Business - 3.2
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
what managers do
planning - setting objectives and analysing etc.
directing - leading and communicating with employees
organising - assembly the human and other resources needed
controlling - reviewing and reporting on business performance
what may planning involve (managers)
setting objectives over which the manager has control or responsibility
gathering and analysing data and producing forecasts and budgets of cash flow, revenue, expenditure and profit (= consumers data like income etc.)
drawing up plans for functional areas like marketing, production, finance and HR
estimate resources necessary for future plans e.g. staff training
contingency planning
plans for unexpected events (must be flexible due to internal and external factors changing them) e.g. fire drills
what does organising involve (managers)
resources needed to fulfil plans will be available in the right quantities at the right time - crucial to be efficient and remain competitive
what does directing involve (managers)
ensuring staff are sufficiently motivated to achieve the targets and goals set - highly motivated employees = more productive (monetary or non-monetary methods)
ensure communication is effective and clear instructions are given e.g. praise
what does controlling involve (managers)
produce financial reports which detail revenue, costs and profits - must then report on performance
monitor employee performance such as productivity, absenteeism and training
monitor social performance like operating in an ethical manner
managers vs leaders
MANAGERS: carefully plan and ensure all the day to day running of the business is carried out effectively to ensure objectives are met
LEADERS: visionaries - not involved in day to day running of the organisation
McGregor’s Theory X
managers will be highly controlling (as believe employees are ‘resources’ which must be exploited
Hard HRM
advantages of Theory X
decisions made quickly as told what to do
more likely to meet deadlines - good in high pressured environments
workers are clear what they need to do
disadvantages of Theory X
high staff turnover - recruitment costs are high
poor relationships between managers and employees
workers may feel ignored
no development or promotion prospects
can be expensive - workers only motivated by money
McGregor’s Theory Y
managers have a much more trusting approach (as thought employees enjoy work) and actively provide opportunities for workers to become involved and take responsibility - delegates
Soft HRM
advantages of Theory Y managers
employees feel valued/listened to
works well where staff need to innovate
less stressful for employees
promotion and development prospects
disadvantages of Theory Y
high trust form which can be taken advantage of
low skilled employees may not find this management style useful
decision making can take time - not useful when emergency
authoritarian management and leadership
wish to retain power and control over workers
lines of communication likely to be one way from top to bottom
dictatorial - formal systems and strict controls
advantages of authoriarian
decisions is quick - deadlines will be met
instructions clear - employees know what to do
good for high risk environments e.g. army
disadvantages of authoritarian
employees cannot use their own initiative - skills not used
no promotion or development prospects
bad for creative jobs or highly educated staff
high staff turnover so recruitment costs high
paternalistic management and leadership
managers consult employees but ultimately resides with the managers alone
will fully explain the reasons for their decision to the staff
regards workforce as a family so welfare of individual workers is paramount
advantages of paternalistic
employees feel valued and motivated
low staff turnover so lower recruitment costs
good for family businesses
disadvantages of paternalistic
staff may feel overlooked
managers are not good at making tough decisions e.g. involving redundancies of staff
democratic management and leadership
consultative - workers are asked to participate fully in decision making
two way communication to provide feedback
decisions based upon majority
advantages of democratic
employees feel valued - increasing motivation as opinions heard
decision making no longer rests on one person as it is collective
lower labour turnover
disadvantages of democratic
employees may lack experience/knowledge necessary
takes time as is a discussion - limitation if emergency
employees may feel annoyed if the decision goes against their wishes
laissez-faire management and leadership
‘hands-off’ approach - minimal input in decision making - left to staff
delegation is essential but little focus or coordination
advantages of laissez faire
employees not micro-managed so less pressure
good where staff are highly educated e.g. solicitors as dealing with their own case load
disadvantages of laissez faire
deadlines may not be met
involves high trust which may be abused
lack of direction for new members of team
not good in emergency situations as no lead
good work not acknowledged
consultative managemet and leadership
consults workers for their opinions and considering their viewpoints
manager ultimately makes the final decision
advantages of consultative
employees feel valued/listened to
decision making improved as alternate viewpoints
labour turnover lower
disadvantages of consultative
time consuming
doesn’t work well where employees are low skilled etc.
