Ch3 - Analyzing EKG Rhythm Strips
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
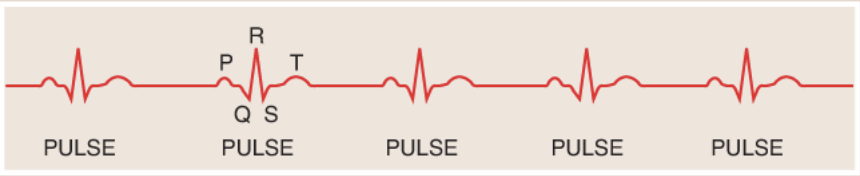
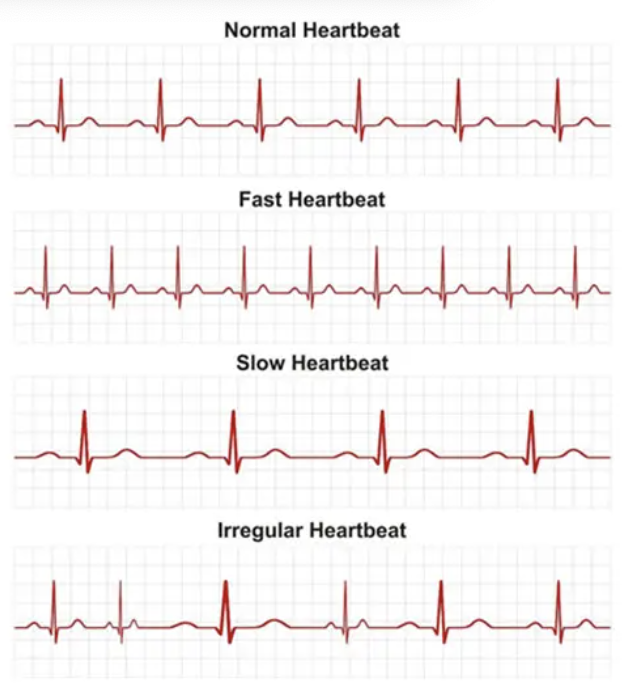
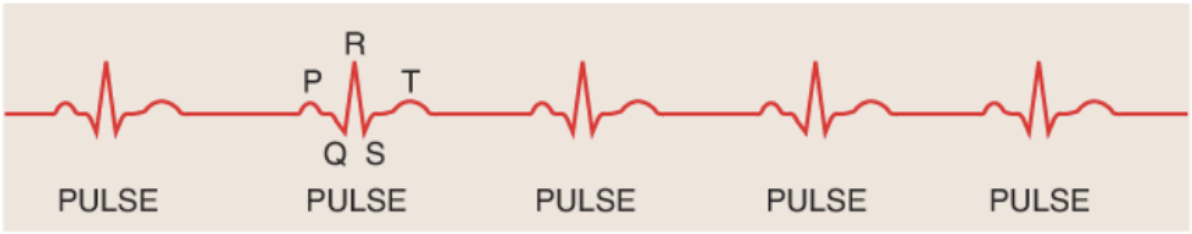
What is a cardiac cycle on the EKG?
The electrical impulses associated with a single heart beat: the P, Q, R, S, and T waves
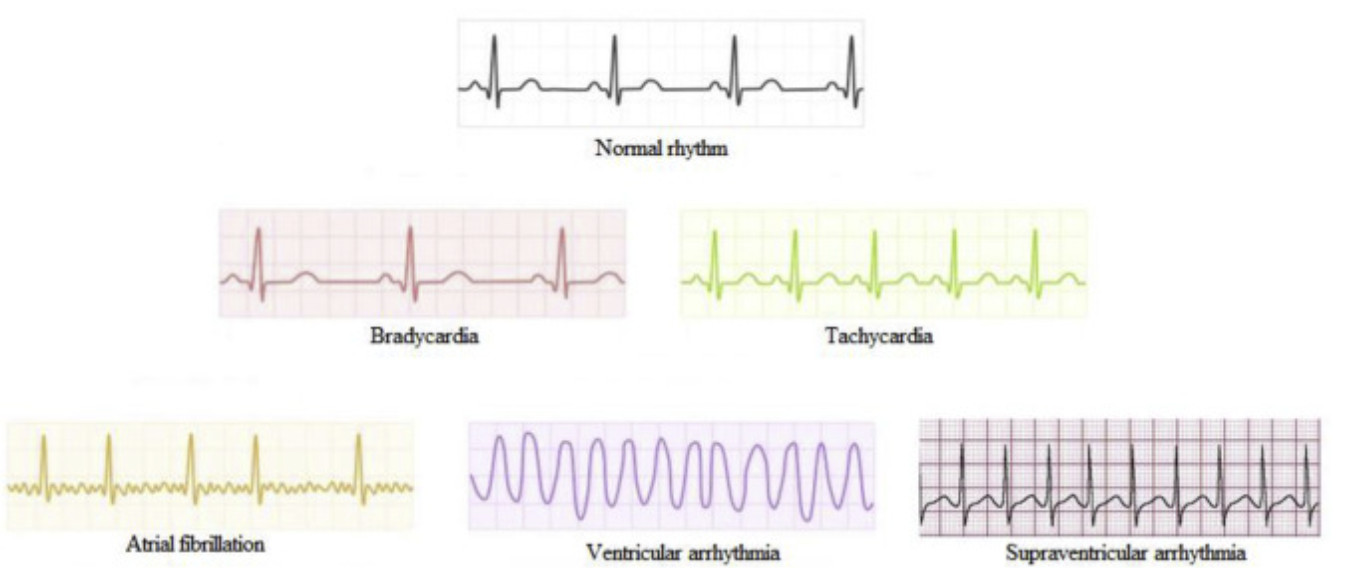
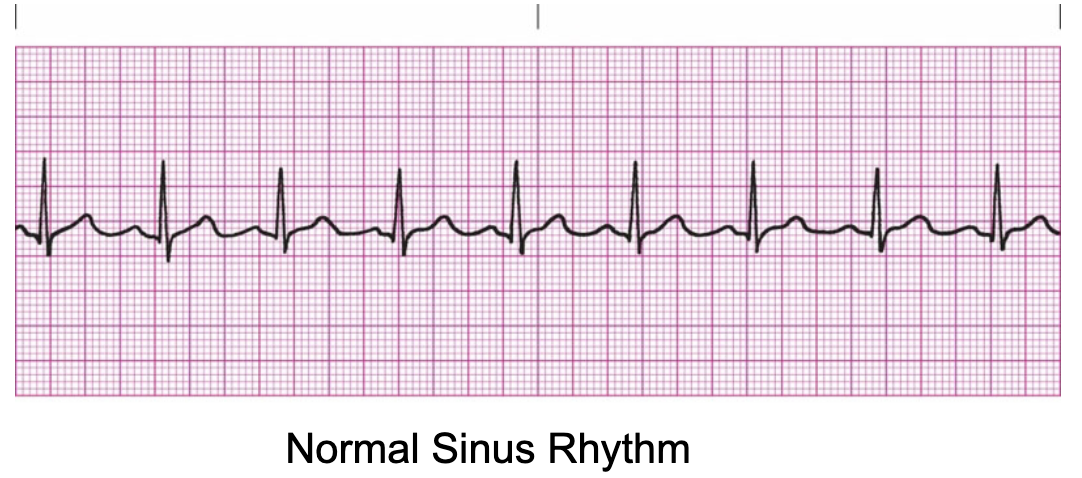
What is the name of the normal cardiac rhythm associated with a healthy heart?
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Why is it necessary to have an organized format for approaching arrhythmia interpretation?
