Tissues and Epithelial Reading and Interpretation
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
skeletal muscle
voluntary movement that produces heat and protects organs, it is attached to bones and around entrance points of the body (i.e. mouth and anus)
cardiac muscle
contracts to pump blood, found in heart
smooth muscle
involuntary and natural movement, moves food, respiration, secretion, contracts to help artery flow, it lines the walls of many organs and passage ways
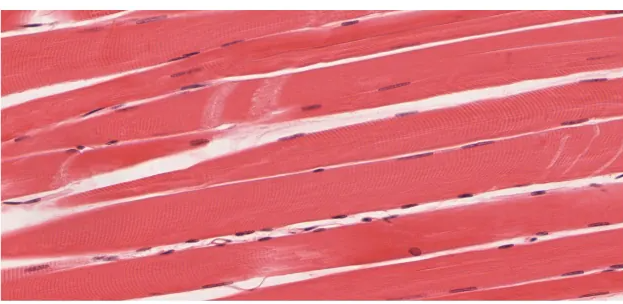
skeletal muscle appearance
stripes, long and cylindrical, peripherally located nuclei
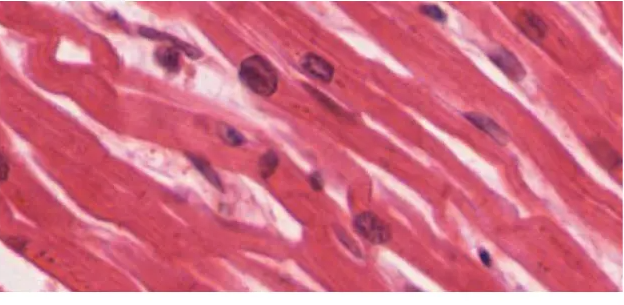
cardiac muscle appearance
short, single central nucleus, branched, straited
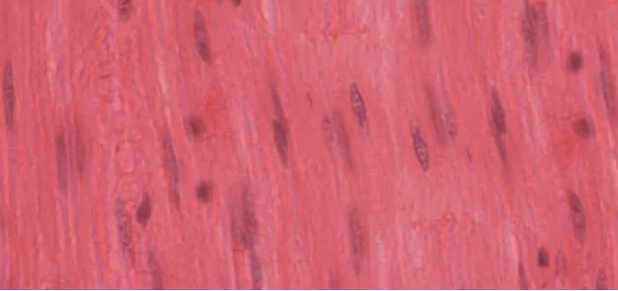
smooth muscle appearance
appears smear like, single nucleus in each fiber
Why is epithelial tissue important?
helps PROTECT and line major organs or passageway, protection from wear or tear
helps with ABSORPTION/PERMEABILITY and SECRETION
helps with nerves SENSORY reception
helps with EXCRETION (illuminating waste)
cell junction/tight junction
connection between cell membranes, help prevent leakage of fluid in simple columnar cells
these type of junctions help prevent leakage of intestinal contents
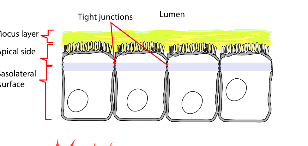
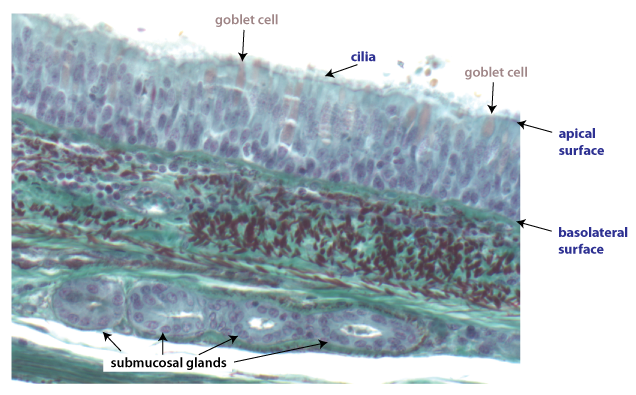
apical membrane
the facing surface of the cell towards the lumen (white space), it can also be found right beneath cilia
basal lamina
part of the tissue that is closer towards underlying body structures (is very thin and can be viewed under microscope apart of basement membrane)
basal membrane
helps hold all tissue and cell together by providing support
reticular lamina
basal lamina is attached to this
What are the four ways to define the layers of an epithelial cell/tissue?
