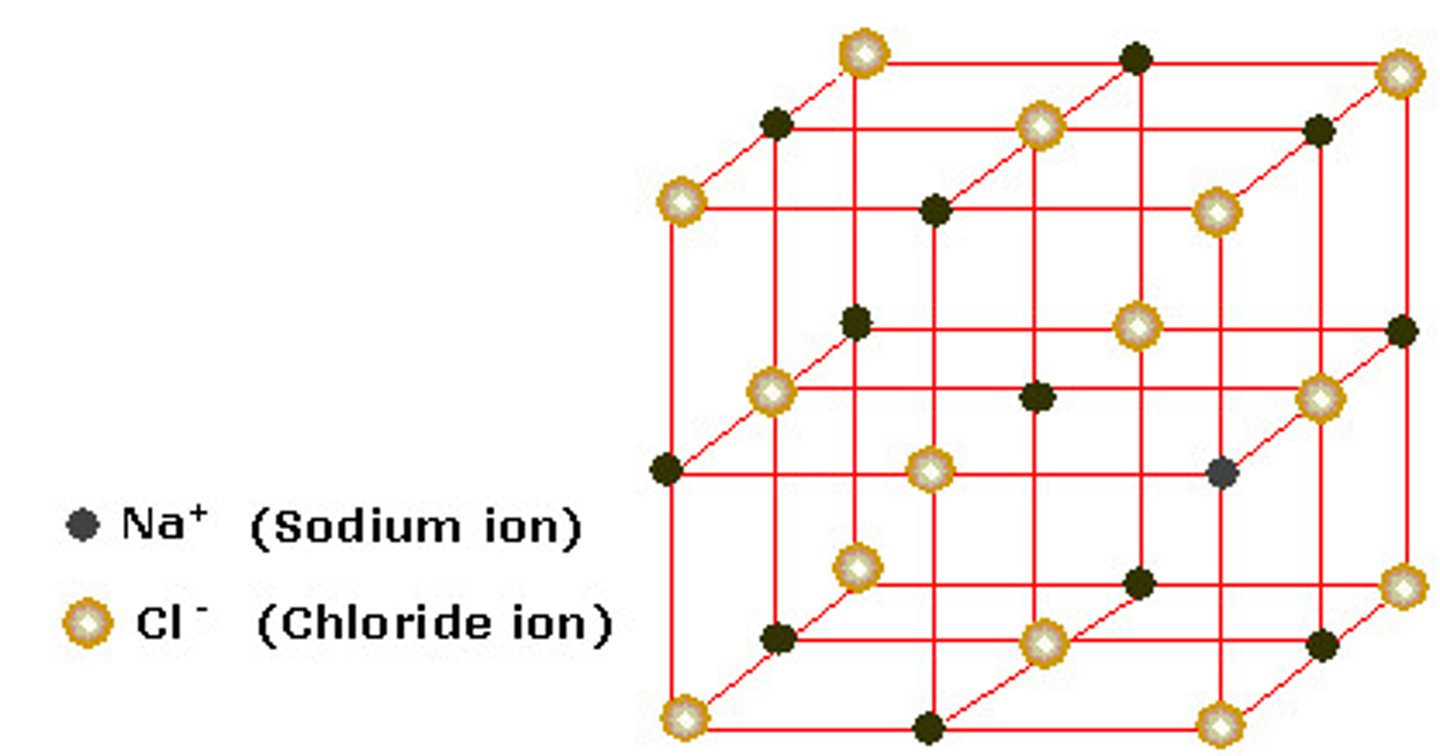
what are the 7 crystal systems?
triclinic
rhombohedral
orthorhombic
monoclinic
cubic
hexagonal
tetragonal
TRUE/FALSE: the hardness of a material depends on its cutting direction
TRUE
What are the 8 allotropes of Carbon?