There are so many possible configurations of EKGs that you would never be able to memorize all of them. You must be able to systematically gather all of the available information and then compare it to the rules for the rhythms. With-out a routine format, you could overlook important clues.
Why do you have to memorize the rules for each of the arrhythmias?
So that you can compare them to the findings on an EKG strip and thus determine the identity of the arrhythmia
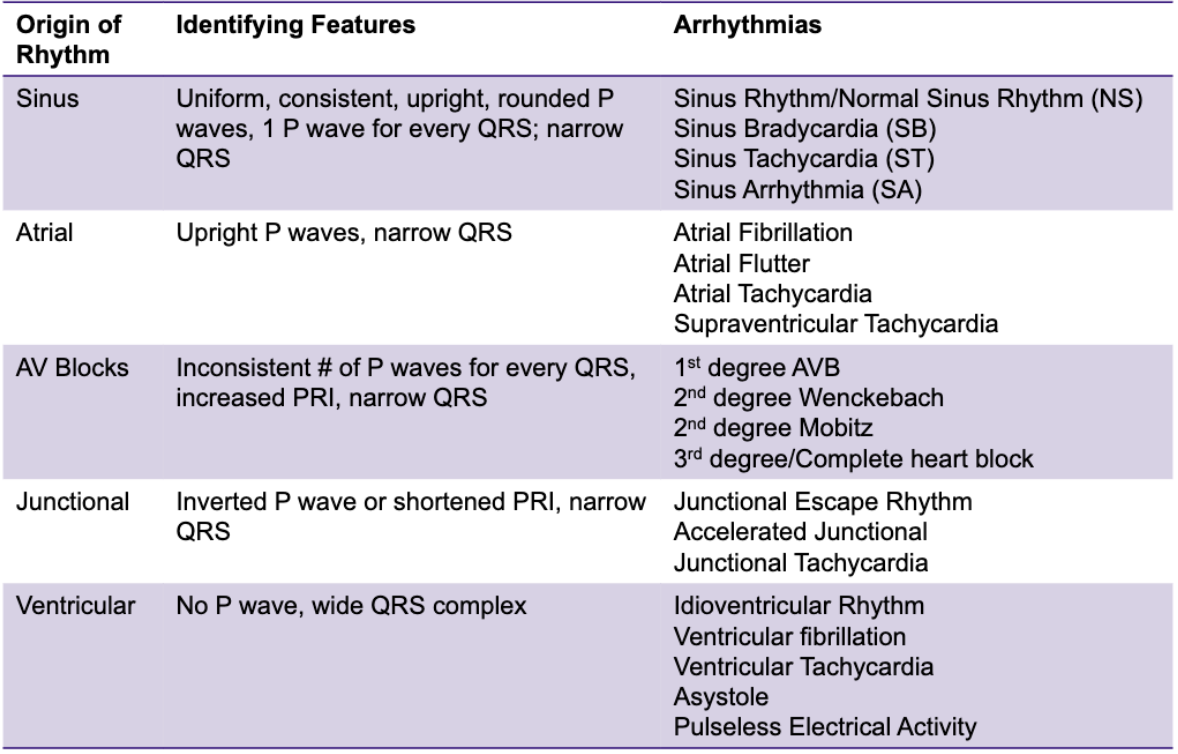
What are the five parts of the analysis format that you learned in this chapter?
