Anaphy Heart and Endocrine
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
patayan na
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Hormones
chemical messengers secreted in small amounts into the extracellular fluid.
Hormones
diffuse into the blood to be transported to their target.
Target tissues or effectors
Hormones circulate through the bloodstream to specific sites called what?
Endocrine
Derived from the Greek words endo, meaning "within," and krino, "to secrete."
Exocrine Glands
Have ducts that carry their secretions to the outside of the body, or into a hollow organ, such as the stomach or intestines.
Endocrinology
The study of the endocrine system.
40 trillion
The body maintains homeostasis by coordinating the activities of nearly how many cells?
Chemical messengers
allow cells to communicate and regulate body activities
Gland
An organ consisting of epithelial cells that specialize in secretion
Autocrine chemical messengers
Stimulates the cell that originally secreted it, influences the activity of the same cell or cell type from which it was secreted
Autocrine
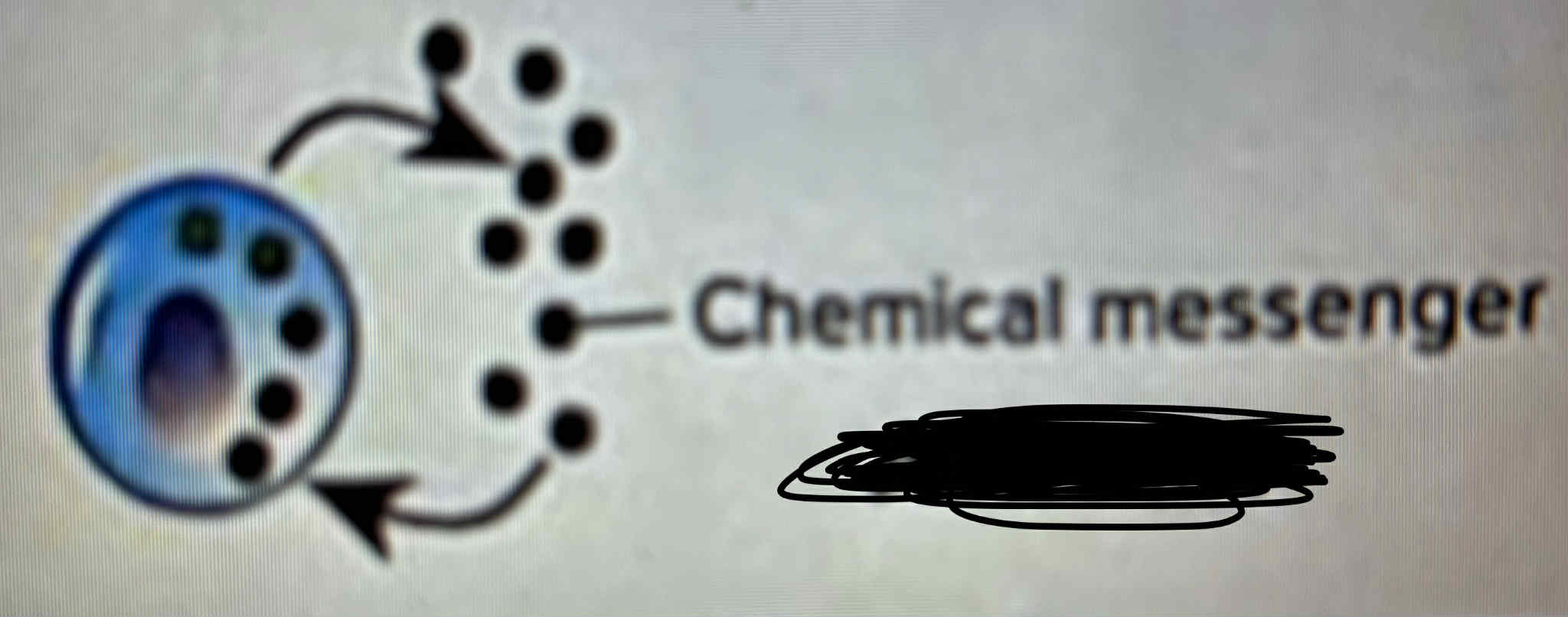
what type of chemical messenger is shown in the picture
Paracrine Chemical Messengers
acts locally in neighbouring cells, secreted into extracellular fluid and affects surrounding cells, has a localized effect on other tissues
Paracrine
what type of chemical messenger is shown in the picture
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers secreted by neurons that activate an adjacent cell. May activate another neuron, muscle cell, or grandular cell. Secreted into a synaptic cleft instead of the blood stream and is technically a paracrine chemical messenger but treated as a separate categoryw
neurotransmitters
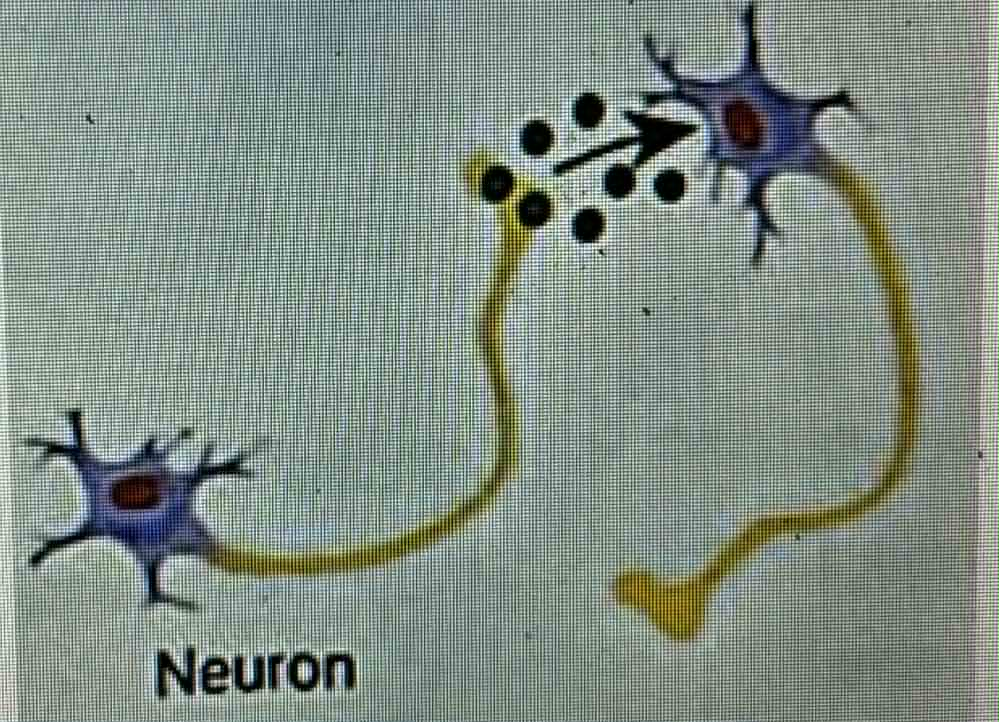
what type of chemical messenger is shown in the photo
Endocrine chemical messengers
secreted into the bloodstream by certain glands and cells, these messengers travel through the blood to their target cells