1) Diamond,
2) Graphite
3) Lonsdaleite
4) C60 (Buckminsterfullerene or buckyball)
5) C540
6) C70
7) Amorphous carbon
8) single-walled carbon nanotube or buckytube
4 examples of things that need single crystalline materials
-Diamond single crystals for abrasives
-Aircraft engine turbine blades (Ni-based superalloy)
-Silicon wafers for IC chips
-Sapphire wafer for LED and optical lenses
Steps for a Product Life-Cycle Assessment
1. Produce a Life-Cycle Inventory for each design
2. Analyze the inputs and outputs for every phase and identify the environmental stressors
3. Add data together for the complete product life cycle and select the design that produces the least amount of environmental stressors
European Union's RoHS restricts the use of the following 6 substances in electrical and electronic equipment
1. Lead
2. Mercury
3. Cadmium
4. Cr^+6
5. & 6. PBB and PBDE (flame retardants)
Apple doesn’t allow PVC
What were the top 4 greenhouse gasses emitted in 2018 and their %'s?
1. Carbon Dioxide - 81%
2. Methane - 10%
3. Nitrous Oxide - 6%
4. Fluorinated Gases - 3%
What are he two sectors that cause the most emissions from energy consumption?
Transportation - 36%
Electricity Generation - 32%
Two main types of material properties
Chemical and Physical
3 mechanical material properties tests
tensile test
impact test
hardness test
Definition of Mechanical Properties
a materials ability to resist various effects caused by mechanical forces/ stresses
What is the Yield Strength and Young's Modulus of steel?
Yield Strength: 250-700 MPa
Young's Modulus: 200 GPa
What is the Yield Strength and Young's Modulus of HDPE (plastic)?
Yield Strength: 26-33 MPa
Young's Modulus: 0.8 GPa
Definition of strain
the materials response to stress
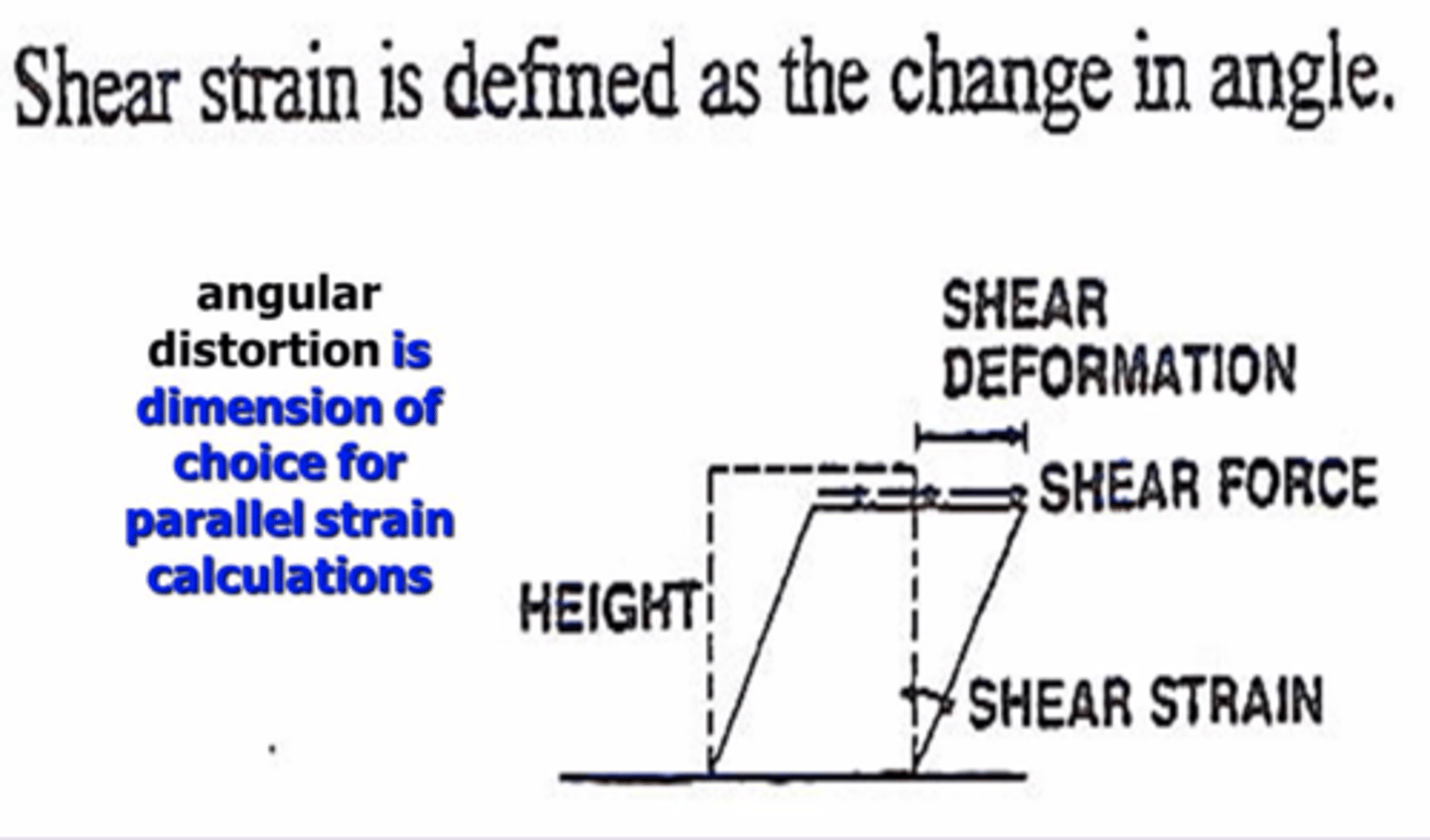
Definition of Shear Strain
shape change
formula for rigidity
rigidity = shear stress/ shear strain
Definition of Ductility
percent elongation at fracture
Ductility formula
(final length - original gage length) / gage length ⋅ 100
definition of deflection
how much a material curves under a load
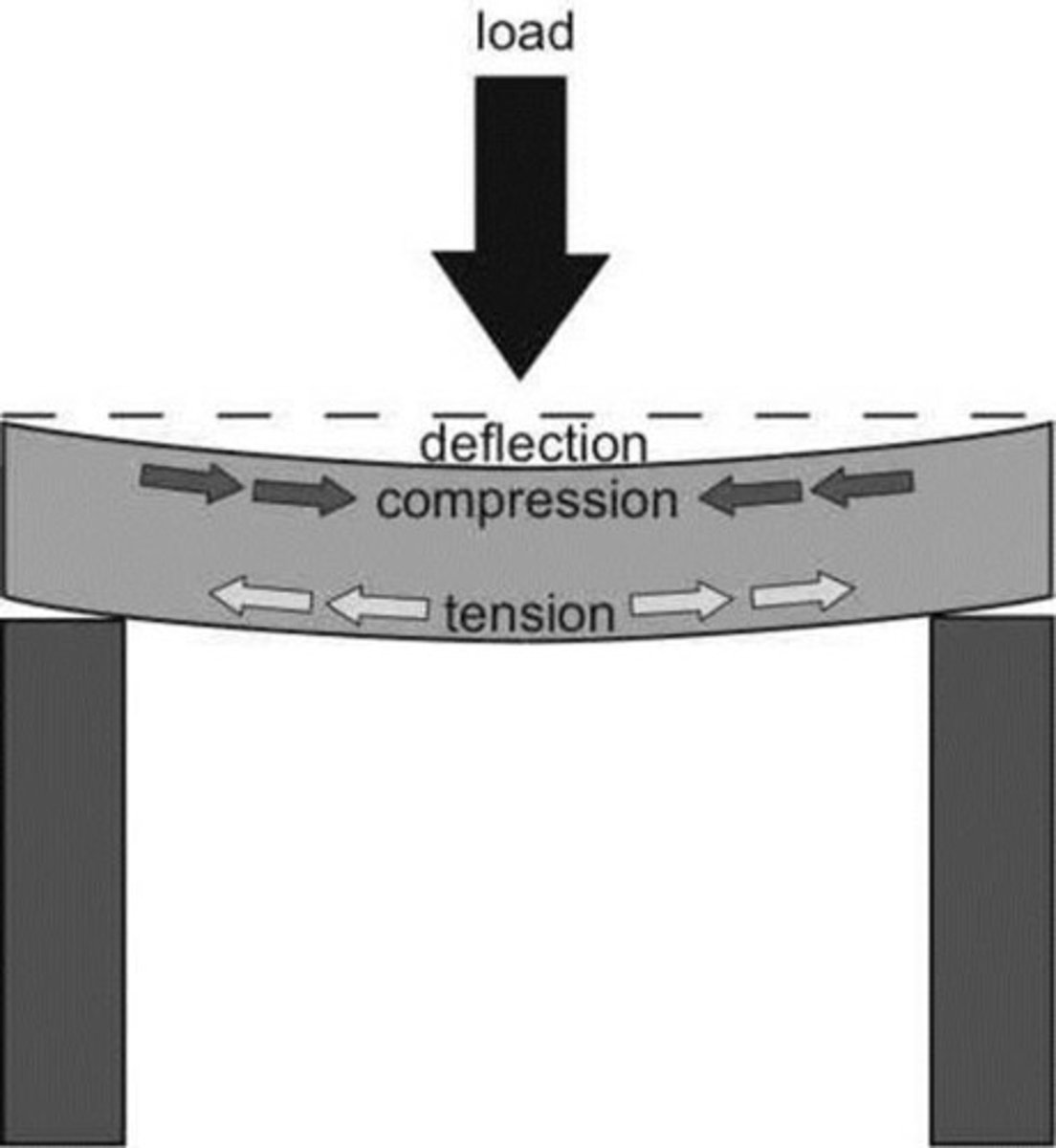
definition of the Modulus of Toughness
The total area under the stress-strain curve to the point of rupture
Toughness is the combination of 2 properties:
strength and ductility
___ temperature = ___ impact energy = ___ ductile
what are two exceptions?