Regularity (rhythm)
Rate
P Wave
PR Interval
QRS complex
How can you tell whether or not an arrhythmia is regular?
Measure the R–R interval or the P–P interval.
What does the phrase “regularly irregular” mean?
There is a pattern to the irregularity.
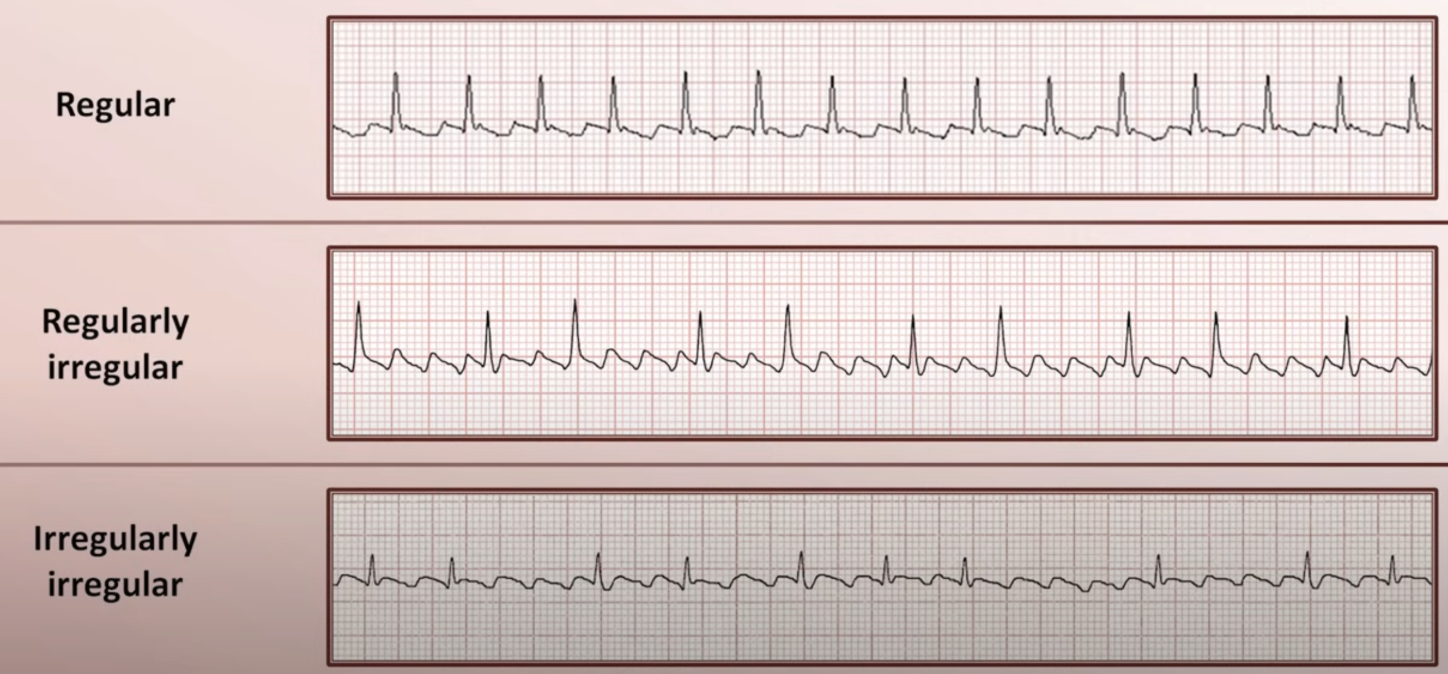
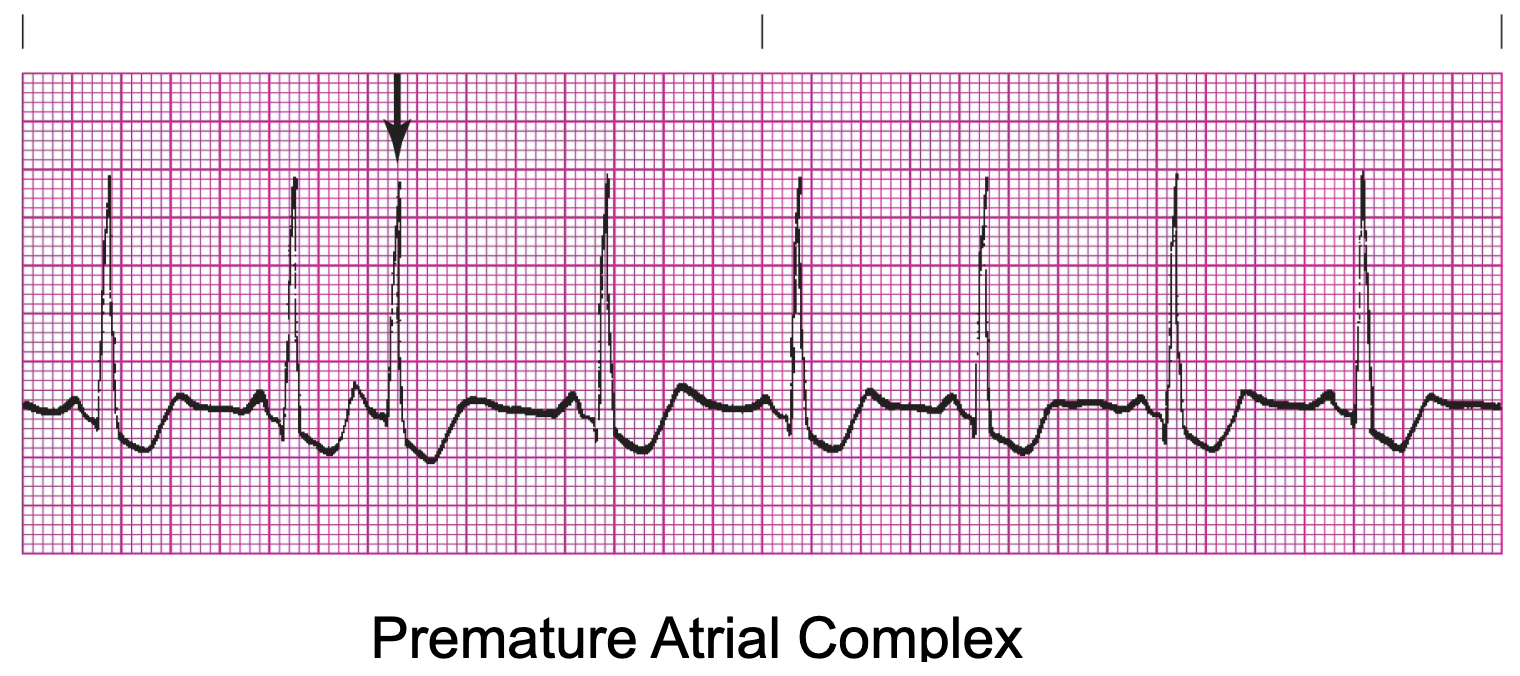
What does the phrase “basically regular” mean?