endocrine
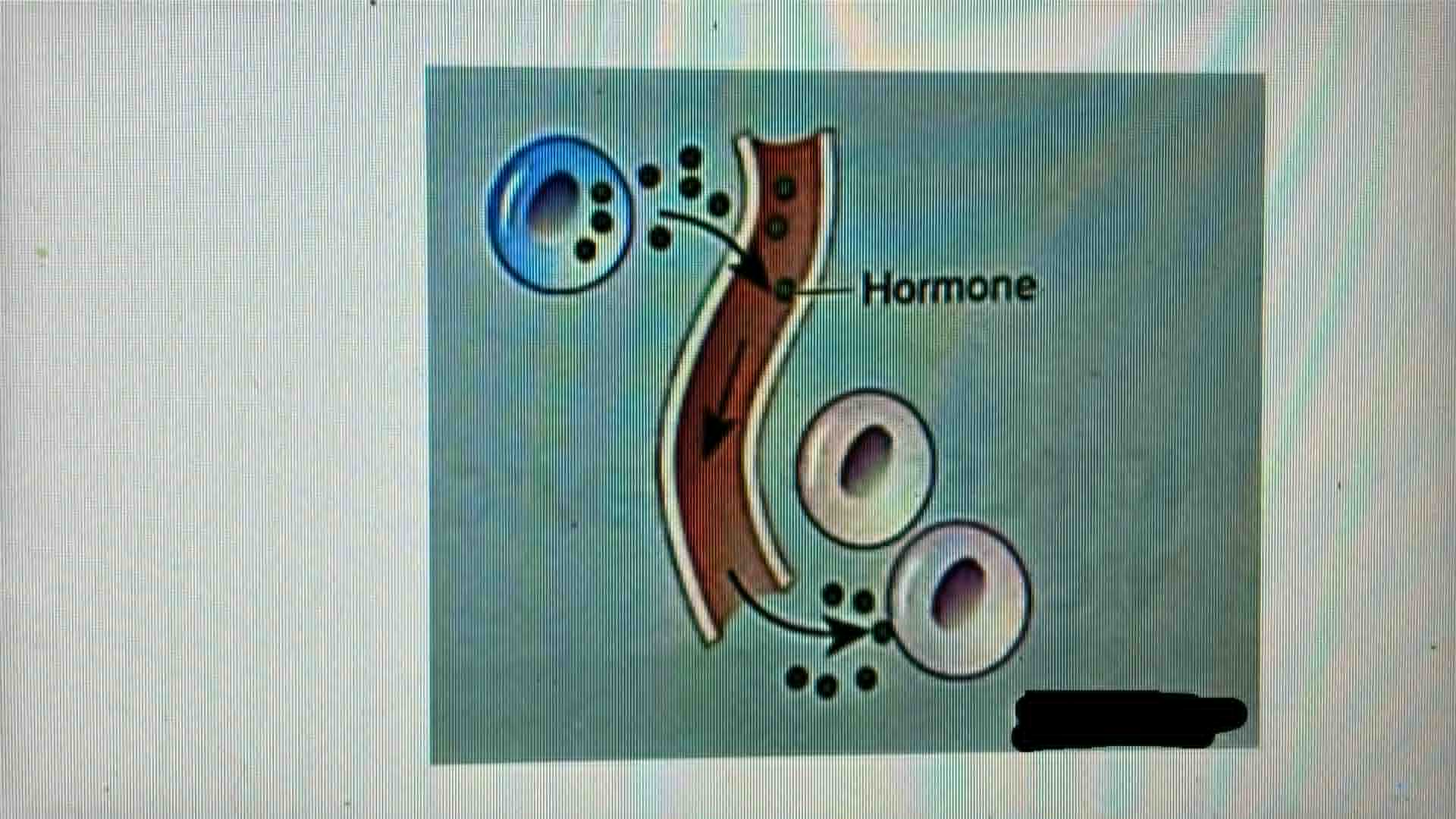
what type of chemical messenger are shown in the photo
endocrine and nervous system
two most important control systems of the body
Humoral, neural, or hormonal stimuli
hormones of the endocrine system are secreted in response to _______, _______ and _____ to reegulate homeostasis
hypersecretion or hyposecretion
many disorders are caused by either these two secretions of homones
regulation of metabolism
controls the rate of nutrient utilization and energy production
control of food intake and digestion
regulates the level of satiation and the break down of food into individual nutrients
modulation of tissue development
influences the development of tissues such as those of the nervous system
regulation of ion levels
help monitor blood pH, as well as Na+, K+ and Ca2+ concentrations in the blood
control of water balance
regulates water balance by controlling the solute concentration of the blood and membrane permeability
regulation of cardiovascular functions
helps regulate the heart rate and blood pressure and prepare the body for physical activity
control of blood glucose and other nutrients
regulates the level of glucose and other nutrients in the blood
control of blood glucose and other nutrients
regulates the levels of glucose and other nutrients in the blood
control of reproductive functions
controls the development and functions of the reproductive systems in males and females
stimulation of uterine contractions and milk release
regulates uterine contractions during delivery and stimulates milk release from the breasts in lactating females
modulation of immune systems function
helps control the production of immune cells
Lipid-soluble and water-soluble hormones
two chemical categories of hormones
cell membrane
excludes most water soluble molecules but allows lipid soluble molecules to pass through