single, psuedostratified, transitional, or stratified
single layered/single
there is only one layer visible and present
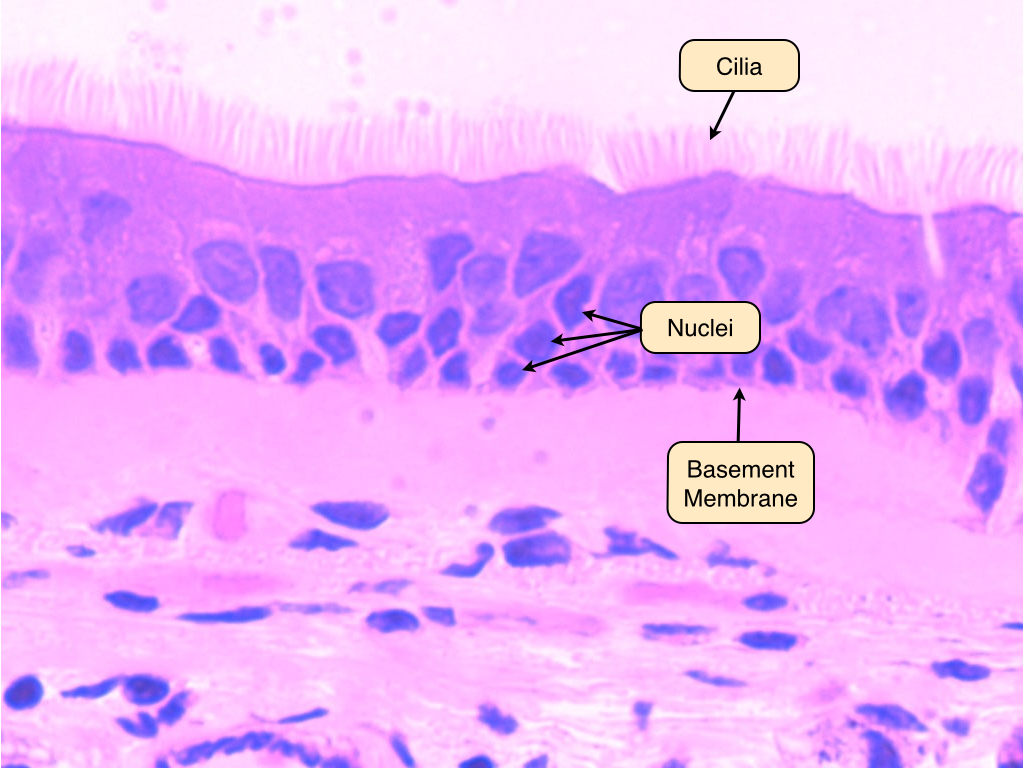
psuedostratified
there is only one layer present, but it appears to have more than one layer because the layers can be irregularly shaped and different sized
stratified
there are MORE than one layer visible and present
transitional
this is only the epithelium cells of the urinary bladder, but there is changing or a variety of layers in different sections visible and present
What are three different ways to identify shape of epithelium cells?
Squamous, cuboidal, and columnar
Squamous
the appearance on thin scales or squished cell membranes, they can look stretched out at times horizontally, have flat nuclei
Cuboidal
relatively equal cell membrane vertically and horizontally, normally rounded nuclei
Columnar
stretched out VERTICALLY, the nuclei are elongated vertically and located on basal side of the cell
Endocrine/EN Glands
think of the endocrine system that SECRETE hormones from endocrine glands
secrete in BLOODSTREAM
helps coordinate the regulation and integration of body responses
Examples of Endocrine Glands
anterior pituitary, thymus, and adrenal cortex
Exocrine/EX Glands
these glands RELEASE into DUCTS that lead to epithelial surface
secretions into lumen of gastrointestinal tract located outside of the body
Example of Exocrine Glands
Mucous, sweat, saliva, breast milk
Technically lumen of gastrointestinal tract
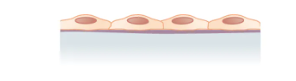
What is the layer and shape of this epithelium?
Simple (one layer) Squamous (squished appearance/squished nucleus)
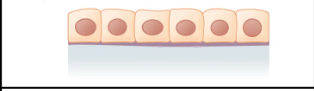
What is the layer and shape of this epithelium?
Simple (one layer) cuboidal (rounded nucleus, more “even” appearance)
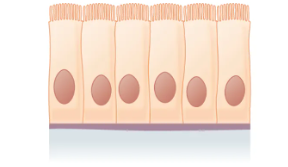
What is the layer and shape of this epithelium?