The underlying rhythm is regular, but it is interrupted by ectopics
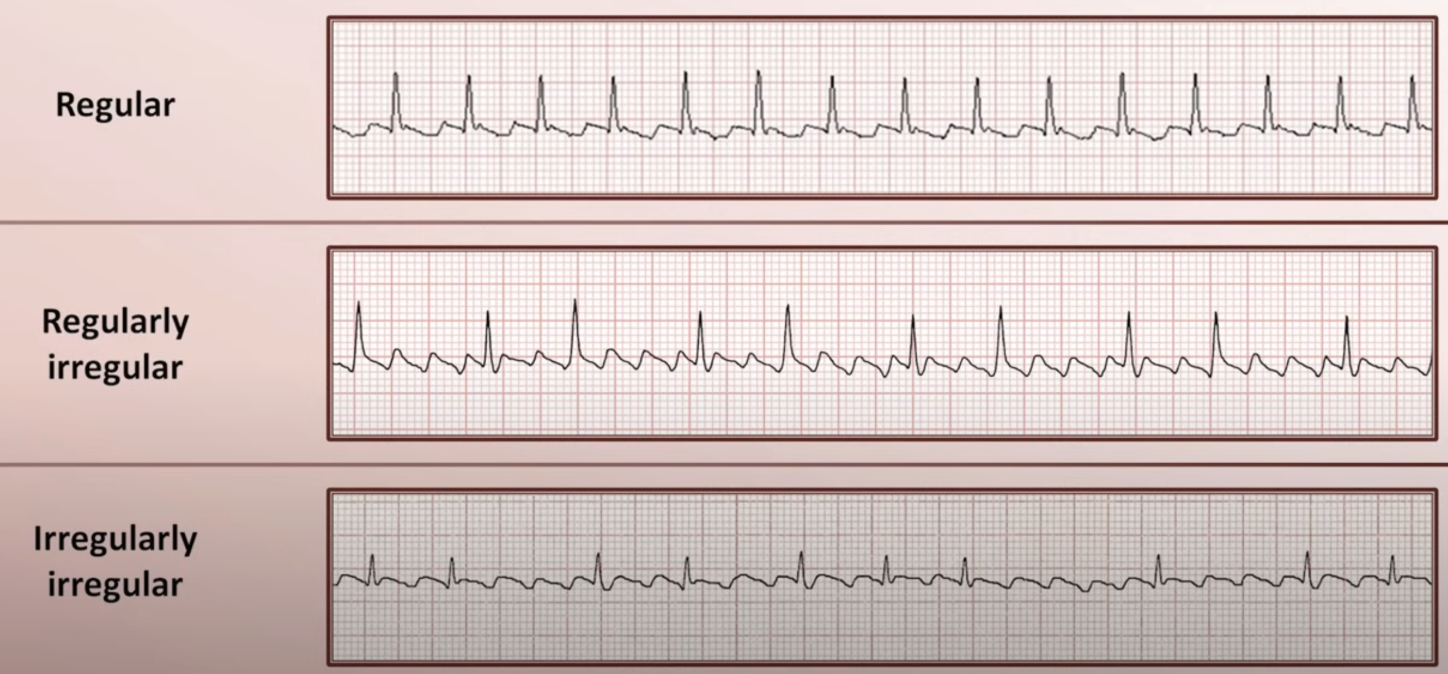
What does it mean when you call an arrhythmia “totally irregular”?
There is no pattern to the irregularity.
If you wanted to calculate accurately the rate of a regular rhythm, you could count the number of small squares between two R waves and divide it into what number?
1500
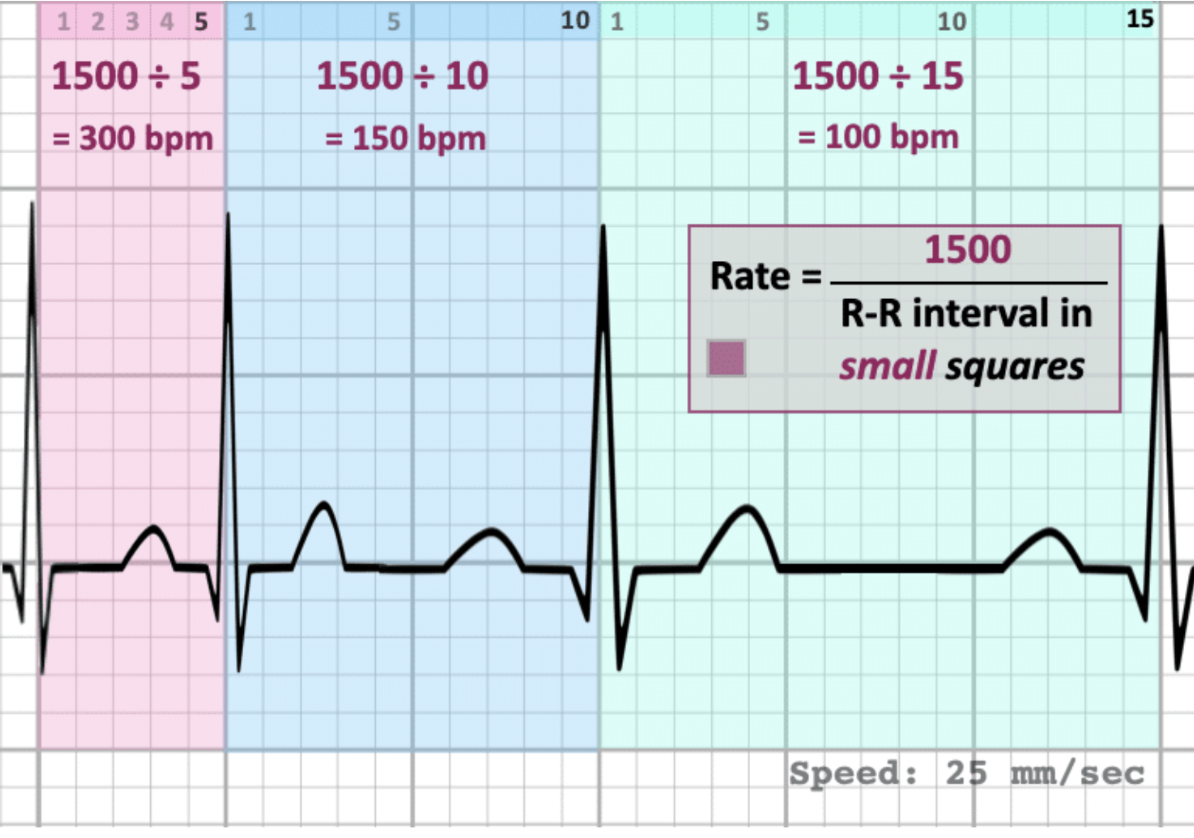
If you counted the number of large squares between two R waves, what number would you divide that total into to determine the heart rate?