higher temp = higher impact energy = more ductile
exceptions: copper and aluminum
creep is the relationship between:
strain and time
definition of viscoelasticity
a property of materials that exhibits both viscous (liquid) and elastic (solid) characteristics when undergoing deformation
viscoelasticity is unique to ___
polymers
What does a fatigue test generate?
a S-N curve (Stress vs Number of load cycles)
what are the 2 types of shore durometer tests and what materials are they used on?
Shore A for rubber
Shore D for hard plastic
definition of metallic bond
sea of free valance electrons
definition of ionic bond
the attraction between oppositely charged ions (cations and anions)
what are the 2 types of physical bonds?
Van der Waals bonds
Hydrogen bonds
what two materials have both chemical and physical bonds?
polymers and graphite
what are the types of crystalline materials?
1. single crystalline (silicon wafer)
2. poly crystalline (metals, ceramics)
3. semi-crystalline (polymers)
what are the 3 most common unit cell types
BCC
FCC
HPC
unit cell types (7)
triclinic
tetragonal
rhombohedral
monoclinic
cubic
orthorhombic
hexagonal
How are Lattice Directions denoted?
[a b c]
How are the family of equivalent planes denoted?
{a b c}
Definition of Allotropic/ Polytrophic materials
materials which can exist in more than one crystal structure
What are the inputs in a product's life cycle? (3)
Energy
Feedstocks
Transportation
What is Life Cycle Inventory (LCI)
Inputs: raw materials, bulk materials, energy, water
Outputs: products, by products, gas emissions, product waste
After analyzing a products life cycle which design should you select?
The one that produces the least amount of environmental stressors in which carbon footprint is the main target
Definition of Embodied Energy
the energy required to produce raw materials from ores and feedstocks
How does using recycled materials affect the life cycle of a product?
Significantly lowers the embodied energy needed
How much embodied energy in Aluminum Alloys?
200 (MJ/Kg)
How much embodied energy in Concrete?
1.2 (MJ/Kg)
How much embodied energy in Device-Grade Silicon?
~2000 MJ/kg
Recycling requires ___% less energy with aluminum
95%
Recycling requires ___% less energy with steel
33%
Recycling requires ___% less energy with paper
40%
Recycling requires ___% less energy with plastic
90%
Recycling requires ___% less energy with glass
30%
Definition of Carbon Footprint
the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions caused directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, event, or product
Definition of greenhouse gases
Gases that trap and hold heat in the atmosphere and contribute to the greenhouse effect
3 Types of Fossil Fuels
coal, oil, natural gas
95% of CO2 emissions come from
Fossil Fuel Combustion
Where does society burn the most fossil fuels and their %'s
1. Electricity Generation - 42%
2. Transportation - 32%
How do we obtain the historical COs levels?
Atlantic ice cores
How much CO2 will be released to the atmosphere by burning 1 gallon of gasoline?
8.887 Kg or 23-26 kg
Definition of stress
what the material feels inside when there is an external force
What units are used to measure stress?
