Ch 7.1
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what are the products of an Sn1 rxn?
racemization
what are the products of an Sn2 reaction?
inversion
what is the number of humps in a diagram equal to?
the steps in the mechanism
if there is steric hinderance at the electrophilic site, what rxn does that favor?
Sn1
what reaction has a more stable carbocation?
Sn1
what factors affect the stability of carbocations?
induction and resonance
what do methyl and primary substrates favor?
Sn2
what do tertiary substrates favor?
Sn1
what can secondary substrates and allylic and benzylic substrates react via?
either mechanism
what does an Sn2 process depend on?
the concentration of the nucleophile
strong nucleophile will speed up rate
weak nucleophile will slow it down
what does an Sn1 process not depend on?
nucelophile
a weak nucleophile disfavors Sn2, which allows _____ to complete sucessfully>
Sn1
what makes a nucleophile strong or weak>
stability, and sterics
what tend to be good nucleophiles
sterically hindered negatively charged molecules
what atoms can be strong nucleophiles when neutral?
larger atoms
has many electrons distant from the nucleus
electron density can be unevenly distributed
what are both Sn1 and SN2 rxs sensitive to?
identity of the leaving group
if leaving group is bad then neither substitution can occur
what make a leaving group good or bad?
stability once it has left with a pair of electrons
induction, resonance, solvation
whats a general rule of leaving groups?
good leaving groups are conjugate bases of strong acids
what are the most common leaving groups?
halides and sufonate ions
iodine best out of halides
triflate best out of sulfonate
what is the most commonly used sulfonate ion?
tosylate
abbreviated as OTs
what does the polar solvent surround?
each species in the mechanism, including transition statew
what should the solvent do in Sn2?
facilitate the collision between the nucleophile and the electrophile
more reactive
what can the solvent affect?
can make the nucleophile more stable and less reactive and the stability of the LG
what solvents promote Sn2 rxns?
polar aprotic
what is a polar aprotic solvent?
contain no hydrogen bonded directly to an electronegative atom
stabilize the counter ion of the nucleophile
will not stabilize anions (nucleophile)
leaving nucleophile mostly naked
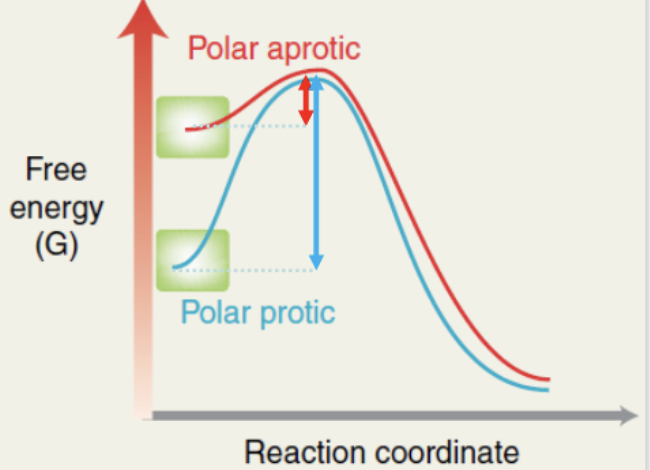
what happens with polar aprotic in Sn2?
nucleophile is less stable and starts with high potential energy
the activation energy will be lower and the reaction faster
how to promote Sn1 reaction?
polar, protic solvent
what is polar protic solvent?
contain at least one hydrogen atom directly connected to an electronegative atom
will hydrogen bond with nucleophile
stabilize it, while the leaving group leaves first
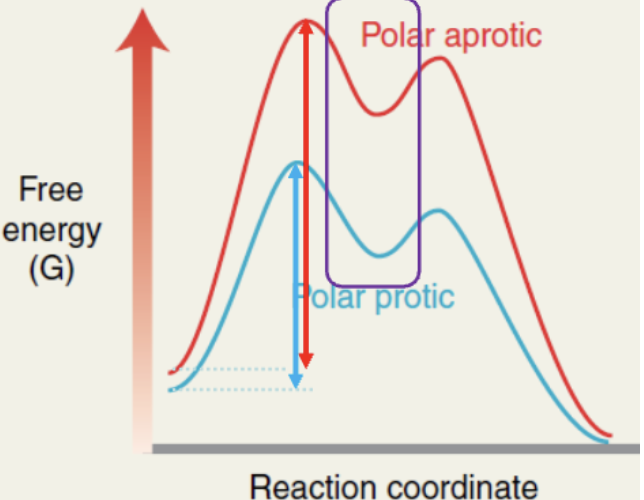
what does a polar proticc solvent do in a Sn1 rxn?
stabilize the full and partial charges that form during the Sn1 mechanism
lowers the energy of the TS and the intermediates
what are some polar aprotic solvents?
DMSO, Acentonitrile, DMF, HMPA
what are some polar protic solvents?
Water, methanol, acetic acid, ammonia, and ethanol
what is the alpha position of a halide?
carbon directly connected to halogen
what is the beta position?
the carbon atoms connected to the alpha position