300
When an arrhythmia is irregular, you should determine the heart rate by counting the number of R waves in 6 seconds and multiplying that total by what number?
10
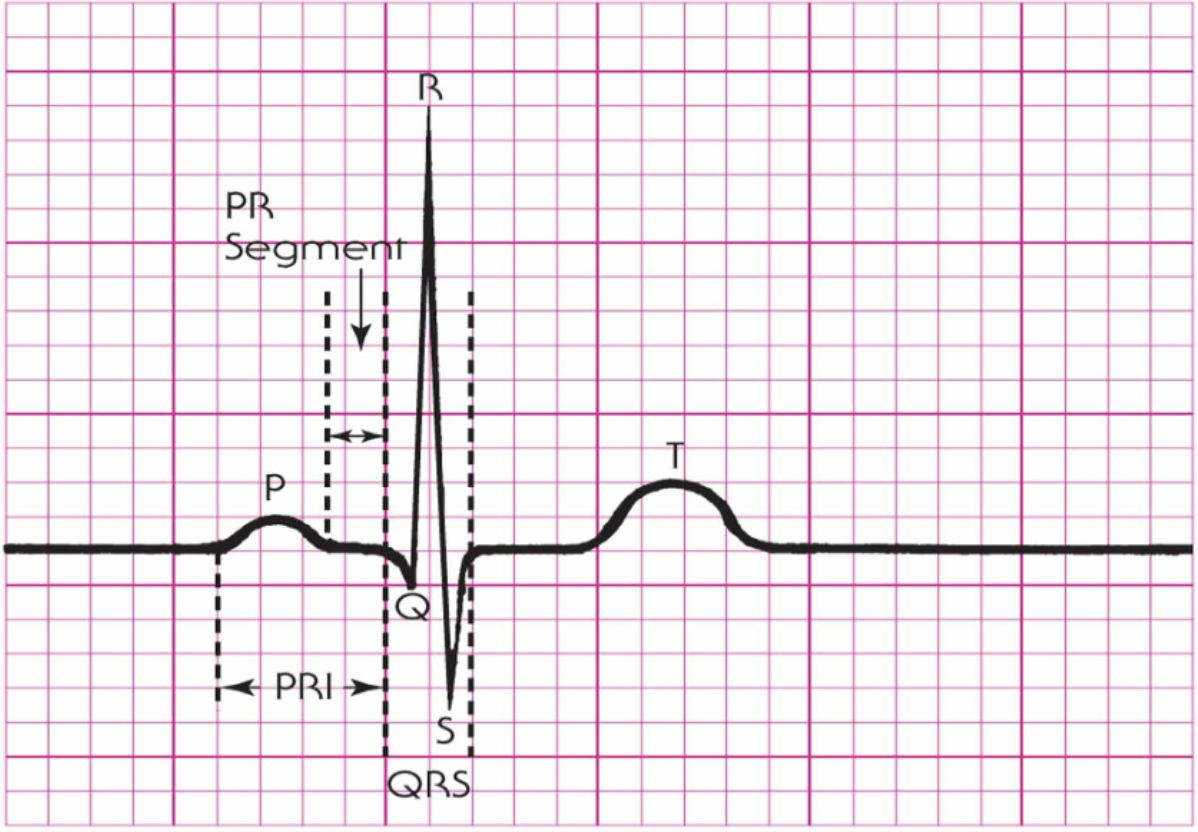
What is the first wave you should try to locate and map out when analyzing a rhythm strip?
P wave
What does a normal sinus P wave look like?
It has a smooth, rounded shape
It is upright
Uniform
Where can you normally find the P wave?
It is usually located immediately in front of the QRS complex.
Are P–P intervals usually regular or irregular?
They are usually very regular
What is meant when a P wave is said to be “lost” in the T wave?