may resent the fact managers make final decision - over-ruled
Tannebaum-Scmidt continuum
autocratic → paternalistic → consultative → democratic → laissez faire
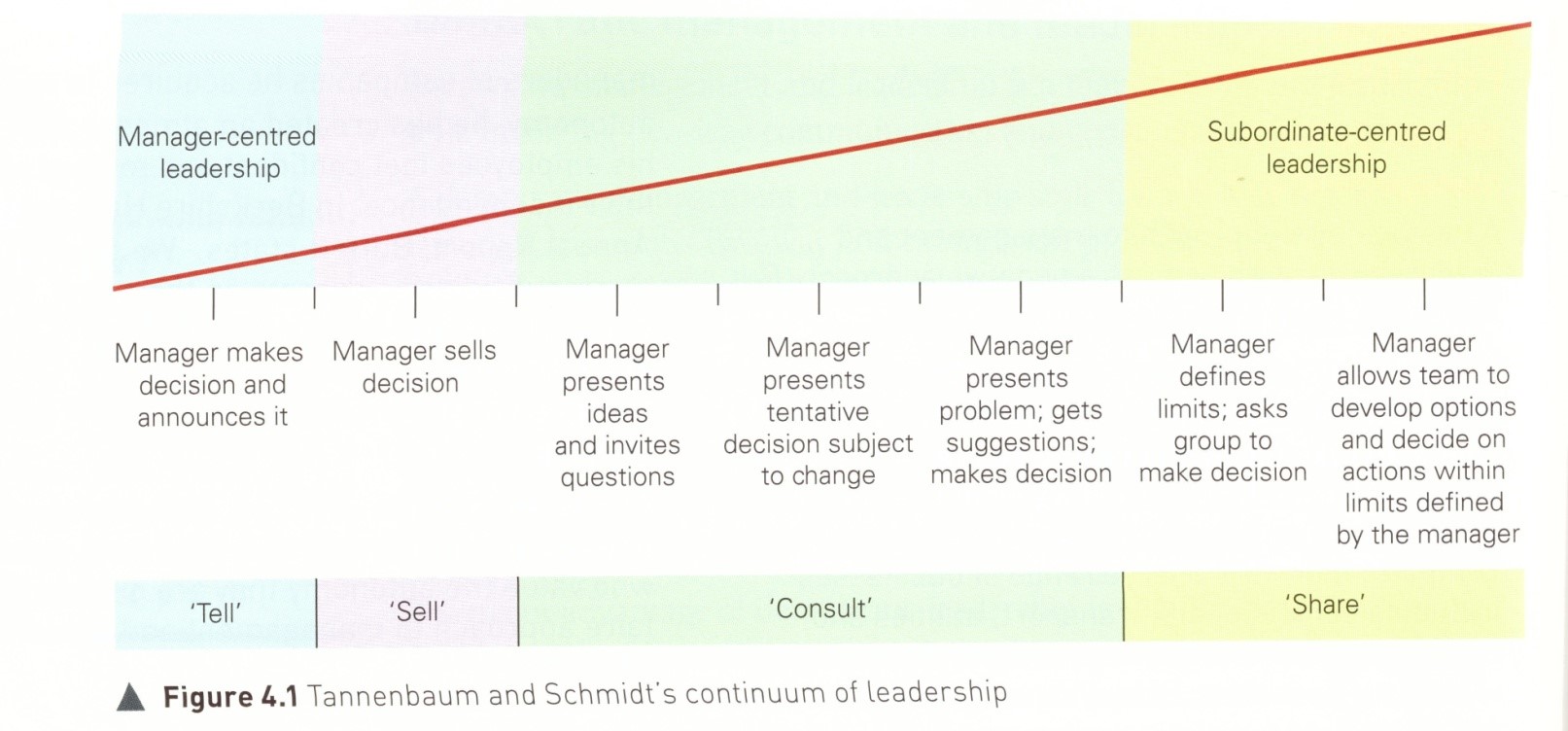
LEVEL 1 (Tannebaum-Schmidt continuum)
team play no active role in decision making and the manager expects the team to carry out their instructions (‘TELL’ - manager makes the decision)
effective when team may be new/inexperienced
LEVEL 2 (Tannebaum-Schmidt continuum)
‘SELL’ - Manager makes the decision and then explains/sells it to the team so benefits from thoughts of workers but manager in control
LEVEL 3 (Tannebaum-Schmidt continuum)
‘CONSULT’ - Manager makes decision and then invites questions so can discuss rationale and listen to subordinates which provides opportunities for staff to participate
LEVEL 4 (Tannebaum-Schmidt continuum)
‘CONSULT’ - manager suggests provisional decision and then invites discussion and then manager makes final decision - team influence decision and so feel more valued and listened to
LEVEL 5 (Tannebaum-Schmidt continuum)
‘CONSULT’ - manager presents problem and then consults with team and then make decision - team have higher level of influence so useful if experienced and have detailed knowledge
LEVEL 6 (Tannebaum-Schmidt continuum)
‘SHARES’ - manager explains situation and so shares the decision making - delegated responsibility but still has some control as set limitations - team has more freedom but manager may still have the final decision
LEVEL 7 (Tannebaum-Schmidt continuum)
‘SHARES’ - allows the team to identify the problem, develop options and make decisions with no limits - team must be experienced and skilled but manager supports and helps implement decision made
How does company structure and span of control influence management and leadership styles?