steroid hormones and thyroid hormones
two categories of hormones based on chemical structure
Steroid hormones
Derived from cholesterol
Thyroid hormones
derived from the amino acid tyrosine
amino acid derivatives, peptides, or proteins
what are the other hormones categorized as
Lipid-soluble hormones
nonpolar molecules
steroid, thyroid, fatty acid derivative hormones
hormones included in lipid-soluble hormones
small size and low solubility in aqueous fluids
What characteristics do unprotected lipid-soluble hormones have that make them easily removed from the blood
breakdown by enzymes, excretion into urine,
twomechanisms that could result in the removal of unprotected lipid-soluble hormones from the body
excreted in urine or in bile
what happens to the hormones that are degraded in the blood
binding proteins
proteins that chaperon lipid-soluble hormones in the blood stream
binding proteins
reduce the rate of degradation or removal from the blood
a few days to several weeks
life span of lipid-soluble hormones in the blood
water-soluble hormones
polar molecules
protein hormones, peptide hormones, and most acid derivative hormones
what hormones are included in water-soluble hormones
humoral
refers to body fluids, including blood
neural
neurons release a neurotransmitter into the synapse with the cell that produce hormone
hormonal
when another hormone controls the release of another hormone
humoral inhibition
generally involves the actions of companion hormones
negative feedback mechanism
hormone’s secretion is inhibited by the hormone itself once blood levels have reached a certain point
positive feedback mechanism
amplifies feedback until the wanted results are given
tropic hormones
hormones that stimulate the secretion
releasing hormones
hormones that travel in the blood to the anterior pituitary gland
inhibition by humoral stimuli
to raise blood pressure, the adrenal cortex secretes aldosterone in response to low blood pressure.