It means that the P wave occurred on or near the T wave and is thus obscured beyond clear identification
UTA = unknown
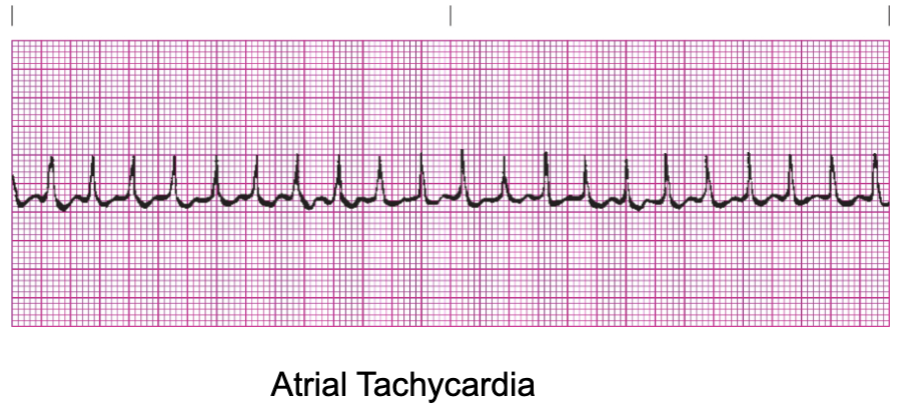
EX: Atrial Tachycardia
In your analysis of a rhythm strip, what waves should you look for after you havr located the P waves?
The QRS and T waves
Why is it important for you to know all these waves and measurements?
Because they reflect cardiac activity
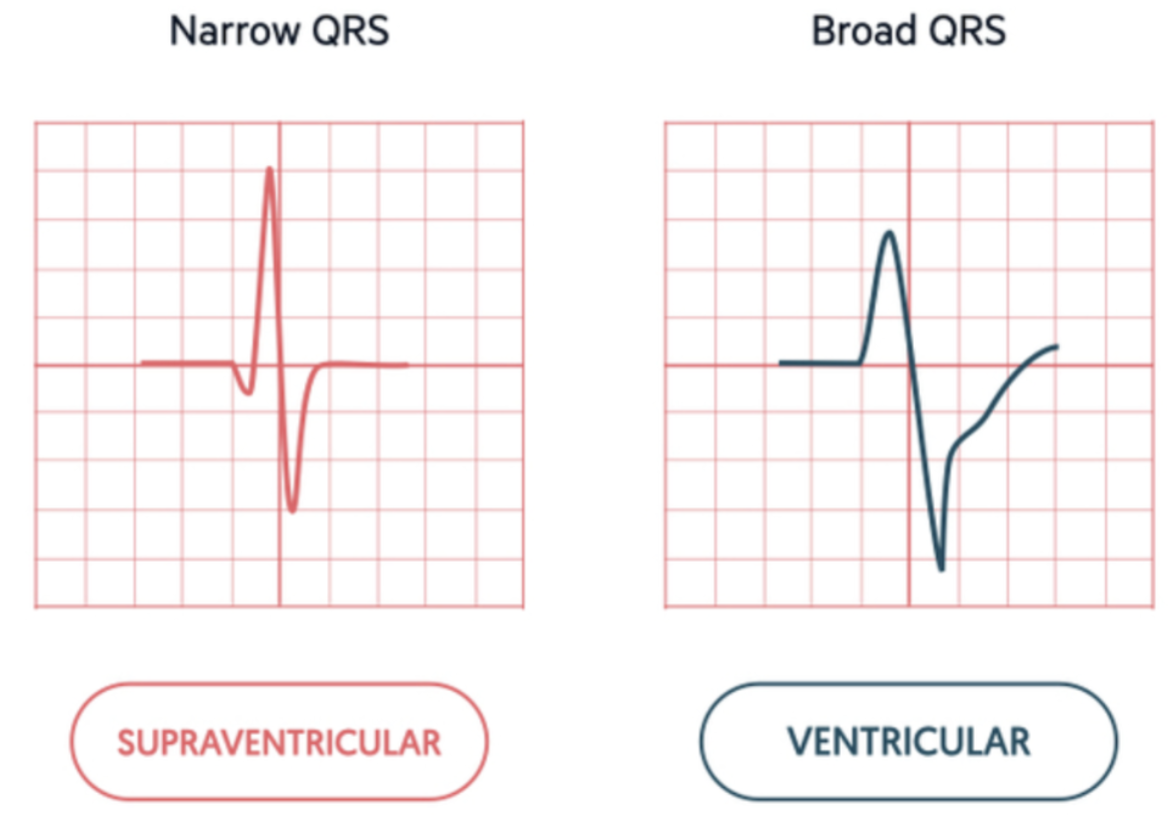
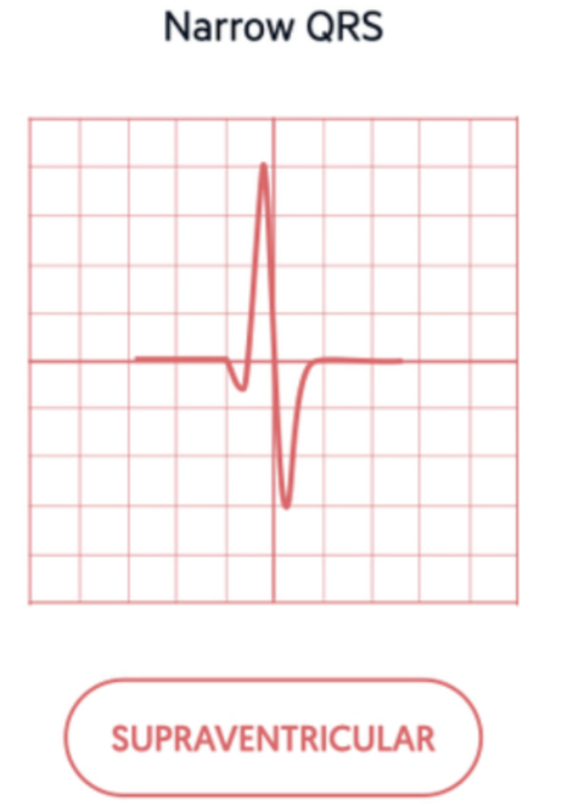
What is “super-ventricular” arrhythmia?