Simple (one layer), columnar (vertically stretched nuclei, tall like columns)
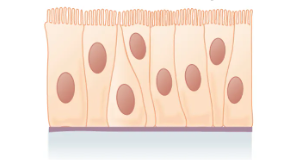
What is the layer and shape of this epithelium?
Psuedostratified (one layer, but appears like multiple), columnar (vertically stretched nuclei, tall like columns)
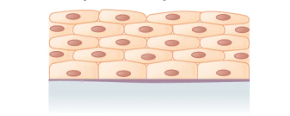
What is the layer and shape of this epithelium?
Stratified (multiple layers), squamous (squished appearance and squished nucleus)
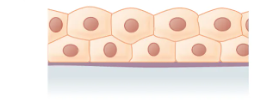
What is the layer and shape of this epithelium?
Stratified ( multiple layers), cuboidal(rounded nucleus, more “even” appearance)
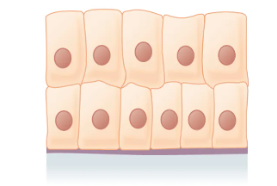
What is the layer and shape of this epithelium?
Stratified (multiple layers), columnar (vertically stretched nuclei, tall like columns)
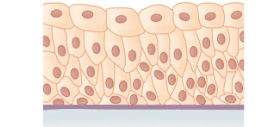
What is the layer and shape of this epithelium?
transitional (changing shapes depending on area, some cuboidal, columnar, or squamous in others)
Simple cells help with ___________.
permeability (allows fluid to pass through)/absorption
Stratified cells help with __________.
protection (think it takes more to get through)
Simple squamous epithelium allows for ____________, and found in _______, _______, and _______________.
rapid diffusion; kidney TUBULES, alveoli of lungs, blood vessels
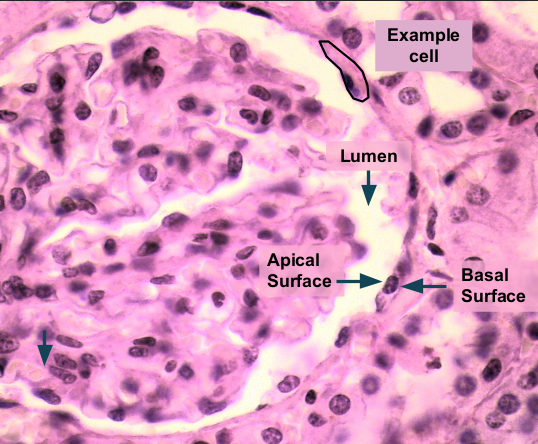
Simple cuboidal epithelium help Golgi apparatus and E.R for _________. It can be found in ___________
secretion; pancreas, salivary glands, and KIDNEYS
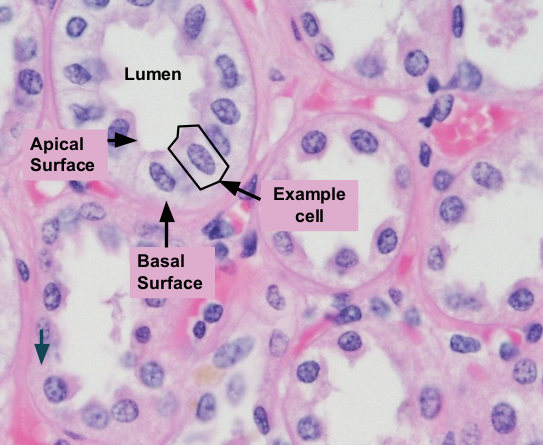
Simple columnar epithelium cells help with _____________. It can also have micro villi attached to it to increase surface area for absorption. It can be found in the ____________.