Atrial Natriuretic peptide
hormone that lowers blood pressure
Aldosterone and ANH
works together to maintain homeostasis of blood pressure
Inhibition by hormonal stimuli
Hormones from the hypothalamus that prevent secretion of tropic hormones from the anterior pituitary gland are an example of?
Inhibiting hormones
hormones that prevent the secretion of tropic hormones from the anterior pituitary
thyroid hormones
can control their own blood levels by inhibiting their anterior pituitary tropic hormone
Receptors
proteins that bind specific hormones to initiate a cellular response
receptor site
the binding region on a receptor molecule for a specific hormone
Specificity
a selective binding of a hormone to its matching receptor
nuclear receptors
receptors located in the nucleus or cytoplasm that regulate gene transcription
Membrane-bound receptors
proteins that span the cell membrane with hormone-binding sites exposed to the outer surface
Lipid-soluble hormones
primarily stimulate protein synthesis
Simple diffusion
how does most steroid hormones enter their target cells
Transport proteins
how do thyroid cells enter their target cells
testosterone
stimulates synthesis of proteins responsible for male sexual characteristics
Aldosterone
stimulates kidney cells to synthesize protein that increase Na+ and K+
Thyroid hormones and Vitamin D
other hormones using nuclear receptor mechanisms
hormone response element
specific nucleotide sequences in DNA recognized by receptor projections
Membrane-bound receptors
these receptors activate responses in two ways. By altering the activity of G proteins at the inner surface of the membrane or by directly altering the activity of intracellular enzymes
Second messengers
molecules produced inside a cell once a hormone or chemical messenger binds to certain membrane-bound receptors
second-messenger system
a mechanism where the second messenger, not the hormone itself, activates the cellular response
Cyclic Adenosine monosphate
is a common second messenger
G proteins
many membrane-bound receptors act through what?
Alpha, Beta, and Gamma
what are the three subunits of G proteins called? from smallest to largest
Guanine nucleutides
what is one of the sub units of g proteins bind to
Adenylate cyclase
enzyme that converts ATP to cAMP
protein kinases
enzymes that regulate the activity of other enzymes
Phosphodiesterase
enzyme that breaks down cAMP to AMP
Signal Amplification
hormones that stimulate the synthesis of second messengers act quickly and have an amplification effect
membrane-bound receptors
ideal for fast responses such as fight or flight response
nuclear receptors
suited for long-term processes such as pregnancy maintenance
Heart at rest, Atria stimulated, atria contract, ventricles stimulated, ventricles contract
what is the coordination of stimulation and contraction of the heart
pacemaker potential
changes in membrane permeability are responsible for producing action potentials and is called what?
depolarization phase
Na+ and Ca2+ voltage-gated channels open
Plateau phase
Na+ channels close, Some K Channels open, and Ca2+ channels remain open
Repolarization phase
K+ channels are open and Ca2+ channels close
Plasma 55%, formed elements - 45%
Composition of blood
Water 91% Protein 7%
composition of liquid matrix in blood or plasma
composition of blood cells and cell fragments