An arrhythmia that originates above the ventricles (SA node, atria, or AV node)
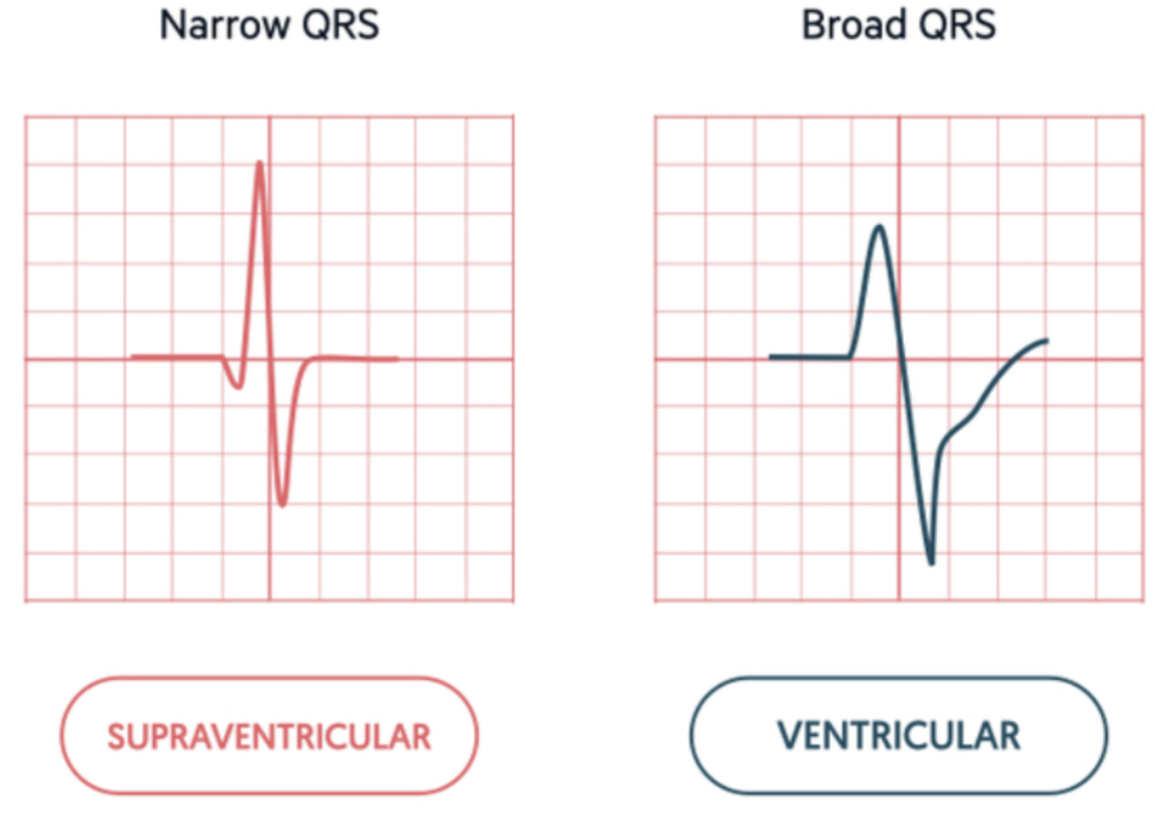
If a QRS complex measures less than 0.12 second, where can you assume that it originated?.
from a supra-ventricular focus
If a QRS complex measures 0.12 second or greater, it could possibly be a supraventricular rhythm with a ventricular conduction disturbance. What is the other possible explanation for a wide QRS complex?
A rhythm that originates in the ventricles will have a QRS measurement of 0.12 seconds or more