tall structure = more likely to be centralised, control is high and more likely to be autocratic (flat structure = opposite)
narrow span of control = more likely to rest decision making with manager rather than subordinates (wide span = opposite)
How do external factors influence management and leadership styles?
rival firms attempting to take over, natural disaster or dangerous faults etc. = authoritarian, task orientated decision making is required
situation is stable + well trained and experienced staff = democratic styles
How does culture influence management and leadership styles?
‘way things are done’ - if staff used to autocratic styles then another approach may not be welcome
hard to impose different styles of management
How does the nature of the task influence management and leadership styles?
complex/simple/urgent/optional etc.
e.g. extremely high risk environment = more likely autocratic styles
How do the employees (+ their skills) influence management and leadership styles?
more skilled and experienced = more independence they may want = more democratic styles
How does the group size influence management and leadership styles?
if the team is large, unskilled and inexperienced = more authoritarian
How do managers (skills/personality) influence management and leadership styles?
if poor interpersonal skills = more autocratic and task focused
How does time frame influence management and leadership styles?
emergency situation = authoritarian style of management as may be effective to ensure all staff remain focused and complete task to deadline
Stages important to decision making
setting objective - shows success
gathering + interpreting information - includes costs + revenue + adv + disadv of alternative decisions (helped by technology)
implementing the decision - allocate resources
reviewing - assess effectiveness to improve future decisions
programmed decisions
deal with familiar problems and the information required to make these decisions is readily available (usually have established rules/procedures/practices) e.g. placing a repeat order
non-programmed decisions
deal with unfamiliar situations which are unstructured, requiring unique solutions (may be risky and require a great deal of expertise)
strategic decisions
what the business is going to do - involves major commitment of resources and the risks are high (made by senior managers and generally over the longer term)
tactical decisions
how the business is going to achieve it - involve fewer resources and can simply involve reordering stock etc. so carried out by lower/middle management
strategic plans
ensure long-term effectiveness and growth (usually two or more years and primarily done by top management)
tactical plans
used as a means of implementing strategic plan over a short-term (primarily done be middle management)
opportunity cost
the benefit foregone by not choosing the next best alternative course of actions
quantitative decision making
involves numbers and structured information (scientific decision making)
data gathered from the internet, customer surveys business records etc.
e.g. the Nectar card - shows purchasing habits
benefits of quantitative decision making
useful when data is available and not too expensive to collect and analyse
limitations of quantitative decision making
not all data is reliable e.g. hard to gather views on unfamiliar products
qualitative decision making
where managers base their decision on a hunch/intuition which is off of opinion and experience
benefits of qualitative decision making
appropriate if not available or inaccurate and may catch customer attention
limitations of qualitative decision making
