3.4.2 DNA + protein synthesis
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Where does transcription occur?
In the nucleus
What does transcription involve?
‘Rewriting’ part of the DNA code into a strand of messenger DNA
Explain what happens in transcription
Relevant section of DNA molecule uncoils + two strands are separated → H-bonds are broken by DNA helicase
One of these strands acts as a template → individual RNA nucleotides line up alongside DNA nucleotide bases on template strand by complementary base pairing
Uracil (RNA) pairs with adenine (DNA)
Individual RNA nucleotides joined by RNA polymerase with phosphodiester bonds → form a polynucleotide strand of mRNA
Two strands of DNA in nucleus will join back together / recoils once mRNA is produced
In eukaryotes, DNA of a gene is made up of both ___ and ___
exons + introns
What are introns + exons?
Exons → sections of the gene that code for the polypeptide
Introns → sections of the gene that don’t
What is pre-mRNA?
The mRNA formed during transcription using DNA, containing both exons + introns
What is splicing of pre-mRNA?
The removal of introns + the joining together of the exons to form mRNA
Where does splicing not occur + why?
In prokaryotes → their DNA doesn’t contain introns
Where does the spliced mRNA strand go?
Leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pore + attaches to a ribosome in the cytoplasm where translation occurs
During translation, what does the sequence of codons on the mRNA used to determine?
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide → carried out by ribosomes in the cytoplasm
In the cytoplasm, how many different types of tRNA is there?
20 different types → a specific type for each of the 20 amino acids
Explain what happens in translation
mRNA binds to a ribosome in the cytoplasm
each tRNA molecule has an anticodon consisting of 3 exposed bases
a tRNA molecule with the complementary anticodon base sequence binds to the first codon on the mRNA strand at ribosome → ribosome has 2 binding sites so 2 tRNA molecules will bind to 2 codons
amino acids on first tRNA molecule joins to amino acid on second tRNA molecule by a peptide bond in a condensation reaction → requires hydrolysis of ATP to release energy + enzyme that’s part of ribosome
first tRNA molecule moves away from ribosome, leaving amino acid behind → collects another amino acid from ‘amino acid pool’ in cytoplasm
ribosome moves along mRNA + other tRNA molecules join in the order determined by the mRNA codons
process continues along mRNA strand until all codons have been ‘read’ up to the stop codon + specific polypeptide is produced
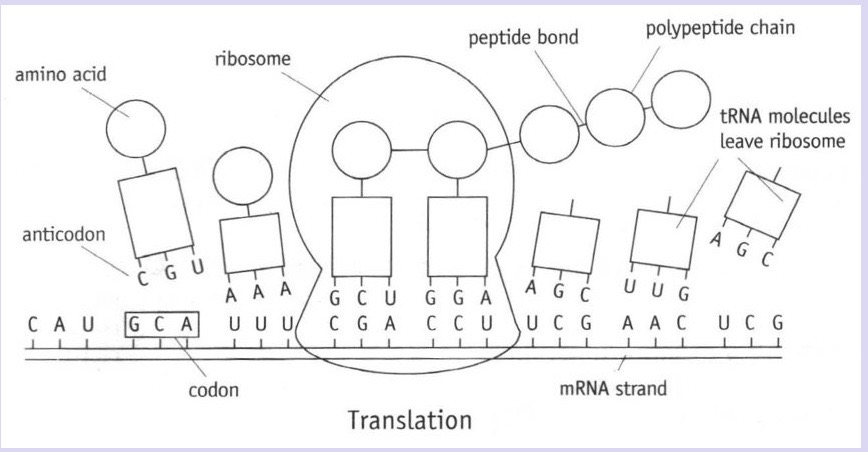
The polypeptide folds itself into its…
secondary + tertiary structure
What ultimately determines which specific polypeptide is produced + why?
Sequence of DNA nucleotides → mRNA strand is transcribed from this DNA template strand