N/m² and Pascal (Pa)
How to calculate stress
force/area
Direction of Tensile stress
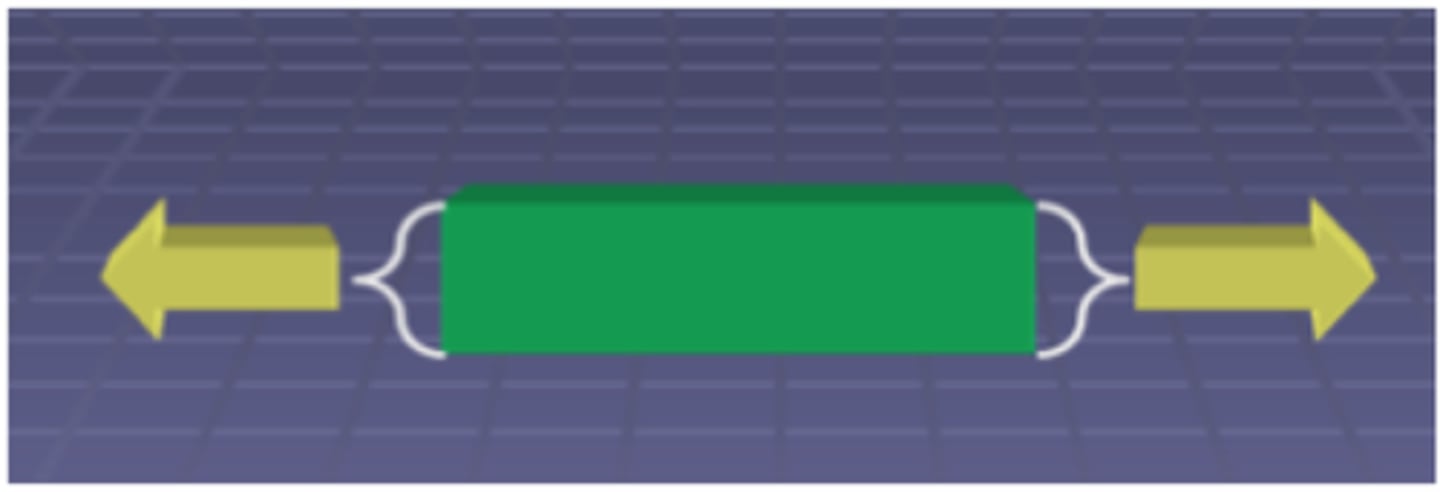

Direction of compressive stress

Definition of Normal Stress and the 2 types
forces are perpendicular to the surface of the material
tensile and compressive
Direction of shear stress
How to calculate normal strain
the change in elongation/original length
Two forms of Normal Strain
longitudinal strain and lateral strain
Definition of Longitudinal strain
The change in length parallel to the stress
(the change in length along the x direction)
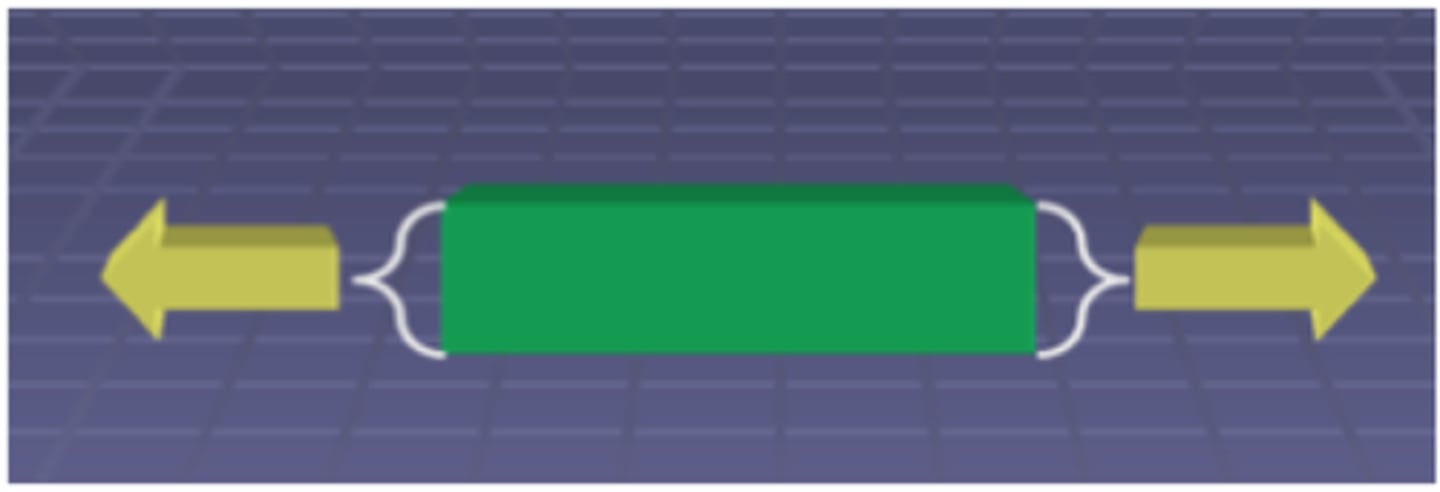

Definition of Lateral strain
The change in length perpendicular to the stress
(the change in length along the y or z direction)
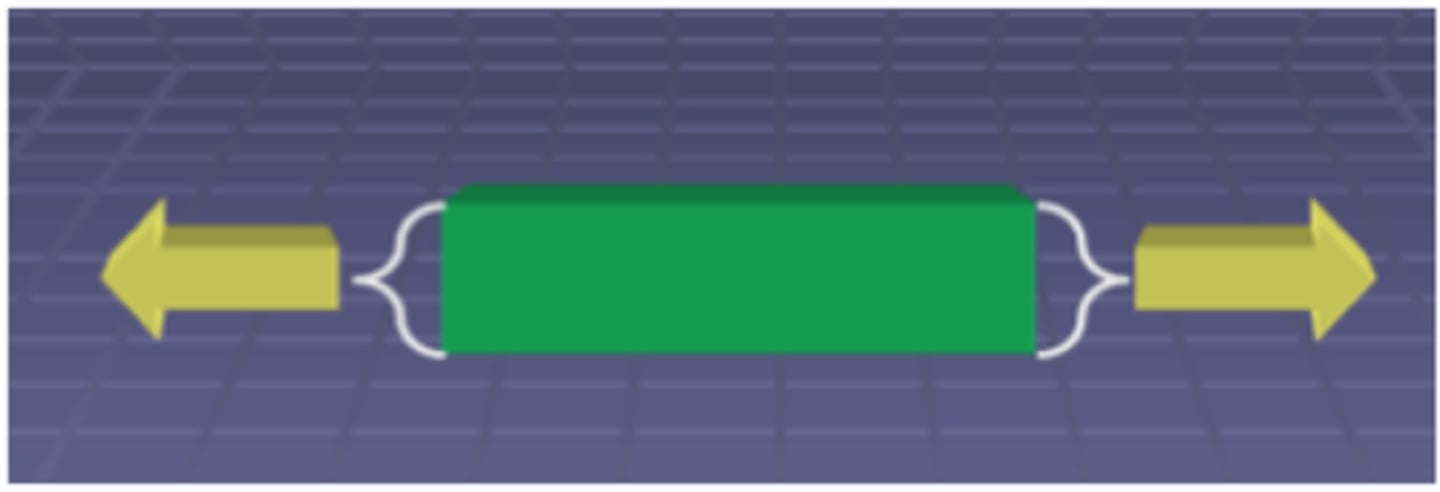

Poisson's Ratio (υ)
-lateral strain/ longitudinal strain
How is Shear Strain measured
an angle in radians
for perfectly incompressible material (materials volume remains constant under load), Poisson's ratio (υ)= __?
0.5
What is the Poisson's Ratio of rubber, steel, glass, cork?
0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 0.0
Definition of Elastic Range
Material will resume its original dimension after load is removed
Definition of Plastic Range
Material has permanent deformation occurs after load is removed
What is the Yield Point
When elastic range ends and plastic range begins
Definition of Tensile Strength
the largest stress a material can bear
You don't want to advertise a material or having more than ___% of its actual Yield Strength or more than ___% of its actual Tensile Strength
no more than 60% of YS
no more than 50% of TS
What is the heart of the Tensile Test Machine?
Load Cell
What is the Elastic Modulus?
The slope of the elastic range of a stress-strain diagram
Formula for stiffness
normal strain/ normal stress
If percent elongation ___ --> Ductile
If percent elongation ___ --> Brittle
>5% --> Ductile
<5% --> Brittle
___ stiff --> ___ brittle
more stiff --> more brittle