may be insufficient time to gather and analyse data and decisions involving the selection of business partner may be based on personality
decision trees
a mathematical model which can be used by managers to help them make the right decision
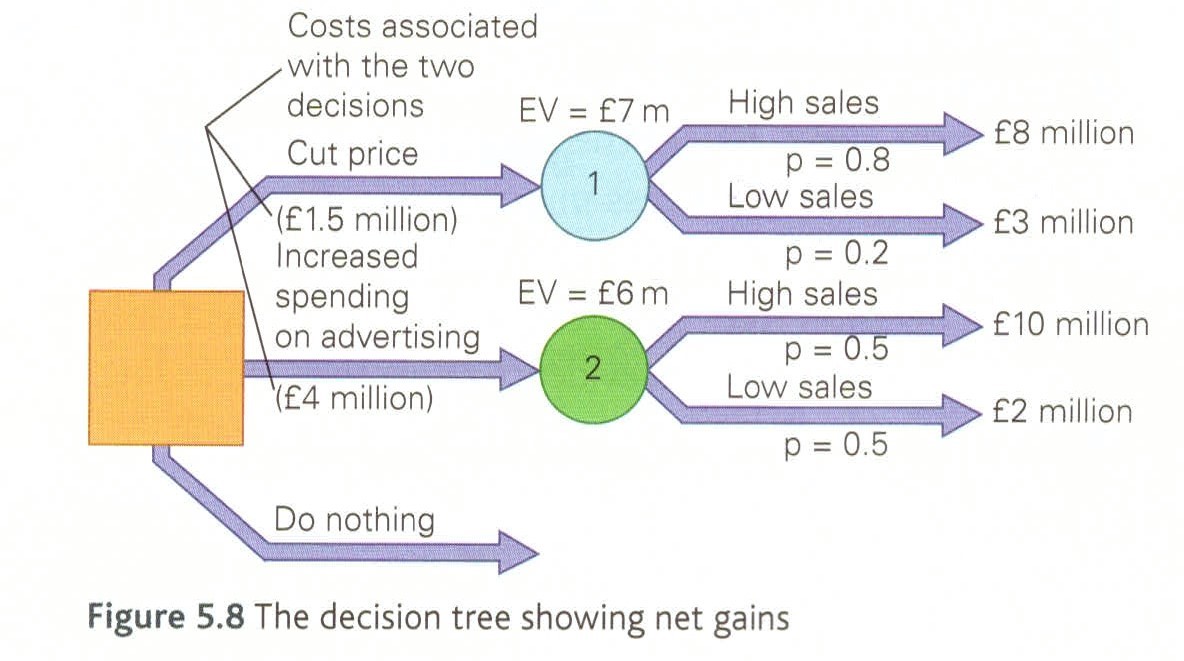
expected value
probability x income generated
net gain
expected value - cots associated
advantages of decision trees
makes manages think about the different options available
may result in a more logical and less rushed process based on evidence rather than gut feeling
forces the manager to quantify the impact of each decision considering the forecast costs, benefits and profitability's of events
disadvantages of decision trees
only includes financial and quantifiable data
use estimates of the profitability of different outcomes and their financial consequences and so value of analaysis depends on this
estimates making them open to manipulation by managers determined to achieve the desired outcome
not effective when broad range of possible outcomes or cannot be easily quantified
less useful for non-programmed or strategic decisions where it is unfamiliar
How do objectives influence decision making?
mission sets out broad purpose so decisions must follow this + must help achieve objectives in specified time scales
How do ethics influence decision making?
do what is morally right and don’t simply choose a course of action which maximises profits - may attract bad publicity
How does risk influence decision making?
non-programmed decisions are high risk and so managers may want to limit these by gathering data and analysing results whereas low risk programmable decisions are more likely to be done quickly
How does the external environment influence decision making?
includes competition, consumers’ income, interest rates, demographic factors and environmental issues which can all increase uncertainty so may delay until situation improves
How do resource constraints influence decision making?
all decisions need resources like time, labour, money and equipment so must ensure these are available
if huge financial risk - manager more likely to take time analysing the correct decision
stakeholders
individuals or groups within society who have an interest in the organisation’s operation and performance e.g. local communities, suppliers, government agencies, shareholders, employees, customers
primary stakeholders
individuals or groups that are affected by a particular business activity e.g. suppliers, customers, employees
secondary stakeholders
groups of individuals or organisations with an indirect functional or financial relationship with the business e.g. local communities
internal stakeholders
those who are considered to be part of the organisation e.g. managers, employees, shareholders
stakeholder map
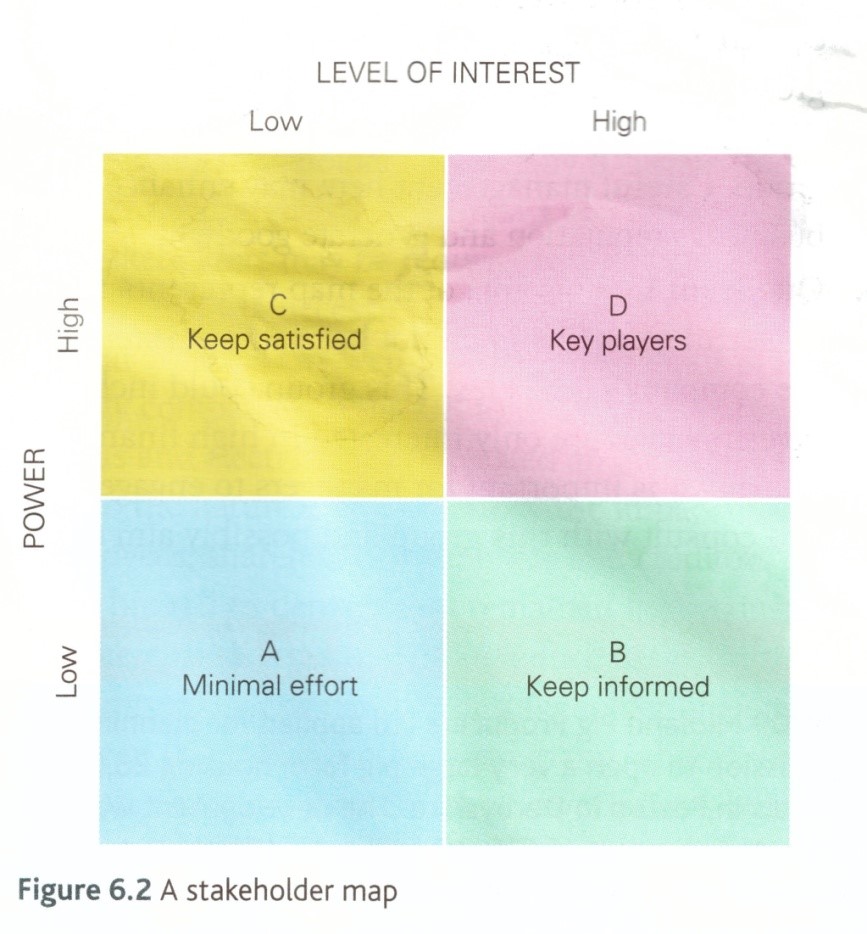
stakeholder mapping uses
help managers consider which stakeholders will be affected by a decision made and then how to address these needs
allows the manager to consider whether or not certain stakeholders need to be consulted or involved in the decision making process itself
STAGE A of stakeholder mapping
minimal effort (LOW INTEREST, LOW POWER) → not powerful meaning managers do not have to worry about this group and only need to update stakeholders using general communications like company website
STAGE B of stakeholder mapping
keep informed (HIGH INTEREST, LOW POWER) → e.g. local communities → managers only need to keep this group informed but careful management may enhance reputation
STAGE C of stakeholder mapping