protection; intestinal wall
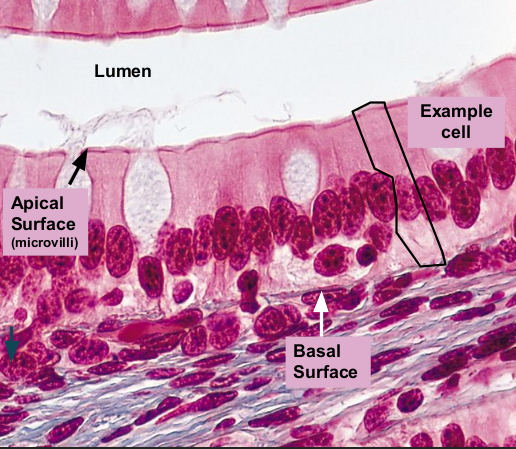
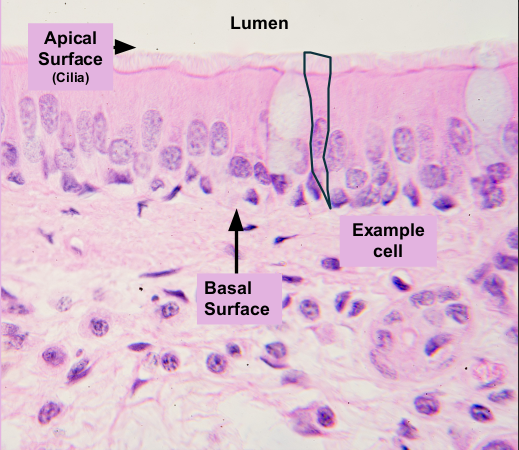
Psuedostratified columnar epithelium helps move ________ through _____________. It contains ________ to help move mucus
mucus; respiratory tract (nasal Cavity, trachea, bronchi); cilia
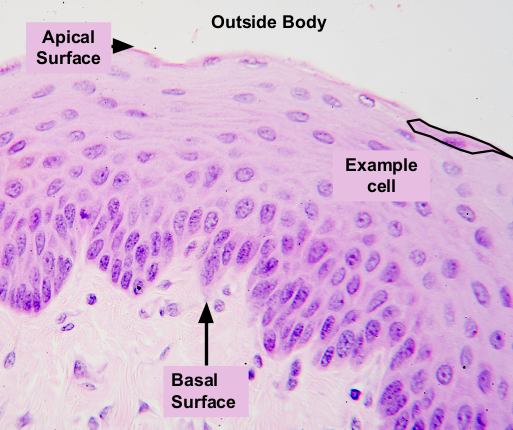
Stratified squamous epithelium are our ___________.
Outerskin
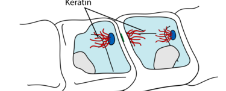
Desmosomes
protein filaments that pass through neighboring cells to HOLD THE CELL TOGETHER
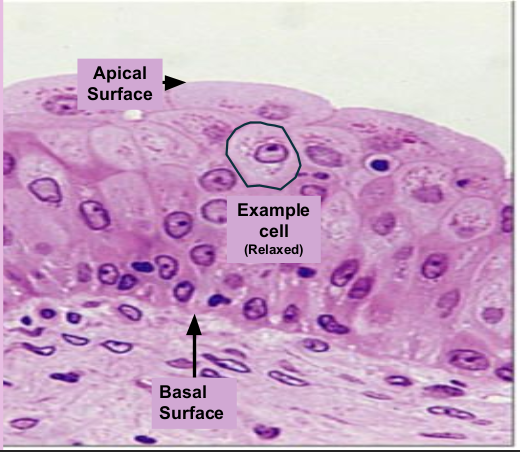
Transitional Epithelium is found in the _____________. These can be rounded and relaxed in one state and stretched in another.
Lining of our bladder
3 things Connective Tissue help with
PROTECTION (hard coverings for delicate organs)
TRANSPORTATION (moving fluids around body with the lymph nodes)
ENERGY STORAGE (glycogen and triglycerides are kept in connective tissue)
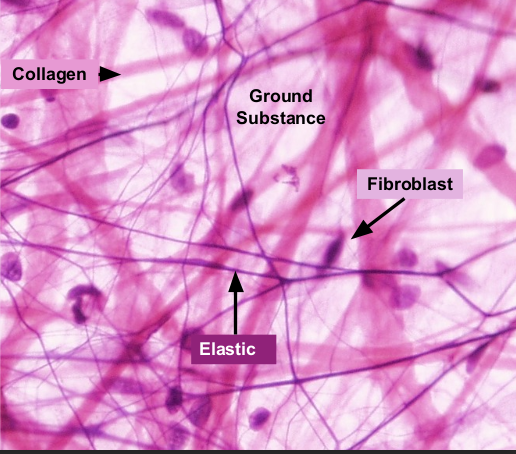
Areolar Connective Tissue
contains, collagen, elastic fibers, and fibroblasts
helps bind other tissues together and part of inflammatory response
part of SKIN and MUSCLE
External surfaces
any surface/organism that comes into DIRECT CONTACT t with the outside environment or the MATERIAL of the outside environment
skin, stomach, mouth, kidney tubules, small intestine, lung alveoli, trachea
Internal surfaces
any surface/organism that lines GLANDS, DUCTS, or VESSELS
vein, inner heart, pancreatic ducts