keep satisfied (LOW INTEREST, HIGH POWER) → e.g. institutional shareholders → managers must enhance and consult to try increase interest, generate positive publicity and gain their different perspectives and expertise
STAGE D of stakeholder mapping
key players (HIGH INTEREST, HIGH POWER) → e.g. key managers → must be consulted and involved in discussions as have the power to directly influence the outcomes of decisions
How do business objectives influence relationships with stakeholders?
e.g. a company committed to pursuing ethical or social objectives would give a high priority to meeting the objectives of as many stakeholders as possible whereas one that focuses on maximising profits may drive to minimise costs which would result in outsourcing production, upsetting employees etc.
How do management and leadership styles influence relationships with stakeholders?
autocratic = unlikely to consider the needs of employees when making decisions and unlikely to foster good relationships with the local community
democratic = likely to receive more support from employees as open two-way communication
How does size and ownership of the business influence relationships with stakeholders?
small businesses = easier to communicate and involve stakeholders in decisions as fewer of them (sole traders)
large businesses (PLCs) = different relationships which if upset, may lead to a poor reputation
How do market conditions influence relationships with stakeholders?
the potential for growth may mean businesses deliberately opt to engage more with customers, employees etc. to gain a competitive advantage and improve reputation
dominant businesses may also be able to exploit businesses by high prices e.g. the big 6 suppliers of gas + electricity and suppliers by threatening withdrawal of their custom
How does the power of stakeholder groups influence relationships with stakeholders?
influence activities and success of a business e.g.
large shareholders may make managers consider the outcomes of decisions more
actively seek to avoid becoming too reliant on a certain customer or supplier for fear that could gain too much influence
How do government policies influence relationships with stakeholders?
uses laws and less formal codes of conduct to ensure relationships wit stakeholders are as harmonious as possible e.g. during privatisation made customers weren’t overcharged
stakeholder engagement advantages
may reduce stakeholder conflict through managers effectively communicating and involving stakeholders in decision making (use stakeholder mapping)
partnership as a way of stakeholder management
involves the stakeholder group in decision making (sharing responsibility) meaning a high amount of two-way communication - most suitable for stakeholders that have high volume of resources
participation as a way of stakeholder management
stakeholders part of the relevant team in decision making and have responsibility to implement that part of a decision or activity - suitable for high power, low interest and high power, high interest
consultation as a way of stakeholder management
finding out the views of the relevant stakeholder groups within guidelines set by the business - expected to respond to questions but have limited power to influence decisions
push communication as a way of stakeholder management
one way communication from the business to the relevant stakeholder groups through emails, podcasts, letters etc.
pull communication as a way of stakeholder mapping
the business communicates with the stakeholder groups only if they choose to communicate with the business e.g. may have details of stakeholders on their database and ‘pull’ info out of system and send letters etc. to them but requires stakeholders to reply